记录SpringBoot学习之旅
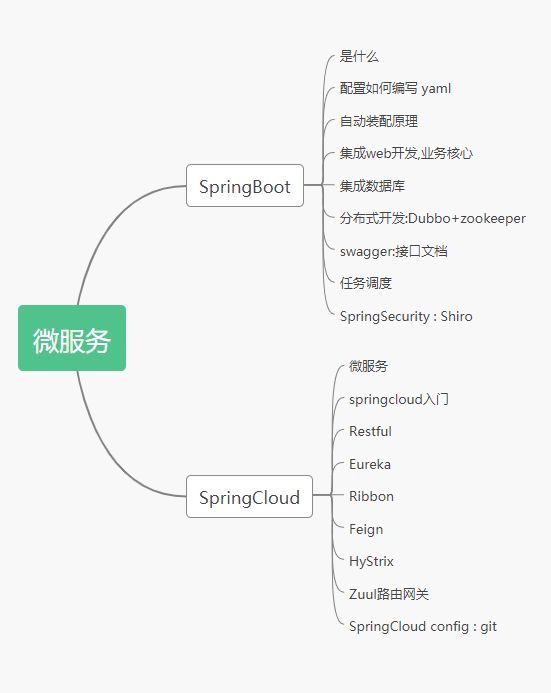
文章目录
- SpringBoot
- 感谢秦老师 指路: [秦老师](https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PE411i7CV)
- 什么是Spring
- Spring是如何简化Java开发的
- 什么 SpringBoot
- 微服务
- 什么是微服务?
- 单体应用架构
- 微服务架构
- 如何构建微服务
- 第一个SpringBoot程序
- 自动装配原理初探
- pom.xml
- 启动器:
- 主程序
- 注解
- @Conditional扩展注解
- 结论:
- SpringApplication
- springboot启动流程
- 关于springboot,谈谈你的理解
- SpringBoot配置
- 配置文件
- YAML
- YAML语法
- 基本语法
- 值的写法
- 松散绑定
- 结论
- JSR303校验
- 配置文件位置优先级
- 为什么可以完成自动配置
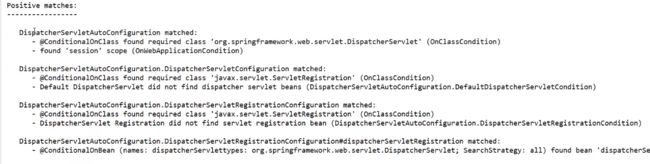
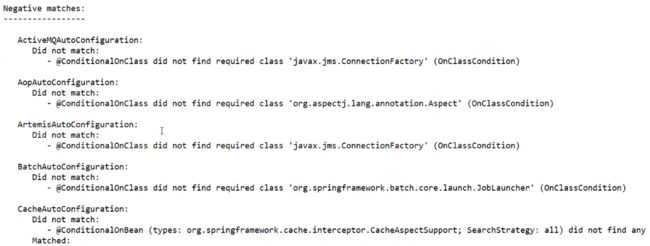
- 查看哪些配置类生效
- SpringBoot Web开发
- 静态资源
- 什么是webjars?
- 静态资源目录
- 总结
- 首页如何定制
- 模板引擎
- 导入依赖:
- 使用thymeleaf:
- 导入约束
- 表达式
- 简单测试一下
- 修改springboot的默认配置
- 方式一
- 扩展装配SpringMVC
- 扩展SpringMVC
- 为什么?
- Springboot整合ORM
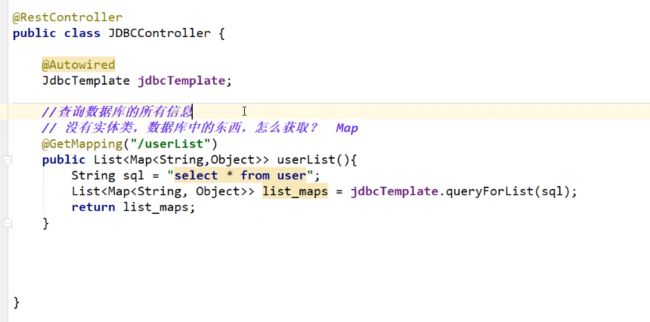
- Springboot整合JDBC
- 简介
- 引入SQL相关依赖
- pom依赖
- 配置信息
- 测试,默认数据源
- 测试jdbcTemplate
- Sringboot整合Druid
- 简介
- 导入依赖
- 配置信息
- DruidConfig配置类
- 实现后台监控功能
- filter
- Springboot整合Mybatis
- 引入依赖
- application.properties(yml也可)
- 测试
- SpringSecurity
- 可以实现的功能
- 环境引入
- 简介
- 引入依赖
- 官方示例
- 授权
- 认证
- 注销
- 问题
- 记住我
- Shiro
- 简介
- 有哪些功能
- shiro架构(外部)
- shiro架构(内部)
- HelloWorld快速实践
- 新建一个helloshiro工程
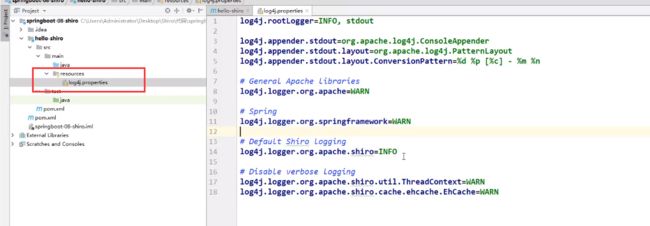
- 配置log4j.properties配置文件
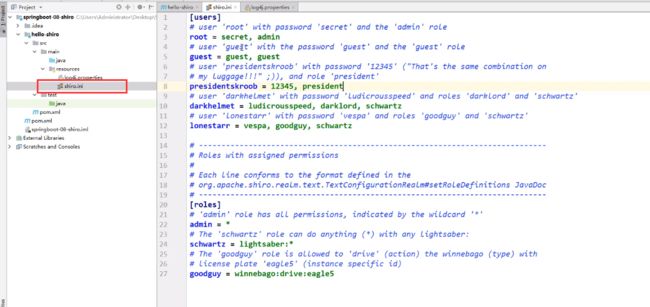
- shiro.ini配置文件
- 把QuickStart.java类建好
- 运行结果
- Springboot集成shiro
- 结构
- pom依赖
- UserRealm.java
- ShiroConfig.java
- Controller
- 测试页面
- 整合mybatis
- application.yml
- application.properties
- pojo
- mapper
- userMapper.xml
- Service
- 改造UserRealm
- 完善ShiroConfig.java
- 任务
- 异步任务
- 邮件任务
- **导入依赖**
- 配置信息
- 一封简单的邮件
- 一封复杂的邮件
- 封装一下代码
- 定时任务
- Cron表达式
SpringBoot
感谢秦老师 指路: 秦老师
什么是Spring
Spring是一个开源框架, 2003 年兴起的一个轻量级的gva开发框架,作者: Rod Johnson。
Spring是为了解决企业级应用开发的复杂性而创建的,简化开发。
Spring是如何简化Java开发的
为了降低Java开发的复杂性,Spring采用了以下4种关键策略:
- 基于POJO的轻量级和最小侵入性编程;
- 通过IOC,依赖注入(DI)和面向接口实现松耦合;
- 基于切面(AOP) 和惯例进行声明式编程;
- 通过切面和模版减少样式代码;
什么 SpringBoot
学过javaweb的同学 就知道,开发-个web应用,从最初开始接触Servlet结合Tomcat,跑出一个Hello Wolrld程序,是要经历特别多的步骤;后来就用了框架Struts,再后来是SpringMVC,到了现在的SpringBoot,过一两年又会有其他web框架出现;不知道你们有没经历过框架不断的演进,然后自己开发项目所有的技术也再不断的变化、改造,反正我是都经历过了,哈哈。言归正传,什么是SpringBoot呢,就是一个javaweb的开发框架,和SpringMVC类似,对比其他javaweb框 架的好处,官方说是简化开发,约定大于配置,you can “just run”,能迅速的开发web应用,几行代码开发一个http接口.
所有的技术框架的发展似乎都遵循了-条主线规律:从一个复杂应用场景衍生-种规范框架,人们只需要进行各种配置而不需要自己去实现它,这时候强大的配置功能成了优点;发展到一定程度之后,人们根据实际生产应用情况,选取其中实用功能和设计精华,重构出一些轻量级的框架;之后为了提高开发效率,嫌弃原先的各类配置过于麻烦,于是开始提倡”约定大于配置”,进而衍生出一些一站式的解决方案。
是的这就是Java企业级应用-> J2EE-> spring-> springboot的过程。
随着Spring不断的发展,涉及的领域越来越多,项目整合开发需要配合各种各样的文件,慢慢变得不那么易用简单,违背了最初的理念,甚至人称配置地狱。Spring Boot正是在这样的一个背景下被抽象出来的开发框架,目的为了让大家更容易的使用Spring、更容易的集成各种常用的中间件、开源软件;
Spring Boot基于Spring开发, Spirng Boot本身并不提供Spring框架的核心特性以及扩展功能,只是用于快速、敏捷地开发新一代基于Spring框架的应用程序。也就是说,它并不是用来替代Spring的解决方案,而是和Spring框架紧密结合用于提升Spring开发者体验的工具。SpringBoot以约定大于配置的核心思想,默认帮我们进行了很多设置,多数Spring Boot应用只需要很少的Spring配置。同时它集成了大量常用的第三方库配置(例如Redis、MongoDB、Jpa、RabbitMQ、Quartz 等等),Spring Boot应用中这些第三方库几乎可以零配置的开箱即用,
简单来说就是SpringBoot其实不是什么新的框架,它默认配置了很多框架的使用方式,就像maven整合了所有的jar包,spring boot整合了所有的框架
Spring Boot 出生名门,从一开始就站在-个比较高的起点,又经过这几年的发展,生态足够完善,Spring Boot 已经当之无愧成为Java 领域最热门的技术。
SpringBoot的主要优点:
- 为所有的Spring开发者更快的入门
- 开箱即用,提供各种默认配置来简化项目配置
- 内嵌式容器简化web项目
- 没有冗余代码生成和XML配置的要求
Springboot starter官方文档 https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.7.RELEASE/reference/html/using-spring-boot.html#using-boot-starter
微服务
什么是微服务?
