tomcat HTTP1.1协议NIO模式
tomcat HTTP1.1协议模块源码
文章目录
- tomcat HTTP1.1协议模块源码
- 先上几篇文章
- 类图
- reactor模式
- SynchronizedStack
- tomcat的线程池(TaskQueue + ThreadPoolExecutor + TaskThreadFactory)
- LimitLatch (tomcat自定义的限连器)
- NioSelectorPool(tomcat包装类)
- SocketBufferHandler + WriteBuffer(tomcat包装类,负责读写bytebuffer)
- NioChannel继承了ByteChannel (tomcat的包类)
- NioSocketWrapper :SocketWrapperBase(从SocketBufferHandler读写数据)
- NioEndpoint(持有selectorPool引用)
- Acceptor
- PollerEvent + Poller(消费者NioEndPoint内部类)
- 一次访问流程
先上几篇文章
netty基础
tomcat总体架构
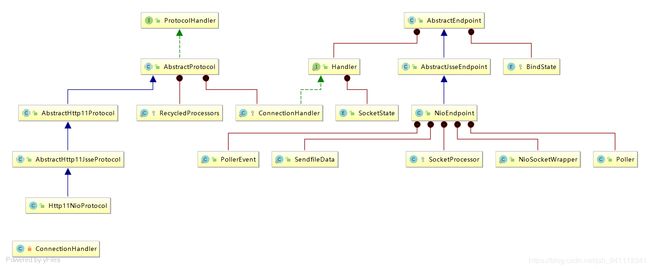
类图
reactor模式
reactor模式
SynchronizedStack
tomcat定义的消费者队列,DEFAULT_SIZE=128,内部由数组+index的形式维护(类似arrayList),同步pop,push,clear方法,expend每次为两倍。
采取策略是:添加时size超过,x2不超过limit发生expend,否则直接返回false,不阻塞
此容器用于作为niochannel的生产者-消费者队列
tomcat的线程池(TaskQueue + ThreadPoolExecutor + TaskThreadFactory)
TaskQueue extends LinkedBlockingQueue
public boolean force(Runnable o) {
if ( parent==null || parent.isShutdown() ) throw new RejectedExecutionException("Executor not running, can't force a command into the queue");
return super.offer(o); // offer单个参数方法是不会阻塞的,如果满了直接false,juc注释上明确说明这个方法性能更好,这个方法在ThreadPoolExecutor 超出容量(发生拒绝策略的时候会发生,见下文)
}
ThreadPoolExecutor // 继承juc的ThreadPoolExecutor
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue workQueue, RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, handler);
prestartAllCoreThreads(); // 父类的方法,会初始化所有core线程
}
public void execute(Runnable command, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) {
submittedCount.incrementAndGet();
try {
super.execute(command);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) { // 超过了
if (super.getQueue() instanceof TaskQueue) {
final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue)super.getQueue();
try {
if (!queue.force(command, timeout, unit)) { // 尝试在此加入队列,失败后直接抛出异常
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Queue capacity is full.");
}
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(x);
}
} else {
submittedCount.decrementAndGet();
throw rx;
}
}
}
至于线程工厂的创建比较简单,一句话
TaskThreadFactory tf = new TaskThreadFactory(getName() + "-exec-", daemon, getThreadPriority());
// 作为守护线程启动,而且线程的名字都有了 xxx-exec 挺好的,tomcat以后先找这个东西
LimitLatch (tomcat自定义的限连器)
默认是maxConnection() ,limit 为1000
private final Sync sync;
private final AtomicLong count; // 维护连接数
private volatile long limit;
private volatile boolean released = false;
private class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer { // juc提供的服务类,专门用于给锁提供实现,简而言之就是1000连接一下都能获得到锁
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public Sync() {
}
@Override
protected int tryAcquireShared(int ignored) {
long newCount = count.incrementAndGet();
if (!released && newCount > limit) {
count.decrementAndGet();
return -1;
} else {
return 1;
}
}
@Override
protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) {
count.decrementAndGet();
return true;
}
}
NioSelectorPool(tomcat包装类)
默认是share模式,通过System.getProperty("org.apache.tomcat.util.net.NioSelectorShared", "true")获取默认为true,
是一个 资源池,其中的资源是selector 放在同步容器中SHARED_SELECTOR = Selector.open();(NIO)创建
SocketBufferHandler + WriteBuffer(tomcat包装类,负责读写bytebuffer)
因为普通的byteBuffer读写需要不断flip模式,读写操作都是在一个bytebuffer上
,SocketBufferHandler通过分别维护一个ReadBuffer, WriteBuffer来方便操作,不知道Netty是不是这样处理的。direct表示是堆内内存还是堆外,优点各不同。
public SocketBufferHandler(int readBufferSize, int writeBufferSize,
boolean direct) {
this.direct = direct;
if (direct) {
readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(readBufferSize);
writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(writeBufferSize);
} else {
readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(readBufferSize);
writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(writeBufferSize);
}
}
WriteBuffer:
private final int bufferSize;
private final LinkedBlockingDeque buffers = new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(); //简单的维护byteBuffer
NioChannel继承了ByteChannel (tomcat的包类)
