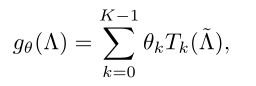Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering论文解读( and code)
《Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering》 提供了已实现的GCN,并且针对 《Spectral Networks and Deep Locally Connected Networks on Graphs》存在的问题:1 计算复杂度高 2 filter并不局部 做出了相应的改进。学习GCN避免不了查看该篇文章。
目录
1 论文贡献:
2 filter and pooling推广
2.1 卷积滤波器 filter
2.2 图池化
2.3 整个GCN过程
3. GCN代码解析
3.1 如何使用GCN -- by MNIST示例
3.2 图卷积具体刨析
1 论文贡献:
a 定义并实现了一个图谱域的卷积公式。
b 所定义的卷积公式严格局部定位,PS他的感受域可以理解为一个直径K的球。
c 计算复杂度低,滤波器复杂度线性。
d 一个的图池化
e 以上都有实现证明,代码公开哦。
2 filter and pooling推广
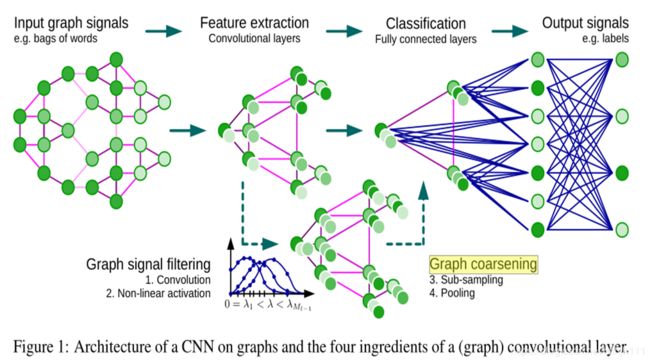
在graph上推广 CNN需要 1 在graph上设计卷积滤波器,2图的池化(图粗化).
2.1 卷积滤波器 filter
卷积公式(不清楚的话参照url: )
改进变化如下图,左为《Spectral Networks and Deep Locally Connected Networks on Graphs》
右为《Convolutional Neural Networks on Graphs with Fast Localized Spectral Filtering》
改进简单说就是将卷积核(or滤波器)的表示函数(可理解为参数θ左)换位多项式函数h(λ)右。
上图第一行左表示卷积核(or滤波器)中的单个单元(PS:在实现时,该单个单元用一个参数θ代表了一个函数,是一种”粗暴近似“,θ可学习)。
第一行右表示卷积核中的单个单元(PS:在实现时,该单个单元实际为多项式函数,α可学习,λ为Laplacian特征值)
第二行表示卷积整个过程的变化(即把改变的卷积滤波器带入整个卷积公式)。
第三行表示卷积核所有单元的变化(即把卷积核中的所有单元替换后的公式形式)。
第四行表示卷积整个过程的公式简洁形式。
PS:不清楚可以借助后文代码解析理解。
2.2 图池化
上图左部分表示使用METIS算法粗化图的方法(借助顶点、顶点之间的关系-边等将图简化),
每级粗化我们可以得到一个粗化图(g0,g1,g2,g3,g4),将该粗化图添加上一些辅助节点(上图右部分上,蓝色圆),使粗化图中每个顶点都有2个孩子,从而构成一个二叉树,将二叉树摊平构成一维信号(上图右部分下),然后对该信号采样即可表示为一次图pooling。这部分作者借助的是之前的工作,我没怎么仔细看,只是大致看代码了解这个构建二叉树于与摊平操作是依靠METIS时的粗话图之间的关系。
2.3 整个GCN过程
3. GCN代码解析
这部分是我最想写的部分,因为之前的太过枯燥,全是公式啥的。
这里分为两部分,1 分析提供的MNIST代码让你明白GCN大致如何用。2 图卷积如何实现的。
3.1 如何使用GCN -- by MNIST示例
本来作者提供了一个使用说明usage.py,但是他是随机构建了数据来解释,这样不免导致难以理解关系,所以这没解释usage.py部分,如需要,推荐阅读 https://blog.csdn.net/duyue3052/article/details/82315463 ,包含了中间数据的直观展示。
作者提供的MNIST包含多个模型对比,我这里直接抽出作者的经典GCN相关,其他除去,方便专注。
mnist.py
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import sys, os
sys.path.insert(0, '..')
