【龙芯1c库】封装串口接口和使用示例
龙芯1c库是把龙芯1c的常用外设的常用功能封装为一个库,类似于STM32库。本文先讲解了龙芯1c库中的串口相关的函数,然后是如何利用这些函数实现串口通信。比如在串口打印helloworld,实现串口echo(即收到什么原封不动的发送回去),如何实现printf。再后是简单介绍一下龙芯1c的串口,最后是讨论一下串口相关的接口函数时如何封装的。
龙芯1c库的git地址是https://gitee.com/caogos/OpenLoongsonLib1c
龙芯1c库中串口接口使用示例
串口接口简介
先来看下串口头文件中提供哪些函数,头文件ls1c_uart.h源码如下
// 串口相关头文件
#ifndef __OPENLOONGSON_UART_H
#define __OPENLOONGSON_UART_H
// 串口模块编号
typedef enum
{
LS1C_UART00 = 0, // 全功能串口UART0可以分为两个四线串口UART00和UART01
LS1C_UART01,
LS1C_UART1,
LS1C_UART2,
LS1C_UART3,
LS1C_UART4,
LS1C_UART5,
LS1C_UART6,
LS1C_UART7,
LS1C_UART8,
LS1C_UART9,
LS1C_UART10,
LS1C_UART11
}ls1c_uart_t;
// 串口信息
typedef struct
{
ls1c_uart_t UARTx; // 串口模块编号
unsigned int baudrate; // 波特率
BOOL rx_enable; // 是否需要使用串口接收数据(使能接收中断),发送默认使能
}ls1c_uart_info_t;
/*
* 获取指定串口模块的基地址
* @UARTx 串口编号
* @ret 基地址
*/
inline void *uart_get_base(ls1c_uart_t UARTx);
/*
* 初始化指定的串口模块
* @uart_info_p 串口模块信息
*/
void uart_init(ls1c_uart_info_t *uart_info_p);
/*
* 初始化串口2
*/
void uart2_init(void);
/*
* 在串口2上打印字符串
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart2_print(const char *str);
/*
* 在调试串口打印字符串
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart_debug_print(const char *str);
/*
* 在调试串口打印一个字符
* @ch 待打印的字符
*/
void uart_debug_putc(unsigned char ch);
/*
* 把中断号转换为串口号
* @IRQn 中断号
* @ret 串口号
*/
inline ls1c_uart_t uart_irqn_to_uartx(int IRQn);
/*
* 发送一个字节
* @uartx 串口号
* @ch 待发送的字符串
*/
void uart_putc(ls1c_uart_t uartx, unsigned char ch);
/*
* 打印一个字符串到指定串口
* @uartx 串口号
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart_print(ls1c_uart_t uartx, const char *str);
#endif一般来说,只需要先调用uart_init()对指定串口初始化,并调用函数pin_set_remap()设置引脚复用,然后即可调用uart_putc()或者uart_print()发送。如果需要接收数据的话,需要调用irq_install()设置中断处理函数,并调用irq_enable()使能相应中断。最后实现中断处理函数即可。
因为我使用的板子是把串口2作为调试串口的,所以头文件中还出现了几个串口2相关的函数。
测试用例
为了进一步演示如何使用这些接口函数,设计了以下几个测试用例。
在串口上打印helloworld
这里以调试串口2为例,在串口2上打印helloworld。代码不多,这里直接贴代码
/*
* 初始化串口2
*/
void uart2_init(void)
{
unsigned int tx_gpio = 37;
unsigned int rx_gpio = 36;
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
// 初始化相关寄存器
debug_uart_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART2;
debug_uart_info.baudrate = 115200;
debug_uart_info.rx_enable = FALSE; // 调试串口只需要打印(发送)功能,不需要接收功能
uart_init(&debug_uart_info);
return ;
}
// 通过串口2打印helloworld
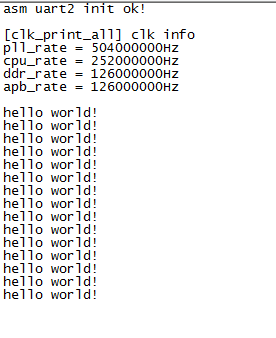
void test_uart2_print_helloworld(void)
{
while (1)
{
uart2_print("hello world!\r\n");
delay_s(1);
}
}运行结果如下
函数printf()
前面已经用函数uart2_print()打印了helloworld,函数printf()也可以打印字符串。那么函数uart2_print和printf()有什么异同?函数uart2_print()只有一个入参,入参是什么样打印出来的字符串就是什么样;而printf()可以有多个参数,入参可以直接是一个字符串,也可以是一个格式,然后后面跟各种参数,printf()内部会将这些参数按照指定的格式生成字符串,并打印出来。实际上,printf()内部最后会调用函数uart2_print()把格式化生成的字符串打印出来。函数printf()使用起来更灵活,一般都是使用函数printf()。
函数printf()是libc中的一个函数,另外专门有一篇有关libc的博文其中对printf有详细的讲解
《【龙芯1c库】移植标准c库libc(libm类似)》
