Spring架构学习(2)通过Properties文件实现依赖注入
还是用上次的生产者——消费者例子,代码如下:
package my.spring.bean.demo;
public interface IoCImpl {
public void run();
}package my.spring.bean.demo;
import my.spring.bean.pojo.Dispatcher;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader;
public class PropertyFileImpl implements IoCImpl {
@Override
public void run() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DefaultListableBeanFactory registry=new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
BeanFactory container=bindViaPropertyFile(registry);
Dispatcher dispatcher=(Dispatcher)container.getBean("dispatcherB");
dispatcher.dispatch();
}
public static BeanFactory bindViaPropertyFile(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry){
PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader reader=new PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader(registry);
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(ClassLoader.getSystemResource("")+"../binding-config.properties");
return (BeanFactory) registry;
}
}
注意properties文件的目录,这里采用ClassLoader获取当前的classpath。
properties文件配置如下,其中包含了“constructor注入”和“setter注入”两种方式
dispatcherB.(class)=my.spring.bean.pojo.Dispatcher
#Introject via constructor
dispatcherB.$0(ref)=producerB
dispatcherB.$1(ref)=consumerB
#Introject by setting properties
#dispatcherB.producer(ref)=producerB
#dispatcherB.consumer(ref)=consumerB
producerB.(class)=my.spring.bean.pojo.Producer
producerB.$0=106
consumerB.(class)=my.spring.bean.pojo.Consumer
consumerB.$0=88具体语法参照SpringAPI中PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader示例说明,当然也可以自己重写语义规则
最后单元测试
package my.spring.bean.demo;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.JUnit4;
@RunWith(JUnit4.class)
public class IoCImplTest {
private static IoCImpl impl=null;
@Test
public void testPropertyFileImpl(){
impl=new PropertyFileImpl();
impl.run();
}
}
这里要对核心类PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader稍作讲解,先看下各个类之间的关系
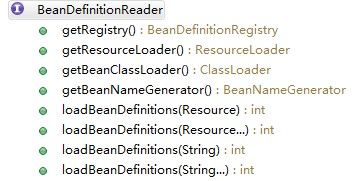
1、BeanDefinationReader:接口从定义上可以看到几个定义函数可以识别几个关键类,BeanDefination(这个是最终需要返回的对象)、ResourceLoader(Resource事实上就是java.io下的InputStreamSource,也就是需要读取的文件流)、ClassLoader(类加载器),其中最核心的方法LoadBeanDefinitions。
2、AbstractBeanDefintionReader:这个抽象类在原来接口基础上定义了以上的关键类成员,然后又添加了Environment成员,然后是类成员的Getter和Setter方法;其中最核心的loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified resource location.
* The location can also be a location pattern, provided that the
* ResourceLoader of this bean definition reader is a ResourcePatternResolver.
* @param location the resource location, to be loaded with the ResourceLoader
* (or ResourcePatternResolver) of this bean definition reader
* @param actualResources a Set to be filled with the actual Resource objects
* that have been resolved during the loading process. May be {@code null}
* to indicate that the caller is not interested in those Resource objects.
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
* @see #getResourceLoader()
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource)
* @see #loadBeanDefinitions(org.springframework.core.io.Resource[])
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, Set actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot import bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
for (Resource resource : resources) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int loadCount = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + loadCount + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return loadCount;
}
}
可见loadBeanDefinitions函数最终返回的是加载的BeanDefinition数量,而loadBeanDefinitions(resource)才是某个实现类对应应该实现的核心方法。
3、PropertiesBeanDefinitionReader:现在具体到某个实现类,该类核心是对Properties文件的读取,因此增加了以下属性
private PropertiesPersister propertiesPersister = new DefaultPropertiesPersister();PropertiesPersister其实就是将文件流持久化到java.utils.Properties中,具体如何转化可以参见DefaultPropertiesPersister的实现;实现加载BeanDefinition的方法代码如下
/**
* Load bean definitions from the specified properties file.
* @param encodedResource the resource descriptor for the properties file,
* allowing to specify an encoding to use for parsing the file
* @param prefix a filter within the keys in the map: e.g. 'beans.'
