LeetCode #153 Candy
文章目录
- 题目
- 分析
- 算法
- 1. 暴力算法
- 2. 一个数组,两次遍历
- 3. 算法2的变种:贪心算法
题目
There are N children standing in a line. Each child is assigned a rating value.
You are giving candies to these children subjected to the following requirements:
- Each child must have at least one candy.
- Children with a higher rating get more candies than their neighbors.
What is the minimum candies you must give?
Example 1:
Input: [1,0,2]
Output: 5
Explanation: You can allocate to the first, second and third child with 2, 1, 2 candies respectively.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,2]
Output: 4
Explanation: You can allocate to the first, second and third child with 1, 2, 1 candies respectively.
The third child gets 1 candy because it satisfies the above two conditions.
分析
要注意的关键点是,只有等级比旁边的小朋友高时,才需要有比他更多的糖果。
如果一个小朋友A的等级和旁边的小朋友B是一样的,那么他的糖果数不需要比B多。
如果A旁边没有其他的小朋友,或者他旁边的另一个小朋友C等级比他高,那么甚至只需要给A一颗糖。
因而,在编写程序中要注意几个邻近的小朋友等级相同的情况。
有一些测试例子:
int r1[3] = {1,0,2}; // 5
int r2[3] = {1,2,2}; // 4
int r3[5] = {0,1,3,2,1}; // 9
int r4[12] = {0,1,6,2,1,7,8,5,4,3,1,9}; // 28
int r5[8] = {1,2,2,3,4,4,5,1}; // 13
int r6[7] = {3,4,4,4,5,5,4}; // 10
int r7[5] = {1,3,4,5,2}; // 11
算法
1. 暴力算法
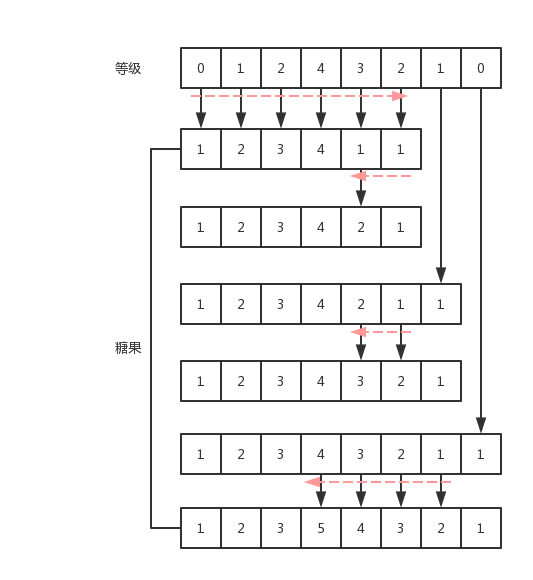
糖果数随着等级的递增而逐次递增1,如果等级出现下降或持平,那么糖果数赋值1。所以,如果有两个相邻的、不同的等级数,而对应的糖果数均为1,那就从后往前遍历,对每个糖果数都增1,直到遇到某个不需要再增1的糖果数。
大致过程如下图所示:
class Solution {
public:
int candy(vector& ratings) {
const int size = ratings.size();
int candies[size] = {0};
int index = 0;
candies[index] = 1;
index++;
while(index != size){
int delta = ratings[index] - ratings[index - 1];
if(delta > 0) candies[index] = candies[index - 1] + 1;
else candies[index] = 1;
if(delta < 0 && candies[index - 1] == 1){
int i2 = index;
while(1){
candies[--i2]++;
if(i2 == 0 || ratings[i2 - 1] <= ratings[i2] || candies[i2 - 1] > candies[i2]) break;
}
}
index++;
}
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
sum += candies[i];
}
return sum;
}
};
在最坏的情况下(所给的等级数组是一个递减的数列),每处理一个数就要遍历前面所有的数,时间复杂度为 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2) 。
用时为 1212 m s 1212ms 1212ms !效率非常低。
2. 一个数组,两次遍历
本质上,每个小朋友的糖果数由两边小朋友的等级和他的等级的相对关系决定。
相对关系大致可以分为三种:
min,小朋友的等级比两边小朋友的等级都低medium,小朋友的等级和两边小朋友的等级一样max,小朋友的等级比两边小朋友的等级都高up,前一个小朋友的等级 < 这个小朋友的等级 < 后一个小朋友的等级down,前一个小朋友的等级 > 这个小朋友的等级 > 后一个小朋友的等级
先从 [0] 遍历到 [N-1] ,如果遇到 min 点和 medium 点,糖果数赋值1;遇到 up 点,糖果数赋值为前一个糖果数+1;遇到 max 点,先赋值-1;遇到 down 点,先赋值-2。
