Dubbo源码(6)-动态代理技术源码解析(2)
文章目录
- 一.Dubbo中的动态代理
- 1.1、Dubbo Invoker领域模型
- 1.2、Invoke在RPC过程中的作用
- 二.RPC调用流程
- 三.动态代理相关源码解析
- 3.1、ProxyFactory
- 3.1.1、AbstractProxyFactory
- 3.1.2、JavassistProxyFactory
- 3.2、InvokerInvocationHandler
- 3.3、AbstractProxyInvoker
- 3.4、bytecode包
本文主要参考自Dubbo官方文档、Dubbo项目源码以及网络文章和相关书籍,并附上自身的一些理解,如有遗漏或错误,还望海涵并指出。谢谢!
------本文基于Dubbo-2.6.1版本
一.Dubbo中的动态代理
1.1、Dubbo Invoker领域模型
在说Dubbo动态代理之前,先来看看Dubbo的Invoker领域模型。
任何框架或组件,总会有核心领域模型,比如:Spring 的 Bean,Struts 的 Action,Dubbo 的 Service,Napoli 的 Queue 等等。这个核心领域模型及其组成部分称为实体域,它代表着我们要操作的目标本身。实体域通常是线程安全的,不管是通过不变类,同步状态,或复制的方式。
服务域也就是行为域,它是组件的功能集,同时也负责实体域和会话域的生命周期管理, 比如 Spring 的 ApplicationContext,Dubbo 的 ServiceManager 等。服务域的对象通常会比较重,而且是线程安全的,并以单一实例服务于所有调用。
什么是会话?就是一次交互过程。会话中重要的概念是上下文,什么是上下文?比如我们说:“老地方见”,这里的“老地方”就是上下文信息。为什么说“老地方”对方会知道,因为我们前面定义了“老地方”的具体内容。所以说,上下文通常持有交互过程中的状态变量等。会话对象通常较轻,每次请求都重新创建实例,请求结束后销毁。
简而言之:把元信息交由实体域持有,把一次请求中的临时状态由会话域持有,由服务域贯穿整个 过程。
百度中关于领域模型的解释:
领域模型是对领域内的概念类或现实世界中对象的可视化表示。 又称概念模型、领域对象模型、分析对象模型。 它专注于分析问题领域本身,发掘重要的业务领域概念,并建立业务领域概念之间的关系。
Invoker是Dubbo 领域模型中非常重要的一个概念,很多设计思路都是向它靠拢。这就使得Invoker渗透在整个实现代码里。而Invoker的实现是基于动态代理的,这也是本文要讲解的重点。
1.2、Invoke在RPC过程中的作用
在整个Dubbo关于RPC通信过程的代码中出现了很多个Invoker,Invoker直译为执行器,那么这些Invoker的作用是什么呢?
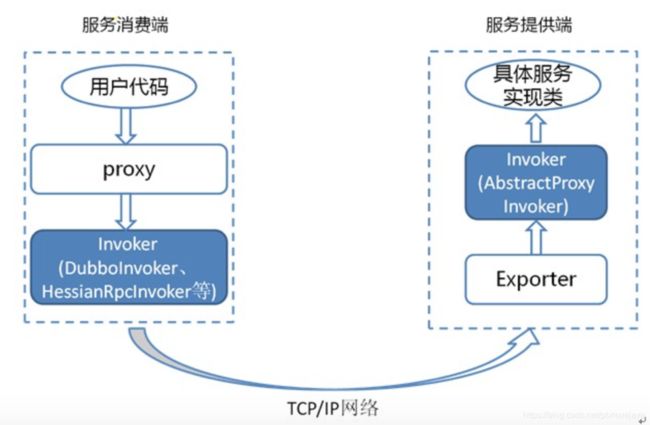
下面来看一张图,简化了Dubbo RPC过程中的其他组件,来直观地看Invoker在这个过程中的作用:
可以看出,在服务提供端中,Invoker封装了具体的实现服务类。
当服务消费端需要通过RPC调用这个服务时,生成proxy调用对应的Invoker,借助网络通知到服务提供端Exporter,然后Exporter调用Invoker执行具体的服务逻辑。
可以看出,Invoker实质上就是由动态代理生成并封装了网络连接和数据处理的逻辑,以屏蔽底层的实现。这就是DUbbo动态代理技术的实际运用了。
二.RPC调用流程
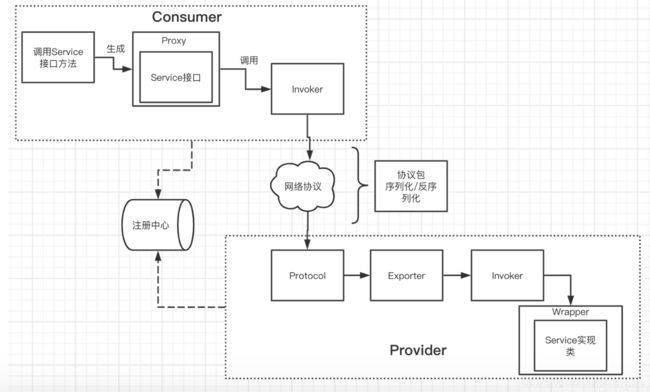
在看源码之前,先来从宏观的层面了解下整个调用的流程,这里忽略了很多细节,只展示最重要的实现,如下图:
整体的流程如下:
- 客户端通过RPC调用Service接口的方法
- 通过动态代理生成一个Proxy代理对象,该对象实现了Service接口,内容大致如下:
public class proxy0 implements ClassGenerator.DC, EchoService, Service {
public static Method[] methods;
private InvocationHandler handler
public void bye(Object paramObject) {
Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramObject;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], arrayOfObject);
}
public String hello(String paramString){ Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramString;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[1], arrayOfObject);
return (String)localObject;
}
public Object $echo(Object paramObject) {
Object[] arrayOfObject = new Object[1];
arrayOfObject[0] = paramObject;
Object localObject = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[2], arrayOfObject);
return (Object)localObject;
}
public proxy0() {
public proxy0(InvocationHandler paramInvocationHandler) {
this.handler = paramInvocationHandler;
}
}
该类通过dubbo-common模块的bytecode模块的 Proxy类使用Javassis动态代理技术生成。
代理类首先实现了Service接口,然后所有的重写方法调用都是集中在了InvocationHandler的invoke方法中执行,这里实质上就是调用了代理对象(封装了许多RPC细节)。
- 服务端接的
Protocol收到了这个RPC调用。 Protocol获取到被调用的Exporter对象Exporter对象获取到Invoker代理对象Invoker代理对象执行Wrapper包装类对象中对应的方法。实质上Wrapper对象内含有Service实现对象,如以下代码:
public class Wrapper1 extends Wrapper implements ClassGenerator.DC
{
public static String[] pns;
public static Map pts;
public static String[] mns;
public static String[] dmns;
public static Class[] mts0;
public static Class[] mts1;
public static Class[] mts2;
public String[] getPropertyNames()
{
return pns;
}
public boolean hasProperty(String paramString)
{
