json和xml功能相似,可以用来传输数据,存储数据以及表达程序当前的状态。
1、下载cjson的源码
https://github.com/DaveGamble/cJSON
2、阅读readme文件可以大概的了解一下cjson的介绍以及使用方法,我尝试着把readme文件做了一下翻译,水平有限,大概意思写在了“cjson工程的readme文件翻译”,可以参考原文来对照看,如果只是想快速应用一下cjson库的话,看完应该能知道如何使用这个cjson库了。
3、源码分析
如果本着不了解其实现无法安心使用的心态的话,可以看一下下面的源码解析。
将头文件和源码进行分开,然后注释都添加在了代码里(基本上都是根据自己对英文的理解进行翻译的),至于测试例程,其实cjson的源码提供了一个test.c。这个文件里面里面提供了一个比较全面的测试用例。附件里面是整理完格式和加了注释后的cJSON源码
cJSON.h:
#ifndef cJSON__h#define cJSON__h#ifdef __cplusplusextern "C"{#endif//以宏的方式定义出的几种cJson对象的类型#define cJSON_False 0#define cJSON_True 1#define cJSON_NULL 2#define cJSON_Number 3#define cJSON_String 4#define cJSON_Array 5#define cJSON_Object 6#define cJSON_IsReference 256#define cJSON_StringIsConst 512//cJSON的数据结构typedef struct cJSON{/* next/prev 用来遍历所有的数组或者对象链表. 一般来说可以调用GetArraySize/GetArrayItem/GetObjectItem 进行操作*/struct cJSON *next,*prev;/* 一个数组或者对象会有一个孩子节点指针指向一个对象或者数组链 */struct cJSON *child;/* 这个节点的类型, 为上面定义的宏 */int type;/* 是节点的值 如果节点的类型是cJSON_String的话 */char *valuestring;/* 是节点的值 如果节点的类型是cJSON_Number的话 */int valueint;/* 是节点的值 如果节点的类型是cJSON_Number的话 */double valuedouble;/* 节点的名字*/char *string;} cJSON;//钩子?将申请内存和释放内存的接口进行管理。typedef struct cJSON_Hooks {void *(*malloc_fn)(size_t sz);void (*free_fn)(void *ptr);} cJSON_Hooks;//为cJSON提供 malloc realloc 和 free函数extern void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks);//提供一个JSON的内存块,返回出从value传入的字符串中携带的json信息使你后续可以进行提取。在完成工作之后要使用cJSON_Delete进行释放extern cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value);//将一个json数据转换为文本数据,用来方便转发和存储。在完成工作之后要释放char *extern char *cJSON_Print(cJSON *item);//将一个json数据转换为不含有任何格式的文本数据,用来方便转发和存储。在完成工作之后要释放char *extern char *cJSON_PrintUnformatted(cJSON *item);/* 使用缓存的策略将json数据打印到缓冲区中. prebuffer是预测的缓存大小. 认为可以很好的减少内存重复分配.* fmt=0 不含有任何格式,* fmt=1 含有格式*/extern char *cJSON_PrintBuffered(cJSON *item,int prebuffer,int fmt);/* 删除整个json结构体和其所有子项 */extern void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c);/* 返回一个对象或者数组中所有的元素个数*/extern int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array);/* 检索数组array中第item个元素,不成功则返回NULL */extern cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array,int item);/*获取"string"指定的对象. 不区分大小写. */extern cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string);/* 用来分析错误的解析.返回一个指向解析错误位置的指针。你可能需要从这个位置往回检查几个字符. 解析成功则返回0. */extern const char *cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void);/*下面的这些调用用来根据指定的类型创建cjson的节点。*/extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void);/*下面的这些用来建立count个节点*/extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers,int count);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers,int count);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers,int count);extern cJSON *cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char **strings,int count);/*将指定的节点添加到数组或者对象中 */extern void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);extern void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);/* 当字符串是常量的时候使用下面这个接口 */extern void cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);/*添加指定的节点到指定的对象或者数组中. 把一个存在的cJSON添加到一个新的cJSON但是又不想销毁已经存在的这个cJSON使用这一组接口*/extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item);extern void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item);/* 从一个数组或者对象中删除指定的节点 */extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which);extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which);extern cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string);extern void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string);/* 更新数组中的节点. */extern void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem); /* 将原有的节点右移. */extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem);extern void cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem);/* 复制一个cJSON对象 */extern cJSON *cJSON_Duplicate(cJSON *item,int recurse);/* Duplicate会创建一个与传入参数完全相同的对象, 在新的内存中需要释放。*当recurse!=0,将会复制这个对象中的所有的孩子节点。*返回对象中的item->next 和 ->prev指针通常是0。*//* ParseWithOpts允许你去指定或者检查字符串是否以NULL结尾, 同时可以检索解析后的字符串的最后一个位置. */extern cJSON *cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value,const char **return_parse_end,int require_null_terminated);//一个精简后的解析框架extern void cJSON_Minify(char *json);/* 宏,用来做快速建立并添加操作. */#define cJSON_AddNullToObject(object,name) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateNull())#define cJSON_AddTrueToObject(object,name) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateTrue())#define cJSON_AddFalseToObject(object,name) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateFalse())#define cJSON_AddBoolToObject(object,name,b) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateBool(b))#define cJSON_AddNumberToObject(object,name,n) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateNumber(n))#define cJSON_AddStringToObject(object,name,s) cJSON_AddItemToObject(object, name, cJSON_CreateString(s))/* 当赋值一个整数的时候, 需要对浮点数也进行同时赋值. */#define cJSON_SetIntValue(object,val) ((object)?(object)->valueint=(object)->valuedouble=(val):(val))#define cJSON_SetNumberValue(object,val) ((object)?(object)->valueint=(object)->valuedouble=(val):(val))#ifdef __cplusplus}#endif#endif
