使用高斯混合模型(GMM)分割图像
使用C++、opencv中的高斯混合模型(GMM)进行图像分割
关于GMM聚类的原理及过程可参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/lin_limin/article/details/81048411
使用聚类的方法分割图像,即将图像的像素点值(通常用彩色图像,像素点值为一个三元数组(b,g,r))作为聚类的元素,从而将图像中所有的点分为n类,达到分割的效果。
代码:
#include "stdafx.h"
#include
#include
using namespace cv;
using namespace ml;
int main(int arc, char** argv)
{
Mat src = imread("C:/Users/lenovo/Desktop/1.jpg");
namedWindow("input", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("input", src);
int width = src.cols;
int height = src.rows;
int dims = src.channels();
int pointsCount = width * height;
Mat points(pointsCount, dims, CV_64FC1);
Mat labels;
//Scalar color[] = { Scalar(0,0,255), Scalar(0,255,0), Scalar(255,0,0) };
//将图像转换为一维数据点,传入训练器进行分类
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++) {
index = i * width + j;
points.at(index, 0) = src.at(i, j)[0];
points.at(index, 1) = src.at(i, j)[1];
points.at(index, 2) = src.at(i, j)[2];
}
}
//GMM分割(基于高斯混合模型的期望最大值)
Ptr em = EM::create();// 生成 EM 期望最大化,其图像分割的方式是基于机器学习的方式
em->setClustersNumber(2);// 设置分类数
em->setCovarianceMatrixType(EM::COV_MAT_SPHERICAL);// 协方差矩阵类型
// 迭代条件,EM训练比KMeans耗时,可能会不收敛,所以迭代次数设大点
em->setTermCriteria(TermCriteria(TermCriteria::COUNT + TermCriteria::EPS, 100, 0.1));
// 进行EM训练,获得分类结果,参数labels与KMeans的labels参数意思一样,速度比KMeans要慢很多
em->trainEM(points, noArray(), labels, noArray());
//将数据点转换为图像并显示
Mat result1 = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
result1 = Scalar::all(0);
Mat result2 = Mat::zeros(src.size(), CV_8UC3);
result2 = Scalar::all(0);
//显示标签为0的部分
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
/*index = i * width + j;
int label = labels.at(index, 0);
result.at(i, j)[0] = color[label][0];
result.at(i, j)[1] = color[label][1];
result.at(i, j)[2] = color[label][2];*/
index = i * width + j;
if (labels.at(index, 0) == 0)
{
result1.at(i, j)[0] = src.at(i, j)[0];
result1.at(i, j)[1] = src.at(i, j)[1];
result1.at(i, j)[2] = src.at(i, j)[2];
}
}
}
//显示标签为1的部分
for (int i = 0; i < height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < width; j++)
{
index = i * width + j;
if (labels.at(index, 0) == 1)
{
result2.at(i, j)[0] = src.at(i, j)[0];
result2.at(i, j)[1] = src.at(i, j)[1];
result2.at(i, j)[2] = src.at(i, j)[2];
}
}
}
//显示
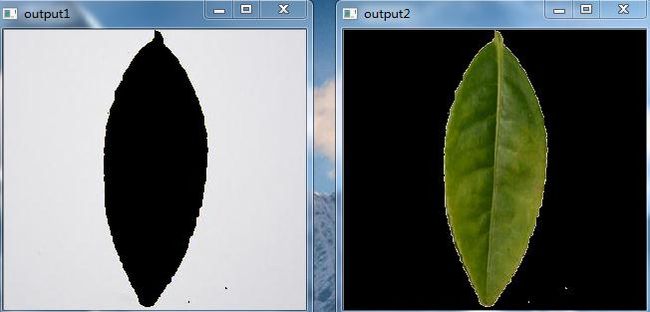
namedWindow("output1", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("output1", result1);
namedWindow("output2", WINDOW_NORMAL);
imshow("output2", result2);
waitKey(0);
return 0;
} 源图像:
结果图:
这里只是展示代码效果,实际上可以根据需要,将其他颜色参数(如H、S、I、L、a、b等)、颜色参数的组合(NRI、NGI、NBI等)作为分类的数据点传入训练器,这样可能会对复杂的分割有帮助。