Geant 4创建TCP客户端,自定义宏命令,输出探测器能量
我在Geant 4软件中主要完成三大功能需求:构建自己所需要的探测器模型;建立TCP客户端;自定义宏命令来输出指定探测器能量沉积。
Geant 4中的蒙特卡罗方法是指一个粒子发射出去之后,会和周围的环境发生反应,一直到发射出去的粒子和它产生的次级粒子都完全发生反应并且泯灭之后,才会发射下面一个粒子,两个事件的发射粒子之间不会发生任何反应,并且Geant 4软件本身不做模拟计算,所有产生的数据都是通过对保存的实验数据进行随机抽样得到的,比如本论文中使用的物理模型为粒子散射到探测器中产生出能量能量沉积,发射一种特定的散射粒子,在相同发射初始能量下,探测器中每个event沉积能量的数据重复率非常高。
-
探测器构建
正方体的探测器边长为15毫米,10乘10堆叠放置100个探测器,如图3.2所示,展示出探测器的堆叠形状,150代表10个探测器堆叠的总长度为150毫米,15代表一个探测器的边长为15毫米,省略号代表其余没有画出的探测器。对每个探测器在G4中进行编号,右上方为第100个,并且从上向下、从右到左开始累减依次编号。
// Absorber
//
G4Box*
sAbsor = new G4Box("Absorber", //name
world_hx, world_hy, world_hz); //dimensions
fLAbsor = new G4LogicalVolume(sAbsor, //shape
fAbsorMaterial, //material
"SensitiveDetector"); //name
int Absorber_number = 100;
for(int i=1; i<11; i++)
{
for(int j=1; j<11; j++) // x axis
{
std::string s1;
std::string s2; // location parameter
s1 = std ::to_string(10-i);
s2 = std ::to_string(10-j);
new G4PVPlacement(0, //no rotation
//100 detector location
G4ThreeVector(2*(10-i)*world_hx ,2*(10-j)*world_hx , 0),
fLAbsor, //logical volume
std::string("Det") + "_L" + s1 + "_R" + s2, //name
fLContain, //mother volume
false, //no boolean operation
Absorber_number); //copy number
Absorber_number--;
}
}
PrintParameters();-
TCP客户端
建立一个TCP客户端通过TCP通道发送数据,这样就很方便的把G4产生的数据发送到其他应用中进行处理,我是发送到上位机软件中显示图像。
//mao add TCP protocol 2
struct sockaddr_in server_addr2;
bzero(&server_addr2, sizeof(server_addr2));
server_addr2.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr2.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr("172.20.157.166");
server_addr2.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT_Qt);
int Qt_sfd;
Qt_sfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, IPPROTO_TCP);
if (Qt_sfd < 0)
{
G4cout << "socket error\n";
exit(0);
}
if (connect(Qt_sfd, (struct sockaddr*) & server_addr2, sizeof(server_addr2)) < 0)
{
G4cout << "Can Not Connect To "
<< "172.20.157.166"
<< G4endl;
exit(1);
}
//open file reading data
std::fstream event_file1;
event_file1.open(STEPPING_FILE, std::ios::in);
if (!event_file1.is_open())
{
G4cout << "the file was not opened"
<< G4endl;
exit(1);
}
std::vector floats;
char Qt_data[500][3] = { '\0' }; //Fill in all blank characters
std::string line;
//read float data
float max_number = 0;
while (std::getline(event_file1, line))
{
std::string strr1 = line;
std::string strr2;
std::vector array1;
//Starting at the zero bit, the length is 4
strr2 = strr1.substr(0, 4);
std::istringstream iss(line);
//Save the maximum value
float val;
iss >> val;
if (val > max_number)
{
max_number = val;
}
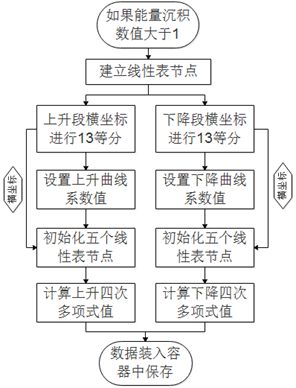
if (val > 2)//Numerical fill algorithm for values greater than 2
{
floats.push_back(0.0);
array1 = fix_data(val); //Numerical filling algorithm
for(G4int jj=0; jj < (int)array1.size(); jj++)
{
floats.push_back(array1[jj]);
}
}
else
{
G4cout << "vector floats = "
<< val
<< G4endl;
floats.push_back(val);
}
}
// close and delete file
//需要对QT传输的数据进行重新修改,不能直接传输字节数据
event_file1.close();
for (int ff = 0; ff < (int)floats.size()+1; ff++)
{
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int num3 = 0;
float Qt_number = 0.0;
if(ff==0) //0 data processed separately
{
//Convert int to ASCII
//TCP transmission of ASCII code data is very easy to handle at the receiving end
Qt_number = (int)floats.size();
num1 = Qt_number / 100;
Qt_data[ff][0] = num1 + '0';
num2 = (Qt_number - num1 * 100) / 10;
Qt_data[ff][1] = num2 + '0';
num3 = (Qt_number - num1 * 100 - num2 * 10) / 1;
Qt_data[ff][2] = num3 + '0';
}
else
{
Qt_number = floats[ff];
num1 = Qt_number / 1;
Qt_data[ff][0] = num1 + '0';
num2 = (Qt_number - num1 * 1.0) / 0.1;
Qt_data[ff][1] = num2 + '0';
num3 = (Qt_number - num1 * 1.0 - num2 * 0.1) / 0.01;
Qt_data[ff][2] = num3 + '0';
}
}
for(int uu=0; uu<(int)floats.size()+1; uu++)
{
G4cout << "Qt_data[uu][] = "
<< Qt_data[uu][0]
<< Qt_data[uu][1]
<< Qt_data[uu][2]
<
//ps Represents an array of coefficient terms
//es Represents an array of exponents