微服务是-种架构风格,它要求我们在开发一个应用的时候,这个应用必须构建成一系 列小服务的组合;可以通过http的方式进行互通。要说微服务架构,先得说说过去我们的单体应用架构。
单体应用架构
所谓单体应用架构(all in one)是指,我们将一个应用的中的所有应用服务都封装在一个应用中。
无论是ERP、CRM或是其他什么系统,你都把数据库访问,web访问,等等各个功能放到一个war包内。
- 这样做的好处是,易于开发和测试;也十分方便部署;当需要扩展时,只需要将war复制多份,然后放到多个服务器上,再做个负载均衡就可以了。
- 单体应用架构的缺点是,哪怕我要修改一个非常小的地方,我都需要停掉整个服务,重新打包、部署这个应用war包。特别是对于一个大型应用,我们不可能吧所有内容都放在一个应用里面,我们如何维护、如何分I合作都是问题。
微服务架构
all in one的架构方式,我们把所有的功能单元放在一个应用里面。然后我们把整个应用部署到服务器上。如果负载能力不行,我们将整个应用进行水平复制,进行扩展,然后在负载均衡。
所谓微服务架构,就是打破之前all in one的架构方式,把每个功能元索独立出来。把独立出来的功能元索的动态组合,需要的功能元索才去拿来组合,需要多一些时 可以整合多个功能元素。所以微服务架构是对功能元索进行复制,而没有对整个应用进行复制。
这样做的好处是:
- 节省了调用资源
- 每个功能元素的服务都是一个可替换的,可独立升级的软件代码.
如何构建微服务
一个大型系统的微服务架构,就像一个复杂交织的神经网络,每-个神经元就是- -个功能元素,它们各自完成自己的功能,然后通过http相互请求调用。比如一个电商系统,查缓存、连数据库、浏览页面、结账、支付等服务都是一个个独立的功能服务,都被微化了,它们作为一个个微服务共同构建了一个庞大的系统。如果修改其中的一个功能,只需要更新升级其中-个功能服务单元即可。
但是这种庞大的系统架构给部署和运维带来很大的难度。于是,spring为我们带来了构建大型分布式微服务的全套、全程产品:
- 构建-个个功能独立的微服务应用单元,可以使用springboot, 可以帮我们快速构建一个 应用;
- 大型分布式网络服务的调用,这部分由spring cloud来完成,实现分布式;
- 在分布式中间,进行流式数据计算、批处理,我们有spring cloud data flow。
- spring为我们想清楚了整个从开始构建应用到大型分布式应用全流程方案。
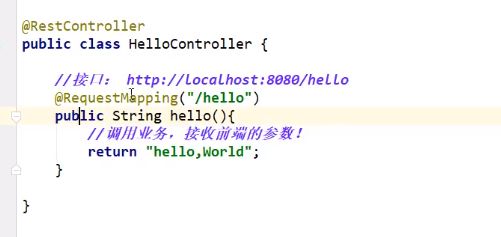
第一个SpringBoot程序
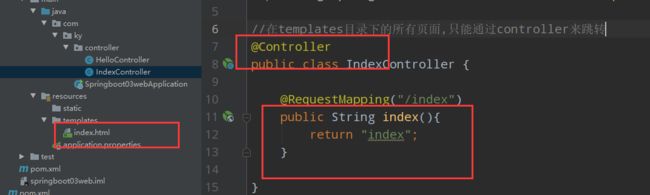
- IDEA整合了Springboot,创建项目时选择Spring Initializer创建项目
- 在启动类同级目录下建包
- 编写controller,加上@RestController注解,就可以不用写@Responsebody了
- 启动类本身就是spring的一个组件,@SpringbootApplication整合@Springbootconfiguration,再进去是@Configuration,最底层是一个@Component
- pom依赖[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8ijOENbH-1590996141553)(upload\image-20200518160954380.png)]
- springboot帮我们自动导入的web依赖[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HNmUlrlx-1590996141554)(upload\image-20200518161047662.png)]
主要有四个部分:
- 项目元数据信息:创建时候输入的Project Metadata部分, 也就是Maven项目的基本元素,包括: groupld、 artifactld、 version、 name、 description等
- parent:继承
spring-boot -starter-parent的依赖管理,控制版本与打包等内容 - dependencies: 项目具体依赖,这里包含了
spring- boot-starter -web用于实现HTTP接口(该依赖中包含了Spring MVC),官网对它的描述是:使用Spring MVC构建Web (包括RESTful) 应用程序的入门者,使用Tomcat作为默认嵌入式容器。spring-boot-starter-test用于编写单元测试的依赖包。更多功能模块的使用我们将在后面逐步展开。 - build: 构建配置部分。默认使用了
spring-boot-maven-plugin,配合spring-boot-starter-parent就可以把Spring Boot应用打包成JAR来直接运行。
自动装配原理初探
pom.xml
- spring-boot-dependencies :核心依赖在父工程中
- 我们在写或者引入一些Springboot依赖的时候,不需要指定版本,就是因为有这些版本仓库
启动器:
-
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId> <artifactId>spri ng-boot-starterartifactId> dependency> -
启动器:说白了就是springboot的启动场景
-
比如spring-boot-starter-web,他就会帮我们自动导入web环境所有的依赖
-
springboot会将所有的功能场景,都变成一个个的启动器
-
如果我们要使用什么功能,就只需要找到对应的启动器就可以了 Starter
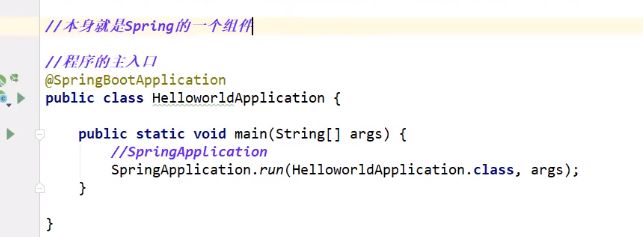
主程序
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloworldApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloworldApplication.class, args);
}
}
注解
-
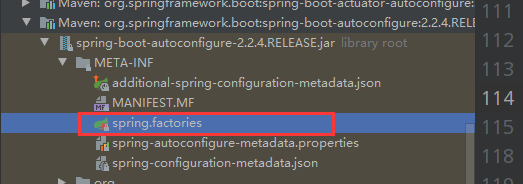
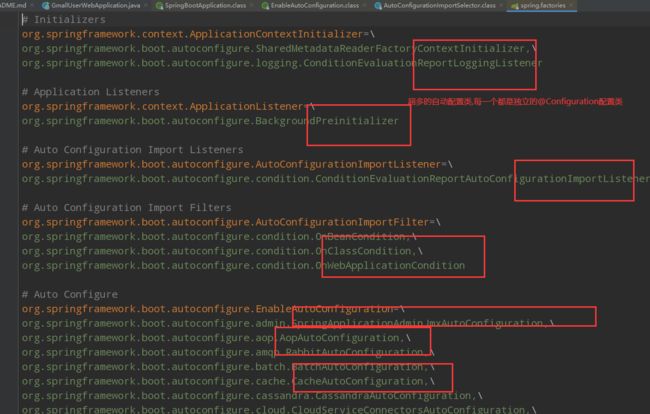
@SpringBootConfiguration : springboot的配置 @Configuration : spring配置类 @Component : 说明这也是一个spring的组件 @EnableAutoConfiguration : 自动配置 @AutoConfigurationPackage : 自动配置包 @Import({Registrar.class}) : 自动配置'包注册' @Import({AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class}) : 自动配置导入选择 @ComponentScan : 扫描当前主启动类同级的包 //获取所有的配置 List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);获取候选的配置
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); return configurations; }META-INF/spring.factories:自动配置的核心文件
每一个自动装配的类(bean)最终会对应一个properties或者yml配置文件,通过导入的方式进行参数绑定,以达到自动配置的效果.
