Memcached源码分析 - 网络模型(1)
Memcached源码分析 - 命令解析(2)
Memcached源码分析 - 数据存储(3)
Memcached源码分析 - 增删改查操作(4)
Memcached源码分析 - 内存存储机制Slabs(5)
Memcached源码分析 - LRU淘汰算法(6)
Memcached源码分析 - 消息回应(7)
Memcached的LRU几种策略
- 惰性删除。memcached一般不会主动去清除已经过期或者失效的缓存,当get请求一个item才会去检查item是否失效。
- flush命令。flush命令会将所有的item设置为失效。
- 创建的时候检查。Memcached会在创建ITEM的时候去LRU的链表尾部开始检查,是否有失效的ITEM,如果没有的话就重新创建。
- LRU爬虫。memcached默认是关闭LRU爬虫的。LRU爬虫是一个单独的线程,会去清理失效的ITEM。
- LRU淘汰。当缓存没有内存可以分配给新的元素的时候,memcached会从LRU链表的尾部开始淘汰一个ITEM,不管这个ITEM是否还在有效期都将会面临淘汰。LRU链表插入缓存ITEM的时候有先后顺序,所以淘汰一个ITEM也是从尾部进行 也就是先淘汰最早的ITEM。
说明:
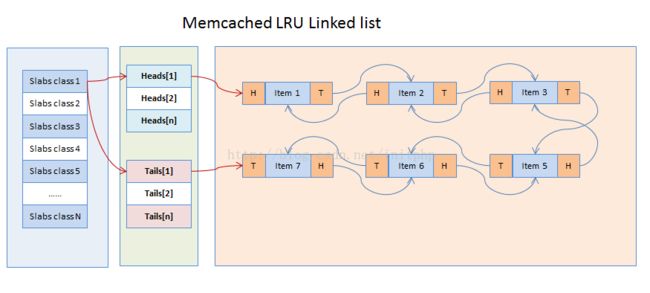
Item.c当中维护了LRU的list列表的数组,其中数组的下表是slabclass的id。
static item *heads[LARGEST_ID]; //存储头部地址
static item *tails[LARGEST_ID]; //存储尾部地址
针对list的操作包括添加到队列(头部插入法)和从队列中删除两个操作。
static void item_link_q(item *it) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[it->slabs_clsid]);
do_item_link_q(it);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[it->slabs_clsid]);
}
static void do_item_link_q(item *it) { /* item is the new head */
item **head, **tail;
assert((it->it_flags & ITEM_SLABBED) == 0);
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
assert(it != *head);
assert((*head && *tail) || (*head == 0 && *tail == 0));
it->prev = 0;
it->next = *head;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it;
*head = it;
if (*tail == 0) *tail = it;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]++;
#ifdef EXTSTORE
if (it->it_flags & ITEM_HDR) {
sizes_bytes[it->slabs_clsid] += (ITEM_ntotal(it) - it->nbytes) + sizeof(item_hdr);
} else {
sizes_bytes[it->slabs_clsid] += ITEM_ntotal(it);
}
#else
sizes_bytes[it->slabs_clsid] += ITEM_ntotal(it);
#endif
return;
}
static void item_unlink_q(item *it) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[it->slabs_clsid]);
do_item_unlink_q(it);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[it->slabs_clsid]);
}
static void do_item_unlink_q(item *it) {
item **head, **tail;
head = &heads[it->slabs_clsid];
tail = &tails[it->slabs_clsid];
if (*head == it) {
assert(it->prev == 0);
*head = it->next;
}
if (*tail == it) {
assert(it->next == 0);
*tail = it->prev;
}
assert(it->next != it);
assert(it->prev != it);
if (it->next) it->next->prev = it->prev;
if (it->prev) it->prev->next = it->next;
sizes[it->slabs_clsid]--;
#ifdef EXTSTORE
if (it->it_flags & ITEM_HDR) {
sizes_bytes[it->slabs_clsid] -= (ITEM_ntotal(it) - it->nbytes) + sizeof(item_hdr);
} else {
sizes_bytes[it->slabs_clsid] -= ITEM_ntotal(it);
}
#else
sizes_bytes[it->slabs_clsid] -= ITEM_ntotal(it);
#endif
return;
}
惰性删除
惰性删除删除其实就是在get数据的时候进行比较判断数据是否过期,这里会跟flush_all命令过期结合起来使用,判断的时候依据了flush_all设置的过期时间settings.oldest_live。
#define refcount_incr(it) ++(it->refcount)
/** wrapper around assoc_find which does the lazy expiration logic */
item *do_item_get(const char *key, const size_t nkey, const uint32_t hv, conn *c, const bool do_update) {
item *it = assoc_find(key, nkey, hv);
if (it != NULL) {
refcount_incr(it);
}
int was_found = 0;
if (it != NULL) {