以上为cjson的头文件中的内容,其中定义cjson结构体以及操作json数据的接口,对于cjson结构体来说通过之前的readme文件可以大致的根据一个样例数据进行示例其在内存中的组织方式,而各个接口的实现则在后续的cjson.c的分析中进行展开。
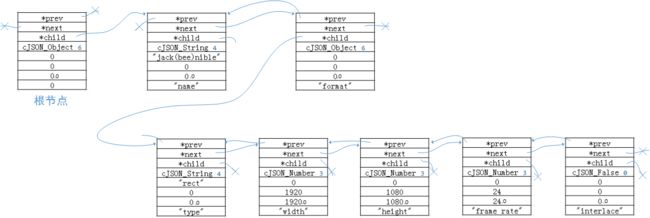
在绘图时,对于cjson结构的组织如下图所示:
图一:cjson的数据结构示意图
{"name": "Jack (\"Bee\") Nimble","format": {"type": "rect","width": 1920,"height": 1080,"interlace": false,"frame rate": 24}}
cjson将上面所示例的json数据在内存中组织方式如下图所示(char*实际情况应为指向动态申请的内存的指针,但为了方便起见
图中约定char*使用值直接替换
):
图二:示例json的组织方式
下面是对于cJSON.c中的源码分析。
cJSON.c
/* cJSON *//* JSON parser in C. */#include#include#include#include#include#include#include#include "cJSON.h"/* ep静态全局指针,指向字符串,*/static const char *ep;/*返回ep所指向字符串的地址,使用const修饰返回值,说明ep所指向的字符串是常量,应该是写死在出错方式上。所以不需要释放其返回的指针的*/const char *cJSON_GetErrorPtr(void){return ep;}/*忽略大小写比较字符串s1和s2, 参数使用const进行修饰,说明内部不会修改这两个值。*static说明文件内作用域,返回整数,*=0 - 相等;*>0 - s1>s2;*<0 - s1*/static int cJSON_strcasecmp(const char *s1,const char *s2){//s1==NULL的情况下,如果s2也是NULL就相等,不然就是s1if (!s1)return (s1==s2)?0:1;//s1不是NULL,但是s2是NULL,那么s1>s2if (!s2)return 1;//不区分大小写,即都以小写形式进行比较,循环比较每个字符。不相等则跳出循环。for(; tolower(*s1) == tolower(*s2); ++s1, ++s2)if(*s1 == 0)//如果这个条件为真,说明s1==s2,s1==NULL。即,两个字串不区分大小写相同return 0;//将不相同的那个字符的小写形式进行相减,可以得到两个串的大小。//强制转换防止报错吧。return tolower(*(const unsigned char *)s1) - tolower(*(const unsigned char *)s2);}/*对静态全局函数指针变量进行赋值,使cJSON_malloc=malloc,使cJSON_free=free*/static void *(*cJSON_malloc)(size_t sz) = malloc;static void (*cJSON_free)(void *ptr) = free;/*静态作用域,返回char*类型指针,该指针指向从str中复制出内容的一块新申请的内存地址,str为const,不可修改*/static char* cJSON_strdup(const char* str){size_t len;char* copy;//获取字符串长度,并考虑了最后一个结束符号。len = strlen(str) + 1;//申请len个长度内存并类型转换和测试是否申请成功,不成功就返回NULL。if (!(copy = (char*)cJSON_malloc(len))) return 0;//申请成功就拷贝len长度个串进去。然后将首地址返回memcpy(copy,str,len);return copy;}/*初始化钩子,其实所谓钩子在这里也就是内存申请和释放接口*/void cJSON_InitHooks(cJSON_Hooks* hooks){//判断传入的指针为NULL,那么就使用系统的申请和释放接口if (!hooks) { /* Reset hooks */cJSON_malloc = malloc;cJSON_free = free;return;}//然后根据传入参数中是否携带指定的申请和释放接口,进行选择使用哪一个内存接口。cJSON_malloc = (hooks->malloc_fn)?hooks->malloc_fn:malloc;cJSON_free = (hooks->free_fn)?hooks->free_fn:free;}/*申请一个cJSON结构体大小的内存,初始化为0,静态作用域*/static cJSON *cJSON_New_Item(void){//申请内存,测试,赋值为0,返回指针。cJSON* node = (cJSON*)cJSON_malloc(sizeof(cJSON));if (node)memset(node,0,sizeof(cJSON));return node;}/*删除一个cJSON结构体,还应该循环将它的所有子项进行删除清理*//*对于c->type的0、1、2、3、4、5、6和256以及512做与预算到底是为什么要这么做呢?*/void cJSON_Delete(cJSON *c){cJSON *next;while (c){//记录c节点的下一个节点。next=c->next;//c->type&cJSON_IsReference将type与256做与运算,判断有孩子节点则进行递归if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->child)cJSON_Delete(c->child);//valuestring不为NULL,需要释放内存if (!(c->type&cJSON_IsReference) && c->valuestring)cJSON_free(c->valuestring);//string不为NULL,需要释放内存if (!(c->type&cJSON_StringIsConst) && c->string)cJSON_free(c->string);//删除这个节点cJSON_free(c);//继续下一个节点c=next;}}/*将输入的num解析成一个数字,然后将结果填充到节点中*静态作用域,const返回值为传入字串解析完后第一个不为数值的位置,解析num到item中*/static const char *parse_number(cJSON *item,const char *num){double n=0,sign=1,scale=0;int subscale=0,signsubscale=1;//是否为负数if (*num=='-')sign=-1,num++;//是否为0if (*num=='0')num++;//如果是十进制就进行解析,临时变量存到n中if (*num>='1' && *num<='9')don=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0');while (*num>='0' && *num<='9');//如果存在小数点,将数字继续转存到n的末尾以整数方式,但是使用scale记录有几位小数if (*num=='.' && num[1]>='0' && num[1]<='9'){num++;don=(n*10.0)+(*num++ -'0'),scale--;while (*num>='0' && *num<='9');}//如果是指数计数方式,记录指数符号,然后将数字进行转存到subscale中if (*num=='e' || *num=='E'){num++;if (*num=='+')num++;else if (*num=='-')signsubscale=-1,num++;while (*num>='0' && *num<='9')subscale=(subscale*10)+(*num++ - '0');}/* number = +/- number.fraction * 10^+/- exponent */n=sign*n*pow(10.0,(scale+subscale*signsubscale));//将计算到的值赋值到item中,int和double项都要赋值。类型赋值为NUMitem->valuedouble=n;item->valueint=(int)n;item->type=cJSON_Number;return num;}/*返回大于x的最小的2的幂,静态作用域*//*在实现上就是把x占用到的最高位为1的位到第0位,都置位为1*/static int pow2gt (int x){//--x是为了防止x直接就是2的幂的情况。--x;x|=x>>1; x|=x>>2; x|=x>>4; x|=x>>8; x|=x>>16;return x+1;}//定义一个printbuffer类型,主要是用来将json数据打印到缓冲区时,进行提供缓存空间的信息。