@Conditional扩展注解
结论:
虽然是有这么多自动配置,但为什么不是每一个都会生效呢?原因是因为在对应的自动配置类中会进行条件判断’@ConditionOnxxx’,条件成立了之后配置才会生效.例如我们导入了web的starter,web相关的配置就会生效,而我们没有开启AOP,那AOP的相关配置就不会生效
- springboot在启动的时候,从类路径下META-INF/spring.factories获取指定的值
- 将这些自动配置的类导入容器,自动配置就会生效,帮我门进行自动配置
- 以前我们需要自动配置的东西,现在springboot帮我门做了
- 整个javaEE,解决方案和自动配置的东西都在spring-boot-autoconfigure包下
- 他会把所有需要导入的组件,以类名的方式返回,这些组件就会被添加到容器
- 容器中也会存在非常多的xxxxAutoConfiguration的文件(@Bean),就是这些类给容器导入了这个场景需要的所有组件
SpringApplication
这个类主要做了以下四个事情
- 推断应用的类型是普通的项目还是web项目
- 查找并加载所有可用初始化器,设置到initializers属性中
- 找出所有的应用程序监听器,设置到listeners属性中
- 推断并设置main方法的定义类,找到运行的主类
查看构造器
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.sources = new LinkedHashSet();
this.bannerMode = Mode.CONSOLE;
this.logStartupInfo = true;
this.addCommandLineProperties = true;
this.addConversionService = true;
this.headless = true;
this.registerShutdownHook = true;
this.additionalProfiles = new HashSet();
this.isCustomEnvironment = false;
this.lazyInitialization = false;
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.setInitializers(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
this.setListeners(this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = this.deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
springboot启动流程
关于springboot,谈谈你的理解
- 自动装配
- run()
SpringBoot配置
配置文件
SpringBoot使用一个全局的配置文件,配置文件名称是固定的
- application.properties
- 语法结构: key=value
- application.yaml
- 语法结构: key: 空格 value
配置文件的作用: 修改springboot自动配置的默认值,因为springboot在底层都给我们自动配置好了
YAML
YAML是"YAML Ain’t a Markup Language" (YAML不是一 种置标语言)的递归缩写。
在开发的这种语言时,YAML的意思其实是: “Yet Another Markup Language” (仍是一种置标语言)
YAML A Markup Language :是一个标记语言
YAML isnot Markup Language :不是一个标记语言
标记语言
以前的配置文件,大多数都是使用xml来配置;比如一个简单的端口配置,我们来对比下yaml和xml
yaml配置:
server:
port: 8080
xml配置:
<server>
<port>8081<port>
server>
YAML语法
基本语法
k:(空格) v
以此来表示一对键值对(空格不能省略) ;以空格的缩进来控制层级关系,只要是左边对齐的一-列数据都是同一个层级的。
注意:属性和值的大小写都是十分敏感的。例子:
server:
port: 8081
path: /hello
值的写法
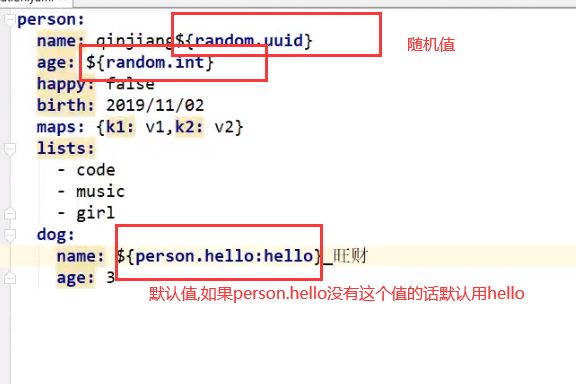
字面量: 普通的值 [数字,布尔值,字符串]
k: v
字面量直接写在后面就可以,字符串默认不用加上双引号或者单引号;
“” 双引号,不会转义字符串里面的特殊字符,特殊字符会作为本身想表示的意思;
比如: name: “kang \n yuan” 输出: kang 换行 yuan
# k=v
# 对空格的要求十分严格
# 普通的key-value
# 可以注入到配置类中
name: deemo
# 对象
student:
name: deemo
age: 21
#行内写法
student1: {name: deemo, age: 21}
# 数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
pets1: [cat,dog,pig]
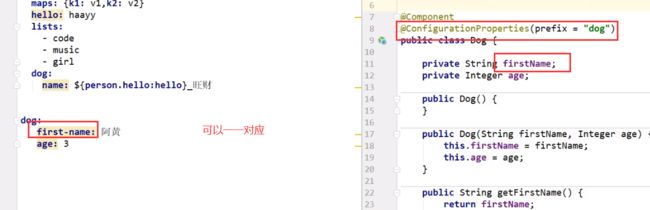
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “yaml配置中的对象”)
把这个注解加在类上,prefix中写yaml中对应的key,就可以为POJO赋值,注意,k-v和POJO中的字段要一一对应
举一反三
我们可以写一个Mybatis的配置类,然后把配置信息写在yaml配置文件中,加上@ConfigurationProperties注解为Mybatis配置类注入值
如果非要用properties呢?
注意:此时必须是UTF-8
用@PropertiesSource(value=“classpath:xxx.properties”)注解,然后在字段上用@Value注解,写SPEL表达式去除配置文件的值就可以
一点骚操作
松散绑定
结论
-
配置yml和配置properties都可以获取到值,强烈推荐 yml
-
如果我们在某个业务中,只需要获取配置文件中的某个值,可以使用一下@value
-
如果说,我们专门编写了-个JavaBean来和配置文件进行映射,
就直接使用@configurationProperties,不要犹豫!
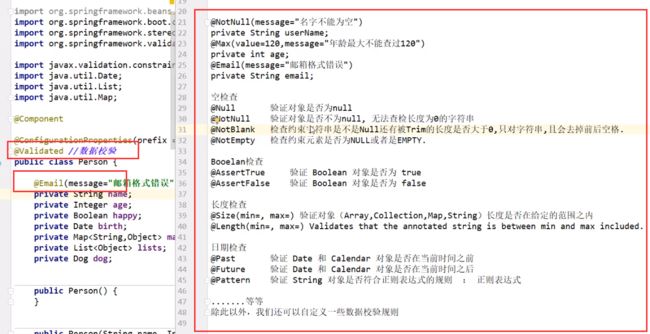
JSR303校验
在类上加上@Validated注解开启数据校验
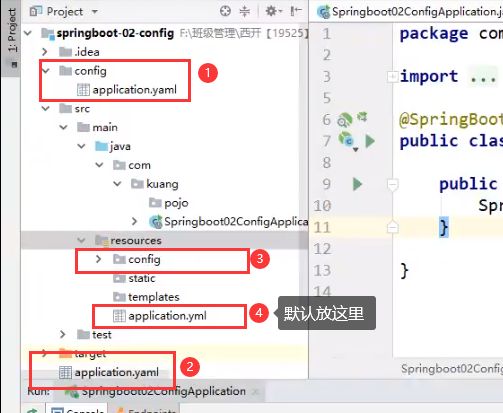
配置文件位置优先级
强制:必须以前缀为application为开头
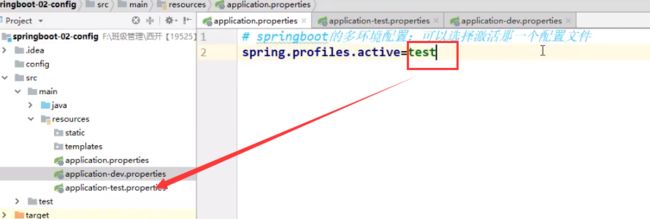
在生产环境中,我们可以在不同位置进行配置,然后达到覆盖的效果
第一种方式.指定properties配置文件:
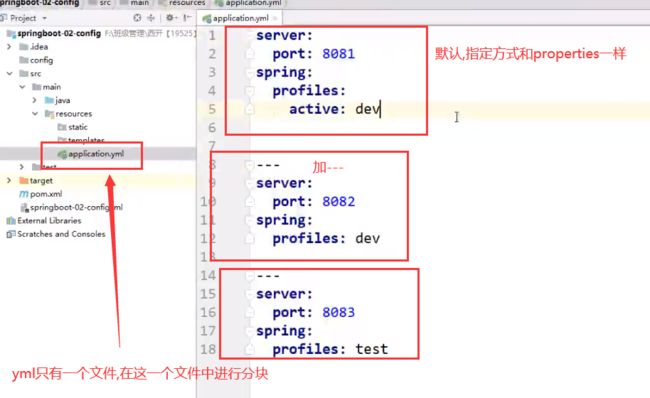
第二种方式:yaml配置文件:
为什么可以完成自动配置
在我们这配置文件中能配置的东西,都存在一个固有的规律
xxxAutoConfiguration:默认值 <—注入----- xxxProperties -----绑定— 配置文件
精髓
-
SpringBoot启动会加载大量的自动配置类
-
我们看我们需要的功能有没有在SpringBoot默认写好的自动配置类当中;
-
我们再来看这个自动配置类中到底配置了哪些组件; (只要我们要用的组件存在在其中,我们就不需要再手动配置了)
-
给容器中自动配置类添加组件的时候,会从properties类中获取某些属性。我们只需要在配置
文件中指定这些属性的值即可;xxxxAutoConfigurartion: 自动配置类; 给容器中添加组件
xxxxProperties: 封装配置文件中相关属性;
查看哪些配置类生效
debug: true
如果配置了log4j之类的,设置log的level为debug,也可以看到
自动配置了并且生效的
大量的没有生效的
没有条件所以没生效的
SpringBoot Web开发
要解决的问题:
- 导入静态资源
- 首页
- jsp, 模板引擎 Thymeleaf
- 装配扩展SpringMVC
- 增删改查
- 拦截器
- 国际化
- …
静态资源
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
//第一种方式,webjars
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache()
.getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{"/webjars/**"}).addResourceLocations(new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/"}).setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
//第二种方式,某路径下的静态资源
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
this.customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(
registry.addResourceHandler(new String[]{staticPathPattern})
.addResourceLocations(
WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(
this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(this.getSeconds(cachePeriod))
.setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
}
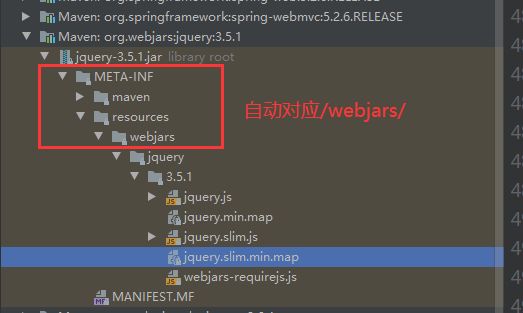
什么是webjars?
