NIPS 2017 深度学习论文集锦 (6) 含部分代码 完结篇
您可能感兴趣
本篇文章基于上述五篇,故论文编号沿用上五篇的编号
[101] The Expressive Power of Neural Networks: A View from the Width
Zhou Lu et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7203-the-expressive-power-of-neural-networks-a-view-from-the-width.pdf
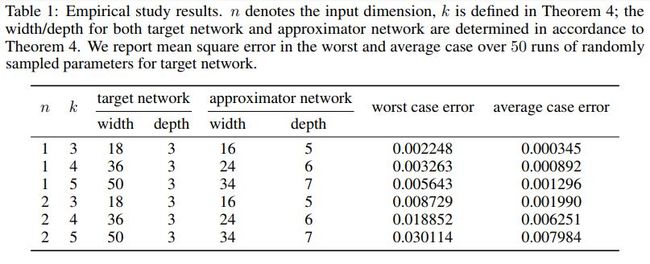
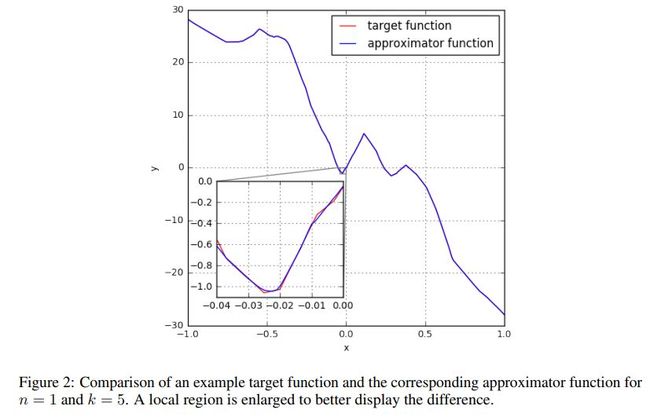
这篇文章主要从宽度(隐含层单元个数)角度讨论神经网络的表达能力,他们证明了针对激活函数为ReLU的神经网络,宽度为n+4的ReLU网络可以逼近任意函数,其中n是输入维度,即输入层单元个数。该文还证明了存在宽的网络不能由深度在多项式约束内的深层窄网络实现,如果深层窄网络的深度超过多项式约束就可以逼近宽的层数比较少的网络,并且准确度很高。
实验结果如下
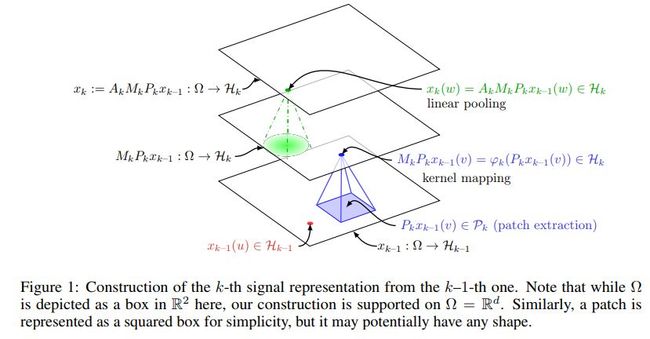
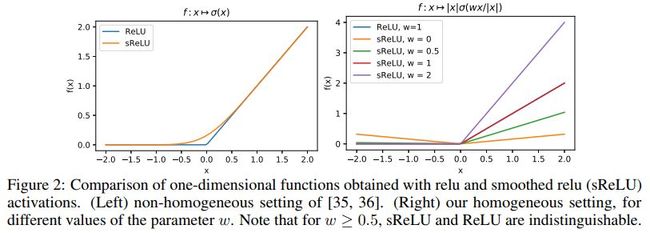
[102] Invariance and Stability of Deep Convolutional Representations
Alberto Bietti, Julien Mairal
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7201-invariance-and-stability-of-deep-convolutional-representations.pdf
本文讨论了深层卷积表示的不变性和稳定性。
网络结构如下
实验结果如下
[103] Value Prediction Network
Junhyuk Oh, Satinder Singh, Honglak Lee
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7192-value-prediction-network.pdf
这篇文章提出了一种新的深度强化学习框架,VPN,Value Prediction Network,它能够学习动态模型,对未来的价值进行预测。
VPN的网络结构如下
Q-value的学习算法如下
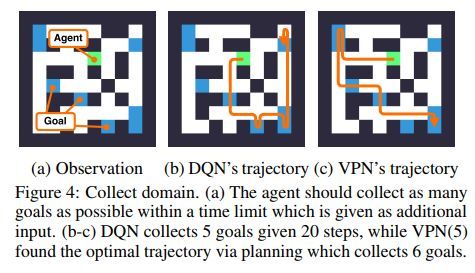