然后从 [N-1] 遍历到 [0] ,如果遇到值为-2的 down 点,赋值为后一个糖果数+1;遇到值为-1的 max 点,比较左右两个点的糖果数大小,取最大值+1的结果作为这个点的糖果数。
大致过程可抽象为下图:
class Solution {
public:
int candy(vector& ratings) {
const int size = ratings.size();
if(size == 0 || size == 0) return size;
int candies[size] = {0};
int sum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
int prev = i == 0 ? ratings[i] : ratings[i - 1];
int here = ratings[i];
int next = i == size - 1? ratings[i] : ratings[i + 1];
if(prev == here && here == next){
candies[i] = 1; // medium
}
else if(prev >= here && here <= next){
candies[i] = 1; // min
}
else if(prev < here && here < next){
candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1; // up
}
else if(prev <= here && here >= next){
candies[i] = -1; // max
}
else{
candies[i] = -2; // down
}
}
for(int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--){
if(candies[i] == -2){
candies[i] = candies[i + 1] + 1;
}
else if(candies[i] == -1){
if(i == 0 || ratings[i - 1] == ratings[i]) candies[i] = candies[i + 1] + 1;
else if(i == size - 1 || ratings[i] == ratings[i + 1]) candies[i] = candies[i - 1] + 1;
else{
candies[i] = candies[i - 1] > candies[i + 1] ? candies[i - 1] : candies[i + 1];
candies[i]++;
}
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
sum += candies[i];
}
return sum;
}
遍历2次,时间复杂度为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N) 。
用时为 20 m s 20ms 20ms 。
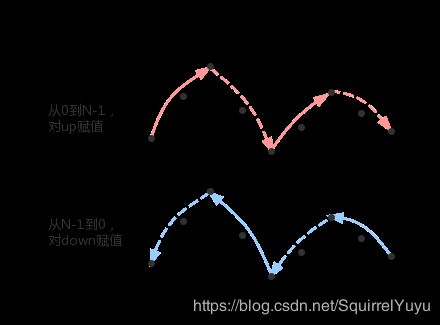
3. 算法2的变种:贪心算法
原理如下图:
跟算法2相比,即是把up赋值和down赋值的过程分开成两个数组 Left2Right 和 Right2Left 。
有:candies[i] = max{Left2Right[i], Right2Left[i]}
比起每次赋值都要和两边的点比较的算法2,算法3每次赋值都只比较一个方向的邻点,大小递增就增1,不递增就置1,更加简便。
代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
int candy(vector& ratings) {
const int size = ratings.size();
if(size == 0 || size == 0) return size;
int left2right[size] = {0};
int right2left[size] = {0};
int sum = 0;
left2right[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < size; i++){
if(ratings[i] > ratings[i - 1]) left2right[i] = left2right[i - 1] + 1;
else left2right[i] = 1;
}
right2left[size - 1] = 1;
for(int i = size - 2; i >= 0; i--){
if(ratings[i] > ratings[i + 1]) right2left[i] = right2left[i + 1] + 1;
else right2left[i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++){
sum += (left2right[i] > right2left[i] ? left2right[i] : right2left[i]);
}
return sum;
}
};
遍历3次,时间复杂度为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N) 。
用时为 36 m s 36ms 36ms 。