给静态资源的一层封装,比如jquery,以maven的方式引入的话,会给他包上一层webjars封装
如上述代码 “/webjars/**” 对应的是 “classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/” 直接输入/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js就可以访问到js文件了
静态资源目录
优先级即为,他们的位置关系 /META-INF/resources/ 优先级最高,最低的是classpath:/public/
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
总结
-
在springboot中,我们可以使用以下方式处理静态资源
- webjars localhost:8080/webjars/
- public, static, /**, resources localhost:8080/
-
优先级: resources > static(默认) > public
首页如何定制
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext, FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, this.getWelcomePage(), this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(this.getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(this.getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
private Optional<Resource> getWelcomePage() {
String[] locations = WebMvcAutoConfiguration.getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
return Arrays.stream(locations).map(this::getIndexHtml).filter(this::isReadable).findFirst();
}
private Resource getIndexHtml(String location) {
return this.resourceLoader.getResource(location + "index.html");
}
注意:此处需要模板引擎的支持(Thymeleaf)
模板引擎
模板引擎的作用就是我们来写一个页面模板,比如有些值呢,是动态的,我们写一些表达式。而这些值,从哪来呢,我们来组装一些数据, 我们把这些数据找到。然后把这个模板和这个数据交给我们模板引擎,模板弓|擎按照我们这个数据帮你把这表达式解析、填充到我们指定的位置,然后把这个数据最终生成一个我们想要的内容给我们写出去, 这就是我们这个模板弓|擎,不管是jsp还是其他模板引擎,都是这个思想。只不过呢,就是说不同模板弓|擎之间,他们可能这个语法有点不一样。其他的我就不介绍了,我主要来介绍一下SpringBoot给我们推荐的Thymeleaf模板引擎,这模板引擎呢,是一个高级语言的模板引擎,他的这个语法更简单。而且呢,功能更强大。
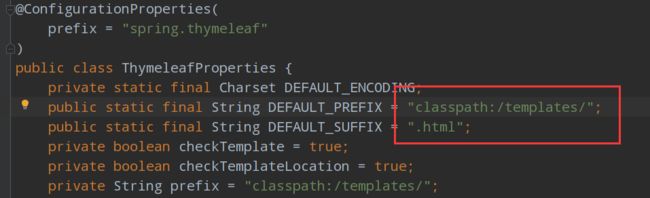
默认路径是在classpath下的templates路径下,文件后缀.html
导入依赖:
官方文档 https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.7.RELEASE/reference/html/appendix-dependency-versions.html#appendix-dependency-versions
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleafartifactId>
<version>2.2.7.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
现在就能跳转成功了
使用thymeleaf:
导入约束
<html xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
表达式
官方文档
https://www.thymeleaf.org/doc/tutorials/3.0/usingthymeleaf.html
所有这些功能可以组合和嵌套:
- Simple expressions:
- Variable Expressions:
${...} - Selection Variable Expressions:
*{...} - Message Expressions:
#{...} - Link URL Expressions:
@{...} - Fragment Expressions:
~{...}
- Variable Expressions:
- Literals
- Text literals:
'one text','Another one!',… - Number literals:
0,34,3.0,12.3,… - Boolean literals:
true,false - Null literal:
null - Literal tokens:
one,sometext,main,…
- Text literals:
- Text operations:
- String concatenation:
+ - Literal substitutions:
|The name is ${name}|
- String concatenation:
- Arithmetic operations:
- Binary operators:
+,-,*,/,% - Minus sign (unary operator):
-
- Binary operators:
- Boolean operations:
- Binary operators:
and,or - Boolean negation (unary operator):
!,not
- Binary operators:
- Comparisons and equality:
- Comparators:
>,<,>=,<=(gt,lt,ge,le) - Equality operators:
==,!=(eq,ne)
- Comparators:
- Conditional operators:
- If-then:
(if) ? (then) - If-then-else:
(if) ? (then) : (else) - Default:
(value) ?: (defaultvalue)
- If-then:
- Special tokens:
- No-Operation:
_
- No-Operation:
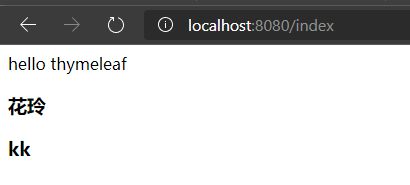
简单测试一下
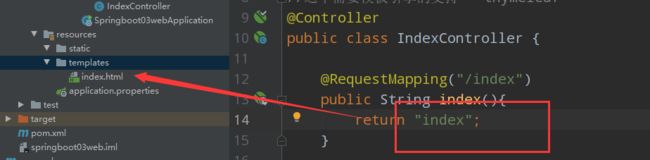
@RequestMapping("/index")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("msg","hello thymeleaf");
model.addAttribute("users", Arrays.asList("花玲","kk"));
return "index";
}
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>indextitle>
head>
<body>
<div th:text="${msg}">div>
<h3 th:each="user:${users}" th:text="${user}">h3>
body>
html>
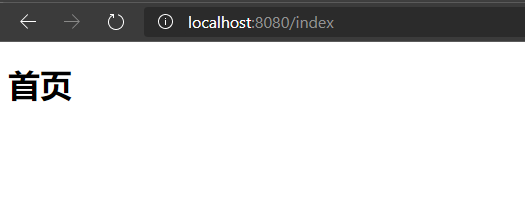
输出
注意
热部署(Ctrl+F9)需要关闭缓存:
spring.thymeleaf.cache=false
修改springboot的默认配置
方式一
这么多的自动配置,原理都是一样的, 通过这个WebMVC的自动配置原理分析,我们要学会一种学习方式,通过源码探究,得出结论;这个结论一定是属于自己的,而且一通百通。
SpringBoot的底层,大量用到了这些设计细节思想,所以,没事需要多阅读源码!得出结论;
SpringBoot在自动配置很多组件的时候,先看容器中有没有用户自己配置的(如果用户自己配置@bean) ,如果有就用用户配置的,如果没有就用自动配置的;如果有些组件可以存在多个,比如我们的视图解析器,就将用户配置的和自己默认的组合起来!
扩展装配SpringMVC
官方文档
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.2.7.RELEASE/reference/html/spring-boot-features.html#boot-features-developing-web-applications
扩展SpringMVC
我们要做的就是编写一个@Configuration注解类, 并且类型要为WebMvcConfigurer, 还不能标注@EnableWebMvc注解;我们去自己写一个;
我们新建一个包叫config, 写一个类MyMvcConfig;
package com.ky.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.View;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
import java.util.Locale;
//如果,你想diy一些定制化的功能,只要写这个组件,然后将它交给springboot,springboot就会帮我们自动装配
//扩展springMvc dispatcherServlet
@Configuration
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//ViewResolver 实现了视图解析器接口的类,我们就可以把它看做视图解析器
@Bean
public ViewResolver myViewResolver(){
return new MyViewResolver();
}
//自定义了一个自己的视图解析器MyViewResolver
public static class MyViewResolver implements ViewResolver{
@Override
public View resolveViewName(String s, Locale locale) throws Exception {
return null;
}
}
}
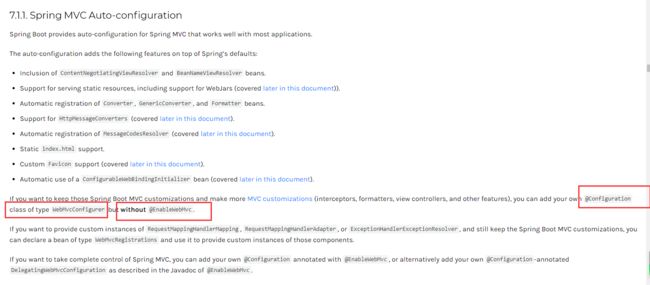
官网中有这么一句话:
If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations (interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own
@Configurationclass of typeWebMvcConfigurerbut without@EnableWebMvc.
@EnableWebMvc是干嘛的?
//如果我们要扩展springmvc,官方建议我们这样去做
@Configuration
@EnableWebMvc //导入了一个类 DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 作用:从容器中获取所有的webmvcconfig
public class MyMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//视图跳转
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/kang").setViewName("index");
}
}
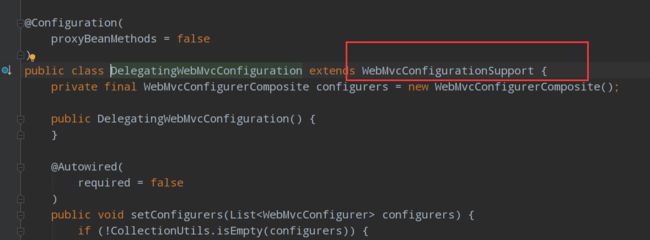
先说结论,@EnableWebMvc相当于覆盖所有默认设置
为什么?
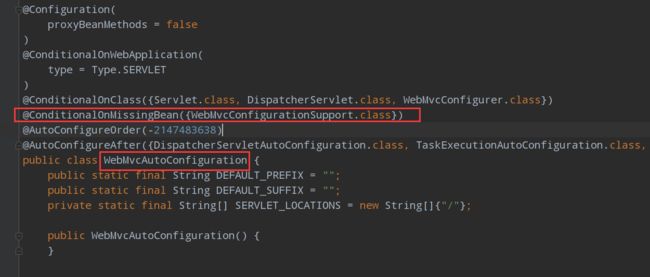
WebMvcAutoConfiguration这个类的主要作用是完成对MVC设置的自动装配
但是条件是在没有导入WebMvcConfigurationSupport这个类的情况下才会生效
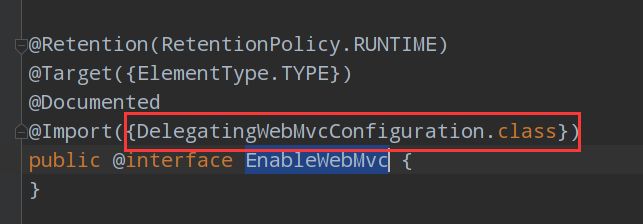
而
@EnableWebMvc导入了DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration这个类
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration这个类继承了WebMvcConfigurationSupport
所以WebMvcAutoConfiguration这个类对MVC的自动设置会全部失效,这是完全接管SpringMVC,而不是对SpringMVC的扩展.