was_found = 1;
//it->time用来记录item最近set/add/replce等操作的时间(get操作不会改变)
//然后判断it->time是否在执行flush命令之前,如果是执行flush之前,说明该item已经失效
if (item_is_flushed(it)) {
// //LRU链表和HASHTABLE上解除绑定
do_item_unlink(it, hv);
STORAGE_delete(c->thread->storage, it);
//删除该Item
do_item_remove(it);
it = NULL;
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.get_flushed++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
was_found = 2;
//检查是否过期,主要是检查有效期时间
//如果数据已经过期,则需要清除
} else if (it->exptime != 0 && it->exptime <= current_time) {
do_item_unlink(it, hv);
STORAGE_delete(c->thread->storage, it);
do_item_remove(it);
it = NULL;
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.get_expired++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (settings.verbose > 2) {
fprintf(stderr, " -nuked by expire");
}
was_found = 3;
} else {
// 省略了一些代码,暂时看不懂
}
}
return it;
}
flush_all命令删除
将settings.oldest_live设置为当前过期时间,然后在惰性删除的时候用于判断数据是否过期,本身flush_all命令不删除数据。
int item_is_flushed(item *it) {
rel_time_t oldest_live = settings.oldest_live;
uint64_t cas = ITEM_get_cas(it);
uint64_t oldest_cas = settings.oldest_cas;
if (oldest_live == 0 || oldest_live > current_time)
return 0;
if ((it->time <= oldest_live)
|| (oldest_cas != 0 && cas != 0 && cas < oldest_cas)) {
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
else if (ntokens >= 2 && ntokens <= 4 && (strcmp(tokens[COMMAND_TOKEN].value, "flush_all") == 0)) {
time_t exptime = 0;
rel_time_t new_oldest = 0;
set_noreply_maybe(c, tokens, ntokens);
pthread_mutex_lock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
c->thread->stats.flush_cmds++;
pthread_mutex_unlock(&c->thread->stats.mutex);
if (ntokens != (c->noreply ? 3 : 2)) {
exptime = strtol(tokens[1].value, NULL, 10);
if(errno == ERANGE) {
out_string(c, "CLIENT_ERROR bad command line format");
return;
}
}
if (exptime > 0) {
new_oldest = realtime(exptime);
} else { /* exptime == 0 */
new_oldest = current_time;
}
if (settings.use_cas) {
settings.oldest_live = new_oldest - 1;
if (settings.oldest_live <= current_time)
settings.oldest_cas = get_cas_id();
} else {
settings.oldest_live = new_oldest;
}
out_string(c, "OK");
return;
}
新建item会检查数据过期
新建item的时候会去检查是否有数据过期,然后进行回收,这个逻辑有一点绕但是我相信我能够讲解清楚,整个过程如下:
- 1.do_item_alloc进入新增item的内存申请流程。
- 2.do_item_alloc_pull进入item申请的逻辑处理,最多处理10次。
- 3.do_item_alloc_pull内部逻辑是尝试通过slabs_alloc申请内存,失败则尝试通过lru_pull_tail方法释放LRU队列中的item变成可用item。
- 4.lru_pull_tail执行释放LRU队列中item的过程,内部包括各种过期item的回收
- 5.在lru_pull_tail当中调用do_item_unlink_nolock进行item回收
- 6.在do_item_unlink_nolock当中调用do_item_unlink_q释放LRU链表,调用do_item_remove回收item为可用item。
item *do_item_alloc(char *key, const size_t nkey, const unsigned int flags,
const rel_time_t exptime, const int nbytes) {
uint8_t nsuffix;
item *it = NULL;
char suffix[40];
size_t ntotal = item_make_header(nkey + 1, flags, nbytes, suffix, &nsuffix);
unsigned int id = slabs_clsid(ntotal);
unsigned int hdr_id = 0;
if (ntotal > settings.slab_chunk_size_max) {
int htotal = nkey + 1 + nsuffix + sizeof(item) + sizeof(item_chunk);