typedef struct{char *buffer; //缓存地址指针int length; //缓存当前的长度int offset; //缓存当前已经使用到的位置。} printbuffer;/**ensure 意为确保的意思,这里可以理解为,确保p所指向的缓冲区中能够提供needed大小的缓冲给打印功能使用*静态作用域,返回缓冲区中可以继续使用的空间的位置。needed在里面做了局部变量,修改使用均无碍,*减少了一个中间变量。*/static char* ensure(printbuffer *p,int needed){char *newbuffer;int newsize;//如果p=NULL,或者p->buffer=NULL,那么为运行时检查错误,返回空指针if (!p || !p->buffer)return 0;//计算将当前所需的空间加上之前已用的空间一共需要内存的数目needed+=p->offset;//如果现在p->buffer足够容下所有的值,那么就返回当前缓存中最后一个可用的位置if (needed<=p->length)return p->buffer+p->offset;/*下面为处理当前缓存不能存下所有的信息的时候*///计算大于当前所需数目的最小2de幂,用来分配内存数目newsize=pow2gt(needed);//申请内存并做错误检查,如果失败那么就置空后返回空指针。newbuffer=(char*)cJSON_malloc(newsize);if (!newbuffer){cJSON_free(p->buffer);p->length=0,p->buffer=0;return 0;}//申请成功后将原有数据拷贝到新空间中。if (newbuffer)memcpy(newbuffer,p->buffer,p->length);//释放原指针,并更新新的缓存信息,然后返回缓存中第一个可用的内存位置。cJSON_free(p->buffer);p->length=newsize;p->buffer=newbuffer;return newbuffer+p->offset;}/*静态作用域函数,意为更新,传入参数为缓存结构,返回当前缓存区已使用的内存偏移量*/static int update(printbuffer *p){char *str;//运行时错误检查if (!p || !p->buffer)return 0;//将str定义到新加入缓存的数据的首地址。然后使用strlen计算新添加长度后加上原有的偏移量进行返回。str=p->buffer+p->offset;return p->offset+strlen(str);}/*静态作用域,将item中的数字打印成字符串,*当p不为NULL时,使用的是p所指向的内存缓冲区,当p为NULL时,使用的是单独申请的内存*/static char *print_number(cJSON *item,printbuffer *p){char *str=0;double d=item->valuedouble;//如果item的数值为0,使用两个字节,根据p是否为空,决定使用从哪里分配的缓存,并将字符串"0"拷贝到缓存中。if (d==0){if (p) str=ensure(p,2);else str=(char*)cJSON_malloc(2); /* special case for 0. */if (str) strcpy(str,"0");}//如果item的数值为整数,21个char肯定装的下,并验证数值的正确性。//(fabs(((double)item->valueint)-d)<=DBL_EPSILON,标示差小于最小误差值,即可以理解为整数,并用INT_MAX、INT_MIN,验证合法性数据。else if (fabs(((double)item->valueint)-d)<=DBL_EPSILON && d<=INT_MAX && d>=INT_MIN){if (p) str=ensure(p,21);else str=(char*)cJSON_malloc(21); /* 2^64+1 can be represented in 21 chars. */if (str) sprintf(str,"%d",item->valueint);}//走到这里,肯定是小数,选用64个字节较为合适。else{if (p) str=ensure(p,64);else str=(char*)cJSON_malloc(64); /* This is a nice tradeoff. */if (str){//如果小数值特别接近零,并且整数部分值特别大,那么就以xxxxx.0方式输出if (fabs(floor(d)-d)<=DBL_EPSILON && fabs(d)<1.0e60)sprintf(str,"%.0f",d);//如果数值比1.0e-6小或者比1.0e9数值大,那么比较适合用科学计数法标示else if (fabs(d)<1.0e-6 || fabs(d)>1.0e9) sprintf(str,"%e",d);//剩余部分直接用小数点形式进行输出else sprintf(str,"%f",d);}}return str;}/*从16进制整数的字符串表达方式转换成无符号整数*//*静态作用域,返回无符号整数,参数不可修改*/static unsigned parse_hex4(const char *str){//将字符串的字符逐个取出进行分析,然后计算到整数中。然后将h左移一个直接再进行下一个数字的解析。最后完成4个字节的整数解析unsigned h=0;if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0;h=h<<4;str++;if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0;h=h<<4;str++;if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0;h=h<<4;str++;if (*str>='0' && *str<='9') h+=(*str)-'0'; else if (*str>='A' && *str<='F') h+=10+(*str)-'A'; else if (*str>='a' && *str<='f') h+=10+(*str)-'a'; else return 0;return h;}/*将输入的文本解析为非转意的c的字符串,然后填充到item中,应该保证str是已经去除开头空字符的串,*,此处的静态字符数组,是用来做utf格式转换的,返回值为解析出一个字符串之后的首地址*/static const unsigned char firstByteMark[7] = { 0x00, 0x00, 0xC0, 0xE0, 0xF0, 0xF8, 0xFC };static const char *parse_string(cJSON *item,const char *str){const char *ptr=str+1;char *ptr2;char *out;int len=0;unsigned uc,uc2;//如果str不以"引号,开头,那么不是一个字符串。if (*str!='\"') {ep=str;return 0;} /* not a string! */while (*ptr!='\"' && *ptr && ++len)if (*ptr++ == '\\')ptr++; /* Skip escaped quotes. *///分配内存并进行检查out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+1); /* This is how long we need for the string, roughly. */if (!out) return 0;ptr=str+1;ptr2=out;while (*ptr!='\"' && *ptr){if (*ptr!='\\')*ptr2++=*ptr++;else{//如果以反斜杠开头的转义字符,则进行下诉的语义转换。只有utf格式转换不是很了解。ptr++;switch (*ptr){case 'b': *ptr2++='\b'; break;case 'f': *ptr2++='\f'; break;case 'n': *ptr2++='\n'; break;case 'r': *ptr2++='\r'; break;case 't': *ptr2++='\t'; break;case 'u': /* transcode utf16 to utf8. */uc=parse_hex4(ptr+1);ptr+=4; /* get the unicode char. *///utf16和utf8之间格式的转换if ((uc>=0xDC00 && uc<=0xDFFF) || uc==0) break; /* check for invalid. */if (uc>=0xD800 && uc<=0xDBFF) /* UTF16 surrogate pairs. */{if (ptr[1]!='\\' || ptr[2]!='u') break; /* missing second-half of surrogate. */uc2=parse_hex4(ptr+3);ptr+=6;if (uc2<0xDC00 || uc2>0xDFFF) break; /* invalid second-half of surrogate. */uc=0x10000 + (((uc&0x3FF)<<10) | (uc2&0x3FF));}len=4;if (uc<0x80) len=1;else if (uc<0x800) len=2;else if (uc<0x10000) len=3; ptr2+=len;switch (len) {case 4: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;case 3: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;case 2: *--ptr2 =((uc | 0x80) & 0xBF); uc >>= 6;case 1: *--ptr2 =(uc | firstByteMark[len]);}ptr2+=len;break;default: *ptr2++=*ptr; break;}ptr++;}}//在结尾填充上'\0',然后将ptr结尾的引号跳过,并返回跳过后所处的位置。