《Spring源码深度解析》---第2章(容器的基本实现)
本文学习《Spring源码深度解析》(郝佳编著),实战笔记。
2.1容器的基本用法
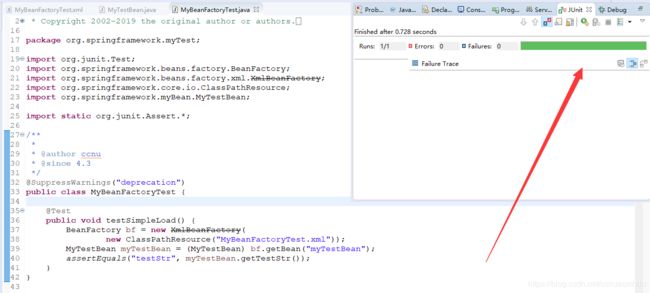
首先笔者导入了spring-beans工程(导入源码方法点击我),在此工程下,结合书中的示例,如下创建文件,验证书中所写!
MyTestBean.java
/*
* Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.myBean;
/**
*
* @author ccnu
* @since 4.3
*/
public class MyTestBean {
private String testStr = "testStr";
public String getTestStr() {
return testStr;
}
public void setTestStr(String testStr) {
this.testStr = testStr;
}
}
MyBeanFactoryTest.xml
MyBeanFactoryTest.java
/*
* Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.myTest;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.XmlBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.myBean.MyTestBean;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
*
* @author ccnu
* @since 4.3
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class MyBeanFactoryTest {
@Test
public void testSimpleLoad() {
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(
new ClassPathResource("MyBeanFactoryTest.xml"));
MyTestBean myTestBean = (MyTestBean) bf.getBean("myTestBean");
assertEquals("testStr", myTestBean.getTestStr());
}
}
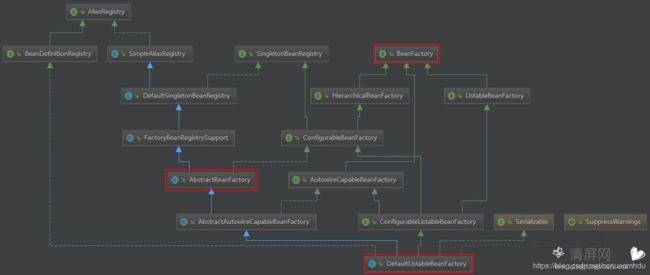
2.4.2核心类介绍
DefaultListableBeanFactory
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory
右键-Open Type Hierarchy,如下:
![]()

据此可以用插件或者直接用power designer等工具画出UML类图。为了节省时间,笔者直接用了百度图片(图片来源链接):
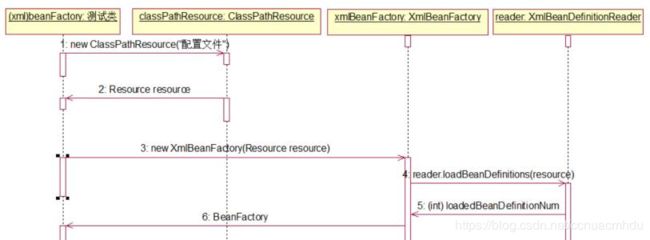
2.5容器的基础XmlBeanFactory
深入分析下面代码的实现:
BeanFactory bf = new XmlBeanFactory(
new ClassPathResource("MyBeanFactoryTest.xml"));
XmlBeanFactory的初始化时序图如下(图片链接地址):
2.5.1配置文件封装
package org.springframework.core.io;
public interface Resource extends InputStreamSource {
boolean exists();
boolean isReadable();
boolean isOpen();
URL getURL() throws IOException;
URI getURI() throws IOException;
File getFile() throws IOException;
long contentLength() throws IOException;
long lastModified() throws IOException;
Resource createRelative(String relativePath) throws IOException;
String getFilename();
String getDescription();
}
InputStreamSource .java
package org.springframework.core.io;
public interface InputStreamSource {
InputStream getInputStream() throws IOException;
}

ClassPathResource类实现了Resource接口,实际例子中用到的就是一个构造方法:

ClassPathResource.java实现的getInputStream方法:

FileSystemResource.java实现的getInputStream方法:

其他类似。
package org.springframework.beans.factory.xml;
@Deprecated
@SuppressWarnings({"serial", "all"})
public class XmlBeanFactory extends DefaultListableBeanFactory {
private final XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(this);
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
this(resource, null);
}
public XmlBeanFactory(Resource resource, BeanFactory parentBeanFactory) throws BeansException {
super(parentBeanFactory);
this.reader.loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
}
}
/**
* Create a new AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.
*/
public AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory() {
super();
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanNameAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanFactoryAware.class);
ignoreDependencyInterface(BeanClassLoaderAware.class);
}
2.5.2
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
跟踪到上面的代码,上面这个方法有两行是核心:
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource); //加载XML文件,获取Document
return registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource); //根据返回的Document,注册Bean信息
追踪doLoadDocument方法如下:
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
最终参数中的getValidationModeForResource方法:
protected int getValidationModeForResource(Resource resource) {
int validationModeToUse = getValidationMode();
// 人为指定了,就用人为指定的约束
if (validationModeToUse != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return validationModeToUse;
}
int detectedMode = detectValidationMode(resource);//未指定,就调这个方法
if (detectedMode != VALIDATION_AUTO) {
return detectedMode;
}
// Hmm, we didn't get a clear indication... Let's assume XSD,
// since apparently no DTD declaration has been found up until
// detection stopped (before finding the document's root tag).
return VALIDATION_XSD;
}
上面这个方法是获取对XML文件的约束模式(XSD、DTD)。下面这个方法就是检查到底用了DTD约束,还是用了XSD约束!方法就是一行一行扫描XML文档,如果包含DOCTYPE就表明是DTD约束,否则就认为是XSD约束。
public int detectValidationMode(InputStream inputStream) throws IOException {
// Peek into the file to look for DOCTYPE.
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
try {
boolean isDtdValidated = false;
String content;
while ((content = reader.readLine()) != null) {
content = consumeCommentTokens(content);
if (this.inComment || !StringUtils.hasText(content)) {
continue;
}
if (hasDoctype(content)) {//如果包含DOCTYPE就是DTD约束
isDtdValidated = true;
break;
}
if (hasOpeningTag(content)) {
// End of meaningful data...
break;
}
}
return (isDtdValidated ? VALIDATION_DTD : VALIDATION_XSD);
}
catch (CharConversionException ex) {
// Choked on some character encoding...
// Leave the decision up to the caller.
return VALIDATION_AUTO;
}
finally {
reader.close();
}
}

关于XML文件的验证(约束)模式,就两种,分别是XSD和DTD,笔者观察到了一个明显的区别就是用DTD约束的XML会有DOCTYPE说明,而XSD约束的XML没有。
DTD约束的XML头:
XSD约束的XML头:
2.7获取Document
追踪代码到registerBeanDefinitions方法:
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
继续追踪到registerBeanDefinitions方法:
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
logger.debug("Loading bean definitions");
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(root);
}
继续追踪到doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法:
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root); //这个方法是空的,受protected修饰,供子类继承覆盖,模板方法模式
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root); //这个方法是空的,受protected修饰,供子类继承覆盖,模板方法模式
this.delegate = parent;
}
继续追踪到parseBeanDefinitions方法:
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);//默认标签的解析
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);//自定义标签的解析
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}