http://blog.csdn.net/caogos/article/details/79551884
标准的libc中的函数printf()是将字符串打印到文件(描述符)中,而这里为了适合裸机编程,对其稍加改造。简单来说就是先调用函数vsprintf()按照入参指定的格式生成待打印的字符串,然后调用串口打印函数uart_debug_print()打印到调试串口上。源码如下
#include
#include
#include "../lib/ls1c_uart.h"
#define PRINTF_BUF_SIZE (512)
int printf (const char *fmt, ...)
{
int len;
va_list ap;
char buf[PRINTF_BUF_SIZE];
va_start(ap, fmt);
// 格式化字符串
len = vsprintf (buf, fmt, ap);
// 调用龙芯1c库中的串口函数打印字符串
uart_debug_print(buf);
va_end(ap);
return (len);
} 串口初始化那部分代码是一样的,只是打印的函数调用printf()即可,测试代码如下
// 测试printf()函数
void test_printf(void)
{
int i = 0;
printf("[%s] hello!\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
while (1)
{
printf("[%s] %d\r\n", __FUNCTION__, i++);
delay_s(1);
}
}串口的收发(串口echo,收到什么原封不动发送回去)
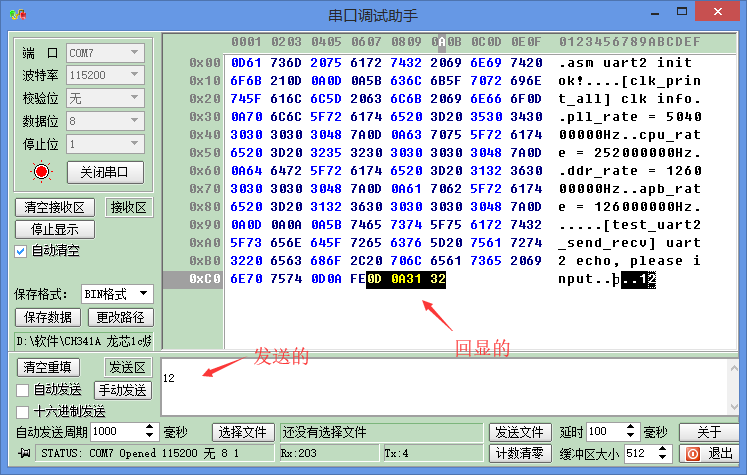
有些时候不但需要串口发送一些数据,还需要从串口接收数据。实现串口echo是一个非常不错的测试用例,即在串口收到什么就原封不动的发送回去,这既能验证串口的收和发,同时测试程序也不会太复杂。
前面打印字符串用的是uart2_print()或者printf(),而这里则用uart_putc(),函数uart_putc()每次只发送一个字符。
串口接收一般采用中断形式,这里也以中断接收为例来讲解,但是发送还是查询方式。
测试串口2的收发
和前面只打印相比,在初始化串口的时候需要打开中断,设置中断处理函数并实现中断处理函数。
串口测试代码如下
/*
* 测试串口2的收发功能是否正常
*/
void test_uart2_send_recv(void)
{
unsigned int tx_gpio = 37;
unsigned int rx_gpio = 36;
ls1c_uart_info_t uart2_info = {0};
printf("\n\n[%s] uart2 echo, please input\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
// 重新初始化串口2(使能接收中断)
uart2_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART2;
uart2_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart2_info.rx_enable= TRUE; // 使能接收中断
uart_init(&uart2_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART2_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART2_IRQ);
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
}
}重点放在中断处理函数是如何实现的。先看源码吧
/*
* 串口的中断处理函数
* 如有需要,可以给每个串口单独写个中断处理函数,或者通过入参"中断号"来区分串口,并单独处理
* @IRQn 中断号
* @param 传递给中断处理函数的参数
*/
void test_uart_irqhandler(int IRQn, void *param)
{
ls1c_uart_t uartx = uart_irqn_to_uartx(IRQn);
void *uart_base = uart_get_base(uartx);
unsigned char iir = reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_IIR_OFFSET);
// 判断是否为接收超时或接收到有效数据
if ((IIR_RXTOUT & iir) || (IIR_RXRDY & iir))
{
// 是,则读取数据,并原样发送回去
while (LSR_RXRDY & reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_LSR_OFFSET))
{
uart_putc(uartx, reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_DAT_OFFSET));
}
}
return ;
}首先,调用uart_irqn_to_uartx()将中断号转换为串口号,这样做的目的是——不同的串口使用相同的中断处理函数。这里偷了个懒,实际使用中可能每个串口接不同的设备,可能需要对接收到的数据做不同的处理,如果那样的话,最好还是每个串口单独写一个中断处理函数。
然后,调用uart_get_base()获取串口的基地址,读取IIR寄存器的值。
然后,再判断是否为接收中断。龙芯1c的串口中断有多种,所以需要先判断一下是否为接收中断,接收中断又有两种形式:接收超时和接收到有效数据。
然后,就是把接收缓存中的数据,逐个读出来,并原封不动的发送回去。
测试结果如下
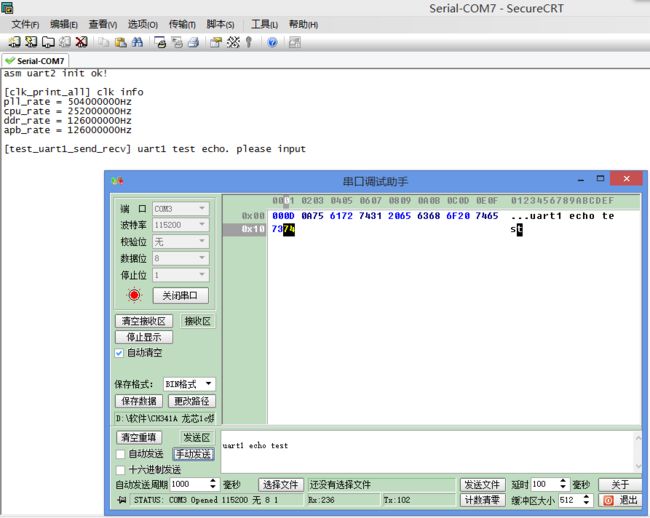
测试串口1的收发
串口1和前面的串口2类似,采用同一个中断处理函数,测试函数如下
/*
* 测试串口1的收发功能是否正常
*/
void test_uart1_send_recv(void)
{
// EJTAG引脚复用比较特殊,除了需要设置复用寄存器外,
// 还需要把引脚JTAG_SEL(注意,不是EJTAG_SEL)拉高,可能板子上有个跳线帽,注意观察