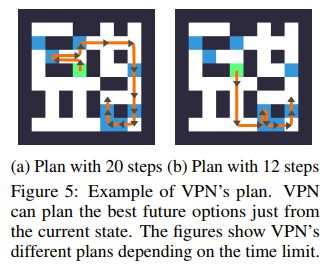
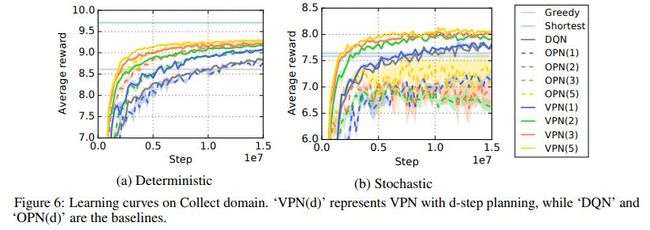
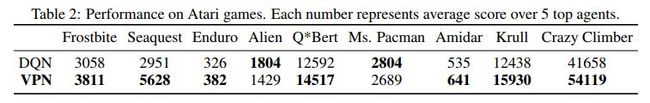
DQN与VPN的效果对比示例如下
代码地址
https://github.com/junhyukoh/value-prediction-network.
[104] Neural Discrete Representation Learning
Aaron van den Oord, Oriol Vinyals, koray kavukcuoglu
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7210-neural-discrete-representation-learning.pdf
这篇文章提出一种新的表示学习的自编码,Vector Quantised Variational AutoEncoder,VQ-VAE,这种变分自编码中的编码网络可以学习离散的编码,并且先验知识是学习得到而非统计得到。
网络结构示例及嵌入空间的可视化示例如下
[105] Learned in Translation: Contextualized Word Vectors
Bryan McCann et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7209-learned-in-translation-contextualized-word-vectors.pdf
这篇文章基于深层LSTM编码提出了上下文词向量,并将其用于情感分析等。
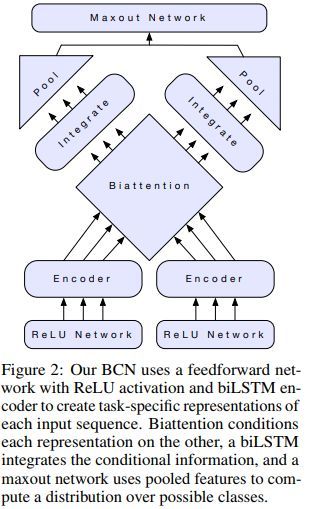
网络结构示例如下,其中BCN表示biattentive classification network
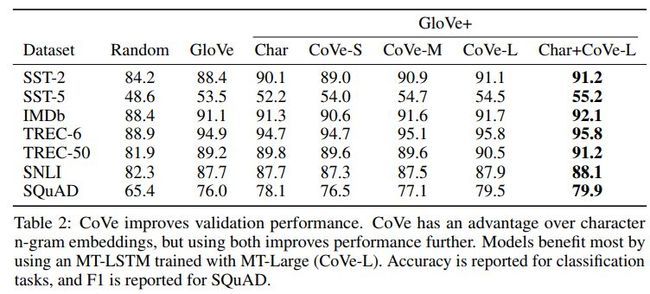
数据集说明如下
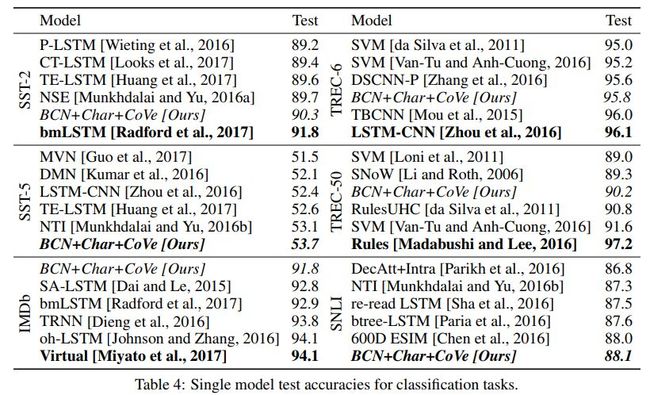
各方法效果对比如下
代码地址
https://github.com/salesforce/cove
[106] Population Matching Discrepancy and Applications in Deep Learning
Jianfei Chen et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7206-population-matching-discrepancy-and-applications-in-deep-learning.pdf
