2020.01.12日常总结
洛 谷 P 2564 [ S C O I 2009 ] 生 日 礼 物 \color{green}{洛谷P2564\ \ \ [SCOI2009]生日礼物} 洛谷P2564 [SCOI2009]生日礼物
【 题 意 】 : \color{blue}{【题意】:} 【题意】: 小西有一条很长的彩带,彩带上挂着各式各样的彩珠。已知彩珠有 N N N个,分为 K K K种。简单的说,可以将彩带考虑为 x x x轴,每一个彩珠有一个对应的坐标(即位置)。某些坐标上可以没有彩珠,但多个彩珠也可以出现在同一个位置上。
小布生日快到了,于是小西打算剪一段彩带送给小布。为了让礼物彩带足够漂亮,小西希望这一段彩带中能包含所有种类的彩珠。同时,为了方便,小西希望这段彩带尽可能 短 \color{red}{短} 短,你能帮助小西计算这个最短的长度么?彩带的长度即为彩带开始位置到结束位置的位置差。
【 思 路 】 : \color{blue}{【思路】:} 【思路】: 尺取法(Two-pointer)法的模板题。
具体地说,就是利用两个指针 l , r l,r l,r, l l l表示当前扫描的区间的左端点, r r r表示右端点。如果区间 [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r]内有所有种类的珠子的话,我们用区间 [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r]的长度 更 新 \color{red}{更新} 更新答案,并且尝试缩短区间 [ l , r ] [l,r] [l,r]的长度(就是把与第 l l l个珠子在同一位置上的珠子和它自己删除)。否则,我们把所有与第 r r r个珠子在同一位置上的珠子和第 r r r个珠子自己加入候选队列。
时 间 复 杂 度 : \color{red}{时间复杂度:} 时间复杂度:因为每个珠子最多加入一次候选队列,且最多被删除一次,所以总的时间复杂度为 O ( N ) O(N) O(N)。当然,我们需要排序,所以时间复杂度为 O ( N × l o g N ) O(N\times log\ N) O(N×log N)。
【 代 码 】 : \color{blue}{【代码】:} 【代码】:
#define gc getchar()
#define g(c) isdigit(c)
inline int read(){
char c=0;int x=0;bool f=0;
while (!g(c)) f=c=='-',c=gc;
while (g(c)) x=x*10+c-48,c=gc;
return f?-x:x;
}
const int N=1001000;
struct Bead{
int position,color;
bool operator < (Bead c) const{
return position<c.position;
}
}a[N];int cnt[100],n,m,tot,l,r,ans;
inline void Insert(int pos){
if (cnt[a[pos].color]==0)
tot++;//珠子总数加一
cnt[a[pos].color]++;
}//Insert the bead pos.
inline void Delete(int pos){
cnt[a[pos].color]--;
if (cnt[a[pos].color]==0)
tot--;//珠子总数减一
}//Delete the bead pos.
int main(){
n=read();m=read();ans=1e9;
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
register int N=read();
for(int j=1;j<=N;j++){
a[++tot].color=i;
a[tot].position=read();
}
}
sort(a+1,a+n+1);l=r=1;
memset(cnt,0,sizeof(cnt));
cnt[a[1].color]=1;tot=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
if (a[i].position==a[i-1].position){
Insert(i);r++;
}
else break;
while (l<=n&&r<=n){
if (tot==m){
ans=min(ans,a[r].position-a[l].position);
Delete(l);++l;//Try to delete l to let ans be smaller.
while (l<=n&&a[l].position==a[l-1].position){
Delete(l);++l;
}//Delete all the beads in the same position.
}
else{
++r;if (r>n) break;Insert(r);
// 不符题意,只能加入更多的珠子
while (a[r].position==a[r+1].position){
r++;if (r>n) break;Insert(r);
}//Insert all the beads in the same position.
}
}
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}
洛 谷 P 5022 旅 行 \color{green}{洛谷P5022\ \ \ 旅行} 洛谷P5022 旅行
【 题 意 】 : \color{blue}{【题意】:} 【题意】:


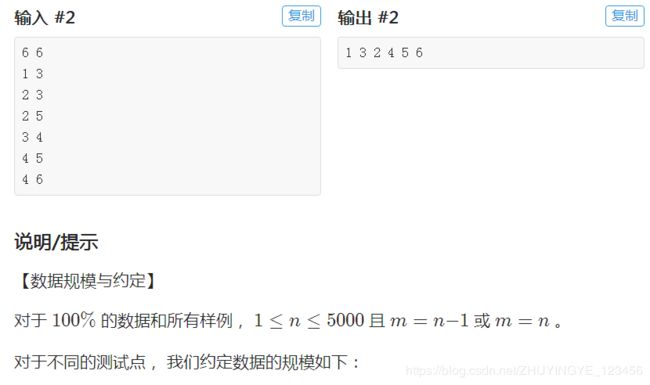
【 思 路 】 : \color{blue}{【思路】:} 【思路】: 首先,拿到这么一道竞赛题目,我们先看题意(废话),然后我们应该看看题目的数据范围。
我们发现前 60 % 60 \% 60%的数据是一棵 树 \color{red}{树} 树,而后 40 % 40 \% 40%的数据是一棵 基 环 树 \color{red}{基环树} 基环树(即一颗树加上一条边)。
我们先来看看一棵树的情况:很简单,只需从 1 1 1开始,每次遍历最小的点即可。直接上代码(代码中的边已经排好序)。
namespace case_one{
int cnt=0;bool vis[5100];
inline void dfs(int u){
ans[++cnt]=u;vis[u]=true;
for(int i=h[u];i;i=e[i].next){
register int to=e[i].to;
if (!vis[to]) dfs(to);
}
}
void simulation_main(){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));dfs(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
}
好的, 60 60 60分到手。
对于基环树的情况,因为 N , M N,M N,M不是很大,所以 O ( N 2 ) O(N^2) O(N2)或 O ( N × M ) O(N\times M) O(N×M)的方法可以通过此题。
因为只有一条边是我们遍历不到的,所以我们可以枚举我们删除哪条边,然后接下来就是一棵树的情况了。
当然这样可能会 T L E TLE TLE,那这么办?
