SpringBoot使用Redis缓存 + @Cacheable, @CachePut, @CacheEvict注解使用
目录
SpringBoot使用Redis缓存
Spring缓存注解@Cache使用
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict 注释介绍
SpringBoot使用Redis缓存 - gdpuzxs - 博客园
https://www.cnblogs.com/gdpuzxs/p/7222309.html
SpringBoot使用Redis缓存
(1)pom.xml引入jar包,如下:
(古月: 使用spring-boot-starter-data-redis库可以, 笔者猜测使用spring-data-redis库也是可以, 查代码发现spring-boot-starter-data-redis库实际上也是引用了spring-data-redis库, 有点starter系列的有点脚手架的概念)
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-redis
(2)修改项目启动类,增加注解@EnableCaching,开启缓存功能,如下:
![]()
package springboot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
@EnableCaching
public class SpringbootApplication{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}![]()
(3)application.properties中配置Redis连接信息,如下:
![]()
# Redis数据库索引(默认为0)
spring.redis.database=0
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=172.31.19.222
# Redis服务器连接端口
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=
# 连接池最大连接数(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-active=8
# 连接池最大阻塞等待时间(使用负值表示没有限制)
spring.redis.pool.max-wait=-1
# 连接池中的最大空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.max-idle=8
# 连接池中的最小空闲连接
spring.redis.pool.min-idle=0
# 连接超时时间(毫秒)
spring.redis.timeout=0![]()
(4)新建Redis缓存配置类RedisConfig,如下:
![]()
package springboot.config;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.cache.CacheManager;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachingConfigurerSupport;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.StringRedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
/**
* Redis缓存配置类
* @author szekinwin
*
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisConfig extends CachingConfigurerSupport{
@Value("${spring.redis.host}")
private String host;
@Value("${spring.redis.port}")
private int port;
@Value("${spring.redis.timeout}")
private int timeout;
//自定义缓存key生成策略
// @Bean
// public KeyGenerator keyGenerator() {
// return new KeyGenerator(){
// @Override
// public Object generate(Object target, java.lang.reflect.Method method, Object... params) {
// StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
// sb.append(target.getClass().getName());
// sb.append(method.getName());
// for(Object obj:params){
// sb.append(obj.toString());
// }
// return sb.toString();
// }
// };
// }
//缓存管理器
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(@SuppressWarnings("rawtypes") RedisTemplate redisTemplate) {
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = new RedisCacheManager(redisTemplate);
//设置缓存过期时间
cacheManager.setDefaultExpiration(10000);
return cacheManager;
}
@Bean
public RedisTemplate redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
StringRedisTemplate template = new StringRedisTemplate(factory);
setSerializer(template);//设置序列化工具
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
private void setSerializer(StringRedisTemplate template){
@SuppressWarnings({ "rawtypes", "unchecked" })
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
}
} ![]()
(5)新建UserMapper,如下:
![]()
package springboot.dao;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Delete;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Insert;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Param;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Update;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheConfig;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import springboot.domain.User;
@Mapper
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "users")
public interface UserMapper {
@Insert("insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
int addUser(@Param("name")String name,@Param("age")String age);
@Select("select * from user where id =#{id}")
@Cacheable(key ="#p0")
User findById(@Param("id") String id);
@CachePut(key = "#p0")
@Update("update user set name=#{name} where id=#{id}")
void updataById(@Param("id")String id,@Param("name")String name);
//如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存
@CacheEvict(key ="#p0",allEntries=true)
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}")
void deleteById(@Param("id")String id);
}![]()
@Cacheable将查询结果缓存到redis中,(key="#p0")指定传入的第一个参数作为redis的key。
@CachePut,指定key,将更新的结果同步到redis中