unsigned int tx_gpio = 3; // EJTAG_TDO/GPIO03
unsigned int rx_gpio = 2; // EJTAG_TDI/GPIO02
ls1c_uart_info_t uart1_info = {0};
printf("[%s] uart1 test echo. please input\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
// 初始化串口
uart1_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART1;
uart1_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart1_info.rx_enable= TRUE;
uart_init(&uart1_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART1_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART1_IRQ);
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
}
}测试结果如下
测试串口3的收发
串口3也类似,测试函数如下
// 测试串口3的收发功能是否正常
void test_uart3_send_recv(void)
{
// EJTAG引脚复用比较特殊,除了需要设置复用寄存器外,
// 还需要把引脚JTAG_SEL(注意,不是EJTAG_SEL)拉高,可能板子上有个跳线帽,注意观察
unsigned int tx_gpio = 1; // EJTAG_TCK/GPIO01
unsigned int rx_gpio = 0; // EJTAG_SEL/GPIO00
ls1c_uart_info_t uart3_info = {0};
printf("[%s] uart3 test echo. please input\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
// 初始化串口
uart3_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART3;
uart3_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart3_info.rx_enable= TRUE;
uart_init(&uart3_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART3_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART3_IRQ);
// 通过串口3先发送一个字符串,用于单独判断发送功能是否正常
uart_print(LS1C_UART3, "uart3 send\r\n");
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
printf("[%s] ......\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
}测试结果如下

测试串口8的收发
串口8也类似,需要注意的地方是
“龙芯1C300A没有串口8,龙芯1C300B才有串口5到串口11这几个串口”
本测试用例是在白菜板V2.1(cpu是1C300B)上测试的。
测试源码如下
// 测试串口8的收发功能是否正常,注意龙芯1C300A没有串口8,龙芯1C300B才有串口5到串口11这几个串口
void test_uart8_send_recv(void)
{
unsigned int tx_gpio = 54; // CAMDATA4/GPIO54/UART8_TX
unsigned int rx_gpio = 55; // CAMDATA5/GPIO55/UART8_RX
ls1c_uart_info_t uart8_info = {0};
printf("[%s] uart8 test echo. please input...\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置引脚复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FIFTH);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FIFTH);
// 初始化串口
uart8_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART8;
uart8_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart8_info.rx_enable= TRUE;
uart_init(&uart8_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART8_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART8_IRQ);
// 通过串口8先发送一个字符串,用于单独判断发送功能是否正常
uart_print(LS1C_UART8, "uart8 send\r\n");
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
printf("[%s] ......\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
}
测试用的完整源码清单
Main.c
