Android OTG (USB Hos) 编程
前言:最近在做一个汽车发动机故障检测的项目,负责APP开发。汽车发动机将各种数据通过OTG传输到Android手机,APP可以实时显示数据。
一、权限
1. 声明支持USB Hos模式
- 在AndroidManifest中声明该应用支持USB Hos模式
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="20" />
<uses-feature
android:name="android.hardware.usb.host"/>
2. 声明应用程序能够获得接入USB设备时的通知
(1)指定USB设备接入时通知
如果USB信息写在应用程序配置文件里,则APP只会响应指定的这个USB设备
如果不指定USB设备,则任何USB设备接入时都能响应并启动应用,但是能不能继续运行就是另一回事了
- 在AndroidManifest中声明指定的USB设备,设备信息存放在resource=”@xml/device_filter” 文件夹下
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.hardware.usb.action.USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED"/>
intent-filter>
<meta-data
android:name="android.hardware.usb.action.USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED"
android:resource="@xml/device_filter" />
activity>- 这是我的USB设备信息
<resources>
<usb-device vendor-id="1155"
product-id="22336"
/>
resources>(2)不指定USB设备接入时通知
- 在AndroidManifest中声明该应用能够获得USB设备接入时的通知
<activity
android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
intent-filter>
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.hardware.usb.action.USB_DEVICE_ATTACHED"/>
intent-filter>
activity>
二、发现设备
1. 列举所有接入设备
略
2. 列举指定设备
在主Activity中的OnCreate()中加入如下代码:
- 获取指定USB设备的Intent,通过的
get方法获得在AndroidManifest中静态注册的Intent传递的USB设备信息Extra
Intent intent = getIntent();
usbManager = (UsbManager)getSystemService(Context.USB_SERVICE);
usbDevice = (UsbDevice) intent.getParcelableExtra(UsbManager.EXTRA_DEVICE);- 获取USB设备信息
deviceName = usbDevice.getDeviceName();
deviceVendor = usbDevice.getVendorId();
deviceText.setText("#Device Info : "+usbDevice.toString()+"\n"+"#Device Name : "+
deviceName+"\n"+"#Device Vendor : "+deviceVendor);注[1]:关于intent.getParcelableExtra()
三、与设备通信
1. 通信权限
在列举完已经接入的USB设备,并和指定设备通信前,获得对该设备的权限是必须的。如果采用指定设备接入并列举的方法,则无需再请求明确的权限,因为getIntent()时已经获得了对该设备的权限;否则应当检查是否有权限,如果用户拒绝了你访问该设备的请求,你会收到一个运行时错误
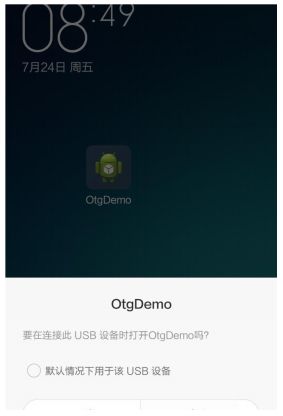
- 我的程序使用Intent发现接入的USB设备并启动应用程序,而且用户允许应用程序处理该Intent,所以该应用可以自动的接收权限。Intent静态注册见AndroidManifest中声明,用户允许接收权限如图:
2. 通信
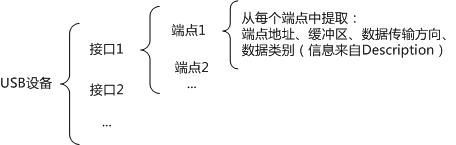
Android中与OTG(USB Hos)相关的API我的翻译在Android API 翻译之 UsbDevice,通信主要就是调用这些API:UsbManager->UsbDevice->UsbInterface->UsbEndpoint->UsbDeviceConnection