from lib import models, graph, coarsening, utils
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import time
# %matplotlib inline
flags = tf.app.flags
FLAGS = flags.FLAGS
flags.DEFINE_integer('number_edges', 8, 'Graph: minimum number of edges per vertex.')
flags.DEFINE_string('metric', 'euclidean', 'Graph: similarity measure (between features).') #相似度测量
flags.DEFINE_bool('normalized_laplacian', True, 'Graph Laplacian: normalized.')
flags.DEFINE_integer('coarsening_levels', 4, 'Number of coarsened graphs.')
flags.DEFINE_string('dir_data', os.path.join('..', 'data', 'mnist'), 'Directory to store data.')
"""# Feature graph 图结构描述,即准备邻接矩阵A的拉普拉斯L"""
def grid_graph(m, corners=False):
z = graph.grid(m) #该函数说白了就产生一个28*28网格的每个点的坐标
dist, idx = graph.distance_sklearn_metrics(z, k=FLAGS.number_edges, metric=FLAGS.metric) #顶点K邻近点计算
A = graph.adjacency(dist, idx) #构建表示图的邻接矩阵 A
# Connections are only vertical or horizontal on the grid. 网格上的连接只有水平或者垂直
# Corner vertices are connected to 2 neightbors only. 转角处的顶点只与两个邻接点连接
if corners:
import scipy.sparse
A = A.toarray()
A[A < A.max()/1.5] = 0
A = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(A)
print('{} edges'.format(A.nnz))
print("{} > {} edges".format(A.nnz//2, FLAGS.number_edges*m**2//2))
return A
t_start = time.process_time()
A = grid_graph(28, corners=False) # "邻接矩阵"
A = graph.replace_random_edges(A, 0) #"添加噪声的邻接矩阵"
graphs, perm = coarsening.coarsen(A, levels=FLAGS.coarsening_levels, self_connections=False) #粗化图
L = [graph.laplacian(A, normalized=True) for A in graphs] #对邻接矩阵进行拉普拉斯变换
print('Execution time: {:.2f}s'.format(time.process_time() - t_start))
#graph.plot_spectrum(L)
del A
"""# Data 准备"""
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.dir_data, one_hot=False)
train_data = mnist.train.images.astype(np.float32)
val_data = mnist.validation.images.astype(np.float32)
test_data = mnist.test.images.astype(np.float32)
train_labels = mnist.train.labels
val_labels = mnist.validation.labels
test_labels = mnist.test.labels
t_start = time.process_time()
train_data = coarsening.perm_data(train_data, perm)
val_data = coarsening.perm_data(val_data, perm)
test_data = coarsening.perm_data(test_data, perm)
print('Execution time: {:.2f}s'.format(time.process_time() - t_start))
del perm
"""# Neural networks"""
common = {}
common['dir_name'] = 'mnist/'
common['num_epochs'] = 20
common['batch_size'] = 100
common['decay_steps'] = mnist.train.num_examples / common['batch_size']
common['eval_frequency'] = 30 * common['num_epochs']
common['brelu'] = 'b1relu'
common['pool'] = 'mpool1'
C = max(mnist.train.labels) + 1 # number of classes
model_perf = utils.model_perf() #模型对比函数
# 参数 for LeNet5-like networks.
common['regularization'] = 5e-4
common['dropout'] = 0.5
common['learning_rate'] = 0.02 # 0.03 in the paper but sgconv_sgconv_fc_softmax has difficulty to converge