return pts.containsKey(paramString);
}
public Class getPropertyType(String paramString)
{
return (Class)pts.get(paramString);
}
public String[] getMethodNames()
{
return mns;
}
public String[] getDeclaredMethodNames()
{
return dmns;
}
public void setPropertyValue(Object paramObject1, String paramString, Object paramObject2)
{
ServiceImpl w;
try
{
w = (ServiceImpl)paramObject1;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(localThrowable);
}
if (paramString.equals("test01"))
{
w.test01 = ((String)paramObject2);
return;
}
if (paramString.equals("demoDAO"))
{
localServiceImpl.setDemoDAO((DemoDAO)paramObject2);
return;
}
throw new NoSuchPropertyException("Not found property \"" + paramString + "\" filed or setter method in class com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.ServiceImpl.");
}
public Object getPropertyValue(Object paramObject, String paramString)
{
ServiceImpl w;
try
{
w = (ServiceImpl)paramObject;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable)
{throw new IllegalArgumentException(localThrowable);
}
if (paramString.equals("test01")) {return localServiceImpl.test01;
}
throw new NoSuchPropertyException("Not found property \"" + paramString + "\" filed or setter method in class com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.ServiceImpl.");
}
public Object invokeMethod(Object paramObject, String paramString, Class[] paramArrayOfClass, Object[] paramArrayOfObject)
throws InvocationTargetException
{ServiceImpl w;
try
{
w = (ServiceImpl)paramObject;
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable1)
{
throw new IllegalArgumentException(localThrowable1);
}
try
{
if ("hello".equals(paramString) && paramArrayOfClass.length == 1) {
return w.hello((String)paramArrayOfObject[0]);
}
if ("bye".equals(paramString) && paramArrayOfClass.length == 1)
{w.bye((Object)paramArrayOfObject[0]);
return null;
}
if ("setDemoDAO".equals(paramString) && paramArrayOfClass.length == 1)
{w.setDemoDAO((DemoDAO)paramArrayOfObject[0]);
return null;
}
}
catch (Throwable localThrowable2)
{
throw new InvocationTargetException(localThrowable2);
}
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Not found method \"" + paramString + "\" in class com.alibaba.dubbo.demo.provider.ServiceImpl.");
}
}
该包装类由dubbo-common模块的bytecode模块的Wrapper类使用Javassist动态代理技术生成。
可以看到到了这一步,其实就是在调用包装类中包装的实现类的具体方法了。
三.动态代理相关源码解析
关于Dubbo的动态代理技术的使用,相关的源码集中在dubbo-rpc模块以及dubbo-common模块下的bytecode包。
dubbo-rpc远程调用模块包含了各种协议的抽象,以及动态代理,只包含一对一的调用,不关心集群的管理。
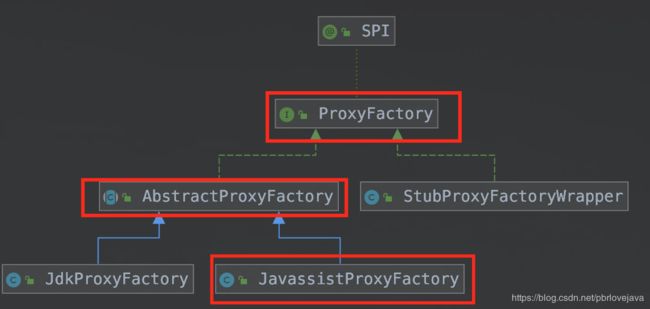
3.1、ProxyFactory
ProxyFactory接口位于dubbo-rpc模块下的dubbo-rpc-api子模块,定义了获取Proxy的方法,以SPI机制做动态拓展,默认使用的是JavassistProxyFactory作为拓展实现类(Javassist做底层的动态代理技术,性能优于Jdk动态代理)。
- ProxyFactory
@SPI("javassist")
public interface ProxyFactory {
/**
* 获取指定的proxy
*
* @param invoker
* @return proxy
*/
@Adaptive({Constants.PROXY_KEY})
<T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
/**
* 获取指定的Invoker
*
* @param
* @param proxy
* @param type
* @param url
* @return invoker
*/
@Adaptive({Constants.PROXY_KEY})
<T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
}
3.1.1、AbstractProxyFactory
- AbstractProxyFactory
public abstract class AbstractProxyFactory implements ProxyFactory {
/*
* 传入invoker获取proxy
*/
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