Springboot整合ORM
Springboot整合JDBC
简介
对于数据访问层,无论是SQL(关系型数据库)还是NOSQL(非关系型数据库),Spring Boot底层都是采用Spring Data的方式进行统一处理。Spring Boot底层都是采用Spring Data的方式进行统一处理各种数据库, Spring Data也是Spring中与Spring Boot、Spring Cloud等齐名的知名项目。
Spring data官网: https://spring.io/projects/spring-data
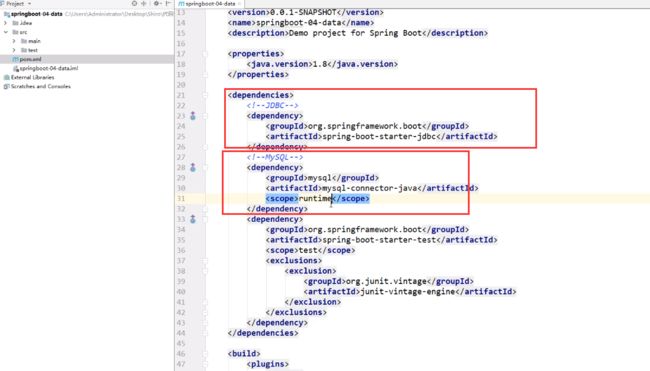
引入SQL相关依赖
![]()
pom依赖
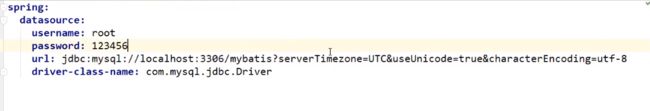
配置信息
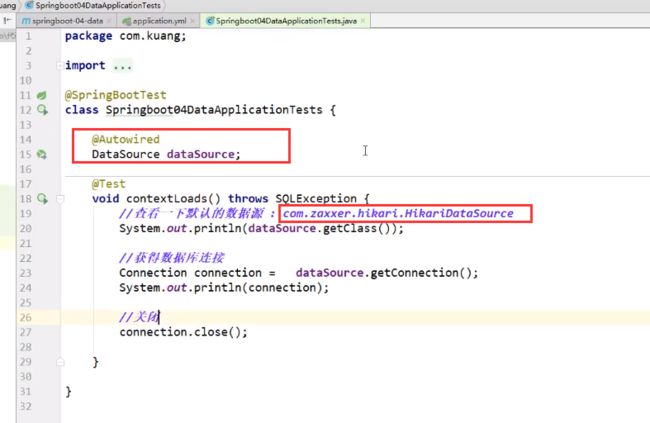
测试,默认数据源
测试jdbcTemplate
增删改查之类的就不演示了,见名知意直接看api就好.
Sringboot整合Druid
简介
Druid是阿里巴巴开源平台上一个数据库连接池实现,结合了C3P0、DBCP、PROXOOL 等DB池的优点,同时加入了日志监控。
Druid可以很好的监控DB池连接和SQL的执行情况,天生就是针对监控而生的DB连接池。
Spring Boot 2.0以上默认使用Hikari数据源,可以说Hikari与Driud都是当前Java Web.上最优秀的数据源,我们来重点介绍SpringBoot如何集成Druid数据源,如何实现数据库监控。
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com. alibaba
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.21version>
dependency>
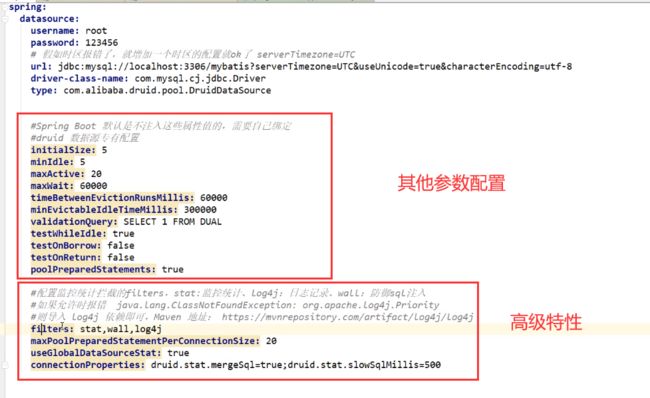
配置信息
当然,如果要用日志功能,需要引入日志依赖
|
<dependency>
<groupId>1og4jgroupId>
<artifactId>1og4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
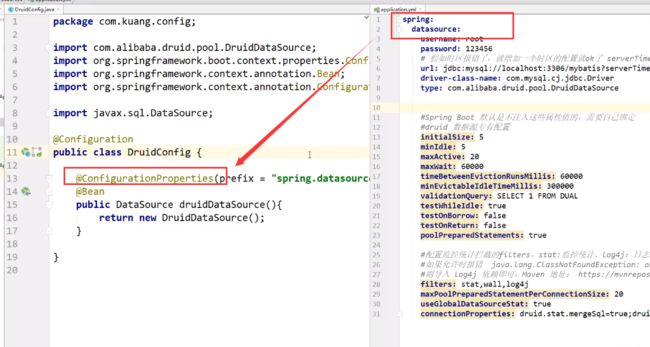
DruidConfig配置类
这样spring容器中就会有我们的Druid数据源了,可以实现一些功能的配置
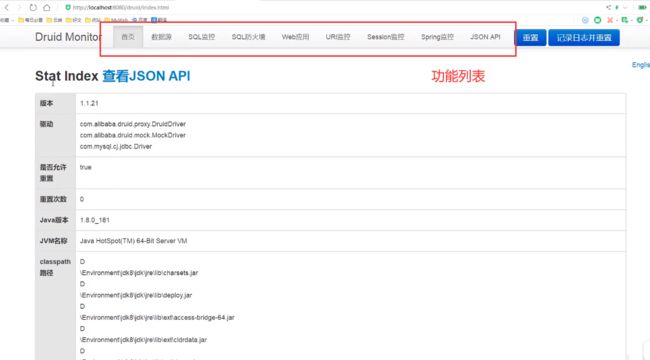
实现后台监控功能
//后台监控
//因为SpringBoot内置了servlet 容器,所以没有web.xmL,替代方法: ServletRegistrationBean
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){
ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> bean = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(
new StatViewServ1et("/druid/**")){
//后台需要有人登陆,账号密码配置
HashMap<String, String> initParameters = new HashMap<>();
//增加配置
initParameters.put( "loginUsername", "admin"); //登key是固定的LoginUsername LoginPassword
initParameters.put("loginPassword" , "123456");
//允许谁可以访问,为空表示所有人可访问
initParameters.put("a11ow", "";
//禁止谁能访问initParameters.put( "deny", "192.168.11.123");
bean.setInitParameters(initParameters); // 设置初始化参数
return bean;
}
自带monitor
filter
//filter
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
FilterRegistrationBean bean = new FilterRegistrationBean();
bean.setFilter(new WebStatFilter());
//可以过滤哪些请求呢?
Map<String, String> initParameters = new HashMap<>(); .
//这些东西不进行统计
initParameters.put("exclusions","*.js,*.css,/druid/*");
bean.setInitParameters(initParameters);
return bean;
}
Springboot整合Mybatis
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>2.1.1version>
dependency>
application.properties(yml也可)
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=123456
spring.datasource.ur1=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysq1.cj.jdbc.Driver
测试
pojo
//此处是导入了lombok的依赖
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@A11ArgsConstructor
public class User {
private int id;
private String name ;
private String pwd ;
}
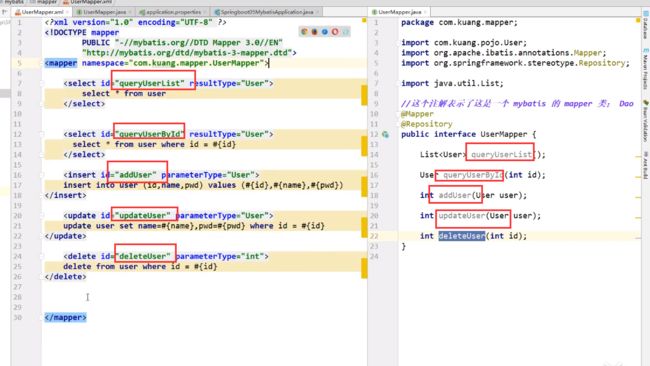
mapper
//这个注解表示了这是一一个 mybatis的mapper类; 我们原来用的@MapperScan,现在用这个就不用写了,都可
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> queryUserList();
User queryUserById(int id);
int addUser(User user);
int updateUser(User user);
int deleteUser(int id);
}
mybatis官方中文文档 https://mybatis.org/mybatis-3/zh/getting-started.html
xxxMapper.xml(这里是官方示例)
<mapper namespace="org.mybatis.example.BlogMapper">
<select id="selectBlog" resultType="Blog">
select * from Blog where id = #{id}
select>
mapper>
整合mybatis配置信息
#整合mybatis
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.kuang.pojo
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml
xml一一对应(当然我们如果用tk的通用mapper就没那么麻烦了)
搞一个Controller测试
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@GetMapping(”/queryUserList" )
public List<User> queryUserList(){
List<User> userlist = userMapper.queryUserList();
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.print1n(user);
}
return userList;
}
}
总的来说
- 导入包
- 配置文件
- mybatis配置
- 编写sq
- service层调用dao层
- controller调用service层
SpringSecurity
web开发中,过滤器拦截器都能做安全相关的东西,安全并不是一个功能性需求(不做安全网站也能跑起来)
但是安全应该是在设计之初就考虑的内容
可以实现的功能
- 功能权限
- 访问权限
- 菜单权限
我们原来实现这些功能–>拦截器,过滤器—>大量的原生代码—>繁琐冗余
环境引入
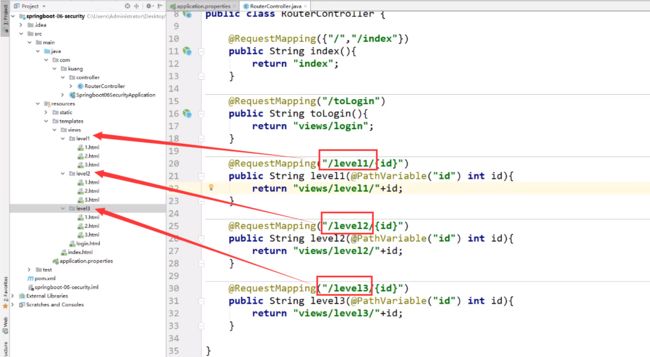
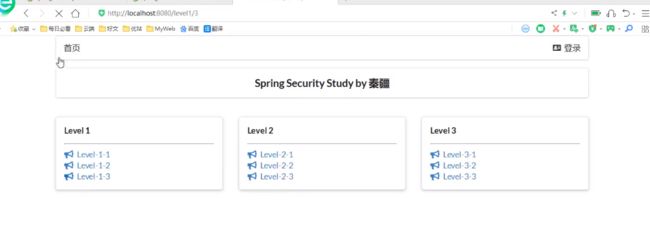
RouteController
通过输入的id直接路由到对应的网页,展示对应的内容
页面展示
因为没有加权限控制,所以了展示所有的信息
Springsecurity是一种AOP的思想,就是横切嘛,不懂得同学了解下就好
简介
Spring Security是针对Spring项目的安全框架,也是Spring Boot底层安全模块默认的技术选型,他可以实现强大的Web安全控制,对于安全控制,我们仅需要引入spring boot-starter-security模块,进行少量的配置,即可实现强大的安全管理!
