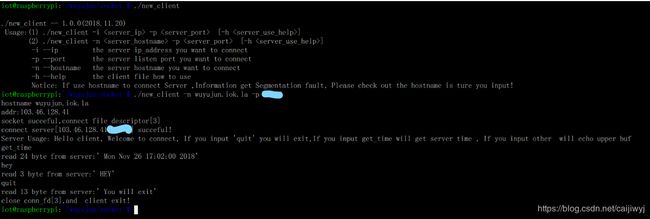
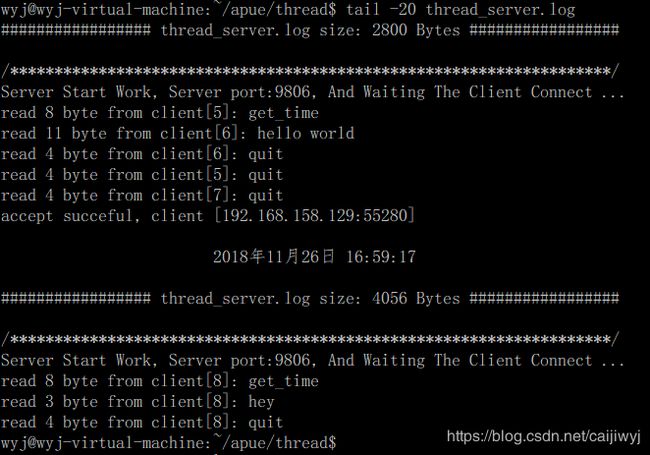
多线程socket服务器
多线程
#include
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
第一个参数为指向线程标识符的指针,返回线程id,线程通过pthread_self()来获取自己的线程ID。
第二个参数用来设置线程属性。
第三个参数是线程运行函数的起始地址。
最后一个参数是运行函数的参数。
线程属性的设置
#include
int pthread_attr_init(pthread_attr_t *attr); //初始化
int pthread_attr_destroy(pthread_attr_t *attr); //用完以后销毁
int pthread_attr_setstacksize(pthread_attr_t *attr, size_t stacksize); //设置线程占用桟大小
int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate); //设置线程分离状态
detachstate:
PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED 分离线程
Threads that are created using attr will be created in a detached state.
PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE 可汇合线程
Threads that are created using attr will be created in a joinable state
int pthread_join(pthread_t thread, void **retval); //如果是可汇合线程,主线程需要执行等待操作,等到子线程执行完毕汇合后,主线程才执行下一步,使用此函数对创建的线程进行资源回收。
互斥锁
所有的线程都是在同一进程空间运行,如果一个资源会被不同的线程访问修改,那么我们把这个资源叫做临界资源,那么对于该资源访问修改相关的代码就叫做临界区,用互斥锁解决共享资源问题。
extern int __pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *attr); //初始化互斥锁
extern int __pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); //加锁,这里是阻塞锁,如果锁被别的线程持有则该函数不会返回
extern int __pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); //测试加锁,非阻塞锁;如果锁现在被别的线程占用则返回非0值,如果没有被占用则返回0;
extern int __pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); //解锁
extern int __pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex); //摧毁释放锁
守护进程
Daemon()程序是一直运行的服务端程序,又称为守护进程。通常在系统后台运行,没有控制终端,不与前台交互。
nochdir:=0将当前目录更改至“/”
noclose:=0将标准输入、标准输出、标准错误重定向至“/dev/null”
#include
int daemon(int nochdir, int noclose);
系统日志syslog
#include
void openlog(const char *ident, int log_options, int facility);
ident通常就写成当前程序的名称以作标记.