#include "../lib/ls1c_public.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_irq.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_gpio.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_delay.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_mipsregs.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_uart.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_sys_tick.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_clock.h"
#include "../example/test_gpio.h"
#include "../example/test_pwm.h"
#include "../example/test_delay.h"
#include "../example/test_simulate_i2c.h"
#include "../example/test_timer.h"
#include "../example/test_fpu.h"
#include "../example/test_i2c.h"
#include "../example/test_uart.h"
#include "../example/test_sys_tick.h"
#include "../example/test_spi.h"
// pmon提供的打印接口
struct callvectors *callvec;
// 硬浮点初始化
void fpu_init(void)
{
unsigned int c0_status = 0;
unsigned int c1_status = 0;
// 使能协处理器1--FPU
c0_status = read_c0_status();
c0_status |= (ST0_CU1 | ST0_FR);
write_c0_status(c0_status);
// 配置FPU
c1_status = read_c1_status();
c1_status |= (FPU_CSR_FS | FPU_CSR_FO | FPU_CSR_FN); // set FS, FO, FN
c1_status &= ~(FPU_CSR_ALL_E); // disable exception
c1_status = (c1_status & (~FPU_CSR_RM)) | FPU_CSR_RN; // set RN
write_c1_status(c1_status);
return ;
}
void bsp_init(void)
{
// 初始化调试串口
uart2_init();
// 硬浮点初始化
fpu_init();
// 初始化异常
exception_init();
// 显示时钟信息
clk_print_all();
return ;
}
int main(void)
{
bsp_init();
// -------------------------测试gpio----------------------
/*
* 测试库中gpio作为输出时的相关接口
* led闪烁10次
*/
// test_gpio_output();
/*
* 测试库中gpio作为输入时的相关接口
* 按键按下时,指示灯点亮,否则,熄灭
*/
// test_gpio_input();
/*
* 测试库中外部中断(gpio输入中断)的相关接口
* 按键被按下后,会产生一个中断
*/
// test_gpio_key_irq();
// ------------------------测试串口-----------------------
// 通过串口2打印helloworld
test_uart2_print_helloworld();
// 测试串口2的收发功能是否正常
// test_uart2_send_recv();
// 测试串口2的收发功能是否正常
// test_uart1_send_recv();
// 测试串口3的收发功能是否正常
// test_uart3_send_recv();
// 测试printf()函数
// test_printf();
// ------------------------测试PWM--------------------------------
// 测试硬件pwm产生连续的pwm波形
// test_pwm_normal();
// 测试硬件pwm产生pwm脉冲
// test_pwm_pulse();
/*
* 测试gpio04复用为pwm,gpio06作为普通gpio使用
* PWM0的默认引脚位GPIO06,但也可以复用为GPIO04
* 当gpio06还是保持默认为pwm时,复用gpio04为pwm0,那么会同时在两个引脚输出相同的pwm波形
* 本函数旨在证明可以在gpio04复用为pwm0时,还可以将(默认作为pwm0的)gpio06作为普通gpio使用
*/
// test_pwm_gpio04_gpio06();
// 测试pwm最大周期
// test_pwm_max_period();
// ------------------------测试软件延时--------------------------------
// 测试延时函数delay_1ms()
// test_delay_1ms();
// 测试延时函数delay_1us()
// test_delay_1us();
// 测试延时函数delay_1s()
// test_delay_1s();
// ------------------------测试模拟I2C------------------------------
// 测试模拟I2C
// test_simulate_i2c_am2320();
// ------------------------测试硬件I2C---------------------------
// 用温湿度传感器测试硬件i2c
// test_i2c_am2320();
// ------------------------测试硬件定时器---------------------------
// 测试硬件定时器的定时功能(读取中断状态位的方式判断是否超时)
// test_timer_poll_time_out();
// 测试硬件定时器的中断
// test_timer_irq();
// 测试硬件定时器的计时
// test_timer_get_time();