也做了对item中相应值的赋值操作。*ptr2=0;if (*ptr=='\"') ptr++;item->valuestring=out;item->type=cJSON_String;return ptr;}/* Render the cstring provided to an escaped version that can be printed. *//*将提供的c字符串打印成可输出的无转意的版本,str为传入字符串,p为缓存指针,返回解析出的字串地址*/static char *print_string_ptr(const char *str,printbuffer *p){const char *ptr;char *ptr2,*out;int len=0,flag=0;unsigned char token;//测试str中是否携带着空格,引号,以及转义字符反斜杠,结果用flag进行标识for (ptr=str;*ptr;ptr++)flag|=((*ptr>0 && *ptr<32)||(*ptr=='\"')||(*ptr=='\\'))?1:0;//如果没有携带上诉的字符,那么根据p指针使用ensure检查内存或者执行分配内存,并进行内存检查。//然后将str中的字符串前后加上引号,存储到out所指向的内存中,并将地址进行返回。if (!flag){len=ptr-str;if (p)out=ensure(p,len+3);elseout=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+3);if (!out)return 0;ptr2=out;*ptr2++='\"';strcpy(ptr2,str);ptr2[len]='\"';ptr2[len+1]=0;return out;}//如果str为NULL,那么就只填上一个双引号间填充空的打印到内存或者缓存。if (!str){if (p) out=ensure(p,3);else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(3);if (!out) return 0;strcpy(out,"\"\"");return out;}ptr=str;while ((token=*ptr) && ++len){if (strchr("\"\\\b\f\n\r\t",token))len++;else if (token<32)len+=5;ptr++;}if (p) out=ensure(p,len+3);else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len+3);if (!out) return 0;//就是转义字符的处理基本上是按照原样输出到输出结果中的。ptr2=out;ptr=str;*ptr2++='\"';while (*ptr){if ((unsigned char)*ptr>31 && *ptr!='\"' && *ptr!='\\') *ptr2++=*ptr++;else{*ptr2++='\\';switch (token=*ptr++){case '\\': *ptr2++='\\'; break;case '\"': *ptr2++='\"'; break;case '\b': *ptr2++='b'; break;case '\f': *ptr2++='f'; break;case '\n': *ptr2++='n'; break;case '\r': *ptr2++='r'; break;case '\t': *ptr2++='t'; break;default: sprintf(ptr2,"u%04x",token);ptr2+=5; break; /* escape and print */}}}*ptr2++='\"';*ptr2++=0;return out;}/* 使用一个对象调用 print_string_ptr (很有用的). *//*将item中的valuestring打印到分配的内存中或者是缓存p中。局部作用域,返回输出值*/static char *print_string(cJSON *item,printbuffer *p) {return print_string_ptr(item->valuestring,p);}/* 声明一些函数原型解析一个值,与打印一个值成对存在。. */static const char *parse_value(cJSON *item,const char *value);static char *print_value(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p);static const char *parse_array(cJSON *item,const char *value);static char *print_array(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p);static const char *parse_object(cJSON *item,const char *value);static char *print_object(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p);/* Utility to jump whitespace and cr/lf *//*跳过空字符或者一个控制字符,即在ascii码中小于等于32的字符*//*静态作用域,常量返回值,其实还是这个串里面的地址。*/static const char *skip(const char *in){while (in && *in && (unsigned char)*in<=32)in++;return in;}/*解析一个对象-创建一个新的根节点,然后进行填充*/cJSON *cJSON_ParseWithOpts(const char *value,const char **return_parse_end,int require_null_terminated){const char *end=0;//新建一个根节点,初始化错误标识,以及检测内存申请状态cJSON *c=cJSON_New_Item();ep=0;if (!c) return 0; /* memory fail *///先将传入的值,进行去除开头的不可见字符后,调用parse_value。end=parse_value(c,skip(value));//如果返回值为NULL,说明解析不成功,删除新创建的节点。if (!end){cJSON_Delete(c);return 0;} /*如果解析失败,ep已经被指向了错误原因了。 *//* 如果我们要求以NULL结尾,那么检测是否以NULL进行结尾的。不然就释放内存并将ep指向出错的位置*/if (require_null_terminated){end=skip(end);if (*end){cJSON_Delete(c);ep=end;return 0;}}//将当前的结束位置进行赋值回传。if (return_parse_end)*return_parse_end=end;return c;}/* cJSON_Parse 调用缺省的选项进行解析*/cJSON *cJSON_Parse(const char *value){return cJSON_ParseWithOpts(value,0,0);}/* 打印cJSON到文本中调用. print_value*/char *cJSON_Print(cJSON *item) {return print_value(item,0,1,0);}/* 打印无格式的cJSON到文本中调用. print_value*/char *cJSON_PrintUnformatted(cJSON *item) {return print_value(item,0,0,0);}/* 打印cJSON到缓存中 调用. print_value*//*item为待解析打印的json数据,prebuffer为预分配到缓存的大小,fmt控制是否需要json格式*/char *cJSON_PrintBuffered(cJSON *item,int prebuffer,int fmt){printbuffer p;p.buffer=(char*)cJSON_malloc(prebuffer);p.length=prebuffer;p.offset=0;return print_value(item,0,fmt,&p);return p.buffer;}/*解析器的核心,遇到什么格式就进行什么格式的解析,从这里进入的解析一般还会递归回来调用这里的功能。*/static const char *parse_value(cJSON *item,const char *value){if (!value) return 0; /* Fail on null. *///三种特定的数据类型,直接赋值item->type,并返回之后的数据。if (!strncmp(value,"null",4)) { item->type=cJSON_NULL; return value+4; }if (!strncmp(value,"false",5)) { item->type=cJSON_False; return value+5; }if (!strncmp(value,"true",4)) { item->type=cJSON_True; item->valueint=1; return value+4; }//如果是引号开头的值传入,那么就进行解析字符串。