log_options 部分选项如下:
1.LOG_CONS 同时写入到控制台 /dev/console。
2.LOG_NDELAY 立即打开日志系统的连接,默认情况下在首次调用syslog() 时才会连接到/dev/log,为了防止后面访问不到/dev/log,比如在openlog()之后调用chroot()。
3.LOG_PERROR 将消息写入到标准错误和系统日志。
4.LOG_PID 在每条消息中加上调用者的进程ID。
facility参数是用来指定记录消息程序的类型。它让指定的配置文件,将以不同的方式来处理来自不同方式的消息。它的值可能为 LOG_KERN、LOG_USER、LOG_MAIL、LOG_DAEMON、LOG_AUTH、LOG_SYSLOG、LOG_LPR、LOG_NEWS、LOG_UUCP、LOG_CRON 或 LOG_AUTHPRIV
#include
void syslog(int priority, const char *format, ...);
syslog为每个事件赋予几个不同的优先级:
LOG_EMERG:紧急情况,需要立即通知技术人员。
LOG_ALERT:应该被立即改正的问题,如系统数据库被破坏,ISP连接丢失。
LOG_CRIT:重要情况,如硬盘错误,备用连接丢失。
LOG_ERR:错误,不是非常紧急,在一定时间内修复即可。
LOG_WARNING:警告信息,不是错误,比如系统磁盘使用了85%等。
LOG_NOTICE:不是错误情况,也不需要立即处理。
LOG_INFO:情报信息,正常的系统消息,比如骚扰报告,带宽数据等,不需要处理。
LOG_DEBUG:包含详细的开发情报的信息,通常只在调试一个程序时使用。
获取时间
struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timep);
struct tm {
int tm_sec; /* seconds */
int tm_min; /* minutes */
int tm_hour; /* hours */
int tm_mday; /* day of the month */
int tm_mon; /* month */
int tm_year; /* year */
int tm_wday; /* day of the week */
int tm_yday; /* day in the year */
int tm_isdst; /* daylight saving time */
};
//int tm_sec 代表目前秒数,正常范围为0-59,但允许至61秒
//int tm_min 代表目前分数,范围0-59
//int tm_hour 从午夜算起的时数,范围为0-23
//int tm_mday 目前月份的日数,范围01-31
//int tm_mon 代表目前月份,从一月算起,范围从0-11
//int tm_year 从1900 年算起至今的年数
//int tm_wday 一星期的日数,从星期一算起,范围为0-6
//int tm_yday 从今年1月1日算起至今的天数,范围为0-365
//int tm_isdst 日光节约时间的旗标
#include
time_t time(time_t *t);
DESCRIPTION
time() returns the time as the number of seconds since the Epoch, 1970-01-01 00:00:00 +0000 (UTC).
//此函数会返回从公元1970年1月1日的UTC时间从0时0分0秒算起到现在所经过的秒数。如果t 并非空指针的话,此函数也会将返回值存到t指针所指的内存。
RETURN VALUE
On success, the value of time in seconds since the Epoch is returned. On error, ((time_t) -1) is returned, and errno is
set appropriately.
ERRORS
EFAULT t points outside your accessible address space.
//成功返回秒数,错误则返回(time_t) -1),错误原因存于errno中
获取文件属性
#include
#include
#include
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
int fstat(int fd, struct stat *buf);
int lstat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* file type and mode */
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
/* Since Linux 2.6, the kernel supports nanosecond
precision for the following timestamp fields.
For the details before Linux 2.6, see NOTES. */
struct timespec st_atim; /* time of last access */
struct timespec st_mtim; /* time of last modification */
struct timespec st_ctim; /* time of last status change */
#define st_atime st_atim.tv_sec /* Backward compatibility */
#define st_mtime st_mtim.tv_sec
#define st_ctime st_ctim.tv_sec
};
服务器
#include
#include /* See NOTES */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define BACKLOG 13
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
#define MSG_STR "Hello Client Welcome to Connect...!"
char cover(char ch) ; //change char to upper
void *thread_work( void *ctx) ; //thread_function
void print_usage(const char *program_name)
{
printf("\n%s -- (2018.11.20)\n", program_name);
printf(" Usage: %s -p [-h ]\n", program_name);
printf(" -p --port the server listen port\n") ;
printf(" -h --help the server file how to use\n");
return ;
}
int main( int argc, char **argv )
{
int listen_fd,client_fd = -1 ;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr ;
struct sockaddr_in cli_addr ;
socklen_t cli_addr_len ;
int opt = -1 ;
int port = 0 ;
pthread_t tid ;
pthread_attr_t thread_attr ;
time_t timep;
struct tm *tim;
int log ; // open server.log to record
char log_name[32] = "thread_server.log" ;
struct stat info_file ; //get file size, if too big, will lseek to SEEK_SET
const char *short_opts = "p:h"; //set option
const struct option long_opts[] = {
{"help", no_argument, NULL, 'h'},
{ "port", required_argument, NULL, 'p'},
{0, 0, 0, 0}
};
while ((opt= getopt_long(argc, argv, short_opts, long_opts,NULL)) != -1)
{
switch (opt)
{
case 'p':
port = atoi(optarg);
break ;
case 'h':
print_usage(argv[0]) ;
return 0;
}
}
if( !port )
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return 0;
}
log = open(log_name, O_RDWR|O_CREAT|O_APPEND, 0666) ;
if(log < 0 )
{
printf("open log_file failure:%s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
return 0 ;
}
if ( daemon(1,1) < 0 ) //set program in backgrund
{
printf("daemon failure: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
if( dup2(log, STDOUT_FILENO) < 0 ) //program running record in "thread_server.log"
{
printf("dup2 failure: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