这篇文章提出一种新的衡量两个分布之间距离的度量方法,Population Matching Discrepancy,PMD,并且提出了学习其中参数的算法。
PMD参数学习的伪代码以及迭代示例如下
各算法效果对比如下
[107] Houdini: Fooling Deep Structured Visual and Speech Recognition Models with Adversarial Examples
Moustapha M. Cisse et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7273-houdini-fooling-deep-structured-visual-and-speech-recognition-models-with-adversarial-examples.pdf
这篇论文提出一种新的生成对抗样本的方法,Houdini。
各方法效果对比如下
[108] Linear Time Computation of Moments in Sum-Product Networks
Han Zhao, Geoffrey J. Gordon
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7265-linear-time-computation-of-moments-in-sum-product-networks.pdf
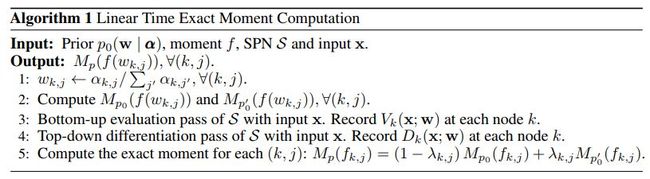
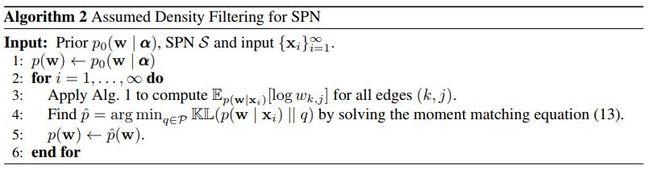
这篇文章提出了一种计算和积网络中动量系数的线性算法。
算法伪代码如下
[109] Attend and Predict: Understanding Gene Regulation by Selective Attention on Chromatin
Ritambhara Singh et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7255-attend-and-predict-understanding-gene-regulation-by-selective-attention-on-chromatin.pdf
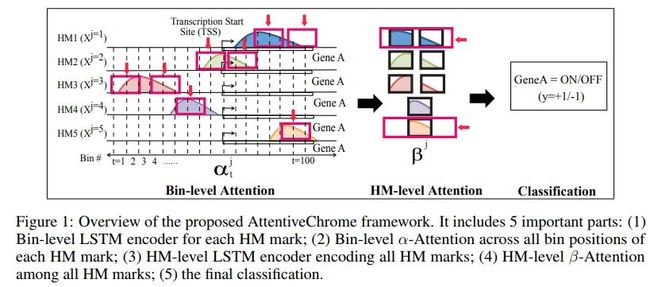