* (can be empty or {@code null})
* @return the number of bean definitions found
* @throws BeanDefinitionStoreException in case of loading or parsing errors
*/
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource, String prefix)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Properties props = new Properties();
try {
InputStream is = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
getPropertiesPersister().load(props, new InputStreamReader(is, encodedResource.getEncoding()));
}
else {
getPropertiesPersister().load(props, is);
}
}
finally {
is.close();
}
return registerBeanDefinitions(props, prefix, encodedResource.getResource().getDescription());
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("Could not parse properties from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
}其中EncodedResource是输入文件流(InputStreamReader)时增加编码。最后registerBeanDefinitions方法遍历Props(这个其实是一个键值对集合Map),每个键值对调用registerBeanDefinition函数实现Properties键值语义解析(如class识别、父类识别、抽象类识别、延迟加载识别、是否多态、是否单例、依赖的类)、注册BeanDefinition(剩下的就是代码实现依赖注入了,这个在前面已经讲得很详细了),该函数十分关键,代码如下:
/**
* Get all property values, given a prefix (which will be stripped)
* and add the bean they define to the factory with the given name
* @param beanName name of the bean to define
* @param map Map containing string pairs
* @param prefix prefix of each entry, which will be stripped
* @param resourceDescription description of the resource that the
* Map came from (for logging purposes)
* @throws BeansException if the bean definition could not be parsed or registered
*/
protected void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, Map map, String prefix, String resourceDescription)
throws BeansException {
String className = null;
String parent = null;
String scope = GenericBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
boolean isAbstract = false;
boolean lazyInit = false;
ConstructorArgumentValues cas = new ConstructorArgumentValues();
MutablePropertyValues pvs = new MutablePropertyValues();
for (Map.Entry entry : map.entrySet()) {
String key = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getKey());
if (key.startsWith(prefix + SEPARATOR)) {
String property = key.substring(prefix.length() + SEPARATOR.length());
if (CLASS_KEY.equals(property)) {
className = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
}
else if (PARENT_KEY.equals(property)) {
parent = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
}
else if (ABSTRACT_KEY.equals(property)) {
String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
isAbstract = TRUE_VALUE.equals(val);
}
else if (SCOPE_KEY.equals(property)) {
// Spring 2.0 style
scope = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
}
else if (SINGLETON_KEY.equals(property)) {
// Spring 1.2 style
String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
scope = ((val == null || TRUE_VALUE.equals(val) ? GenericBeanDefinition.SCOPE_SINGLETON :
GenericBeanDefinition.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE));
}
else if (LAZY_INIT_KEY.equals(property)) {
String val = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
lazyInit = TRUE_VALUE.equals(val);
}
else if (property.startsWith(CONSTRUCTOR_ARG_PREFIX)) {
if (property.endsWith(REF_SUFFIX)) {
int index = Integer.parseInt(property.substring(1, property.length() - REF_SUFFIX.length()));
cas.addIndexedArgumentValue(index, new RuntimeBeanReference(entry.getValue().toString()));
}
else {
int index = Integer.parseInt(property.substring(1));
cas.addIndexedArgumentValue(index, readValue(entry));
}
}
else if (property.endsWith(REF_SUFFIX)) {
// This isn't a real property, but a reference to another prototype
// Extract property name: property is of form dog(ref)
property = property.substring(0, property.length() - REF_SUFFIX.length());
String ref = StringUtils.trimWhitespace((String) entry.getValue());
// It doesn't matter if the referenced bean hasn't yet been registered:
// this will ensure that the reference is resolved at runtime.
Object val = new RuntimeBeanReference(ref);
pvs.add(property, val);
}
else {
// It's a normal bean property.
pvs.add(property, readValue(entry));
}
}
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Registering bean definition for bean name '" + beanName + "' with " + pvs);
}
// Just use default parent if we're not dealing with the parent itself,
// and if there's no class name specified. The latter has to happen for
// backwards compatibility reasons.
if (parent == null && className == null && !beanName.equals(this.defaultParentBean)) {
parent = this.defaultParentBean;
}
try {
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.createBeanDefinition(
parent, className, getBeanClassLoader());
bd.setScope(scope);
bd.setAbstract(isAbstract);
bd.setLazyInit(lazyInit);
bd.setConstructorArgumentValues(cas);
bd.setPropertyValues(pvs);
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, bd);
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(resourceDescription, beanName, className, ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new CannotLoadBeanClassException(resourceDescription, beanName, className, err);
}
}