ByteChannel是socketChannel的接口
简单的封装了 Poller, SocketChannel, NioSocketWrapper ,SocketBufferHandler 继续往下走
NioSocketWrapper :SocketWrapperBase(从SocketBufferHandler读写数据)
默认protected int bufferedWriteSize = 64 * 1024;
以读取为例:
@Override
public int read(boolean block, ByteBuffer to) throws IOException {
int nRead = popu lateReadBuffer(to); // 成功没
if (nRead > 0) {
return nRead;
}
// 调整socketBufferHandler , 下面先跳过
int limit = socketBufferHandler.getReadBuffer().capacity();
if (to.remaining() >= limit) {
to.limit(to.position() + limit);
nRead = fillReadBuffer(block, to);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Socket: [" + this + "], Read direct from socket: [" + nRead + "]");
}
updateLastRead();
} else {
// Fill the read buffer as best we can.
nRead = fillReadBuffer(block);
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Socket: [" + this + "], Read into buffer: [" + nRead + "]");
}
updateLastRead();
// Fill as much of the remaining byte array as possible with the
// data that was just read
if (nRead > 0) {
nRead = populateReadBuffer(to);
}
}
return nRead;
}
NioEndpoint(持有selectorPool引用)
private volatile ServerSocketChannel serverSock = null;
private volatile CountDownLatch stopLatch = null;
private SynchronizedStack eventCache; // 缓存,只是避免GC
private SynchronizedStack nioChannels;
protected int acceptorThreadCount = 1;
protected int acceptorThreadPriority = Thread.NORM_PRIORITY;
private int maxConnections = 10000;
private int pollerThreadCount = Math.min(2,Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()); // 我的电脑是4核(处理),这里就是2
@Override // 该方法tomcat启动时就会执行
public void bind() throws Exception {
initServerSocket(); // 最终调用 serverSock = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// Initialize thread count defaults for acceptor, poller
if (acceptorThreadCount == 0) {
// FIXME: Doesn't seem to work that well with multiple accept threads
acceptorThreadCount = 1;
}
if (pollerThreadCount <= 0) {
//minimum one poller thread
pollerThreadCount = 1;
}
setStopLatch(new CountDownLatch(pollerThreadCount)); // 栅栏为2
// Initialize SSL if needed
initialiseSsl();
selectorPool.open(); .// 初始化selectorPool
}
// 在HTTP第一次访问的时候会调用
public void startInternal() throws Exception {
if (!running) {
running = true;
paused = false;
processorCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getProcessorCache());
eventCache = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getEventCache());
nioChannels = new SynchronizedStack<>(SynchronizedStack.DEFAULT_SIZE,
socketProperties.getBufferPool());
// Create worker collection
if ( getExecutor() == null ) {
createExecutor();
// 使用的是tomcat定义的线程池,上文讲过了,默认线程数是server.xml 里面配置的,如果不改的话是200, core线程10,60s空闲时间
}
initializeConnectionLatch(); // 前面提过的限制连接器
// Start poller threads
pollers = new Poller[getPollerThreadCount()]; // 默认是2,2个消费者线程
for (int i=0; i Acceptor
负责接受socketchannel封装入socket = endpoint.serverSocketAccept();
然后调用setSocketOptions(SocketChannel socket)放入队列等待后续处理
PollerEvent + Poller(消费者NioEndPoint内部类)
pollerEvent的功能时负责改变socketchannel的注册事件
,实现runnable,然而实际上并不会并发执行,会直接在poller里被run调用
private NioChannel socket;
private int interestOps;
private NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper;
public void run() {
if (interestOps == OP_REGISTER) {
try {
// 这里并不是使用原生的NIO,而是tomcat对其封装后的类
socket.getIOChannel().register(
socket.getPoller().getSelector(), SelectionKey.OP_READ, socketWrapper); // socket完成了nio向selector注册事件
} catch (Exception x) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.registerFail"), x);
}
} else {
final SelectionKey key = socket.getIOChannel().keyFor(socket.getPoller().getSelector());
try {
if (key == null) {
socket.socketWrapper.getEndpoint().countDownConnection(); // 减小限流器的数
((NioSocketWrapper) socket.socketWrapper).closed = true;
} else {
final NioSocketWrapper socketWrapper = (NioSocketWrapper) key.attachment();
if (socketWrapper != null) {
//we are registering the key to start with, reset the fairness counter.