common['decay_rate'] = 0.95
common['momentum'] = 0.9
common['F'] = [32, 64] #每次卷积的输出feature大小
common['K'] = [25, 25] #每个卷积核的多项式项数
common['p'] = [4, 4] #每次卷积后的池化大小,池化次数与卷积次数一致
common['M'] = [512, C] #全连接层输出
# Architecture of TF MNIST conv model (LeNet-5-like).
if True:
name = 'Chebyshev_test' # 'Chebyshev'
params = common.copy()
params['dir_name'] += name
params['filter'] = 'chebyshev5' #使用chebyshev5所建的滤波器
model_perf.test(models.cgcnn(L, **params), name, params,
train_data, train_labels, val_data, val_labels, test_data, test_labels)
model_perf.show()
'''
#or 使用下面的代码可以在训练后不显示评价结果,而是直接训练。
model = models.cgcnn(L, **params)
accuracy, loss, t_step = model.fit(train_data, train_labels, val_data, val_labels)
'''
由上述代码可知数据关系为:
为了构建网络,我们需要提供描述graph的邻接矩阵A(这个图的描述设置将影响GCN性能),以便帮助网络构成滤波器。
而原始数据会由粗化返回的重排关系重新组织为3D数据(样例编号N,顶点编号M,该顶点上特征F),他们将输入到网络中真正进行卷积。
3.2 图卷积具体刨析
本章将逐级展开GCN,分析其实现
1 从 mnist.py 开始,发现网络构建是借助 来自models.py的class cgcnn(base_model)
models.cgcnn(L, **params)2 models.py中的 class cgcnn(base_model)
这里的cgcnn继承自models.py中的base_model(作者构建了几种网络对比,而其中的卷积是不同实现,所以用基类来省去重复部分),base_model包含了一个“神经网络类”的一些通用函数,如fit(),predict(),evaluate(),build_graph()等函数,自然我们需要首先看base_model中的build_graph()
def build_graph(self, M_0):
"""Build the computational graph of the model."""
self.graph = tf.Graph()
with self.graph.as_default():
# Inputs.
with tf.name_scope('inputs'):
self.ph_data = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (self.batch_size, M_0), 'data')
self.ph_labels = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, (self.batch_size), 'labels')
self.ph_dropout = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, (), 'dropout')
# Model.
op_logits = self.inference(self.ph_data, self.ph_dropout) #!!!!!!#
self.op_loss, self.op_loss_average = self.loss(op_logits, self.ph_labels, self.regularization)
self.op_train = self.training(self.op_loss, self.learning_rate,
self.decay_steps, self.decay_rate, self.momentum)
self.op_prediction = self.prediction(op_logits)
# Initialize variables, i.e. weights and biases.
self.op_init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# Summaries for TensorBoard and Save for model parameters.
self.op_summary = tf.summary.merge_all()
self.op_saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5)
self.graph.finalize()上面的是一般正常构建步骤,唯一特殊点的是,self.inference调用self._inference直接返回预测,所以必然每个子类的_inference实现将是关键
op_logits = self.inference(self.ph_data, self.ph_dropout) #!!!!!!#
----------排版分割-------------------
def inference(self, data, dropout):
"""
something .....
"""
logits = self._inference(data, dropout)
return logits3 以cgcnn中的_inference为例分析(models.py中的其他是论文中提到的其他模型或配置实现),cgcnn为作者提出的基准模型。
def _inference(self, x, dropout):
# Graph convolutional layers.
x = tf.expand_dims(x, 2) # N x M x F=1
for i in range(len(self.p)): #依据池化次数,设置卷积(池化and卷积一对一)
with tf.variable_scope('conv{}'.format(i+1)): #此scope中的为一次图卷积
with tf.name_scope('filter'): #卷积中的滤波器
x = self.filter(x, self.L[i], self.F[i], self.K[i])
with tf.name_scope('bias_relu'): #卷积中的激活函数
x = self.brelu(x)
with tf.name_scope('pooling'): #卷积后的池化
x = self.pool(x, self.p[i])