记住几个类:
- WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter: 自定义Security策略
适配器模式 - AuthenticationManagerBuilder: 自定义认证策略
建造者模式 - @EnableWebSecurity: 开启WebSecurity模式 @Enablexxxx—>开启某个功能
Spring Security的两个主要目标是“认证”和"授权”(访问控制)
“认证”(Authentication)
"授权”(Authorization)
这个概念是通用的,而不是只在Spring Security中存在。
参考官网: https://spring.io/projects/spring-security#overview
查看项目中的版本,找到对应的帮助文档: https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.2.4.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-securityartifactId>
dependency>
核心的就是AOP,config,web
官方示例
https://docs.spring.io/spring-security/site/docs/5.2.4.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#hello-web-security-java-configuration
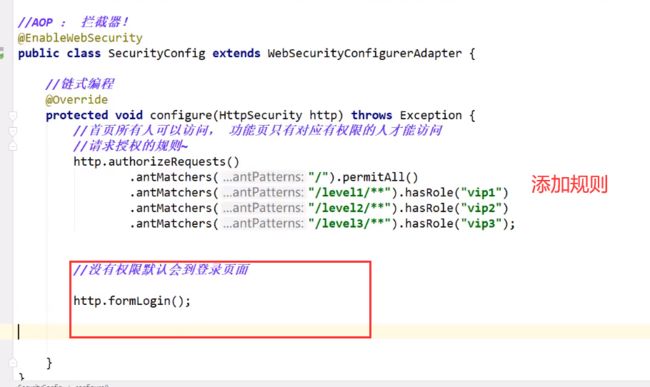
@EnableWebSecurity
public class Config extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.apply(customDsl())
.flag(true)
.and()
...;
}
}
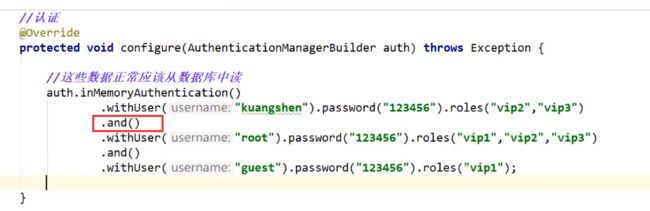
授权
效果
设置跳转登录页面之后可以自动跳转到登录页
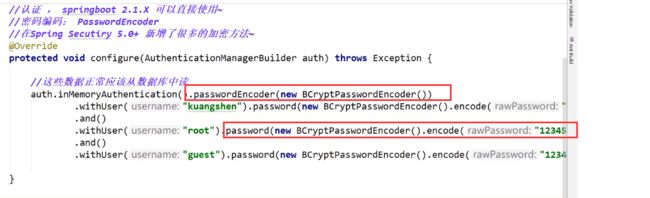
认证
注意:此处在springboot2.1.x中可以直接使用,在Spring Security 5.0中新增了很多加密方法,如果未设置会报错
解决方案:
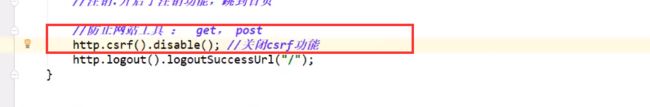
注销
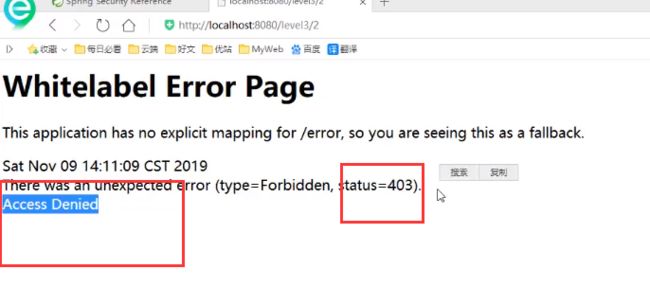
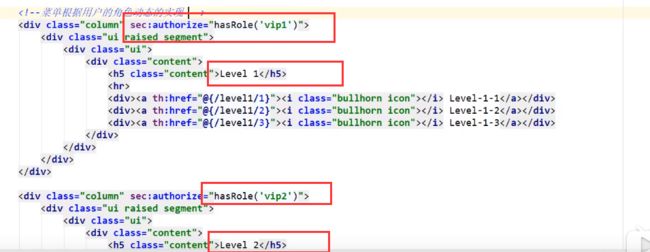
问题
现在我们只是可以通过security达到让用户只能点击对应权限的模块,但是还不能做到只能让用户直接看到他自己的模块
![]()
解决方案
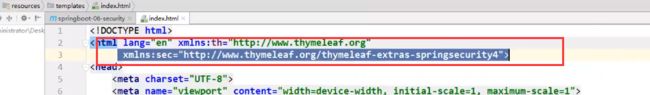
SpringSecurity整合thymeleaf
引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extrasgroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity4artifactId>
<version>3.0.4.RELEASEversion>
dependency>
前端页面修改
导入命名空间
修改页面
SecurityConfig修改
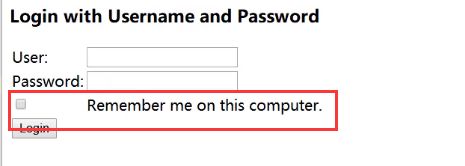
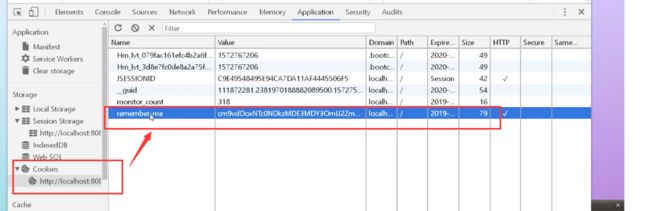
记住我
效果
其实是往cookie和session中丢了个value
害,兄弟萌自己看吧,这里有点绕,笔记文字不好描述 https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PE411i7CV?p=37
Shiro
简介
- Apache Shiro是一个Java的安全(权限)框架。
- Shiro 可以非常容易的开发出足够好的应用,其不仅可以用在JavaSE环境,也可以用在JavaEE环境。
- Shiro可以完成,认证,授权,加密,会话管理,Web集成,缓存等。
- 下载地址: http://shiro.apache.org/

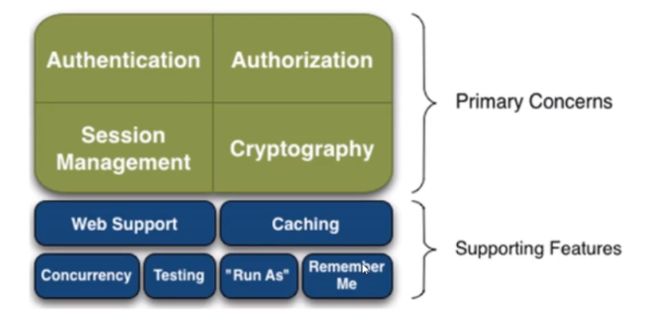
有哪些功能
- Authentication:身份认证、登录,验证用户是不是拥有相应的身份;
- Authorization:授权,即权限验证,验证某个已认证的用户是否拥有某个权限,即判断用户能否进行什么操作,如:验证某个用户是否拥有某个角色,或者细粒度的验证某个用户对某个资源是否具有某个权限!