if (settings.use_cas) {
htotal += sizeof(uint64_t);
}
hdr_id = slabs_clsid(htotal);
it = do_item_alloc_pull(htotal, hdr_id);
if (it != NULL)
it->it_flags |= ITEM_CHUNKED;
} else {
it = do_item_alloc_pull(ntotal, id);
}
// 省略一堆代码
return it;
}
item *do_item_alloc_pull(const size_t ntotal, const unsigned int id) {
item *it = NULL;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
uint64_t total_bytes;
if (!settings.lru_segmented) {
lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, 0, 0, 0, NULL);
}
// 先尝试申请新的内存
it = slabs_alloc(ntotal, id, &total_bytes, 0);
if (settings.temp_lru)
total_bytes -= temp_lru_size(id);
if (it == NULL) {
// 再尝试lru_pull_tail执行COLD_LRU当中释放item
if (lru_pull_tail(id, COLD_LRU, total_bytes, LRU_PULL_EVICT, 0, NULL) <= 0) {
if (settings.lru_segmented) {
// 最后尝试lru_pull_tail执行HOT_LRU当中释放item
lru_pull_tail(id, HOT_LRU, total_bytes, 0, 0, NULL);
} else {
break;
}
}
} else {
break;
}
}
return it;
}
slabs_alloc是尝试申请slab的过程,主要是为了使得当前slab下有可用的item可供申请,具体逻辑自行阅读不是特别复杂。
void *slabs_alloc(size_t size, unsigned int id, uint64_t *total_bytes,
unsigned int flags) {
void *ret;
pthread_mutex_lock(&slabs_lock);
ret = do_slabs_alloc(size, id, total_bytes, flags);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&slabs_lock);
return ret;
}
static void *do_slabs_alloc(const size_t size, unsigned int id, uint64_t *total_bytes,
unsigned int flags) {
slabclass_t *p;
void *ret = NULL;
item *it = NULL;
p = &slabclass[id];
if (total_bytes != NULL) {
*total_bytes = p->requested;
}
// 如果slab下可用的item个数为空,就进入slab的申请流程
if (p->sl_curr == 0 && flags != SLABS_ALLOC_NO_NEWPAGE) {
do_slabs_newslab(id);
}
//申请以后取p->slots的头部指针,然后将头部指针指向下一个位置
if (p->sl_curr != 0) {
it = (item *)p->slots;
p->slots = it->next;
if (it->next) it->next->prev = 0;
it->it_flags &= ~ITEM_SLABBED;
it->refcount = 1;
p->sl_curr--;
ret = (void *)it;
} else {
ret = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
lru_pull_tail是指释放内存的过程,包括过期数据的释放,各种HOT_LRU,COLD_LRU等队列的释放等,核心就是释放内存。
do_item_unlink_nolock内部会释放item到可用item队列当中。
int lru_pull_tail(const int orig_id, const int cur_lru,
const uint64_t total_bytes, const uint8_t flags, const rel_time_t max_age,
struct lru_pull_tail_return *ret_it) {
item *it = NULL;
int id = orig_id;
int removed = 0;
int tries = 5;
item *search;
item *next_it;
void *hold_lock = NULL;
unsigned int move_to_lru = 0;
uint64_t limit = 0;
id |= cur_lru;
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[id]);
// 获取slabclass对应id的LRU队列的队尾元素
search = tails[id];
for (; tries > 0 && search != NULL; tries--, search=next_it) {
next_it = search->prev;
// 如果item内容为空,则继续往LRU列表尾部搜索。
if (search->nbytes == 0 && search->nkey == 0 && search->it_flags == 1) {
if (flags & LRU_PULL_CRAWL_BLOCKS) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[id]);
return 0;
}
tries++;
continue;
}
// 如果item被其它worker引用锁定等情况,则继续往LRU列表尾部搜索。
uint32_t hv = hash(ITEM_key(search), search->nkey);
if ((hold_lock = item_trylock(hv)) == NULL)
continue;