# Fully connected hidden layers.
N, M, F = x.get_shape()
x = tf.reshape(x, [int(N), int(M*F)]) # N x M
for i,M in enumerate(self.M[:-1]):
with tf.variable_scope('fc{}'.format(i+1)):
x = self.fc(x, M)
x = tf.nn.dropout(x, dropout)
# Logits linear layer, i.e. softmax without normalization.
with tf.variable_scope('logits'):
x = self.fc(x, self.M[-1], relu=False)
return x4 分解上述代码scope('filter'),发现他是借助getattr()重新与指定函数绑定,如和chebyshev2()绑定,这里我们以chebyshev2()(PS 该函数即为filter,且为作者提出的经典类型,功能应该和chebyshv5()相同,只不过通过numpy实现,而chebyshev5借助TF实现,)为例展开解释filter如何编写的(numpy比TF实现看起来更好理解)。
def chebyshev2(self, x, L, Fout, K):
"""
Filtering with Chebyshev interpolation
Implementation: numpy.
Data: x of size N x M x F
N: number of signals
M: number of vertices
F: number of features per signal per vertex
"""
N, M, Fin = x.get_shape()
N, M, Fin = int(N), int(M), int(Fin)
# Rescale Laplacian. Copy to not modify the shared L.
L = scipy.sparse.csr_matrix(L)
L = graph.rescale_L(L, lmax=2)
# Transform to Chebyshev basis
x = tf.transpose(x, perm=[1, 2, 0]) # M x Fin x N
x = tf.reshape(x, [M, Fin*N]) # M x Fin*N #将X所有点所有特征放到一个维度上,得X
def chebyshev(x): #在X上用用chebyshev,返回T_k X(py_func将X转到numpy array运行)
return graph.chebyshev(L, x, K)
x = tf.py_func(chebyshev, [x], [tf.float32])[0] # K x M x Fin*N
x = tf.reshape(x, [K, M, Fin, N]) # K x M x Fin x N # 维度转换
x = tf.transpose(x, perm=[3,1,2,0]) # N x M x Fin x K
x = tf.reshape(x, [N*M, Fin*K]) # N*M x Fin*K
# Filter: Fin*Fout filters of order K, i.e. one filterbank per feature.
W = self._weight_variable([Fin*K, Fout], regularization=False) #权重乘法
x = tf.matmul(x, W) # N*M x Fout
return tf.reshape(x, [N, M, Fout]) # N x M x Fout从上面可以看到,先将x转换到稀疏矩阵的形式,然后维度变形,之后在其上使用graph.chebyshev()应用chebyshev多项式的迭代计算函数,获得T_k,即论文中使用chebyshev来计算T_k---下图左, 来近似diag(λ)^k---下图右),同时我们注意到下面公式里含有求和(关于k),而上面代码中并没有,而是通过增加权重参数(w本为【Fin*Fout】,现为【Fin*k,Fout】)将其从求和变为x*w(shape(w) = [Fin*k,Fout])的形式。
def chebyshev(L, X, K):
"""Return T_k X where T_k are the Chebyshev polynomials of order up to K.
Complexity is O(KMN)."""
'''来自于graph.py
返回T_k X,其中T_k是最多为K阶的Chebyshev多项式。'''
M, N = X.shape
assert L.dtype == X.dtype
# L = rescale_L(L, lmax)
# Xt = T @ X: MxM @ MxN.
Xt = np.empty((K, M, N), L.dtype)
# Xt_0 = T_0 X = I X = X.
Xt[0, ...] = X
# Xt_1 = T_1 X = L X.
if K > 1:
Xt[1, ...] = L.dot(X)
# Xt_k = 2 L Xt_k-1 - Xt_k-2.
for k in range(2, K):
Xt[k, ...] = 2 * L.dot(Xt[k-1, ...]) - Xt[k-2, ...]
return Xt上面的chebyshev即借助chebyshev的多项式递推性质而写。获得T_k后经过适当变形处理,即可和需要学习的参数θ相乘,然后返回结果,至此一次filter()结束,PS 这里为何可用chebyshev多项式近似我不太熟悉,没有深究,有熟悉的同学请评论或私信我。
5 之后的self.brelu(x),self.pool(x, self.p[i]) 并不是作者提出(PS:pool也挺有意思,其重新组织为1D信号时需要采取的粗化与重排),此次并不过多说明。(PS主要是太懒了)