SpringBoot入门教程04——Environment详解
SpringBoot入门教程04——Environment详解
前言
上一节我们讲述了SpringBoot配置文件详解 传送门
细心的同学会发现里面其实有一个小坑
比如我们修改user.properties文件,修改后内容如下:
user.name=henry1111
user.age=16
重启应用,打开浏览器打开浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/user,浏览器显示:
Henry-16
跟预期的henry1111-16不太一样,为什么呢?
我们再看一个例子
引入Environment
在controller包下,新建EnvController类,内容如下
@RestController
public class EnvController {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/env")
public String env(){
System.out.println(env.getProperty("user.name"));
System.out.println(env.getProperty("user.age"));
return env.getProperty("user.name")+"-"+env.getProperty("user.age");
}
}
然后重启应用,打开浏览器打开浏览器输入http://127.0.0.1:8080/env,浏览器显示:
Henry-16
我们知道Environment类的实例存放的时spring容器的配置信息,输出以上内容,与请求http://127.0.0.1:8080/user是一致的,但是与user.properties中的配置不一致,为什么呢?下面我们详细分析一下。
StandardServletEnvironment
在EnvController类的env()方法打个断点,然后请求http://127.0.0.1:8080/env,在idea可以看到env的详细信息

如图,env实质是StandardServletEnvironment类的实例,继续追踪代码可知,getProperty实质就是遍历循环propertySources,如果当前propertySource.getProperty(key)的值为null就继续遍历,如果值不为null就直接返回该值
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver类getProperty方法代码如下
@Nullable
protected <T> T getProperty(String key, Class<T> targetValueType, boolean resolveNestedPlaceholders) {
if (this.propertySources != null) {
Iterator var4 = this.propertySources.iterator();
while(var4.hasNext()) {
PropertySource<?> propertySource = (PropertySource)var4.next();
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Searching for key '" + key + "' in PropertySource '" + propertySource.getName() + "'");
}
Object value = propertySource.getProperty(key);
if (value != null) {
if (resolveNestedPlaceholders && value instanceof String) {
value = this.resolveNestedPlaceholders((String)value);
}
this.logKeyFound(key, propertySource, value);
return this.convertValueIfNecessary(value, targetValueType);
}
}
}
if (this.logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
this.logger.trace("Could not find key '" + key + "' in any property source");
}
return null;
}
在本例中env的propertySources有11个元素,其中最后一个元素对应到我们自定义的配置文件user.properties,
可以看到该元素中user.name和user.age与配置文件中是一致的,但是该元素是在列表最末,假如前面的元素中已经能找到user.name,那么env.getProperty(“user.name”)返回的就是别的值。
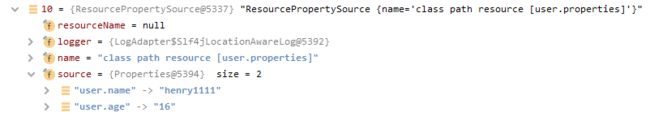
那就试着去找一下user.name,在第5个元素,下标为4的systemProperties中果然找到了user.name。
鉴于一个一个找比较麻烦,我们用代码打印一下environment中都有哪些key值,修改一下EnvController,代码如下:
@RestController
public class EnvController {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@RequestMapping("/env")
public String env(){
StandardServletEnvironment environment = (StandardServletEnvironment) env;
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
Iterator<PropertySource<?>> iterator = propertySources.iterator();
while (iterator.hasNext()) {
PropertySource<?> propertySource = iterator.next();
if (propertySource instanceof MapPropertySource) {
MapPropertySource mapPropertySource = (MapPropertySource) propertySource;
String[] propertyNames = mapPropertySource.getPropertyNames();
for (String s : propertyNames) {
System.out.println(s+":"+mapPropertySource.getProperty(s));
}
}
}
return env.getProperty("user.name")+"-"+env.getProperty("user.age");
}
}
执行日志,我就不贴了,大家可以自己跑一下看看输出。
总结
学完本节,我们对Springboot配置文件的加载过程应该有比较深的理解,下面做一个简单总结
- JVM启动时,系统属性和环境变量传递给JVM
- springboot启动时先扫描@Controller,@Component,@Configuration,@Service等注解,找到声明让spring容器管理实例的类
- 看这些类上有没有@PropertySource注解,如果有则去加载该注解指定的配置文件
- 把所有的配置信息都给到Environment实例管理,配置信息根据来源不同有不同的优先级,比如系统属性和环境变量的优先级高于用户自定义properties文件的优先级
- 再判断这些类上有没有@ConfigurationProperties注解,如果有则从Environment实例中取值通过反射赋值
- @Value注解与@ConfigurationProperties注解类似,也从Environment实例中取值通过反射赋值
踩坑
@PropertySource("") 时,idea开发环境启动也都成功,但是通过maven打包运行,就会报java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Malformed \uxxxx encoding.
关于这个错误,网上大部分说配置文件中有’\‘或者文件路径有中文,检查了半天也没找到’\'和中文,一开始百思不得其解,后面才仔细研究了一下springboot配置文件启动加载的过程,才有了本篇文章
看完文本我们知道,
- @PropertySource注解只要在一个被spring容器管理的类上,那么不管在哪个类上实质是一样的,只是我们一般会写在对应的JavaBean配置类上
- @PropertySource("")没有指定文件名,该注解等于没用
- 去掉@PropertySource("") 注解maven打包运行立马正常了