// ------------------------测试硬浮点(FPU)---------------------------
// 测试使用硬浮点进行浮点数的加减乘除
// test_fpu();
// ------------------------测试滴答定时器---------------------------
// 通过获取当前tick值来测试滴答定时器,默认已经使能了滴答定时器,每秒1000个tick
// test_sys_tick();
// ------------------------测试硬件SPI---------------------------
// 用tm7705测试硬件SPI
// 具体为tm7705+ntc热敏电阻实现温度测量(3d打印机就可以采用此方案测量温度)
// test_spi_tm7705();
// ------------------------测试CAN---------------------------
// 详情请参考文件test_can.c
while (1)
;
return(0);
}test_uart.c
// 测试串口的源文件
#include "../lib/ls1c_public.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_uart.h"
#include "../lib/start.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_irq.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_pin.h"
#include "../lib/ls1c_delay.h"
/*
* 串口的中断处理函数
* 如有需要,可以给每个串口单独写个中断处理函数,或者通过入参"中断号"来区分串口,并单独处理
* @IRQn 中断号
* @param 传递给中断处理函数的参数
*/
void test_uart_irqhandler(int IRQn, void *param)
{
ls1c_uart_t uartx = uart_irqn_to_uartx(IRQn);
void *uart_base = uart_get_base(uartx);
unsigned char iir = reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_IIR_OFFSET);
// 判断是否为接收超时或接收到有效数据
if ((IIR_RXTOUT & iir) || (IIR_RXRDY & iir))
{
// 是,则读取数据,并原样发送回去
while (LSR_RXRDY & reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_LSR_OFFSET))
{
uart_putc(uartx, reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_DAT_OFFSET));
}
}
return ;
}
/*
* 测试串口2的收发功能是否正常
*/
void test_uart2_send_recv(void)
{
unsigned int tx_gpio = 37;
unsigned int rx_gpio = 36;
ls1c_uart_info_t uart2_info = {0};
printf("\n\n[%s] uart2 echo, please input\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
// 重新初始化串口2(使能接收中断)
uart2_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART2;
uart2_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart2_info.rx_enable= TRUE; // 使能接收中断
uart_init(&uart2_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART2_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART2_IRQ);
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
}
}
/*
* 测试串口1的收发功能是否正常
*/
void test_uart1_send_recv(void)
{
// EJTAG引脚复用比较特殊,除了需要设置复用寄存器外,
// 还需要把引脚JTAG_SEL(注意,不是EJTAG_SEL)拉高,可能板子上有个跳线帽,注意观察
unsigned int tx_gpio = 3; // EJTAG_TDO/GPIO03
unsigned int rx_gpio = 2; // EJTAG_TDI/GPIO02
ls1c_uart_info_t uart1_info = {0};
printf("[%s] uart1 test echo. please input\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
// 初始化串口
uart1_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART1;
uart1_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart1_info.rx_enable= TRUE;
uart_init(&uart1_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART1_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART1_IRQ);
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
}
}
// 测试串口3的收发功能是否正常
void test_uart3_send_recv(void)
{
// EJTAG引脚复用比较特殊,除了需要设置复用寄存器外,