if (*value=='\"') { return parse_string(item,value); }//解析数字if (*value=='-' || (*value>='0' && *value<='9')) { return parse_number(item,value); }//解析数组,if (*value=='[') { return parse_array(item,value); }//解析一个对象,递归着if (*value=='{') { return parse_object(item,value); }//如果到了这里,那么就置ep指针到出错的字串位置,然后返回0;ep=value;return 0; /* failure. */}/*打印一个值到文本方式中. *//*item为待打印的对象,depth 当前对象到根节点的深度 fmt 是否打印json格式, p为缓存入口*//*返回将item中数据组织成一个串的起始地址,也会被递归的调用,一般情况下*/static char *print_value(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p){char *out=0;if (!item) return 0;if (p){//使用缓存模式进行打印,验证类型进入不同的打印方式cJSON_Object,cJSON_Array会递归调用的switch ((item->type)&255){case cJSON_NULL: {out=ensure(p,5); if (out) strcpy(out,"null"); break;}case cJSON_False: {out=ensure(p,6); if (out) strcpy(out,"false"); break;}case cJSON_True: {out=ensure(p,5); if (out) strcpy(out,"true"); break;}case cJSON_Number: out=print_number(item,p);break;case cJSON_String: out=print_string(item,p);break;case cJSON_Array: out=print_array(item,depth,fmt,p);break;case cJSON_Object: out=print_object(item,depth,fmt,p);break;}}else{switch ((item->type)&255){//不适用缓存方式进行打印值,cJSON_Object,cJSON_Array会递归调用的case cJSON_NULL: out=cJSON_strdup("null"); break;case cJSON_False: out=cJSON_strdup("false");break;case cJSON_True: out=cJSON_strdup("true"); break;case cJSON_Number: out=print_number(item,0);break;case cJSON_String: out=print_string(item,0);break;case cJSON_Array: out=print_array(item,depth,fmt,0);break;case cJSON_Object: out=print_object(item,depth,fmt,0);break;}}return out;}/* 根据输入的文本,建立一个数组 */static const char *parse_array(cJSON *item,const char *value){cJSON *child;if (*value!='[') {ep=value;return 0;} /* not an array! *///验证为数组的value,对类型进行赋值,对value进行去除不可见字符,并判断空对象数组。item->type=cJSON_Array;value=skip(value+1);if (*value==']') return value+1; /* empty array. *///为数组建立一个孩子节点。并检查内存分配,跳过不可见字符,并调用parse_value取得值item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item();if (!item->child) return 0; /* memory fail */value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */if (!value) return 0;//如果还有兄弟节点,即数组有多个元素,那么进行循环创建,链接,解析值。while (*value==','){cJSON *new_item;if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item;value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1)));if (!value) return 0; /* memory fail */}//检查是否存在数组结束的右括号,然后返回结束位置,或者置位错误指向出错位置,然后返回0if (*value==']') return value+1; /* end of array */ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */}/* 将对象数组打印成文本 */static char *print_array(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p){char **entries;char *out=0,*ptr,*ret;int len=5;//获得数组的孩子,即第一个元素cJSON *child=item->child;int numentries=0,i=0,fail=0;size_t tmplen=0;//计算有多少个元素在这个数组里。/* How many entries in the array? */while (child) numentries++,child=child->next;/*如果这个数组为空,那么就打印一个[]出来就好了。*/if (!numentries){if (p) out=ensure(p,3);else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(3);if (out) strcpy(out,"[]");return out;}//如果是以缓存方式打印出来的话进这个分支if (p){/* Compose the output array. *///先将[括号写进缓存中i=p->offset;ptr=ensure(p,1);if (!ptr) return 0; *ptr='['; p->offset++;//从第一个孩子开始进行遍历child=item->child;while (child && !fail){ //打印这个孩子值到缓存中,并更新缓存中offset值。print_value(child,depth+1,fmt,p);p->offset=update(p);//判断是否需要格式打印,并根据此进行分配空间,格式化的会在有空格符号插入if (child->next){len=fmt?2:1;ptr=ensure(p,len+1);if (!ptr)return 0;*ptr++=',';if(fmt)*ptr++=' ';*ptr=0;p->offset+=len;}//遍历传递child=child->next;}//输出右括号,并将out指向这次填充的最开始处ptr=ensure(p,2);if (!ptr) return 0; *ptr++=']';*ptr=0;out=(p->buffer)+i;}else{//不使用缓存,那么就根据元素个数申请二维字符指针,并检查内存申请,初始化指针为NULL。/* Allocate an array to hold the values for each */entries=(char**)cJSON_malloc(numentries*sizeof(char*));if (!entries) return 0;memset(entries,0,numentries*sizeof(char*));/* 遍历所有的元素 */child=item->child;while (child && !fail){//使用中间变量进行遍历并将结果全都放入二维指针中。ret=print_value(child,depth+1,fmt,0);entries[i++]=ret;//判断是否解析值出错。并计算长度if (ret)len+=strlen(ret)+2+(fmt?1:0);elsefail=1;child=child->next;}//如果没有解析错误,那么尝试分配一个输出的数组。/* If we didn't fail, try to malloc the output string */if (!fail) out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len);/* If that fails, we fail. *///如果分配失败,那么这次打印就失败了。if (!out) fail=1;/* 处理错误情况,将之前申请的所有内存进行释放*/if (fail){for (i=0;i<numentries;i++)if (entries[i])cJSON_free(entries[i]);cJSON_free(entries);return 0;}//没有错误情况,那么就将所有的字符串全都复制到新开辟的大的串中,准备输出。/* Compose the output array. */*out='[';ptr=out+1;*ptr=0;for (i=0;i<numentries;i++){tmplen=strlen(entries[i]);memcpy(ptr,entries[i],tmplen);ptr+=tmplen;if (i!=numentries-1) {*ptr++=',';if(fmt)*ptr++=' ';*ptr=0;}cJSON_free(entries[i]);}cJSON_free(entries);*ptr++=']';*ptr++=0;}return out;}/* 根据文本输入,创建一个json对象. */static const char *parse_object(cJSON *item,const char *value){cJSON *child;if (*value!