// 接口数组
Class<?>[] interfaces = null;
// 获取invoker的url,再获取url中的interfaces配置
String config = invoker.getUrl().getParameter("interfaces");
// 解析接口配置
if (config != null && config.length() > 0) {
// 获取到接口全限定名数组
String[] types = Constants.COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(config);
if (types != null && types.length > 0) {
// 额外申请接口数组长度+2
interfaces = new Class<?>[types.length + 2];
// 第一个位置放置invoker自身实现的接口
interfaces[0] = invoker.getInterface();
// EchoService接口用于回声测试
interfaces[1] = EchoService.class;
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
// 使用反射生成接口class
interfaces[i + 1] = ReflectUtils.forName(types[i]);
}
}
}
if (interfaces == null) {
interfaces = new Class<?>[]{invoker.getInterface(), EchoService.class};
}
// 模板方法模式,让具体实现类实现getProxy(invoker, interfaces)的逻辑
return getProxy(invoker, interfaces);
}
public abstract <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] types);
}
3.1.2、JavassistProxyFactory
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.javassist.JavassistProxyFactory是ProxyFactory的默认拓展实现类:
- JavassistProxyFactory
/**
* JavaassistRpcProxyFactory,ProxyFactory默认拓展实现类
*/
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
/*
* 获取proxy,这里需要看Proxy类和InvokerInvocationHandler的源码
*/
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
/*
* 获取invoker,不能够获取类名含有$的proxy
*/
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
// TODO Wrapper cannot handle this scenario correctly: the classname contains '$'
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
@Override
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
}
};
}
}
3.2、InvokerInvocationHandler
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.InvokerInvocationHandler基于Jdk的InvocationHandler做了一层封装实现:
- InvokerInvocationHandler
public class InvokerInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
private final Invoker<?> invoker;
public InvokerInvocationHandler(Invoker<?> handler) {
this.invoker = handler;
}
/*
* 执行proxy的方法
*/
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 获取方法名
String methodName = method.getName();
// 获取方法参数
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = method.getParameterTypes();
// 如果proxy为Object,则直接使用method执行
if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) {
return method.invoke(invoker, args);
}
// 下面三个方法统一使用invoker直接调用
if ("toString".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.toString();
}
if ("hashCode".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 0) {
return invoker.hashCode();
}
if ("equals".equals(methodName) && parameterTypes.length == 1) {
return invoker.equals(args[0]);
}
// 除此之外的其他用户方法,采用invoker.invoke的方式来执行
return invoker.invoke(new RpcInvocation(method, args)).recreate();
}
}
3.3、AbstractProxyInvoker
com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.proxy.AbstractProxyInvoker实现了Invoker,可以获取到RPC调用的执行结果:
- AbstractProxyInvoker
public abstract class AbstractProxyInvoker<T> implements Invoker<T> {
// 被代理的接口实现类
private final T proxy;
// 被代理的接口
private final Class<T> type;
// 传入URL对象
private final URL url;
/*
* 构造方法
*/
public AbstractProxyInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
if (proxy == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("proxy == null");