// 还需要把引脚JTAG_SEL(注意,不是EJTAG_SEL)拉高,可能板子上有个跳线帽,注意观察
unsigned int tx_gpio = 1; // EJTAG_TCK/GPIO01
unsigned int rx_gpio = 0; // EJTAG_SEL/GPIO00
ls1c_uart_info_t uart3_info = {0};
printf("[%s] uart3 test echo. please input\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_FOURTH);
// 初始化串口
uart3_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART3;
uart3_info.baudrate = 115200;
uart3_info.rx_enable= TRUE;
uart_init(&uart3_info);
// 设置中断处理函数
irq_install(LS1C_UART3_IRQ, test_uart_irqhandler, NULL);
irq_enable(LS1C_UART3_IRQ);
// 通过串口3先发送一个字符串,用于单独判断发送功能是否正常
uart_print(LS1C_UART3, "uart3 send\r\n");
while (1)
{
delay_s(1);
printf("[%s] ......\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
}
}
// 测试printf()函数
void test_printf(void)
{
int i = 0;
printf("[%s] hello!\r\n", __FUNCTION__);
while (1)
{
printf("[%s] %d\r\n", __FUNCTION__, i++);
delay_s(1);
}
}
// 通过串口2打印helloworld
void test_uart2_print_helloworld(void)
{
while (1)
{
uart2_print("hello world!\r\n");
delay_s(1);
}
}test_uart.h
// 测试串口的头文件
#ifndef __OPENLOONGSON_TEST_UART_H
#define __OPENLOONGSON_TEST_UART_H
/*
* 测试串口2的收发功能是否正常
*/
void test_uart2_send_recv(void);
/*
* 测试串口1的收发功能是否正常
*/
void test_uart1_send_recv(void);
// 测试串口3的收发功能是否正常
void test_uart3_send_recv(void);
// 测试printf()函数
void test_printf(void);
// 通过串口2打印helloworld
void test_uart2_print_helloworld(void);
#endif封装串口接口
我认为串口本身并不复杂,相关寄存器也只有几个,而linux等操作系统为了实现shell等,把本来简单的串口整的“好像很复杂的样子”。所以这里直接把1c库中串口相关函数的源码贴出来,代码不多,对照芯片手册,详细很快能看懂。
ls1c_uart.c
// 串口相关源码
#include
#include
#include "ls1c_public.h"
#include "ls1c_regs.h"
#include "ls1c_pin.h"
#include "ls1c_uart.h"
#include "ls1c_clock.h"
#include "start.h"
#include "ls1c_irq.h"
// 串口线路状态寄存器的位域
#define LS1C_UART_LSR_TE (1 << 6)
#define LS1C_UART_LSR_TFE (1 << 5)
// 打印缓存的大小
#define LS1C_UART_PRINT_BUF_SIZE (256)
// 调试串口信息
ls1c_uart_info_t debug_uart_info = {0};
/*
* 获取指定串口模块的基地址
* @UARTx 串口编号
* @ret 基地址
*/
inline void *uart_get_base(ls1c_uart_t UARTx)
{
void *base = NULL;
switch (UARTx)
{
case LS1C_UART00:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART00_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART01:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART01_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART1:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART1_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART2:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART2_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART3:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART3_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART4:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART4_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART5:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART5_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART6:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART6_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART7:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART7_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART8:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART8_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART9:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART9_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART10:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART10_BASE;
break;
case LS1C_UART11:
base = (void *)LS1C_UART11_BASE;
break;
default:
break;
}
return base;
}
/*
* 初始化指定的串口模块
* @uart_info_p 串口模块信息
*/
void uart_init(ls1c_uart_info_t *uart_info_p)
{
void *uart_base = uart_get_base(uart_info_p->UARTx);
unsigned long baudrate_div = 0;
// 禁止所有中断
reg_write_8(0, uart_base + LS1C_UART_IER_OFFSET);
// 接收FIFO的中断申请Trigger为14字节,清空发送和接收FIFO,并复位
reg_write_8(0xc3, uart_base + LS1C_UART_FCR_OFFSET);
// 设置波特率
reg_write_8(0x80, uart_base + LS1C_UART_LCR_OFFSET);
baudrate_div = clk_get_cpu_rate() / 16 / uart_info_p->baudrate / 2;
reg_write_8((baudrate_div >> 8) & 0xff, uart_base + LS1C_UART_MSB_OFFSET);
reg_write_8(baudrate_div & 0xff, uart_base + LS1C_UART_LSB_OFFSET);
// 8个数据位,1个停止位,无校验
reg_write_8(0x03, uart_base + LS1C_UART_LCR_OFFSET);
// 使能接收中断
if (TRUE == uart_info_p->rx_enable)
{
reg_write_8(IER_IRxE|IER_ILE , uart_base + LS1C_UART_IER_OFFSET);
}
return ;
}
/*
* 判断FIFO是否为空
* @uartx 串口号
* @ret TRUE or FALSE
*/
BOOL uart_is_transmit_empty(ls1c_uart_t uartx)
{
void *uart_base = uart_get_base(uartx);
unsigned char status = reg_read_8(uart_base + LS1C_UART_LSR_OFFSET);
if (status & (LS1C_UART_LSR_TE | LS1C_UART_LSR_TFE))
{
return TRUE;
}
else
{
return FALSE;
}
}
/*
* 发送一个字节
* @uartx 串口号
* @ch 待发送的字符串
*/
void uart_putc(ls1c_uart_t uartx, unsigned char ch)
{
void *uart_base = uart_get_base(uartx);
// 等待
while (FALSE == uart_is_transmit_empty(uartx))
;
// 发送
reg_write_8(ch, uart_base + LS1C_UART_DAT_OFFSET);
return ;
}
/*
* 打印一个字符串到指定串口
* @uartx 串口号
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart_print(ls1c_uart_t uartx, const char *str)
{
while ('\0' != *str) // 判断是否为字符串结束符
{
uart_putc(uartx, *str); // 发送一个字符
str++;
}
return ;
}
/*
* 初始化串口2
*/
void uart2_init(void)
{
unsigned int tx_gpio = 37;
unsigned int rx_gpio = 36;
// 设置复用
pin_set_remap(tx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
pin_set_remap(rx_gpio, PIN_REMAP_SECOND);
// 初始化相关寄存器
debug_uart_info.UARTx = LS1C_UART2;
debug_uart_info.baudrate = 115200;
debug_uart_info.rx_enable = FALSE; // 调试串口只需要打印(发送)功能,不需要接收功能
uart_init(&debug_uart_info);
return ;
}
/*
* 在串口2上打印字符串
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart2_print(const char *str)
{
uart_print(LS1C_UART2, str);
return ;
}
/*
* 在调试串口打印字符串