='{') {ep=value;return 0;} /* 文本不是对象格式 *///设置类型,跳过不可见字符,并检查是否为空的数组item->type=cJSON_Object;value=skip(value+1);if (*value=='}') return value+1; /* empty array. *///创建一个孩子对象,检查内存,item->child=child=cJSON_New_Item();if (!item->child) return 0;//使用child->valuestring获得待解析的字符串,然后将child->valuestring的值给child->stringvalue=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value)));if (!value) return 0;child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0;//检查时候对应有值,成对,不然就错误if (*value!=':') {ep=value;return 0;} /* fail! *///将:后的值获取出来赋值给child,并且指针移到获取该值后字串的第一个可见字符处value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */if (!value) return 0;//如果存在,号 那么说明后续还要继续进行解析。并进行循环。while (*value==','){//创建对象,并链接到链表中,然后进行解析值。如果出现了object,那么还是要递归调用。cJSON *new_item;if (!(new_item=cJSON_New_Item())) return 0; /* memory fail */child->next=new_item;new_item->prev=child;child=new_item;value=skip(parse_string(child,skip(value+1)));if (!value) return 0;child->string=child->valuestring;child->valuestring=0;if (*value!=':') {ep=value;return 0;} /* fail! */value=skip(parse_value(child,skip(value+1))); /* skip any spacing, get the value. */if (!value) return 0;}//检查是否出现结束的右大括号。返回最后一个值结束的位置,或者返回0并置位epif (*value=='}') return value+1; /* end of array */ep=value;return 0; /* malformed. */}/* 将一个对象,打印到文本中 */static char *print_object(cJSON *item,int depth,int fmt,printbuffer *p){char **entries=0,**names=0;char *out=0,*ptr,*ret,*str;int len=7,i=0,j;//获取根节点的孩子节点cJSON *child=item->child;int numentries=0,fail=0;size_t tmplen=0;/* Count the number of entries. *///计算其内包含的节点个数while (child) numentries++,child=child->next;/* Explicitly handle empty object case *///如果是个空的json对象,那么就打印一个空的花括号对。根据是否有格式选择转义字符//根据p决定将这个字符串输出的位置。//这里depth可以计算应该缩进的字符数if (!numentries){if (p) out=ensure(p,fmt?depth+4:3);else out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(fmt?depth+4:3);if (!out) return 0;ptr=out;*ptr++='{';if (fmt) {*ptr++='\n';for (i=0;i<depth-1;i++) *ptr++='\t';}*ptr++='}';*ptr++=0;return out;}//如果是要求打印到缓存中去,那么进入这个处理逻辑if (p){/* Compose the output: *///计算内训需求,将左括号和换行符输出到缓存中i=p->offset;len=fmt?2:1; ptr=ensure(p,len+1); if (!ptr) return 0;*ptr++='{'; if (fmt) *ptr++='\n'; *ptr=0; p->offset+=len;//遍历孩子节点的子节点child=item->child;depth++;while (child){//fmt格式输出,那么先打印应该输入的缩进再说。if (fmt){ptr=ensure(p,depth); if (!ptr) return 0;for (j=0;j<depth;j++) *ptr++='\t';p->offset+=depth;}//打印字符串到缓存中,并更新offset值print_string_ptr(child->string,p);p->offset=update(p);//处理冒号和格式len=fmt?2:1;ptr=ensure(p,len); if (!ptr) return 0;*ptr++=':';if (fmt) *ptr++='\t';p->offset+=len;//将值解析出来放到p指向的缓存中,然后更新offsetprint_value(child,depth,fmt,p);p->offset=update(p);//计算长度,确保内存容量,检查是否还有后续节点,然后换行后进行下一个节点的遍历len=(fmt?1:0)+(child->next?1:0);ptr=ensure(p,len+1); if (!ptr) return 0;if (child->next) *ptr++=',';if (fmt) *ptr++='\n';*ptr=0;p->offset+=len;child=child->next;}//将右括号合上ptr=ensure(p,fmt?(depth+1):2); if (!ptr) return 0;if (fmt) for (i=0;i<depth-1;i++) *ptr++='\t';*ptr++='}';*ptr=0;out=(p->buffer)+i;}else{//不使用缓存的情况下,先分配二维字符指针出来,并检查内存。初始化为0/* Allocate space for the names and the objects */entries=(char**)cJSON_malloc(numentries*sizeof(char*));if (!entries) return 0;names=(char**)cJSON_malloc(numentries*sizeof(char*));if (!names) {cJSON_free(entries);return 0;}memset(entries,0,sizeof(char*)*numentries);memset(names,0,sizeof(char*)*numentries);/* Collect all the results into our arrays: *///循环递归将所有的值都挂载在二维数组上child=item->child;depth++;if (fmt) len+=depth;while (child){names[i]=str=print_string_ptr(child->string,0);entries[i++]=ret=print_value(child,depth,fmt,0);if (str && ret) len+=strlen(ret)+strlen(str)+2+(fmt?2+depth:0); else fail=1;child=child->next;}/* Try to allocate the output string *///申请一个总的输出字串数组,检查内存if (!fail) out=(char*)cJSON_malloc(len);if (!out) fail=1;/* Handle failure *///分配失败,那么将所有的已分配的内存均进行释放if (fail){for (i=0;i<numentries;i++) {if (names[i]) cJSON_free(names[i]);if (entries[i]) cJSON_free(entries[i]);}cJSON_free(names);cJSON_free(entries);return 0;}//将打印到各个子内存中的数据都拷贝一份到要返回的大内存中。并将原有的子内存进行释放/* Compose the output: */*out='{';ptr=out+1;if (fmt)*ptr++='\n';*ptr=0;for (i=0;i<numentries;i++){if (fmt) for (j=0;j<depth;j++) *ptr++='\t';tmplen=strlen(names[i]);memcpy(ptr,names[i],tmplen);ptr+=tmplen;*ptr++=':';if (fmt) *ptr++='\t';strcpy(ptr,entries[i]);ptr+=strlen(entries[i]);if (i!