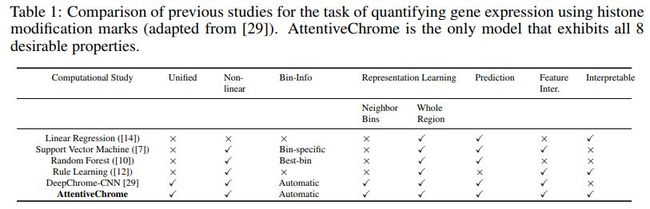
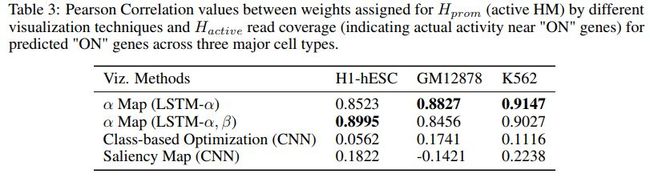
这篇文章提出基于注意力的深度学习框架,AttentiveChrome,用于对控制基因调节的染色质之间的关联进行建模。
框架图示如下
各算法对比如下
代码地址
www.deepchrome.org
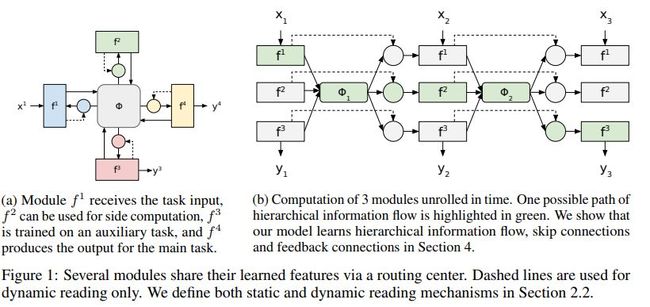
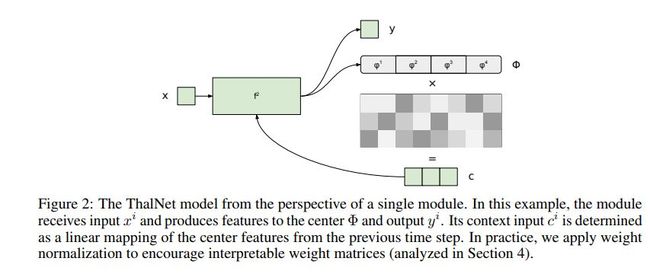
[110] Learning Hierarchical Information Flow with Recurrent Neural Modules
Danijar Hafner et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7249-learning-hierarchical-information-flow-with-recurrent-neural-modules.pdf
这篇文章基于RNN提出了一种新的深度学习算法,ThalNet。
网络结构示例如下
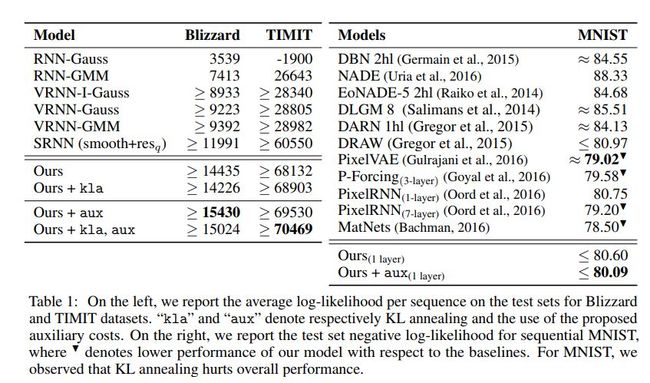
[111] Z-Forcing: Training Stochastic Recurrent Networks
Anirudh Goyal et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7248-z-forcing-training-stochastic-recurrent-networks.pdf
这篇文章主要讨论如何训练随机RNN。
各网络结构对比如下
各模型效果对比如下
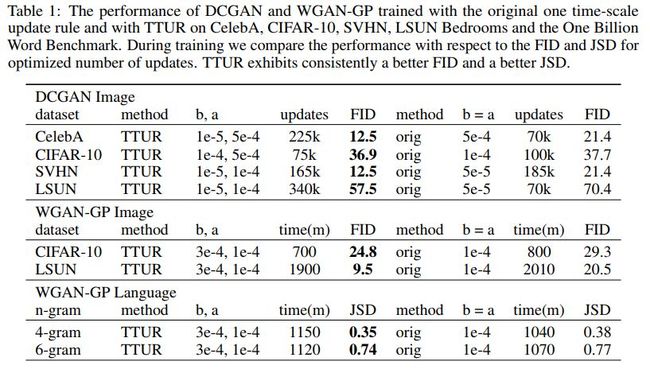
[112] GANs Trained by a Two Time-Scale Update Rule Converge to a Local Nash Equilibrium
Martin Heusel et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7240-gans-trained-by-a-two-time-scale-update-rule-converge-to-a-local-nash-equilibrium.pdf
这篇文章提出了训练GAN的新算法,two time-scale update rule (TTUR),这种算法对判别器和生成器利用不同的学习率。
各方法效果对比如下