- Session Manager:会话管理,即用户登录后就是第一次会话, 在没有退出之前,它的所有信息都在会话中; 会话可以是普通的JavaSE环境,也可以是Web环境;
- Cryptography:加密,保护数据的安全性,如密码加密存储到数据库中,而不是明文存储;
- Web Support: Web支持,可以非常容易的集成到Web环境;
- Caching:缓存,比如用户登录后,其用户信息,拥有的角色、权限不必每次去查,这样可以提高效率
- Concurrency: Shiro支持多线程应用的并发验证,即,如在一个线程中开启另- 个线程,能把权限自动的传播过去
- Testing:提供测试支持;
- Run As:允许一个用户假装为另-一个用户(如果他们允许)的身份进行访问;
- Remember Me:记住我,这个是非常常见的功能,即一次登录后,下次再来的话不用登录了
shiro架构(外部)
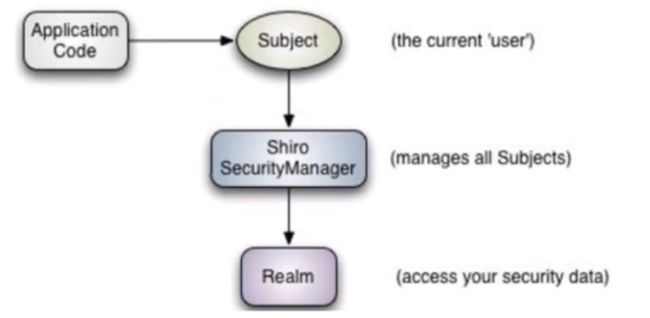
从外部程序来看shiro,即从应用程序角度来观察如何使用shiro完成工作:
- subject:应用代码直接交互的对象是Subject, 也就是说Shiro的对外API核心就是Subject, Subject代表了当前的用户,这个用户不-定是- -个具体的人,与当前应用交互的任何东西都是Subject, 如网络爬虫,机器人等,与ubject的所有交互都会委托给SecurityManager; Subject其实是一 个门面, SecurityManageer 才是实际的执行者
- SecurityManager:安全管理器,即所有与安全有关的操作都会与SercurityManager交互,并且它管理着所有的Subject,可以看出它是Shiro的核心,它负责与Shiro的其他组件进行交互,它相当于SpringMVC的DispatcherServlet的角色
- Realm: Shiro从Realm获取安全数据(如用户,角色,权限),就是说SecurityManager 要验证用户身份,那么它需要从Realm获取相应的用户进行比较,来确定用户的身份是否合法;也需要从Realm得到用户相应的角色、权限,进行验证用户的操作是否能够进行,可以把Realm看 成DataSource;
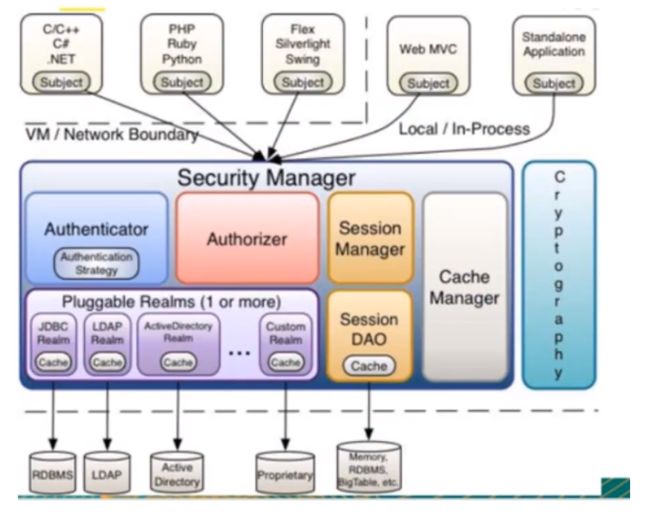
shiro架构(内部)
- Subject:任何可以与应用交互的’用户’;
- Security Manager:相当于SpringMVC中的DispatcherServlet; 是Shiro的心脏,所有具体的交互都通过Security Manager进行控制,它管理者所有的Subject,且负责进行认证,授权,会话,及缓存的管理。
- Authenticator:负责Subject认证,是一个扩展点,可以自定义实现;可以使用认证策略(Authentication Strategy),即什么情况下算用户认证通过了;
- Authorizer:授权器,即访问控制器,用来决定主体是否有权限进行相应的操作;即控制着用户能访问应用中的那些功能;
- Realm:可以有一一个或者多个的realm,可以认为是安全实体数据源,即用于获取安全实体的,可以用JDBC实现,也可以是内存实现等等,由用户提供;所以一般在应用中都需要实现自己的realm
- SessionManager:管理Session生命周期的组件,而Shiro并不仅仅可以用在Web环境, 也可以用在普通的JavaSE环境中
- CacheManager:缓存控制器,来管理如用户,角色,权限等缓存的;因为这些数据基本.上很少改变,放到缓存中后可以提高访问的性能;
- Cryptography:密码模块,Shiro 提高了- -些常 见的加密组件用于密码加密,解密等
HelloWorld快速实践
官方文档: http://shiro.apache.org/tutorial.html
下载地址: http://shiro.apache.org/download.html#latestGit
github: https://github.com/apache/shiro
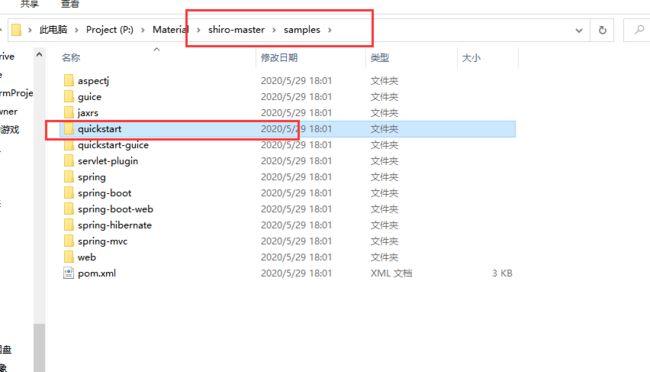
quickstart
git pull之后可以看到quickstart文件夹,可以去看看里面的start代码
新建一个helloshiro工程
配置log4j.properties配置文件
shiro.ini配置文件
如果想要语法高亮需要安装ini插件
把QuickStart.java类建好
/**
* Simple Quickstart application showing how to use Shiro's API.
*
* @since 0.9 RC2
*/
public class Quickstart {
private static final transient Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Quickstart.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建带有配置领域、用户、角色和权限的Shiro SecurityManager的最简单方法是使用简单的INI配置。
// 我们将使用一个工厂读取.ini文件,并返回一个SecurityManager实例:
// 使用类路径根目录下的shiro.ini文件
// (file:和url前缀分别从文件和url加载):
Factory<SecurityManager> factory = new IniSecurityManagerFactory("classpath:shiro.ini");
SecurityManager securityManager = factory.getInstance();
// 对于这个简单的示例quickstart,可以将SecurityManager作为一个JVM单例进行访问。
// 大多数应用程序不会这样做,而是依赖于它们的容器配置或web.xml。
// 这超出了简单的快速入门的范围,所以我们只做最基本的,感知感知强烈。
SecurityUtils.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
// 现在,简单的shiro环境已经设置好了,让我们看看您可以做些什么:
// 获取当前执行用户: 重点,subject 三大对象之一
Subject currentUser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
// 通过当前用户拿到session
Session session = currentUser.getSession();
session.setAttribute("someKey", "aValue");
String value = (String) session.getAttribute("someKey");
if (value.equals("aValue")) {
log.info("Retrieved the correct value! [" + value + "]");
}
// 判断当前用户是否被认证
if (!currentUser.isAuthenticated()) {
UsernamePasswordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken("lonestarr", "vespa");
token.setRememberMe(true); //设置记住我
try {
currentUser.login(token); //执行了登录操作
} catch (UnknownAccountException uae) {
log.info("There is no user with username of " + token.getPrincipal());
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
log.info("Password for account " + token.getPrincipal() + " was incorrect!");
} catch (LockedAccountException lae) {
log.info("The account for username " + token.getPrincipal() + " is locked. " +
"Please contact your administrator to unlock it.");
}
// . .在这里捕获更多的异常(可能是特定于您的应用程序的自定义异常?
catch (AuthenticationException ae) {
// 意料之外的条件,是个错误?
}
}
// 说出他们是谁:打印它们的标识主体(在本例中为用户名):
log.info("User [" + currentUser.getPrincipal() + "] logged in successfully.");
// 测试角色
if (currentUser.hasRole("schwartz")) {
log.info("May the Schwartz be with you!");
} else {
log.info("Hello, mere mortal.");
}
// 粗粒度
// 测试类型化权限(不是实例级)
if (currentUser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wield")) {
log.info("You may use a lightsaber ring. Use it wisely.");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, lightsaber rings are for schwartz masters only.");
}
// 细粒度
// 一个(非常强大的)实例级权限:
if (currentUser.isPermitted("winnebago:drive:eagle5")) {
log.info("You are permitted to 'drive' the winnebago with license plate (id) 'eagle5'. " +
"Here are the keys - have fun!");
} else {
log.info("Sorry, you aren't allowed to drive the 'eagle5' winnebago!");
}
// done! 登出
currentUser.logout();
System.exit(0);
}
}
总的来说主要的就几个方法:
Subject currentuser = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
Session session = currentuser.getSession();
currentuser.isAuthenticated()
currentuser.getPrincipa1()
currentuser.hasRole("schwartz")
currentuser.isPermitted("lightsaber:wie1d")
currentUser.logout();
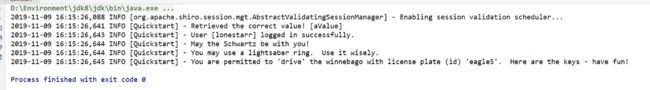
运行结果
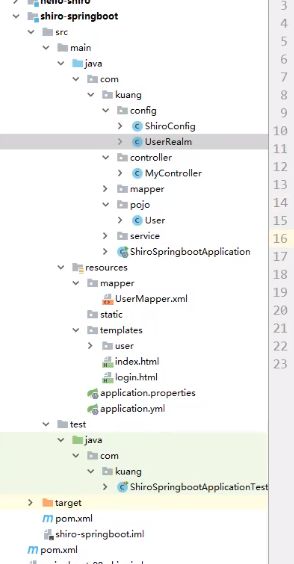
Springboot集成shiro
Subject 用户
Securi tyManager 管理所有用户
Realm 连接数据
结构
pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf
<artifactId>thymeleaf-spring5artifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.thymeleaf.extras
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-java8timeartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.theborakompanionigroupId>
<artifactId>thymeleaf-extras-shiroartifactId>
<version>2.0.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.5.3version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shirogroupId>
<artifactId>shiro-spring-boot-web-starterartifactId>
<version>1.5.3version>
dependency>
UserRealm.java
//自定义的UserRealm extends Authoriz ingReaLm
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
System.out.println("执行了授权");
return null;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticat ionInfo( AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException{
System.out.println("执行了认证");
//用户名,密码 数据库中取 此处伪装一下
String name = "root";
String password = "123456";
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePas swordToken) token;
if(!userToken.getUsername().equals(name)){
return null; //抛出异常 UnknownAccountException
}
//密码认证,shiro做
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo("",password,"");
}
}
ShiroConfig.java
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean :3
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getshiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifler("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//添加shiro的内置过滤器
/**
anon: 无需认 证就可以访问
authc: 必须认证了才能让问
user: 必须拥有记住我功能才能用
perms: 拥有对菜 个资源的权限才能访间:
role: 拥有某个角色权限1能访间
*/
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
filterMap.put("/user/add", "authc");
filterMap.put("/user/update", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
//设置登录请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
return bean;
}
//DafaultWebSecurityManager :2
@Bean(name="securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRea1m") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联UserRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRea1m) ; .