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart_debug_print(const char *str)
{
uart_print(debug_uart_info.UARTx, str);
return ;
}
/*
* 在调试串口打印一个字符
* @ch 待打印的字符
*/
void uart_debug_putc(unsigned char ch)
{
uart_putc(debug_uart_info.UARTx, ch);
return ;
}
/*
* 把中断号转换为串口号
* @IRQn 中断号
* @ret 串口号
*/
inline ls1c_uart_t uart_irqn_to_uartx(int IRQn)
{
ls1c_uart_t uartx = LS1C_UART2;
switch (IRQn)
{
/* 串口UART00和UART01的中断号还待确定
case LS1C_UART00_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART00;
break;
case LS1C_UART01_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART01;
break;
*/
case LS1C_UART1_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART1;
break;
case LS1C_UART2_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART2;
break;
case LS1C_UART3_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART3;
break;
case LS1C_UART4_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART4;
break;
case LS1C_UART5_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART5;
break;
case LS1C_UART6_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART6;
break;
case LS1C_UART7_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART7;
break;
case LS1C_UART8_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART8;
break;
case LS1C_UART9_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART9;
break;
case LS1C_UART10_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART10;
break;
case LS1C_UART11_IRQ:
uartx = LS1C_UART11;
break;
default:
uartx = LS1C_UART2;
break;
}
return uartx;
} ls1c_uart.h
// 串口相关头文件
#ifndef __OPENLOONGSON_UART_H
#define __OPENLOONGSON_UART_H
// 串口模块编号
typedef enum
{
LS1C_UART00 = 0, // 全功能串口UART0可以分为两个四线串口UART00和UART01
LS1C_UART01,
LS1C_UART1,
LS1C_UART2,
LS1C_UART3,
LS1C_UART4,
LS1C_UART5,
LS1C_UART6,
LS1C_UART7,
LS1C_UART8,
LS1C_UART9,
LS1C_UART10,
LS1C_UART11
}ls1c_uart_t;
// 串口信息
typedef struct
{
ls1c_uart_t UARTx; // 串口模块编号
unsigned int baudrate; // 波特率
BOOL rx_enable; // 是否需要使用串口接收数据(使能接收中断),发送默认使能
}ls1c_uart_info_t;
/*
* 获取指定串口模块的基地址
* @UARTx 串口编号
* @ret 基地址
*/
inline void *uart_get_base(ls1c_uart_t UARTx);
/*
* 初始化指定的串口模块
* @uart_info_p 串口模块信息
*/
void uart_init(ls1c_uart_info_t *uart_info_p);
/*
* 初始化串口2
*/
void uart2_init(void);
/*
* 在串口2上打印字符串
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart2_print(const char *str);
/*
* 在调试串口打印字符串
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart_debug_print(const char *str);
/*
* 在调试串口打印一个字符
* @ch 待打印的字符
*/
void uart_debug_putc(unsigned char ch);
/*
* 把中断号转换为串口号
* @IRQn 中断号
* @ret 串口号
*/
inline ls1c_uart_t uart_irqn_to_uartx(int IRQn);
/*
* 发送一个字节
* @uartx 串口号
* @ch 待发送的字符串
*/
void uart_putc(ls1c_uart_t uartx, unsigned char ch);
/*
* 打印一个字符串到指定串口
* @uartx 串口号
* @str 待打印的字符串
*/
void uart_print(ls1c_uart_t uartx, const char *str);
#endif更多更完整的代码,请移步到git查看。
感谢阅读!