注[2]:Android OTG API 示意图
通过代码测试,发现我的OTG设备有2个Interface,其中Interface-0有一个Endpoint-0(输入);Interface-1有两个Endpoint(其中Endpoint-0是输入,Endpoint-1是输出)。故在代码中调用Interface-1实现数据收发
- 与USB设备连接并收发数据写到了button点击事件里
UsbInterface usbInterface = usbDevice.getInterface(1);
UsbEndpoint inEndpoint = usbInterface.getEndpoint(0);
UsbEndpoint outEndpoint = usbInterface.getEndpoint(1);
UsbDeviceConnection connection = usbManager.openDevice(usbDevice);
connection.claimInterface(usbInterface, true);
sendString = "0xa5";
sendBytes = HexString2Bytes(sendString);
int out = connection.bulkTransfer(outEndpoint, sendBytes, sendBytes.length, 5000);
displayToast("发送:"+out+" # "+sendString+" # "+sendBytes);
receiveBytes = new byte[32];
int in = connection.bulkTransfer(inEndpoint, receiveBytes, receiveBytes.length, 10000);
receiveString = Bytes2HexString(receiveBytes);
displayToast("应答:"+in+" # "+receiveString+" # "+receiveBytes.length); 和USB通信有几点要说明:
USB通信协议中有4中传输模式,分别是:
①Bulk Transaction
②Interrupt Transaction
③Control Transation
④Isochronous Transaction
我采用了Bulk Transaction的传输模式,关于这一部分的了解可以参考USB通信协议Bulk Transaction顾名思义是大块数据传输事务:
①in表示输入事务处理:USB主机从总线上某个USB设备上接收数据包;
②out表示输出事务处理:USB主机把一个数据包输出到总线上某个USB设备的接收过程
四、备注
注1:关于getParcelableExtra()
Intent获取: 当在startActivity中传入一个隐式Intent时,首先通过对Intent解析,决定启动哪一个Activity
信息传递:获取该Intent中的数据和动作,
intent.getParcelableExtra(UsbManager.EXTRA_DEVICE)中的UsbManager.EXTRA_DEVICE就是存储在该Intent的extras bundle中的USB设备信息Parcelable意义:Parcelable属于Android编程中进程间通信(IPC)的一种机制,在两个Activity间传递简单的数据如String,可以直接通过intent.putExtra(String,s);在两个Activity间传递类对象,则需要通过Parcelable接口
Parcelable的原理:将要传递的类内的属性分解为存储在Parcel中的基本类型,而这些类型是可以跨进程边界封送的;使用时将要传递类直接implements Parcelable即可实现接口类
注2: USB设备和USB设备组
注3:Android中使用无线连接adb调试
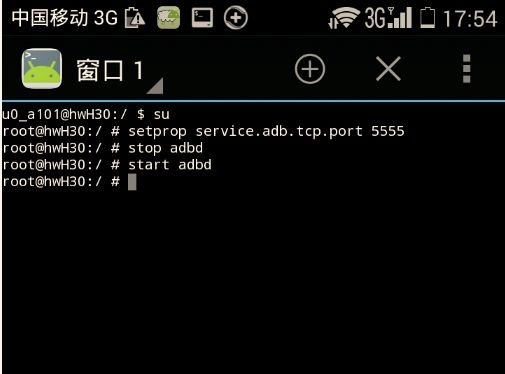
手机只有一个USB口,插上OTG设备就无法看log…了?其实可以使用无线连接adb调试,步骤如下:
下载一个有root权限的终端应用,我下了一个终端模拟器,还挺好用,应该要root手机咯
通过终端模拟器对adb连接端口进行设置,输入如下指令:
设置PC端,进入到Android-SDK/platforms目录,运行如下命令:
adb connect ip.address:5555
通过点击手机wifi,就能查到本机ip,我的是192.168.1.100
设置无误,就可以得到正确输出:connect to …
这样,就可以使用adb对手机进行调试了,在Eclipse的设备列表中也有device的信息辣~(≧▽≦)/~
五、后记
Android OTG编程和BLE4.0其实是非常类似的,都属于Android同外设的通信,前者是串口通信,后者是无线通信。不妨将Android BLE (蓝牙4.0) 编程和OTG编程进行比较学习。