强化学习学习总结(一)——Qlearning
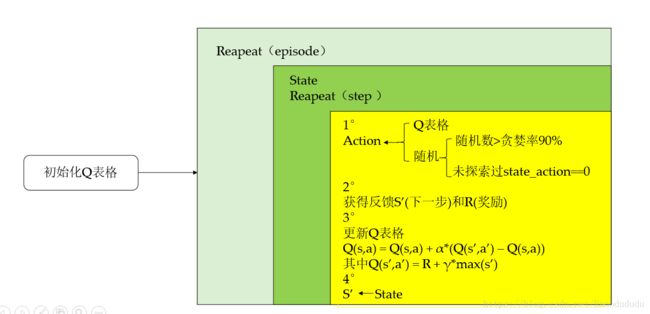
一、Qlearning算法思想构架
二、Qlearing算法程序实现
1.导入
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import time2.给定初始值
N_STATES = 6 # 总长度the length of the 1 dimensional world
ACTIONS = ['left', 'right'] # Q表格的行为available actions
EPSILON = 0.9 # 贪婪率greedy police
ALPHA = 0.1 # 学习率learning rate
GAMMA = 0.9 # 最大Q(s')的衰减率→Q表现实值 discount factor
MAX_EPISODES = 6 # 最大循环数maximum episodes
FRESH_TIME = 0.3 # 更新时间fresh time for one move3.创建Q表函数
def build_q_table(n_states, actions):
table = pd.DataFrame(
np.zeros((n_states, len(actions))), # 初始化Q表值q_table initial values
columns=actions, # actions's name
)
# print(table) # show table
return table4.创建行动选择函数
def choose_action(state, q_table):
# This is how to choose an action
state_actions = q_table.iloc[state, :]
if (np.random.uniform() > EPSILON) or ((state_actions == 0).all()): #当在贪婪率之外或还没探索过时随机选择行动act non-greedy or state-action have no value这个state还没探索过
action_name = np.random.choice(ACTIONS)
else: # act greedy #挡在贪婪率之内选择Q表对应最大值的行动
action_name = state_actions.idxmax()
return action_name5.创建反馈函数
'''获取反馈S'(下一步)和 R(当前步对应奖励) '''
def get_env_feedback(S, A):
# This is how agent will interact with the environment
if A == 'right': # move right
if S == N_STATES - 2: # terminate
S_ = 'terminal'
R = 1 #奖励
else:
S_ = S + 1
R = 0
else: # move left
R = 0
if S == 0:
S_ = S # reach the wall
else:
S_ = S - 1
return S_, R
6.更新环境
def update_env(S, episode, step_counter):
# This is how environment be updated
env_list = ['-']*(N_STATES-1) + ['T'] # '---------T' our environment
if S == 'terminal':
interaction = 'Episode %s: total_steps = %s' % (episode+1, step_counter)
print('\r{}'.format(interaction), end='')
time.sleep(2)
print('\r ', end='')
else:
env_list[S] = 'o'
interaction = ''.join(env_list)
print('\r{}'.format(interaction), end='')
time.sleep(FRESH_TIME)7.QLearning算法程序
def rl():
# main part of RL loop
q_table = build_q_table(N_STATES, ACTIONS)
for episode in range(MAX_EPISODES):
step_counter = 0
S = 0
is_terminated = False
update_env(S, episode, step_counter) #更新环境
while not is_terminated:
A = choose_action(S, q_table)
S_, R = get_env_feedback(S, A) # take action & get next state and reward
q_predict = q_table.loc[S, A] #估计值
if S_ != 'terminal': #真实值
q_target = R + GAMMA * q_table.iloc[S_, :].max() # next state is not terminal
else:
q_target = R # next state is terminal
is_terminated = True # terminate this episode
q_table.loc[S, A] += ALPHA * (q_target - q_predict) # 更新Q表update
S = S_ # move to next state #下一步
update_env(S, episode, step_counter+1) #更新环境
step_counter += 1
return q_table
if __name__ == "__main__":
q_table = rl()
print('\r\nQ-table:\n')
print(q_table)8.演示结果
Q-table:
left right
0 0.00000 0.000057
1 0.00000 0.001138
2 0.00003 0.012839
3 0.00000 0.102839
4 0.00000 0.468559
5 0.00000 0.000000