我们可以考虑剪枝,今天而言,就是如果当前的答案一定不会更优时,就可以返回进行下一次搜索了。
具体的看代码(一样,边已经排好序了):
namespace case_two{
int cnt=0,res[5100],du,dv;
bool vis[5100],flag;
inline bool check(int u,int v){
if (u==du&&v==dv)
return false;
if (u==dv&&v==du)
return false;
return true;
}
void dfs(int u){
if (u<ans[cnt]) flag=true;
if (flag) res[cnt++]=u;
else if (u>ans[cnt]){
/*cnt--;*/return;
}
else cnt++;vis[u]=true;
for(int i=h[u];i;i=e[i].next){
register int to=e[i].to;
if (!vis[to]&&check(u,to)) dfs(to);
}
}
void simulation_main(){
memset(ans,127,sizeof(ans));
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
// memset(res,0,sizeof(res));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
du=b[i].from;dv=b[i].to;
cnt=0;flag=false;dfs(1);
if (cnt==n) memcpy(ans,res,sizeof(res));
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
}
最后讲讲如何把边排序。如果大家用vector的话,那很简单。但是众所周知,STL很慢,这题用vector就很可能 T L E TLE TLE(当然,不是一定,还得看看人品运气)。
所以我们只能用 链 式 前 向 星 \color{red}{链式前向星} 链式前向星解决。其实我们只需要把所有的边按边权 从 大 到 小 \color{red}{从大到小} 从大到小排序(为什么要从大到小,因为链式前向星加入边后,遍历时会反过来,所以从大到小插入,就代表从小到大访问),然后依次加入即可。具体看代码:
int main(){
// freopen("t1.in","r",stdin);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i].from);
scanf("%d",&a[i].to);
a[i+m].from=a[i].to;
a[i+m].to=a[i].from;
b[i].from=a[i].from;
b[i].to=a[i].to;
}
sort(a+1,a+2*m+1);
for(int i=1;i<=2*m;i++)
add(a[i].from,a[i].to);
}
然后就是整题的代码了……
【 代 码 】 : \color{blue}{【代码】:} 【代码】:
int n,m,ans[5100];
struct edge{
int from,to;
bool operator < (edge c) const{
return to>c.to;
}
}a[10100],b[5100];
struct node{
int next,to;
}e[10100];int h[5100],tot;
inline void add(int a,int b){
e[++tot]=(node){h[a],b};h[a]=tot;
// e[++tot]=(node){h[b],a};h[b]=tot;
}
namespace case_one{
int cnt=0;bool vis[5100];
inline void dfs(int u){
ans[++cnt]=u;vis[u]=true;
for(int i=h[u];i;i=e[i].next){
register int to=e[i].to;
if (!vis[to]) dfs(to);
}
}
void simulation_main(){
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));dfs(1);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
}
namespace case_two{
int cnt=0,res[5100],du,dv;
bool vis[5100],flag;
inline bool check(int u,int v){
if (u==du&&v==dv)
return false;
if (u==dv&&v==du)
return false;
return true;
}
void dfs(int u){
if (u<ans[cnt]) flag=true;
if (flag) res[cnt++]=u;
else if (u>ans[cnt]){
/*cnt--;*/return;
}
else cnt++;vis[u]=true;
for(int i=h[u];i;i=e[i].next){
register int to=e[i].to;
if (!vis[to]&&check(u,to)) dfs(to);
}
}
void simulation_main(){
memset(ans,127,sizeof(ans));
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
// memset(res,0,sizeof(res));
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
du=b[i].from;dv=b[i].to;
cnt=0;flag=false;dfs(1);
if (cnt==n) memcpy(ans,res,sizeof(res));
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
printf("%d ",ans[i]);
}
}
int main(){
// freopen("t1.in","r",stdin);
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%d",&a[i].from);
scanf("%d",&a[i].to);
a[i+m].from=a[i].to;
a[i+m].to=a[i].from;
b[i].from=a[i].from;
b[i].to=a[i].to;
}
sort(a+1,a+2*m+1);
for(int i=1;i<=2*m;i++)
add(a[i].from,a[i].to);
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
// for(int j=h[i];j;j=e[j].next)
// printf("An edge from %d to %d\n",i,e[j].to);
if (m==n-1) case_one::simulation_main();
else case_two::simulation_main();
return 0;
}