/* Listen and Bind */
listen_fd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0) ;
if(listen_fd < 0)
{
printf("creat socket failure : %s \n", strerror(errno) ) ;
return -2 ;
}
printf("creat socket suceeful, listen_fd descriptor[%d]\n", listen_fd) ;
memset(&serv_addr, 0, sizeof(serv_addr));
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET ;
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(port) ;
serv_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY) ;
memset(&cli_addr, 0, sizeof(serv_addr));
int reuse = 1 ;
setsockopt(listen_fd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &reuse, sizeof(reuse)); // Reuseaddr
if ( bind(listen_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr) ) < 0 )
{
printf("socket bind failure : %s\n", strerror(errno) ) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
if ( listen(listen_fd ,BACKLOG) < 0 )
{
printf("socket listen failure: %s\n", strerror(errno) ) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
/* Accpect and ask client */
while(1)
{
printf("\n/********************************************************************/\n") ;
localtime(&timep) ;
time(&timep);
tim = localtime(&timep);
printf("Server Start Work, Server port:%d, And Waiting The Client Connect ...\n", port) ;
/* accpect client */
client_fd = accept(listen_fd,(struct sockaddr*) &cli_addr, &cli_addr_len) ;
if(client_fd < 0)
{
printf("accept failure: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
return -3 ;
}
printf("accept succeful, client [%s:%d] \n", inet_ntoa(cli_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(cli_addr.sin_port) ) ;
printf("\n %d年%d月%d日 %d:%d:%d\n", (1900 + tim->tm_year), ( 1 + tim->tm_mon), tim->tm_mday, tim->tm_hour, tim->tm_min, tim->tm_sec);
/* create thread to ask client */
if( pthread_attr_init(&thread_attr) ) //On success, these functions return 0; on error, they return a nonzero error number.
{
printf("pthread_attr_init failure: %s\n", strerror(errno) ) ;
return -4 ;
}
if( pthread_attr_setstacksize( &thread_attr, 120*1024) ) //int pthread_attr_setstackaddr(pthread_attr_t *attr, void *stackaddr);success,functions return 0;
{
printf("pthread_attr_setstacksize failure: %s\n", strerror(errno) ) ;
return -5 ;
}
if( pthread_attr_setdetachstate( &thread_attr, PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED ))
/* int pthread_attr_setdetachstate(pthread_attr_t *attr, int detachstate); detach: PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED, PTHREAD_CREATE_JOINABLE, success return 0; */
{
printf("pthread_attr_setdetachstate failure: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
return -6 ;
}
/* Get log size */
if(stat(log_name, &info_file) < 0 )
{
printf("Stat failed: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
printf("\n################# %s size: %ld Bytes #################\n",log_name, info_file.st_size) ;
if( pthread_create( &tid, &thread_attr, thread_work,(void *)client_fd) ) //create thread
{
printf("pthread_create failure: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
return -7 ;
}
}
cleanup:
close(log) ;
close(listen_fd) ;
close(client_fd) ;
return 0 ;
}
void *thread_work( void *ctx )
{
int client_fd ;
int rv = -1 ;
int i ;
char buf[BUF_SIZE] ;
char wbuf[BUF_SIZE] = "Hello client, Welcome to connect, If you input 'quit' you will exit,If you input get_time will get server time , If you input other will echo upper buf" ;
time_t ticks ;
if( !ctx )
{
printf("Invalid input arguments in %s()\n", __FUNCTION__) ; // _FUNCTION get the function name
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
client_fd = (int)ctx ;
if (write( client_fd, wbuf, strlen(wbuf) ) < 0 )
{
printf("write to client[%d] failure: %s and thread will exit!\n", client_fd, strerror(errno) ) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
while(1)
{
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
rv = read( client_fd, buf, sizeof(buf) ) ;
if(rv < 0 )
{
printf("read to client[%d] failure: %s and thread will exit!\n", client_fd, strerror(errno) ) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
if( rv == 0 )
{
printf("client[%d] disconnect and thread will exit!\n", client_fd) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
printf("read %d byte from client[%d]: %s\n", rv, client_fd, buf) ;
fflush(stdout) ;
bzero(wbuf,sizeof(wbuf)) ;
if( strcmp(buf, "quit") == 0)
{
if (write( client_fd, "You will exit,Good bye!", strlen("You will exit") ) < 0 )