@CacheEvict,指定key,删除缓存数据,allEntries=true,方法调用后将立即清除缓存
(6)service层与controller层跟上一篇整合一样,启动redis服务器,redis服务器的安装与启动可以参考之前的博客,地址如下:
http://www.cnblogs.com/gdpuzxs/p/6623171.html
(7)配置log4j日志信息,如下:
![]()
## LOG4J配置
log4j.rootCategory=DEBUG,stdout
## 控制台输出
log4j.appender.stdout=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.stdout.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.stdout.layout.ConversionPattern=%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} %5p %c{1}:%L - %m%n![]()
(8)验证redis缓存
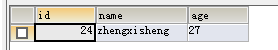
首先我们向user表总插入一条数据,数据库显示如下:
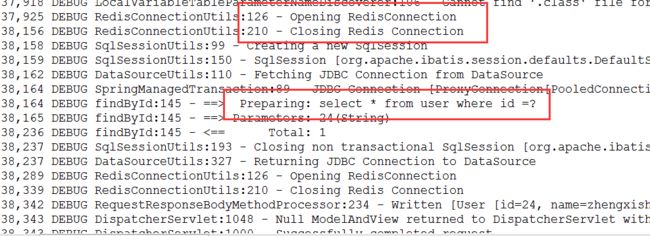
现在,我们查询一下user表中id=24的数据,观擦控制台输出的信息,如下:
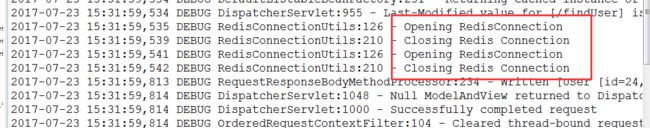
通过控制台输出信息我们可以知道,这次执行了数据库查询,并开启了Redis缓存查询结果。接下来我们再次查询user表中id=24的数据,观察控制台,如下:
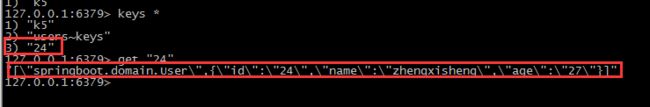
通过控制台输出信息我们可以知道,这次并没有执行数据库查询,而是从Redis缓存中查询,并返回查询结果。我们查看redis中的信息,如下:
方法finduser方法使用了注解@Cacheable(key="#p0"),即将id作为redis中的key值。当我们更新数据的时候,应该使用@CachePut(key="#p0")进行缓存数据的更新,否则将查询到脏数据。
============================================================
============================================================
============================================================
Spring缓存注解@Cache使用 - 架构师之路 - CSDN博客
https://blog.csdn.net/zheng963/article/details/50011325
Spring缓存注解@Cache使用
参考资料
http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/opensource/os-cn-spring-cache/
http://swiftlet.net/archives/774
缓存注解有以下三个:
@Cacheable @CacheEvict @CachePut
(古月: 使用前需要在项目启动文件中加上@EnableCaching注解来让上面三个注解生效)
@Cacheable(value=”accountCache”),这个注释的意思是,当调用这个方法的时候,会从一个名叫 accountCache 的缓存中查询,如果没有,则执行实际的方法(即查询数据库),并将执行的结果存入缓存中,否则返回缓存中的对象。这里的缓存中的 key 就是参数 userName,value 就是 Account 对象。“accountCache”缓存是在 spring*.xml 中定义的名称。
示例:
Java代码 ![]()
- @Cacheable(value="accountCache")// 使用了一个缓存名叫 accountCache
- public Account getAccountByName(String userName) {
- // 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
- System.out.println("real query account."+userName);
- return getFromDB(userName);
- }
@CacheEvict 注释来标记要清空缓存的方法,当这个方法被调用后,即会清空缓存。注意其中一个 @CacheEvict(value=”accountCache”,key=”#account.getName()”),其中的 Key 是用来指定缓存的 key 的,这里因为我们保存的时候用的是 account 对象的 name 字段,所以这里还需要从参数 account 对象中获取 name 的值来作为 key,前面的 # 号代表这是一个 SpEL 表达式,此表达式可以遍历方法的参数对象,具体语法可以参考 Spring 的相关文档手册。
示例:
Java代码 ![]()
- @CacheEvict(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")// 清空accountCache 缓存
- public void updateAccount(Account account) {
- updateDB(account);
- }
- @CacheEvict(value="accountCache",allEntries=true)// 清空accountCache 缓存
- public void reload() {
- reloadAll()
- }
- @Cacheable(value="accountCache",condition="#userName.length() <=4")// 缓存名叫 accountCache
- public Account getAccountByName(String userName) {
- // 方法内部实现不考虑缓存逻辑,直接实现业务
- return getFromDB(userName);
- }
@CachePut 注释,这个注释可以确保方法被执行,同时方法的返回值也被记录到缓存中,实现缓存与数据库的同步更新。
示例:
Java代码 ![]()
- @CachePut(value="accountCache",key="#account.getName()")// 更新accountCache 缓存
- public Account updateAccount(Account account) {
- return updateDB(account);
- }
@Cacheable、@CachePut、@CacheEvict 注释介绍
通过上面的例子,我们可以看到 spring cache 主要使用两个注释标签,即 @Cacheable、@CachePut 和 @CacheEvict,我们总结一下其作用和配置方法。
表 1. @Cacheable 作用和配置方法
@Cacheable 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
| @Cacheable 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
表 2. @CachePut 作用和配置方法
@CachePut 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存,和 @Cacheable 不同的是,它每次都会触发真实方法的调用
| @CachePut 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) 或者 @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
表 3. @CacheEvict 作用和配置方法
@CachEvict 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据一定的条件对缓存进行清空
| @CacheEvict 主要的参数 | ||
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”mycache”) 或者 @CachEvict(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才清空缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”, condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
| allEntries | 是否清空所有缓存内容,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则方法调用后将立即清空所有缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,allEntries=true) |
| beforeInvocation | 是否在方法执行前就清空,缺省为 false,如果指定为 true,则在方法还没有执行的时候就清空缓存,缺省情况下,如果方法执行抛出异常,则不会清空缓存 | 例如: @CachEvict(value=”testcache”,beforeInvocation=true) |