ENVI学习之0001
一、ENVI是什么
ENVI是一个完整的遥感图像处理平台,其软件处理技术覆盖了图像数据的输入、输出、定标、图像增强、纠正、正射校正、镶嵌、数据融合以及各种变换、信息提取、图像分类、与GIS的整合、DEM及三维信息提取、雷达数据处理、三维立体显示分析,提供了专业可靠的波谱分析工具和高光谱分析工具。
二、功能模块(ENVI有什么)
ENVI是以模块化的方式组成的,可扩充模块包括:
①大气校正模块(Atmospheric Correction)-----校正由大气气溶胶等引起的散射和由于漫反射引起的邻域效应,消除大气和光照等因素对地物反射的影响,获得地物反射率和辐射率、地表温度等真实物理模型参数,同时可以进行卷云和不透明云层的分类。
②立体像对高程提取模块(DEM Extraction)-----可以从卫星图像或航空图像的立体像对中快速获得DEM数据,同时还可以交互量测特征地物的高度或者收集3D特征并导出为3D Shapefile格式文件。
③ 面向对象的空间特征提取模块(ENVI EX)-----根据图像空间和光谱特征,从高分辨率全色或者多光谱数据中提取特征信息。包含了一个人性化的操作平台、常用图像处理工具、流程化图像分析工具、面向对象特征提取工具(FX)等。
④ 正射校正扩展模块(Orthorectification)-----提供基于传感器物理模型的图像正射校正功能,一次可以完成大区域、若干景图像和多传感器的正射校正,并能以镶嵌结果的方式输出,提供接边线、颜色平衡等工具。
⑤ 高级雷达处理扩展模块(Sarscape)-----提供完整的雷达处理功能,包括基本SAR数据的数据导入、多视、几何校正、辐射校正、去燥、特征提取等一系列基本处理功能;调焦模块扩展了基础模块的调焦功能,采用经过优化的调焦算法,能够充分利用处理器的性能实现数据快速处理;提供基于Gamma/Gaussian分布式模型的滤波核,能够最大限度地去除斑点噪声,同时保留雷达图像的纹理属性和空间分辨率信息;可生成干涉图像、相干图像、地面断层图。主要功能包括:SLC像对交叠判断、多普勒滤波、脉冲调节、干涉图像生成、单列干涉图生成等;对极化SAR和极化干涉SAR数据的处理;永久散射体模块能用来确定特征地物在地面上产生的mm级的位移。
⑥ NITF图像处理扩展模块(Certified NITF)---读写、转化、显示标准NITF格式文件。
三、工程化应用(ENVI能做什么)
① 读取几乎任何图像类型和格式
ENVI支持各种类型航空和航天传感器的图像,包括全色、多光谱、高光谱、雷达、热红外、地形数据、GPS数据、激光雷达等。ENVI可以读取超过80种的数据格式,包括HDF、Geodatabase、GeoTIFF和JITC认证的NITF等格式。
②准备图像
ENVI提供自动预处理工具,可以快速、轻松地预处理图像,以便进行查看浏览或其它分析。通过ENVI,可以对图像进行以下处理:
:几何/正射校正
:图像(自动)配准
:图像定标
:大气校正
:创建矢量叠加
:确定感兴趣区域(ROI)
:创建数字高程模型(DEM)
:图像融合、掩膜和镶嵌
:调整大小、旋转、数据类型转换
③ 探测图像
④分析图像
1)数据分析工具
2)光谱分析工具
光谱分析通过像素在不同波长范围上的反应,来获取有关物质的信息。
: 监督和非监督方法进行图像分类
:使用强大的光谱库识别光谱特征
:检测和识别目标
:识别感兴趣的特征
:对感兴趣物质的分析和制图
:执行像素级和亚像素级的分析
:使用分类后处理工具完善分类结果
:使用植被分析工具计算森林健康度
⑤自定义遥感图像应用
ENVI建立于一个强大的开发语言---IDL之上。IDL允许对其特性和功能进行扩展或自定义,以符合用户的具体要求。
四、ENVI可利用资源
①ENVI自带内容丰富的帮助文件以及软件操作手册;
②www.ittvis.com
五、ENVI文件存储格式
① 文件系统和存储
ENVI栅格文件格式:ENVI使用的是通用栅格数据格式,包含一个简单的二进制文件(a simple flat binary)和一个相关的ASCII(文本)的头文件;
:头文件
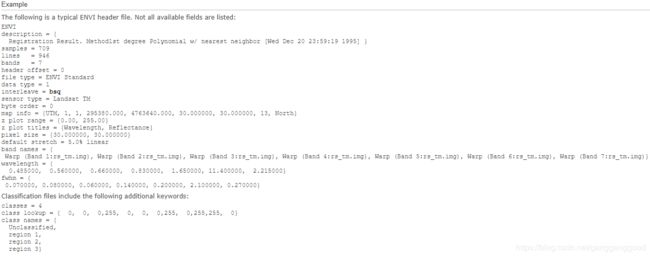
The ENVI Header Format
The following table lists header fields in alphabetical order. Red text indicates a required field for ENVI-format files. See Example for an example header file.