return securityManager;
}
//创建realm 对象 需要自定义类 :1
@Bean(name="userRealm")
public UserRealm userRealm() {
return new UserRealm();
}
}
Controller
@Controller
public class MyController {
@RequestMapping({"/","/index"})
public String toIndex(Model model){
model.addAttribute( "msg","hello,Shiro");
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/add")
public String add(){
return "user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/update")
public String update(){
return "user/update" ;
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password,Model model){
//获取当前的用户
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//封装用户的登录数据
UsernamePas swordToken token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username , password);
try{
subject.login(token); //执行登录方法,如果没有异常就说明oK了
//Subject currentSubject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//Sesson session = currentSubject.getSession();
return "index";
}catch (UnknownAccountException uae) { //用户名不存在
model.addAttribute("msg","用户名错误");
return "login";
} catch (IncorrectCredentialsException ice) {
model.addAttribute("msg","密码错误"); //密码不存在
return "login";
}
}
@RequestMapping("/noauth")
@ResponseBody
public String unauthorized( ){
return "未经投权无法访间此页面";
}
}
测试页面
index
<html lang="en" xmlns :th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns :shiro="http:// Www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-shiro">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Tit1etitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>首页h1>
<div shiro:notAuthenticated="">
<a th:href="@{/toLogin}">登录a>
div>
<p th:text="${msg}">p>
<hr>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:add">
<a th:href="@{/user/add}">adda>
div>
<div shiro:hasPermission="user:update">
<a th:href="@{/user/update}">updatea>
div>
body>
html>
login
<html lang="en" xmlns :th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>登录h1>
<hr>
<p th:text="${msg}" style="color: red;">p>
add
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>addh1>
body>
html>
update
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Titletitle>
head>
<body>
<h1>updateh1>
body>
html>
整合mybatis
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok
<artifactId>lombokkartifactId>
<version>1.16.10version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysq1
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>1og4j
<artifactId>1og4jartifactId>
<version>1.2.17version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com. alibaba
<artifactId>druidartifactId>
<version>1.1.12version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter
<version>2.1.0version>
dependency>
在这里BB一句,我觉得只引入一个mybatis的starter就可了
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
application.yml
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
#?serverTimezone=UTC解决时区的报错
ur1: jdbc:mysql://1ocalhost:3306/mybatis?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysq1.cj.jdbc.Driver
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
#Spring Boot 默认足不注入这些届性值的。需要自己绑定
#druid数据源专有配置
initialsize: 5
minIdle: 5
maxActive: 20
maxWait: 60000
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 300000
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
testWhileIdle: true
testOnBorrow: false
testOnReturn: false
poolPreparedStatements: true
#配置监控统计拦截的filters, stat: 监控统计、Log4j:日志记录、wall:防御sqL注入
#如果允许时报错java. Lang. ClassNotFoundException: org. apache. log4j. Priority
#则导入Log4j 依赖即可,Maven地址: https://mvnrepository. com/artifact/log4j/Log4j
filters: sta,wall,log4j
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSq1=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=500
application.properties
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.kuang.pojo
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
pojo
User.java
@Data
@A11ArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String pwd;
private String perms;
}
mapper
@Repository
@Mapper
public interface UserMpper {
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
userMapper.xml
<mapper namespace="com.kuang.mapper.UserMapper">
Service
//service接口
public interface UserService {
public User queryUserByName(String name);
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
pub1ic User queryUserByName(String name) {
return userMapper.queryUserByName(name);
}
}
测试一下
@SpringBootTest
class ShiroSpringbootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
UserServiceImpl userService;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.print1n(userService.queryUserByName("kuangshen"));
}
}
可以,底层没问题了
改造UserRealm
//自定义的UserRealm extends Authoriz ingReaLm
public class UserRealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principals) {
System.out.println("执行了授权");
SimpleAuthorizationInfo info = new SimpleAuthorizationInfo();
//info.addStringPermission("user:add");
//拿到当前登录的这个对象
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
User currentUser = (User)subject.getPrincipal(); //取得是下面认证时return的user
//设置当前用户的权限
info.addStringPermission(currentUser.getPerms());
return info;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticat ionInfo( AuthenticationToken token) throws AuthenticationException{
System.out.println("执行了认证");
UsernamePasswordToken userToken = (UsernamePas swordToken) token;
//连接数据库查询用户
User user = userService.queryUserByName(userToken.getUsername());
if(user == null){
//没有这个人
return null;
}
//可以加密: MD5: 123456:e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e MD5加盐:123456+username f052d3f8344c2afe6263843456d15be2
//密码认证,shiro做
return new SimpleAuthenticationInfo(user,user.getPwd(),""); //传递user,上面授权才能拿到
}
}
完善ShiroConfig.java
@Configuration
public class ShiroConfig {
//ShiroFilterFactoryBean :3
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getshiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifler("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager defaultWebSecurityManager){
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
//设置安全管理器
bean.setSecurityManager(defaultWebSecurityManager);
//添加shiro的内置过滤器
/**
anon: 无需认 证就可以访问
authc: 必须认证了才能让问
user: 必须拥有记住我功能才能用
perms: 拥有对菜 个资源的权限才能访间:
role: 拥有某个角色权限1能访间
*/
//filterMap.put("/user/add","authc");
//filterMap.put("/user/update", "authc");
//拦截
Map<String, String> filterMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//授权,正常情况下会跳转到未授权页面
filterMap.put("/user/add", "perms[user:add]");
filterMap.put("/user/update", "perms[user:update]");
filterMap.put("/user/*", "authc");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
//设置登录请求
bean.setLoginUrl("/toLogin");
//设置未授权页面
bean.setUnauthorizedUr1("/noauth");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterMap);
return bean;
}
//DafaultWebSecurityManager :2
@Bean(name="securityManager")
public DefaultWebSecurityManager getDefaultWebSecurityManager(@Qualifier("userRea1m") UserRealm userRealm){
DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
//关联UserRealm
securityManager.setRealm(userRea1m) ; .
return securityManager;
}
//创建realm 对象 需要自定义类 :1
@Bean(name="userRealm")
public UserRealm userRealm() {
return new UserRealm();
}
//整合ShiroDialect: 用来整合shiro和thymeleaf
@Bean
public ShiroDialect getShiroDialect(){
return new ShiroDialect();
}
}
任务
-
异步任务
-
定时任务
-
邮件发送
异步任务
主要是使用spring的@Async注解
@Service
public class AsyncService {
//告诉spring这是一个异步的方法
@Async
public void hello(){
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("数据正在处理.....");
}
}
@RestController
public class AsyncController {
@Autowired
AsyncService asyncService;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
asyncService.hello();//停止三秒,转圈
return "ok";
}
}
主类上开启异步功能
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableAsync
public class SpringbootTaskApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootTaskApplication.class, args);
}
}
如果service中不告诉spring hello方法是个异步的方法,那么用户请求了hello方法后会阻塞三秒等待服务器返回数据,这是十分影响用户体验的
我们加上@Async注解之后在用户访问了controller中的hello方法后Browser会立即收到响应,服务器会异步的处理任务,提升用户体验.
邮件任务
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-mailartifactId>
dependency>
配置信息
spring.mail.username=邮箱地址
spring.mail.password=密码
spring.mail.host=smtp.qq.com
#开启加密验证
spring.mail.properties.mail.smtp.ssl.enablr=true
一封简单的邮件
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
//一个简单的邮件
SimpleMailMessage mailMessage = new SimpleMailMessage();
mailMessage.setSubject("这是一封测试邮件");
mailMessage.setText("测试测试测试");
mailMessage.setTo("收件人邮箱地址");
mailMessage.setFrom("发件人邮箱地址");
mailSender.send(mailMessage);
}
一封复杂的邮件
@Autowired
JavaMailSenderImpl mailSender;
@Test
void contextLoads1() throws MessagingException {
//一个复杂的邮件
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
//组装
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,true);
helper.setSubject("这是一封复杂的测试邮件");
helper.setText("努力每一天
",true);
//附件
helper.addAttachment("test.png",new File("C:/Users/admin/Desktop/upload/image-20200518145905217.png"));
helper.setTo("收件人邮箱地址");
helper.setFrom("发件人邮箱地址");
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
可以看到发送成功
封装一下代码
/**
* @param html yes or not open the html style text
* @param subject input your subject
* @param text your text content
* @param attachmentFileName attachmentName
* @param pathName your real filePathName
* @param from sender
* @param to receiver
* @throws MessagingException
* @Author ImDeemo
*/
public void sendMail(Boolean html, String subject, String text, String attachmentFileName, File pathName,String from,String to) throws MessagingException {
//一个复杂的邮件
MimeMessage mimeMessage = mailSender.createMimeMessage();
//组装
MimeMessageHelper helper = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage,true);
helper.setSubject(subject);
helper.setText(text,html);
//附件
helper.addAttachment(attachmentFileName,pathName);
helper.setTo(to);
helper.setFrom(from);
mailSender.send(mimeMessage);
}
提示:此处方法可以进行重载以满足各种方法需求,比如不传附件之类的
定时任务
spring提供了两个定时任务接口
TaskExecutor 任务执行者
TaskScheduler 任务调度者=
在SpringbootApplication主类启动类上加上@EnableScheduling注解,开启定时功能
@EnableScheduling //开启定时功能的注解
@Scheduled //什么时候执行
Cron表达式
秒 分 时 日 月 周几
//在一个特定的时间执行这行代码
/**
* 30 15 10 * * ? 每天10点15分30秒执行一次
* 30 0/5 10,18 * * ? 每天10点和18点,每隔五分钟执行一次
* 0 15 10 ? * 1-6 每个月的周一到周六 10:15执行一次
*/
@Scheduled(cron = "0 * * * * 0-7")
public void hello(){
System.out.println("hello,你被执行了");
}
百度有很多cron表达式在线网站,可以进去看看