=numentries-1) *ptr++=',';if (fmt) *ptr++='\n';*ptr=0;cJSON_free(names[i]);cJSON_free(entries[i]);}//补齐右括号cJSON_free(names);cJSON_free(entries);if (fmt) for (i=0;i<depth-1;i++) *ptr++='\t';*ptr++='}';*ptr++=0;}return out;}/* Get Array size/item / object item. *///获取数组的元素个数int cJSON_GetArraySize(cJSON *array){cJSON *c=array->child;int i=0;while(c)i++,c=c->next;return i;}//获取array中第item个元素的入口cJSON *cJSON_GetArrayItem(cJSON *array,int item){cJSON *c=array->child;while (c && item>0)item--,c=c->next;return c;}//获取对象object中名字为string的item。cJSON *cJSON_GetObjectItem(cJSON *object,const char *string){cJSON *c=object->child;while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string))c=c->next;return c;}/* Utility for array list handling. *///将item链接到prev之后static void suffix_object(cJSON *prev,cJSON *item) {prev->next=item;item->prev=prev;}/* Utility for handling references. *///创建一个参照对象,复制一个item,新item的type为cJSON_IsReferencestatic cJSON *create_reference(cJSON *item){cJSON *ref=cJSON_New_Item();if (!ref)return 0;memcpy(ref,item,sizeof(cJSON));ref->string=0;ref->type|=cJSON_IsReference;ref->next=ref->prev=0;return ref;}/* Add item to array/object. *//*添加项目到数组或者对象之中*///将item添加到array中void cJSON_AddItemToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item){//获得array的第一个节点cJSON *c=array->child;if (!item)return;if (!c)//如果原本就是空的数组{array->child=item;}else{//找到最后一个节点,然后将item挂上while (c && c->next)c=c->next;suffix_object(c,item);}}/*将一个项目item,名字为string,添加到object中*/void cJSON_AddItemToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item){if (!item) return;if (item->string) //清理原有的名字cJSON_free(item->string);item->string=cJSON_strdup(string);cJSON_AddItemToArray(object,item);//将object当成一个array来看待}//将一个名字为字符串常量的item,添加到object中,设置type为cJSON_StringIsConstvoid cJSON_AddItemToObjectCS(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item){if (!item) return;if (!(item->type&cJSON_StringIsConst) && item->string)cJSON_free(item->string);item->string=(char*)string;item->type|=cJSON_StringIsConst;cJSON_AddItemToArray(object,item);}//将item复制一份出来,添加到array中void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToArray(cJSON *array, cJSON *item) {cJSON_AddItemToArray(array,create_reference(item));}//将名字为string的item复制一份出来,添加到object中void cJSON_AddItemReferenceToObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *item) {cJSON_AddItemToObject(object,string,create_reference(item));}//将array中的第which个item从array中摘取下来,作为返回值。cJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which){cJSON *c=array->child;while (c && which>0)c=c->next,which--;if (!c) return 0;if (c->prev)//找到第which个item,从链中摘下来c->prev->next=c->next;if (c->next)c->next->prev=c->prev;if (c==array->child) //如果是第一个孩子节点array->child=c->next;c->prev=c->next=0;return c;}//从array中删除第which个元素void cJSON_DeleteItemFromArray(cJSON *array,int which) {cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(array,which));}//从object中摘除名字为string的item,返回这个itemcJSON *cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string){int i=0;cJSON *c=object->child;while (c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string))i++,c=c->next;//遍历找到这个string名字的itemif (c)//找到了就从object中把它移除。return cJSON_DetachItemFromArray(object,i);return 0;}//将指定名字string的item从object中删除void cJSON_DeleteItemFromObject(cJSON *object,const char *string) {cJSON_Delete(cJSON_DetachItemFromObject(object,string));}/* 插入一个newitem到第which个位置,如果不存在这个位置,那么就随意加到一个位置*/void cJSON_InsertItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem){cJSON *c=array->child;while (c && which>0)c=c->next,which--;if (!c){//如果遍历完或者which个,没有找到有效的item,那么就将newitem插入到array中cJSON_AddItemToArray(array,newitem);return;}//将newitem挂载节点c的前面newitem->next=c;newitem->prev=c->prev;c->prev=newitem;if (c==array->child) //为第一个节点array->child=newitem;elsenewitem->prev->next=newitem;}void cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(cJSON *array,int which,cJSON *newitem){cJSON *c=array->child;while (c && which>0)c=c->next,which--;if (!c)//找不到第which个itemreturn;//将newitem插入到第which个item个位置,将原有的item摘下来(c)。