| Field |
Description |
| acquisition time |
Data acquisition time string that conforms to the ISO-8601 standard. The string can be in any of the following formats: YYYY-MM-DD YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS.DZ YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS:Dooo:mm Where:
|
| band names |
The names of image bands. |
| bands |
The number of bands per image file. |
| bbl |
Lists the bad band multiplier values of each band in an image, typically 0 for bad bands and 1 for good bands. |
| byte order |
The order of the bytes in integer, long integer, 64-bit integer, unsigned 64-bit integer, floating point, double precision, and complex data types. Use one of the following:
|
| class lookup |
Lists class colors using RGB color definitions for classification files. For example, black is |
| class names |
Lists class names for classification files. |
| classes |
Defines the number of classes, including unclassified regions, for classification files. |
| cloud cover |
Percentage of cloud cover within the raster. |
| complex function |
Specifies the values to calculate from a complex image and to use when displaying the image, calculating statistics for the image, or writing the image to a new file. Values include |
| coordinate system string |
When you save a georeferenced file to ENVI raster format, ENVI adds a A geographic coordinate system (for example, Geographic Lat/Lon) string contains the word coordinate system string = GEOGCS["GCS_WGS_1984", DATUM["D_WGS_1984", SPHEROID["WGS_1984",6378137.0,298.257223563]], PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0], UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]] A projected coordinate system string contains the word coordinate system string = PROJCS["WGS_1984_South_Georgia_Lambert", GEOGCS["GCS_WGS_1984", DATUM["D_WGS_1984", SPHEROID["WGS_1984",6378137.0,298.257223563]], PRIMEM["Greenwich",0.0], UNIT["Degree",0.0174532925199433]], PROJECTION["Lambert_Conformal_Conic"], PARAMETER["False_Easting",0.0], PARAMETER["False_Northing",0.0], PARAMETER["Central_Meridian",-37.0], PARAMETER["Standard_Parallel_1",-54.0], PARAMETER["Standard_Parallel_2",-54.75], PARAMETER["Latitude_Of_Origin",-55.0], UNIT["Meter",1.0]] See Coordinate System Strings for more information. |
| data gain values |
Gain values for each band. Units are W/(m2 * µm * sr). |
| data ignore value |
Pixel values that should be ignored in image processing. |
| data offset values |
Offset values for each band. |
| data reflectance gain values |
An array of reflectance gain values. With Landsat-8 files, the reflectance gains have been scaled by the sine of the sun elevation, as follows: data reflectance gain values = REFLECTANCE_MULT_BAND_1/sin(sun elevation) |
| data reflectance offset values |
An array of reflectance offset values. With Landsat-8 files, the reflectance offsets have been scaled by the sine of the sun elevation, as follows: data reflectance offset values = REFLECTANCE_ADD_BAND_1/sin(sun elevation) |
| data type |
The type of data representation:
|
| default bands |
Indicates which band numbers to automatically load into the Data Manager Greyscale or R, G, and B fields every time the file is opened. By default, a new image is automatically loaded when a file that has default bands defined in its header is opened. If only one band number is used, then ENVI loads a greyscale image. |
| default stretch |
Determines what type of stretch (% linear, linear range, Gaussian, equalization, square root) to use when ENVI displays the image. |
| dem band |
Index (starting at 1) of a selected DEM band associated with the image. The dem band is not written if the DEM file contains a single band, or if the first band of an image was chosen. In these cases, the dem band value defaults to 0. |
| dem file |
Path and filename of a DEM associated with the image. |
| description |
A string describing the image or the processing performed. |
| file type |
The ENVI-defined file type, such as a certain data format and processing result. The available file types are listed in the |
| fwhm |