if (refcount_incr(search) != 2) {
itemstats[id].lrutail_reflocked++;
if (settings.tail_repair_time &&
search->time + settings.tail_repair_time < current_time) {
itemstats[id].tailrepairs++;
search->refcount = 1;
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
continue;
}
}
if ((search->exptime != 0 && search->exptime < current_time)
|| item_is_flushed(search)) {
itemstats[id].reclaimed++;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) {
itemstats[id].expired_unfetched++;
}
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
STORAGE_delete(ext_storage, search);
do_item_remove(search);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
removed++;
continue;
}
/* If we're HOT_LRU or WARM_LRU and over size limit, send to COLD_LRU.
* If we're COLD_LRU, send to WARM_LRU unless we need to evict
*/
switch (cur_lru) {
case HOT_LRU:
limit = total_bytes * settings.hot_lru_pct / 100;
case WARM_LRU:
if (limit == 0)
limit = total_bytes * settings.warm_lru_pct / 100;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_ACTIVE) != 0) {
search->it_flags &= ~ITEM_ACTIVE;
removed++;
if (cur_lru == WARM_LRU) {
itemstats[id].moves_within_lru++;
do_item_update_nolock(search);
do_item_remove(search);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
} else {
itemstats[id].moves_to_warm++;
move_to_lru = WARM_LRU;
do_item_unlink_q(search);
it = search;
}
} else if (sizes_bytes[id] > limit ||
current_time - search->time > max_age) {
itemstats[id].moves_to_cold++;
move_to_lru = COLD_LRU;
do_item_unlink_q(search);
it = search;
removed++;
break;
} else {
/* Don't want to move to COLD, not active, bail out */
it = search;
}
break;
case COLD_LRU:
it = search; /* No matter what, we're stopping */
if (flags & LRU_PULL_EVICT) {
if (settings.evict_to_free == 0) {
/* Don't think we need a counter for this. It'll OOM. */
break;
}
itemstats[id].evicted++;
itemstats[id].evicted_time = current_time - search->time;
if (search->exptime != 0)
itemstats[id].evicted_nonzero++;
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_FETCHED) == 0) {
itemstats[id].evicted_unfetched++;
}
if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_ACTIVE)) {
itemstats[id].evicted_active++;
}
LOGGER_LOG(NULL, LOG_EVICTIONS, LOGGER_EVICTION, search);
STORAGE_delete(ext_storage, search);
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
removed++;
if (settings.slab_automove == 2) {
slabs_reassign(-1, orig_id);
}
} else if (flags & LRU_PULL_RETURN_ITEM) {
/* Keep a reference to this item and return it. */
ret_it->it = it;
ret_it->hv = hv;
} else if ((search->it_flags & ITEM_ACTIVE) != 0
&& settings.lru_segmented) {
itemstats[id].moves_to_warm++;
search->it_flags &= ~ITEM_ACTIVE;
move_to_lru = WARM_LRU;
do_item_unlink_q(search);
removed++;
}
break;
case TEMP_LRU:
it = search; /* Kill the loop. Parent only interested in reclaims */
break;
}
if (it != NULL)
break;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[id]);
if (it != NULL) {
if (move_to_lru) {
it->slabs_clsid = ITEM_clsid(it);