//n Represents the number of the unary polynomials
void EventAction::InitList(SqList & list1,G4double ps[],G4int es[],G4int n)
{
for(int i=0;i EventAction::fix_data(float x)
{
float x_mid1 = 0;
float y_mid1 = 0;
std::vector array1;
for(int i=0; i<13; i++)
{
x_mid1 = 90 * i / 12 + 39;
y_mid1 = x * up_equ(x_mid1);
array1.push_back(y_mid1);
}
for(int j=0;j<13;j++)
{
x_mid1 = 158 * j / 12 + 129;
y_mid1 = x * down_equ(x_mid1);
array1.push_back(y_mid1);
}
return array1;
}
-
自定义宏命令
为了可以在mac脚本文件中通过宏命令(/testhadr/stepping/seDSN 55)选择Geant 4中特定探测器输出能量沉积。先建立SteppingActionMessenger类继承于SteppingAction类并且初始化,因为探测器的序数为整数,所以把fsteppingCmd4设置为整数命令的构造函数,设置宏命令的名字为detector number范围为大于零。SetNewValue函数中判断是否为fsteppingCmd4命令,如果是就对seDSN宏命令传入的参数通过SetADetectorNumber函数对探测器序号赋值。当总体程序执行到SteppingAction类的时候,通过SetADetectorNumber函数获取探测器序号筛选出指定探测器能量沉积保存到文件中。
SteppingActionMessenger.hh
#ifndef SteppingActionMessenger_h
#define SteppingActionMessenger_h 1
#include "globals.hh"
#include "G4UImessenger.hh"
class G4UIcmdWithAnInteger;
class G4UIdirectory;
class SteppingAction;
//....oooOO0OOooo........oooOO0OOooo........oooOO0OOooo........oooOO0OOooo......
class SteppingActionMessenger : public G4UImessenger
{
public:
SteppingActionMessenger(SteppingAction*);
~SteppingActionMessenger();
//其实完全可以不是纯虚函数,毕竟是自己设置接口
virtual void SetNewValue(G4UIcommand*, G4String);
private:
SteppingAction* fstepping;
using G4UImessenger::SetNewValue;
G4UIdirectory* fTesthadrDir;
G4UIdirectory* fstepDir;
G4UIcmdWithAnInteger* fsteppingCmd4;
};
//....oooOO0OOooo........oooOO0OOooo........oooOO0OOooo........oooOO0OOooo......
#endif
SteppingActionMessenger.cc
#include "G4UIcmdWithAnInteger.hh"
#include "G4UIcommand.hh"
#include "G4UIparameter.hh"
#include "SteppingActionMessenger.hh"
#include "SteppingAction.hh"
SteppingActionMessenger::SteppingActionMessenger(SteppingAction* stepping)
:fstepping(stepping)
{
fTesthadrDir = new G4UIdirectory("/testhadr/");
fTesthadrDir->SetGuidance("commands specific to this example");
G4bool broadcast = false;
fstepDir = new G4UIdirectory("/testhadr/stepping/", broadcast);
fstepDir->SetGuidance("steping action commands");
fsteppingCmd4 = new G4UIcmdWithAnInteger("/testhadr/stepping/seDSN", this);
fsteppingCmd4->SetGuidance("Select detector sequence number");
fsteppingCmd4->SetParameterName("number", false);
fsteppingCmd4->SetRange("number>0");
fsteppingCmd4->AvailableForStates(G4State_PreInit, G4State_Idle);
fsteppingCmd4->SetToBeBroadcasted(false);
}
SteppingActionMessenger::~SteppingActionMessenger()
{
delete fsteppingCmd4;
delete fTesthadrDir;
delete fstepDir;
}
void SteppingActionMessenger::SetNewValue(G4UIcommand* command, G4String MyValue)
{
if (command == fsteppingCmd4)
{
fstepping->SetADetectorNumber(fsteppingCmd4->GetNewIntValue(MyValue));
}
}
-
输出探测器能量沉积
输出探测器内的粒子能量沉积到文件中。
//Select a specific detector serial number
void SteppingAction::SetADetectorNumber(G4int value)
{
select_number = value;
}
void SteppingAction::UserSteppingAction(const G4Step* aStep)
{
//前面部分代码省略
auto touchable = aStep -> GetPreStepPoint() -> GetTouchable();
auto physical = touchable -> GetVolume();
Stepping_detector_Number = physical-> GetCopyNo();
auto detector_name = physical->GetName();
fEventAction->detector_Number=Stepping_detector_Number;
fEventAction->AddEdep(aStepEdep);
G4double edepStep = aStep->GetTotalEnergyDeposit();
if (edepStep <= 0.) return;
fEventAction->AddEdep(edepStep);
Tstop = clock();//Record end time
std::ofstream step_file1;
step_file1.open(STEPPING_FILE, std::ios::app);
if(Stepping_detector_Number == select_number) //select detector number
{
if (step_file1.is_open())
{
step_file1
//Set the numerical accuracy of the output energy deposition
<< setiosflags(std::ios::fixed) << setiosflags(std::ios::right)
<< std::setprecision(4)//4 digit precision
<< aStepEdep
<< G4endl;
}
}
step_file1.close();
}
-
acknowledgement
以后在工作中也不会再接触G4了,这是自己毕业设计的一部分,希望给你提供帮助,减少重复工作的时间!
非常感谢中科大的潘子文和Geant 4(564893516)群中的各位朋友提供的帮助!