Lists full-width-half-maximum (FWHM) values of each band in an image. Units should be the same as those used for wavelength and set in the wavelength units parameter. |
| geo points |
Geographic corners for non-georeferenced files. You can enter between one and four pixel locations and their corresponding latitudes and longitudes. Following is an example: geo points = { 1.0000, 1.0000, 32.89380137, -117.07201460, 1002.0000, 1.0000, 32.87364744, -116.95855862, 1.0000, 1002.0000, 32.80628336, -117.09960891, 1002.0000, 1002.0000, 32.78615422, -116.98625969} |
| header offset |
The number of bytes of embedded header information present in the file. ENVI skips these bytes when reading the file. See Row Offsets for more information. The default value is 0 bytes. |
| interleave |
Refers to whether the data interleave is BSQ, BIL, or BIP. |
| lines |
The number of lines per image for each band. |
| map info |
Lists geographic information in the following order:
See Enter Map Information for Georeferenced Files for further details. |
| pixel size |
Indicates x and y pixel size in meters for non-georeferenced files. |
| product type |
Indicates the product type. For WorldView and QuickBird products, valid values include:
For NPP VIIRS products, valid values include:
|
| projection info |
If you defined a custom projection in ENVI Classic, this field contains that map information. A |
| read procedures |
Spatial and spectral read routines that define custom file readers. |
| reflectance scale factor |
The value that, when divided into your data, would scale it from 0-1 reflectance. For example, if the value of 10,000 in your data represents a reflectance value of 1.0, enter a reflectance scale factor of 10,000. |
| rpc info |
Lists rational polynomial coefficient (RPC) geolocation information for files that have RPC reference information instead of a standard map projection. |
| samples |
The number of samples (pixels) per image line for each band. |
| security tag |
A string with security information inherited from formats that typically contain security classification levels (such as NITF). |
| sensor type |
Instrument types, such as Landsat TM, SPOT, RADARSAT, and so on. The available sensor types are listed in the |
| solar irradiance |
Top of the atmosphere solar irradiance per band. Units are W/(m2 * µm). |
| spectra names |
A comma-separated list of spectra names enclosed in {curly brackets}; for spectral library files only. |
| sun azimuth |
Angle of the sun (in degrees) from due north in a clockwise direction. |
| sun elevation |
Angle of the sun (in degrees) above the horizon. |
| wavelength |
Lists the center wavelength values of each band in an image. Units should be the same as those used for the |
| wavelength units |
Text string indicating the wavelength units. ENVI accepts the following strings: Micrometers um Nanometers nm Millimeters mm Centimeters cm Meters m Wavenumber Angstroms GHz MHz Index Unknown |
| x start |
Defines the image coordinates for the upper-left pixel in the image. Images that are spatial subsets of larger images often use an image coordinate system that references the parent (or larger) image so that you can link and dynamically overlay the two images. The default values for the upper-left pixel are (0,0). The reference (tie point) pixels in the Changing these values does not affect the way ENVI reads the image data from the file. |
| z plot average |
The number of pixels in the x and y directions to average for Z plots. |
| z plot range |
The default minimum and maximum values for Z plots. |
| z plot titles |
The x and y axis titles for Z plots. |
: 数据文件
通用栅格数据都会存储为二进制的字节流,通常它将以BSQ(band sequential,按波段顺序存储)、BIP(band interleaved by pixel,按波段像元交叉存储)或者BIL(band interleaved by line,按波段行交叉存储)的方式进行存储。
BSQ
BSQ是最简单的存储格式,提供了最佳的空间处理能力。它先将图像同一波段的数据逐行存储下来,再以相同的方式存储下一波段的数据。如果要获取图像单个波普波段的空间点(X,Y)的信息,那么采用BSQ方式存储是最佳的选择。
BIP
BIP格式提供了最佳的波谱处理能力。以BIP格式存储的图像,将按顺序存储所有波段的第一个像素,接着是第二个像素的所有波段,然后是第三个像素的所有波段,等等,交叉存取直到所有像素都存完为止。这种格式为图像数据波谱(Z)的存取提供了最佳的性能。
BIL
以BIL格式存储的图像,将先存储第一个波段的第一行,接着是第二个波段的第一行,然后是第三个波段的第一行,交叉存取直到所有波段都存储完为止。每个波段随后的行都将按照类似的方式交叉存储。BIL是介于空间处理和波谱处理之间的一种折中的存储格式,也是大多数ENVI处理操作中所推荐使用的文件格式。
六、ENVI主菜单命令及其功能
七、常见卫星数据格式