SDOI2013 淘金
题目描述
小 Z在玩一个 叫做《淘金者》的游戏。游戏的世界是一个 二维坐标 。 X轴、Y轴 坐标范围均为 1..N 。初始的时候,所有的整数坐标点上均有一块金子,共 N∗N 块。
一阵风吹过, 金子的位置发生了一些变化。细心的小Z发现, 初始 在 (i,j) 坐标 处的金子会变到 (f(i),f(j)) 坐标 处。其中 f(x) 表示 x 各位数字的乘积 ,例如 f(99)=81,f(12)=2,f(10)=0 。如果金子变化后的坐标不在 1..N 的范围内,我们认为这块金子已经 被移出游戏。 同时可以发现, 对于变化之后的游戏局面, 某些 坐 标上的金子数量可能 不止一块 ,而另外一些坐标上可能已经没有金子 。这次变化 之后, 游戏将不会再对 金子的位置和数量进行改变,玩家可以开始采集工作。
小 Z很懒 ,打算 只进行 只进行 K 次采集 。每次采集可以得到某 一个坐标上的所有 金子 ,采集之后该坐标上的金子数变为 0。
现在小 Z希望知道,对于变化之后的游戏局面,在采集次数为 K 的前提下, 最多可以采集到少块金子?
答案可能很大,小 Z希望得到 1000000007(109+7) 取模之后的答案。
Input
共一行,包含两个正整数 N, K 。
Output
一个整数 ,表示最多可以采集到的金子数量。
Sample Input
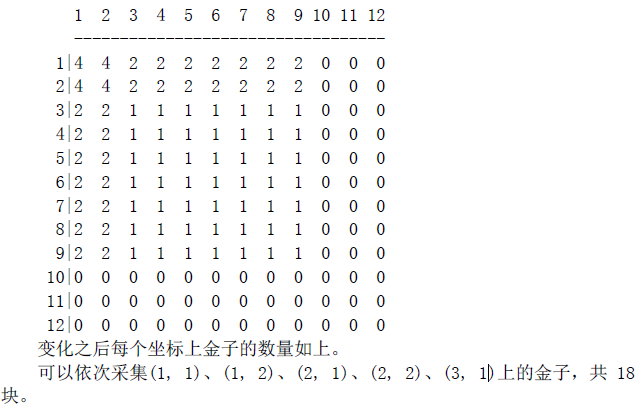
12 5
Sample Output
18
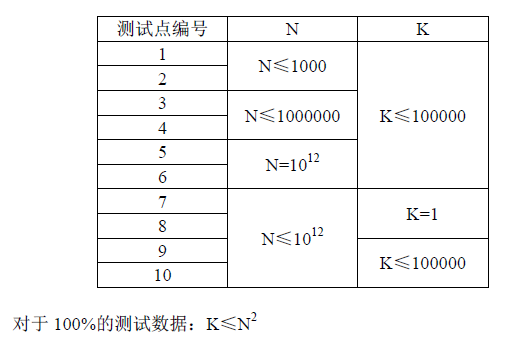
数据范围
样例解释
题解
我们可以发现 x,y 坐标是不相关的。
我们设 y=f(x) 接下来我们的任务就是求 y 的个数。
易得, y 可以表示成 2p1∗3p2∗5p3∗7p4 ,又可得 y 的数量很少,只有大概20000个。我们就顺理成章想到用数位dp了。
设状态 Fi,j,k 表示从高至低dp到第 i 位,前 i 位的积为 j ,前 i 位是否与原数的前 i 位相同(这一位只有0或1)。
Fi,j,0⇒Fi+1,j∗k,0,1⩽k⩽9
Fi,j,1 的情况读者可以自己推一下。
参考代码
#includereturn a.b < b.b;
}
void add(int x,note1 pq,ll ad) {
if (!g[x].count(pq))
next.push(pq);
g[x][pq]+=ad;
}
void Pre(ll n){
ll t1=0,t2=0;
while (n) {
num[++num[0]]=n % 10;
n /= 10;
}
note1 tmp;
tmp.a=0;
tmp.b=1;
now.push(tmp);
g[num[0]+1][tmp]=1;
fd(i,num[0],1) {
while (!now.empty()) {
note1 tmp=now.front();
now.pop();
ll way=g[i+1][tmp];
if (!tmp.a) {
fo(j,1,num[i]) {
if (j==num[i]) {
note1 pq;
pq.a=0;
pq.b=tmp.b*j;
add(i,pq,way);
}
else {
note1 pq;
pq.a=1;
pq.b=tmp.b*j;
add(i,pq,way);
}
}
}
else {
fo(j,1,9){
note1 pq;
pq.a=1;
pq.b=tmp.b*j;
add(i,pq,way);
}
}
}
note1 tmp;
tmp.a=1;
tmp.b=1;
if (i>1) add(i,tmp,1);
while (!next.empty()) {
note1 tmp=next.front();
next.pop();
if (i==1&&!tmp.a) t1=tmp.b,t2=g[1][tmp];
now.push(tmp);
}
}
while (!now.empty()) {
note1 tmp=now.front();
now.pop();
if (tmp.a==0) continue;
f[++f[0]]=g[1][tmp];
if (tmp.b==t1) f[f[0]]+=t2,t1=0;
}
if (t1>0) f[++f[0]]=t2;
}
bool cmp(int i,int j){
return i>j;
}
struct note{
ll w;
int x,y;
};
bool operator < (note i,note j){
return i.w q;
void main2(){
fo(i,1,f[0]) {
note tmp;
tmp.w=f[i]*f[1];
tmp.x=i;
tmp.y=1;
q.push(tmp);
}
ll ans=0;
fo(i,1,m) {
if (q.empty()) break;
note now=q.top();
q.pop();
ans=(ans+now.w) % mo;
if (now.y!=f[0]) {
now.w=f[now.x]*f[now.y+1];
now.y++;
q.push(now);
}
}
printf("%lld",ans);
}
int main(){
scanf("%lld%lld",&n,&m);
Pre(n);
sort(f+1,f+f[0]+1,cmp);
main2();
return 0;
}