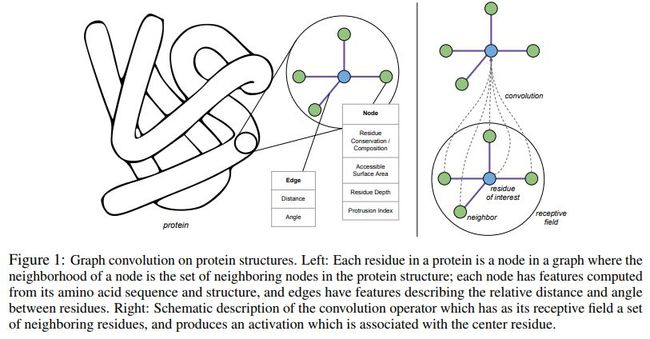
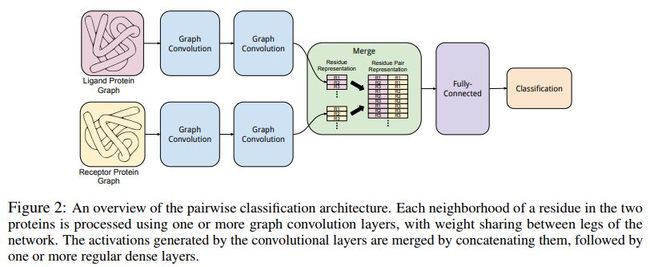
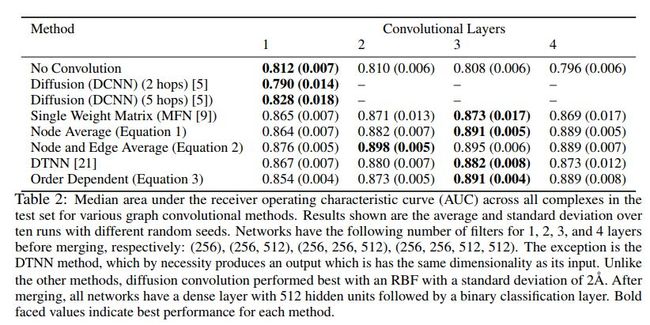
[113] Protein Interface Prediction using Graph Convolutional Networks
Alex Fout et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7231-protein-interface-prediction-using-graph-convolutional-networks.pdf
这篇文章提出了空间图卷积网络,用于预测蛋白质之间的相互作用。
网络结构示例如下
各方法效果对比如下
代码地址
https://github.com/fouticus/pipgcn
数据集地址
https://zenodo.org/record/1127774,
[114] Good Semi-supervised Learning That Requires a Bad GAN
Zihang Dai et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7229-good-semi-supervised-learning-that-requires-a-bad-gan.pdf
这篇文章主要讨论半监督学习与GAN的关系。
各方法效果对比如下
代码地址
https://github.com/kimiyoung/ssl_bad_gan
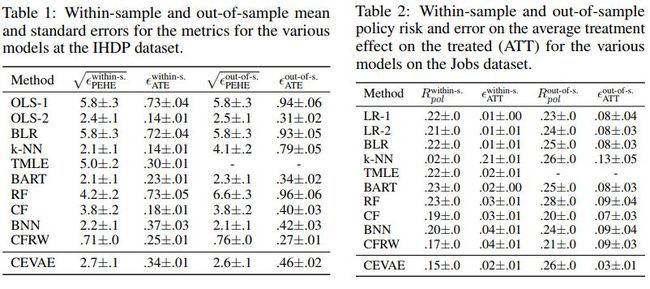
[115] Causal Effect Inference with Deep Latent-Variable Models
Christos Louizos et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7223-causal-effect-inference-with-deep-latent-variable-models.pdf
这篇文章主要讨论深层隐含变量模型在随机影响推理中的应用,模型名称为Causal Effect Variational Autoencoder (CEVAE),该模型基于变分自编码。
网络结构示例如下
各方法效果对比如下
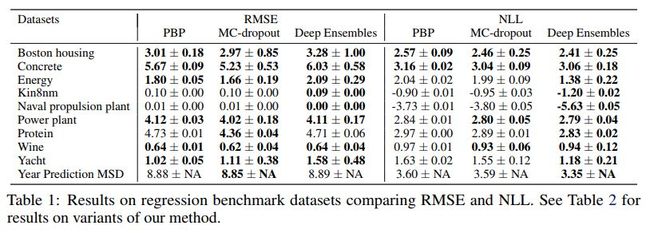