}
if (type == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface == null");
}
if (!type.isInstance(proxy)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(proxy.getClass().getName() + " not implement interface " + type);
}
this.proxy = proxy;
this.type = type;
this.url = url;
}
public Class<T> getInterface() {
return type;
}
public URL getUrl() {
return url;
}
public boolean isAvailable() {
return true;
}
public void destroy() {
}
/*
* 执行代理方法,获取到RPC调用结果
*/
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
try {
return new RpcResult(doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments()));
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
return new RpcResult(e.getTargetException());
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RpcException("Failed to invoke remote proxy method " + invocation.getMethodName() + " to " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
protected abstract Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable;
@Override
public String toString() {
return getInterface() + " -> " + (getUrl() == null ? " " : getUrl().toString());
}
}
- RpcResult
public class RpcResult implements Result, Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6925924956850004727L;
// RPC调用结果
private Object result;
private Throwable exception;
// 额外附加信息
private Map<String, String> attachments = new HashMap<String, String>();
public RpcResult() {
}
public RpcResult(Object result) {
this.result = result;
}
public RpcResult(Throwable exception) {
this.exception = exception;
}
public Object recreate() throws Throwable {
if (exception != null) {
throw exception;
}
return result;
}
/**
* @see com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcResult#getValue()
* @deprecated Replace to getValue()
*/
@Deprecated
public Object getResult() {
return getValue();
}
/**
* @see com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.RpcResult#setValue(Object)
* @deprecated Replace to setValue()
*/
@Deprecated
public void setResult(Object result) {
setValue(result);
}
public Object getValue() {
return result;
}
public void setValue(Object value) {
this.result = value;
}
public Throwable getException() {
return exception;
}
public void setException(Throwable e) {
this.exception = e;
}
public boolean hasException() {
return exception != null;
}
public Map<String, String> getAttachments() {
return attachments;
}
/**
* Append all items from the map into the attachment, if map is empty then nothing happens
*
* @param map contains all key-value pairs to append
*/
public void setAttachments(Map<String, String> map) {
if (map != null && map.size() > 0) {
attachments.putAll(map);
}
}
public String getAttachment(String key) {
return attachments.get(key);
}
public String getAttachment(String key, String defaultValue) {
String result = attachments.get(key);
if (result == null || result.length() == 0) {
result = defaultValue;
}
return result;
}
public void setAttachment(String key, String value) {
attachments.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RpcResult [result=" + result + ", exception=" + exception + "]";
}
}
3.4、bytecode包
上述的代码都基于dubbo-rpc-api子模块进行分析,下面基于dubbo-common模块的bytecode包,基于Javassit动态编译技术做了高性能的动态代理实现,用以生成wrapper与proxy的代码。
// TODO