newitem->next=c->next;newitem->prev=c->prev;if (newitem->next)newitem->next->prev=newitem;if (c==array->child)array->child=newitem;elsenewitem->prev->next=newitem;c->next=c->prev=0;cJSON_Delete(c);//将摘下来的c节点清除掉}//将object中名字为string的item替换为newitemvoid cJSON_ReplaceItemInObject(cJSON *object,const char *string,cJSON *newitem){int i=0;cJSON *c=object->child;while(c && cJSON_strcasecmp(c->string,string))i++,c=c->next;//找到名字为string的这个itemif(c){newitem->string=cJSON_strdup(string);//需要重新分配一个内存作为名字string的值cJSON_ReplaceItemInArray(object,i,newitem);//插入到前文找到的第i个位置}}/* Create basic types: *///创建一个NULL类型的cjson对象objectcJSON *cJSON_CreateNull(void) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item)item->type=cJSON_NULL;return item;}//创建一个True类型的cjson对象objectcJSON *cJSON_CreateTrue(void) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item)item->type=cJSON_True;return item;}//创建一个False类型的cjson对象objectcJSON *cJSON_CreateFalse(void) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item)item->type=cJSON_False;return item;}//创建一个Bool类型的cjson对象object,然后根据b的值决定item->type是等于cJSON_True还是cJSON_FalsecJSON *cJSON_CreateBool(int b) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item)item->type=b?cJSON_True:cJSON_False;return item;}//创建一个cJSON_Number类型的cjson对象object,其值为numcJSON *cJSON_CreateNumber(double num) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item){item->type=cJSON_Number;item->valuedouble=num;item->valueint=(int)num;}return item;}//创建一个cJSON_String类型的cjson对象object,其值为stringcJSON *cJSON_CreateString(const char *string) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item){item->type=cJSON_String;item->valuestring=cJSON_strdup(string);}return item;}//创建一个cJSON_Array类型的cjson对象objectcJSON *cJSON_CreateArray(void) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item)item->type=cJSON_Array;return item;}//创建一个cJSON_Object类型的cjson对象objectcJSON *cJSON_CreateObject(void) {cJSON *item=cJSON_New_Item();if(item)item->type=cJSON_Object;return item;}/* Create Arrays: *//*创建数组*///创建一个int类型的array,array中有count个元素,值分别为numbercJSON *cJSON_CreateIntArray(const int *numbers,int count){int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();//创建一个arrayfor(i=0;a && i<count;i++){//创建number类型的对象,并赋值n=cJSON_CreateNumber(numbers[i]);if(!i)//第一个元素为孩子节点a->child=n;else //其他为兄弟节点挂接方式suffix_object(p,n);p=n;}return a;}//创建一个float类型的array,array中有count个元素,值分别为numbercJSON *cJSON_CreateFloatArray(const float *numbers,int count) {int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();for(i=0;a && i<count;i++){n=cJSON_CreateNumber(numbers[i]);if(!i)a->child=n;else suffix_object(p,n);p=n;}return a;}//创建一个double类型的array,array中有count个元素,值分别为numbercJSON *cJSON_CreateDoubleArray(const double *numbers,int count) {int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();for(i=0;a && i<count;i++){n=cJSON_CreateNumber(numbers[i]);if(!i)a->child=n;else suffix_object(p,n);p=n;}return a;}//创建一个string类型的array,array中有count个元素,值分别为numbercJSON *cJSON_CreateStringArray(const char **strings,int count) {int i;cJSON *n=0,*p=0,*a=cJSON_CreateArray();for(i=0;a && i<count;i++){n=cJSON_CreateString(strings[i]);if(!i)a->child=n;else suffix_object(p,n);p=n;}return a;}/* 复制item并返回,recurse决定是否递归的将item的子节点也都复制一份 */cJSON *cJSON_Duplicate(cJSON *item,int recurse){cJSON *newitem,*cptr,*nptr=0,*newchild;/* Bail on bad ptr *///item值非法if (!item) return 0;/* Create new item *///创建一个新的item,并检查内存newitem=cJSON_New_Item();if (!newitem) return 0;/* Copy over all vars *///拷贝所有的值到newitem中newitem->type=item->type&(~cJSON_IsReference),newitem->valueint=item->valueint,newitem->valuedouble=item->valuedouble;if (item->valuestring){newitem->valuestring=cJSON_strdup(item->valuestring);if (!newitem->valuestring){cJSON_Delete(newitem);return 0;}}//如果是valuestring的值if (item->string){newitem->string=cJSON_strdup(item->string);if (!newitem->string){cJSON_Delete(newitem);return 0;}}//名字name的值/* If non-recursive, then we're done! *///判断是否需要递归的进行复制子节点if (!recurse) return newitem;/* Walk the ->next chain for the child. *///走到子节点上,然后遍历整个链表进行递归的复制。cptr=item->child;while (cptr){//是个递归的过程,可以尝试gdb单步跟踪理解。newchild=cJSON_Duplicate(cptr,1); /* Duplicate (with recurse) each item in the ->next chain */if (!newchild) {cJSON_Delete(newitem);return 0;}//如果没有成功申请子节点内存,那么就报错返回if (nptr){nptr->next=newchild,newchild->prev=nptr;nptr=newchild;} /* 是兄弟节点则挂链*/else{newitem->child=newchild;nptr=newchild;} /* 是孩子节点则设置指针 */cptr=cptr->next;}return newitem;}//一个mini版本的json数据遍历功能void cJSON_Minify(char *json){char *into=json;while (*json){if (*json==' ') json++;else if (*json=='\t') json++; /* Whitespace characters. */else if (*json=='\r') json++;else if (*json=='\n') json++;else if (*json=='/' && json[1]=='/') while (*json && *json!='\n') json++; /* double-slash comments, to end of line. */else if (*json=='/' && json[1]=='*') {while (*json && !(*json=='*' && json[1]=='/')) json++;json+=2;} /* multiline comments. */else if (*json=='\"'){*into++=*json++;while (*json && *json!='\"'){if (*json=='\\') *into++=*json++;*into++=*json++;}*into++=*json++;} /* string literals, which are \" sensitive. */else *into++=*json++; /* All other characters. */}*into=0; /* and null-terminate. */}
附件列表