int ops = key.interestOps() | interestOps;
socketWrapper.interestOps(ops); // 修改了socket注册事件
key.interestOps(ops);
} else {
socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);
}
}
} catch (CancelledKeyException ckx) {
try {
socket.getPoller().cancelledKey(key);
} catch (Exception ignore) {}
}
}
}
private Selector selector;
private AtomicLong wakeupCounter = new AtomicLong(0);
private final SynchronizedQueue events =new SynchronizedQueue<>();
public Poller() throws IOException {
this.selector = Selector.open(); // 初始化的时候就初始化了一个NIO 选择器
}
@Override
public void run() {
// Loop until destroy() is called
while (true) {
boolean hasEvents = false;
try {
if (!close) { // 可以想象,肯定有个方法可以把close设置
hasEvents = events();
if (wakeupCounter.getAndSet(-1) > 0) {
//if we are here, means we have other stuff to do
//do a non blocking select
keyCount = selector.selectNow();
} else {
keyCount = selector.select(selectorTimeout);
}
wakeupCounter.set(0);
}
if (close) {
events();
timeout(0, false);
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException ioe) {
log.error(sm.getString("endpoint.nio.selectorCloseFail"), ioe);
}
break;
}
} catch (Throwable x) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(x);
log.error("",x);
continue;
}
//either we timed out or we woke up, process events first
if ( keyCount == 0 ) hasEvents = (hasEvents | events());
Iterator iterator =
keyCount > 0 ? selector.selectedKeys().iterator() : null;
while (iterator != null && iterator.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey sk = iterator.next();
NioSocketWrapper attachment = (NioSocketWrapper)sk.attachment();
if (attachment == null) {
iterator.remove();
} else {
iterator.remove();
processKey(sk, attachment); // 处理,见下文
}
}//while
//process timeouts
timeout(keyCount,hasEvents);
}//while
getStopLatch().countDown();
}
// 新启动一个(或者复用之前的)线程交给它来处理剩下的操作
public boolean processSocket(SocketWrapperBase socketWrapper,
SocketEvent event, boolean dispatch) {
try {
if (socketWrapper == null) {
return false;
}
SocketProcessorBase sc = processorCache.pop();
if (sc == null) {
sc = createSocketProcessor(socketWrapper, event);
} else {
sc.reset(socketWrapper, event);
}
Executor executor = getExecutor();
if (dispatch && executor != null) {
executor.execute(sc);
} else {
sc.run();
}
} catch (RejectedExecutionException ree) {
getLog().warn(sm.getString("endpoint.executor.fail", socketWrapper) , ree);
return false;
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This means we got an OOM or similar creating a thread, or that
// the pool and its queue are full
getLog().error(sm.getString("endpoint.process.fail"), t);
return false;
}
return true;
}
处理的细节最后会交给:Http11Processor,中间省略了繁琐的协议分发,因为tomcat不只支持HTTP协议
一次访问流程
- 从
Acceper断点进入,在serversocketchannel.accept获取socket之后,会注册到Poller中,注意:是在accepter中调用poller的registery方法(注意,只注册读事件),相当于accepter -> poller线程间协作是通过pollerevent队列 - poller 获取pollevent后调用selector方法,进入process具体事件
SocketProcessor分发请求Http11Processor.service 方法非常复杂
inputBuffer.init(socketWrapper); // 初始化16k,下同,默认使用堆内内存
outputBuffer.init(socketWrapper);
然后调用parseHeader方法,下面是部分代码
chr = byteBuffer.get();
if (chr == Constants.CR) {
// Skip
} else if (chr == Constants.LF) {
return HeaderParseStatus.DONE;
} else { // 只有不为CR,LF才正式开始
byteBuffer.position(byteBuffer.position() - 1);
break;
}
..... 处理 处理比较复杂,建议直接源码
- 读取报文后进行一些列属性的封装,然后交给CoyoteAdapter进行处理,接下来就是servlet的内容了