{
printf("write to client[%d] failure: %s and thread will exit!\n", client_fd, strerror(errno) ) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
sleep(1) ; //client send quit close(client_fd) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
else if( strcmp(buf, "get_time") == 0) //send time to client
{
ticks = time(NULL) ;
snprintf( wbuf, sizeof(wbuf), "%.24s",ctime(&ticks)) ;
if(write( client_fd, wbuf, strlen(wbuf)) <0 )
{
printf("write to client[%d] failure: %s and thread will exit!\n", client_fd, strerror(errno)) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
}
else //echo buf to client
{
for(i=0 ; i < rv; i++ )
{
buf[i] = cover(buf[i]) ;
}
if (write( client_fd, buf, strlen(buf) ) < 0 )
{
printf("write to client[%d] failure: %s and thread will exit!\n", client_fd, strerror(errno) ) ;
close(client_fd) ;
pthread_exit(NULL) ;
}
}
}
}
char cover(char ch)
{
if(ch>'z'||ch<'a')
{
return ch ;
}
else
return (ch - ('a' - 'A') );
}
客户端
#include
#include /* See NOTES */
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define BUF_SIZE 1024
void print_usage(const char *program_name)
{
printf("\n%s -- 1.0.0(2018.11.20)\n", program_name);
printf(" Usage:(1) %s -i -p [-h ]\n", program_name);
printf(" (2) %s -n -p [-h ]\n", program_name);
printf(" -i --ip the server ip_address you want to connect\n") ;
printf(" -p --port the server listen port you want to connect\n") ;
printf(" -n --hostname the server hostname you want to connect\n") ;
printf(" -h --help the client file how to use\n");
return ;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
int conn_fd ;
struct sockaddr_in serv_addr ;
char buf[BUF_SIZE] ;
char send_buf[32] ;
int rv = -1 ;
int opt = -1 ;
int port = 0 ;
char* ip = NULL ;
char* hostname = NULL;
struct hostent *hostnp;
const char *short_opts = "n:i:p:h";
const struct option long_opts[] = {
{"help", no_argument, NULL, 'h'},
{"hostname", required_argument,NULL,'n'},
{"port", required_argument, NULL, 'p'},
{"ip", required_argument, NULL, 'i'},
{0, 0, 0, 0},
};
while ((opt= getopt_long(argc, argv, short_opts, long_opts,NULL)) != -1)
{
switch (opt)
{
case 'p':
port = atoi(optarg);
break ;
case 'i':
ip = optarg ;
break ;
case 'n':
hostname = optarg ;
break ;
case 'h':
print_usage(argv[0]) ;
return 0;
}
}
if( ( ( !port) || (!hostname) ) && ( (!ip) || (!port) ) )
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return 0;
}
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)) ;
if ( hostname )
{
if( (hostnp = gethostbyname(hostname) ) == NULL )
{
printf("get host by name failure: %s\n", strerror(h_errno)) ;
return 0 ;
}
printf("hostname %s\n", hostnp->h_name);
ip = inet_ntoa( * (struct in_addr *)hostnp->h_addr );
printf("addr:%s\n",ip) ;
}
conn_fd = socket( AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0 ) ;
if(conn_fd < 0)
{
printf("creat socket failure : %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
return -1 ;
}
printf("socket suceeful,connect file descriptor[%d]\n" ,conn_fd) ;
memset(&serv_addr, 0, sizeof(serv_addr)) ;
serv_addr.sin_port = htons(port) ;
serv_addr.sin_family = AF_INET ;
inet_aton(ip, &serv_addr.sin_addr);
if( connect(conn_fd, (struct sockaddr*)&serv_addr, sizeof(serv_addr)) < 0 )
{
printf("connect failure[%s:%d] : %s\n", inet_ntoa(serv_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(serv_addr.sin_port), strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
printf("connect server[%s:%d] succeful!\n", inet_ntoa(serv_addr.sin_addr), ntohs(serv_addr.sin_port)) ;
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)) ;
rv = read(conn_fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) ;
if(rv < 0)
{
printf("read from server failed: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
if(rv == 0)
{
printf("disconnect with server!\n") ;
}
printf("Server Usage: %s\n", buf) ;
while(1)
{
scanf("%s", send_buf) ;
if(write(conn_fd, send_buf, strlen(send_buf)) < 0 ) {
printf("Write to server failed: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)) ;
rv = read(conn_fd, buf, sizeof(buf)) ;
if(rv < 0)
{
printf("read from server failed: %s\n", strerror(errno)) ;
goto cleanup ;
}
if(rv == 0)
{
printf("disconnect with server!\n") ;
goto cleanup ;
}
printf("read %d byte from server:' %s'\n", rv, buf) ;
if( strcmp(send_buf, "quit") == 0)
{
break ;
}
}
printf("close conn_fd[%d],and client exit!\n", conn_fd) ;
cleanup:
close(conn_fd) ;
return 0 ;
}