[116] Simple and Scalable Predictive Uncertainty Estimation using Deep Ensembles
Balaji Lakshminarayanan, Alexander Pritzel, Charles Blundell
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7219-simple-and-scalable-predictive-uncertainty-estimation-using-deep-ensembles.pdf
这篇文章利用深层集成算法来估计预测的不确定性。
算法伪代码示例如下
各方法效果对比如下
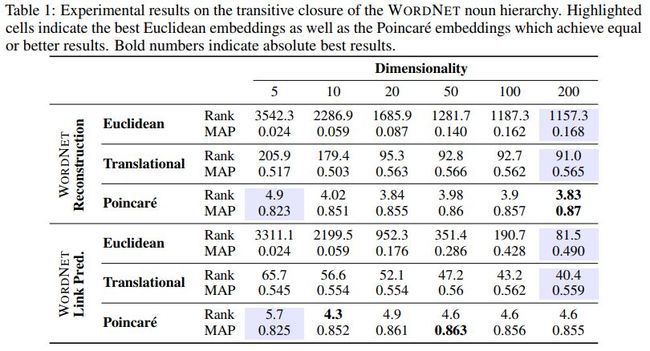
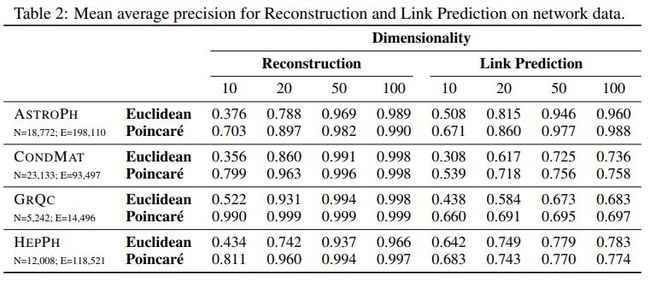
[117] Poincaré Embeddings for Learning Hierarchical Representations
Maximillian Nickel, Douwe Kiela
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7213-poincare-embeddings-for-learning-hierarchical-representations.pdf
这篇文章利用庞加莱嵌入来学习分层表示。
各方法效果对比如下
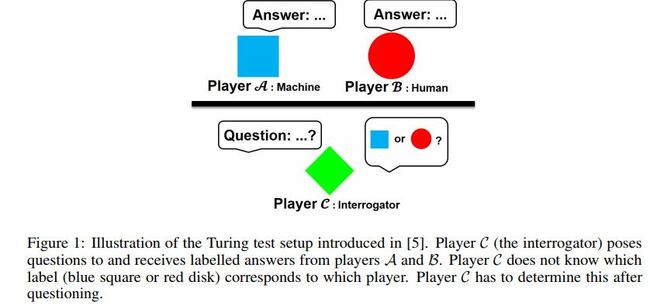
[118] Generalizing GANs: A Turing Perspective
Roderich Gross et al.
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/7211-generalizing-gans-a-turing-perspective.pdf
这篇文章从图灵测试的角度来泛化GAN。
图灵测试示例如下
[119] Mean Field Residual Networks: On the Edge of Chaos
Ge Yang, Samuel Schoenholz
https://papers.nips.cc/paper/6879-mean-field-residual-networks-on-the-edge-of-chaos.pdf
这篇文章将平均场理论用于残差网络。
![]()
本公众号专注于机器学习(主要包含但不限于深度学习)相关知识分享,其中涉及自然语言处理以及图像处理前沿论文等,欢迎大家关注(长按->识别图中二维码->关注)交流