it->slabs_clsid |= move_to_lru;
item_link_q(it);
}
if ((flags & LRU_PULL_RETURN_ITEM) == 0) {
do_item_remove(it);
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
}
}
return removed;
}
void do_item_unlink_nolock(item *it, const uint32_t hv) {
MEMCACHED_ITEM_UNLINK(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, it->nbytes);
if ((it->it_flags & ITEM_LINKED) != 0) {
it->it_flags &= ~ITEM_LINKED;
STATS_LOCK();
stats_state.curr_bytes -= ITEM_ntotal(it);
stats_state.curr_items -= 1;
STATS_UNLOCK();
item_stats_sizes_remove(it);
assoc_delete(ITEM_key(it), it->nkey, hv);
// 从LRU的链表中删除
do_item_unlink_q(it);
// 回收到可用的item列表当中
do_item_remove(it);
}
}
LRU爬虫线程定时清理
首先需要启动爬虫线程,这里通过pthread_create进行线程启动。
int start_item_crawler_thread(void) {
int ret;
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_crawler_lock);
do_run_lru_crawler_thread = 1;
// 启动item_crawler_thread线程
if ((ret = pthread_create(&item_crawler_tid, NULL,
item_crawler_thread, NULL)) != 0) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_crawler_lock);
return -1;
}
pthread_cond_wait(&lru_crawler_cond, &lru_crawler_lock);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_crawler_lock);
return 0;
}
- item_crawler_thread线程是真正执行过期数据遍历的工作线程,遍历的逻辑其实很巧妙的,外层遍历所有的slab,内层遍历slab下对应的item,按照slab1->item1;slab2->item2的顺序循环遍历,结束的标记是所有的item都完成遍历。
- lru_crawler_class_done用于标记遍历是否完成。
- active_crawler_mod.mod->eval回调crawler_expired_eval释放过期item。
static void *item_crawler_thread(void *arg) {
int i;
int crawls_persleep = settings.crawls_persleep;
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_crawler_lock);
pthread_cond_signal(&lru_crawler_cond);
settings.lru_crawler = true;
while (do_run_lru_crawler_thread) {
pthread_cond_wait(&lru_crawler_cond, &lru_crawler_lock);
while (crawler_count) {
item *search = NULL;
void *hold_lock = NULL;
for (i = POWER_SMALLEST; i < LARGEST_ID; i++) {
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[i]);
search = do_item_crawl_q((item *)&crawlers[i]);
uint32_t hv = hash(ITEM_key(search), search->nkey);
crawlers[i].checked++;
if (!active_crawler_mod.mod->needs_lock) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[i]);
}
if (search == NULL ||
(crawlers[i].remaining && --crawlers[i].remaining < 1)) {
if (settings.verbose > 2)
fprintf(stderr, "Nothing left to crawl for %d\n", i);
lru_crawler_class_done(i);
continue;
}
// 核心评估item是否过期
active_crawler_mod.mod->eval(&active_crawler_mod, search, hv, i);
if (hold_lock)
item_trylock_unlock(hold_lock);
if (active_crawler_mod.mod->needs_lock) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[i]);
}
if (crawls_persleep-- <= 0 && settings.lru_crawler_sleep) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_crawler_lock);
usleep(settings.lru_crawler_sleep);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_crawler_lock);
crawls_persleep = settings.crawls_persleep;
} else if (!settings.lru_crawler_sleep) {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_crawler_lock);
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_crawler_lock);
}
}
}
STATS_LOCK();
stats_state.lru_crawler_running = false;
STATS_UNLOCK();
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_crawler_lock);
return NULL;
}
static void lru_crawler_class_done(int i) {
crawlers[i].it_flags = 0;
crawler_count--;
do_item_unlinktail_q((item *)&crawlers[i]);
do_item_stats_add_crawl(i, crawlers[i].reclaimed,
crawlers[i].unfetched, crawlers[i].checked);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[i]);
if (active_crawler_mod.mod->doneclass != NULL)
active_crawler_mod.mod->doneclass(&active_crawler_mod, i);
}
static void crawler_expired_eval(crawler_module_t *cm, item *search, uint32_t hv, int i) {
struct crawler_expired_data *d = (struct crawler_expired_data *) cm->data;
pthread_mutex_lock(&d->lock);
crawlerstats_t *s = &d->crawlerstats[i];
int is_flushed = item_is_flushed(search);
if ((search->exptime != 0 && search->exptime < current_time)
|| is_flushed
) {
crawlers[i].reclaimed++;
s->reclaimed++;
if (settings.verbose > 1) {
int ii;
char *key = ITEM_key(search);
// 释放相关item内存并回收item
do_item_unlink_nolock(search, hv);
do_item_remove(search);
} else {
// 省略相关代码
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&d->lock);
}
我们可以理解这部分功能是为了开始过期数据爬虫工作的前置工作。
这里的核心逻辑设置了那些需要遍历的sid的标记位设置,crawlers[sid].it_flags = 1。
int lru_crawler_start(uint8_t *ids, uint32_t remaining,
const enum crawler_run_type type, void *data,
void *c, const int sfd) {
int starts = 0;
bool is_running;
//省略相关代码,这里只需要关注do_lru_crawler_start
for (int sid = POWER_SMALLEST; sid < POWER_LARGEST; sid++) {
if (ids[sid])
starts += do_lru_crawler_start(sid, remaining);
}
if (starts) {
pthread_cond_signal(&lru_crawler_cond);
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_crawler_lock);
return starts;
}
static int do_lru_crawler_start(uint32_t id, uint32_t remaining) {
uint32_t sid = id;
int starts = 0;
pthread_mutex_lock(&lru_locks[sid]);
if (crawlers[sid].it_flags == 0) {
if (settings.verbose > 2)
fprintf(stderr, "Kicking LRU crawler off for LRU %u\n", sid);
crawlers[sid].nbytes = 0;
crawlers[sid].nkey = 0;
// 核心在于把爬虫需要处理的slab的flag设置为1
crawlers[sid].it_flags = 1; /* For a crawler, this means enabled. */
crawlers[sid].next = 0;
crawlers[sid].prev = 0;
crawlers[sid].time = 0;
if (remaining == LRU_CRAWLER_CAP_REMAINING) {
remaining = do_get_lru_size(sid);
}
if (remaining) remaining++;
crawlers[sid].remaining = remaining;
//
crawlers[sid].slabs_clsid = sid;
crawlers[sid].reclaimed = 0;
crawlers[sid].unfetched = 0;
crawlers[sid].checked = 0;
// 伪装item挂到LRU的链表尾部开始遍历
do_item_linktail_q((item *)&crawlers[sid]);
crawler_count++;
starts++;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&lru_locks[sid]);
if (starts) {
STATS_LOCK();
stats_state.lru_crawler_running = true;
stats.lru_crawler_starts++;
STATS_UNLOCK();
}
return starts;
}
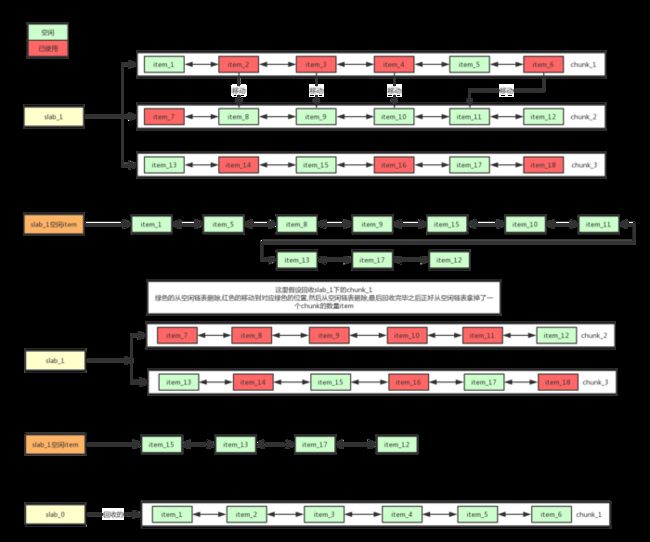
过期数据清理效果图
参考文章
memcached LRU队列状态转换
《Memcached源码分析 - Memcached源码分析之LRU算法(6)》
Memcache-LRU爬虫线程-源码分析