高性能IO模型分析-浅析Select、Poll、Epoll机制(三)
文章目录
- 一、Select机制
- API简介
- 运行机制
- Select的缺陷
- 二、Poll机制
- API简介
- 运行机制
- Poll的缺陷
- 三、Epoll机制
- API简介
- 运行机制
- 工作模式
- Epoll的优点
- 四、Select、Poll、Epoll机制的对比
- 五、Epoll的使用场景
本章(第三章)内容其实和第二章内容,都是第一张内容的延伸。第二章内容是第一章内容的延伸,本章内容则是第一章内容再往底层方面的延伸,也是面试中考察网络方面知识时,可能会问到的几个点。
select、poll、epoll都是I/O多路复用的机制。I/O多路复用就是通过一种机制,一个进程可以监视多个文件描述符,一旦某个描述符就绪(读就绪或写就绪),能够通知程序进行相应的读写操作 。
但是,select,poll,epoll本质还是同步I/O(I/O多路复用本身就是同步IO)的范畴,因为它们都需要在读写事件就绪后线程自己进行读写,读写的过程阻塞的。而异步I/O的实现是系统会把负责把数据从内核空间拷贝到用户空间,无需线程自己再进行阻塞的读写,内核已经准备完成。
一、Select机制
API简介
linux系统中/usr/include/sys/select.h文件中对select方法的定义如下:
/* fd_set for select and pselect. */
typedef struct
{
/* XPG4.2 requires this member name. Otherwise avoid the name
from the global namespace. */
#ifdef __USE_XOPEN
__fd_mask fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->fds_bits)
#else
__fd_mask __fds_bits[__FD_SETSIZE / __NFDBITS];
# define __FDS_BITS(set) ((set)->__fds_bits)
#endif
} fd_set;
/* Check the first NFDS descriptors each in READFDS (if not NULL) for read
readiness, in WRITEFDS (if not NULL) for write readiness, and in EXCEPTFDS
(if not NULL) for exceptional conditions. If TIMEOUT is not NULL, time out
after waiting the interval specified therein. Returns the number of ready
descriptors, or -1 for errors.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int select (int __nfds, fd_set *__restrict __readfds,
fd_set *__restrict __writefds,
fd_set *__restrict __exceptfds,
struct timeval *__restrict __timeout);
int __nfds是fd_set中最大的描述符+1,当调用select时,内核态会判断fd_set中描述符是否就绪,__nfds告诉内核最多判断到哪一个描述符。
__readfds、__writefds、__exceptfds都是结构体fd_set,fd_set可以看作是一个描述符的集合。 select函数中存在三个fd_set集合,分别代表三种事件,readfds表示读描述符集合,writefds表示读描述符集合,exceptfds表示异常条件描述符集合。当对应的fd_set = NULL时,表示不监听该类描述符。
timeval __timeout用来指定select的工作方式,即当文件描述符尚未就绪时,select是永远等下去,还是等待一定的时间,或者是直接返回
函数返回值int表示: 就绪描述符的数量,如果为-1表示产生错误 。
运行机制
Select会将全量fd_set从用户空间拷贝到内核空间,并注册回调函数, 在内核态空间来判断每个请求是否准备好数据 。select在没有查询到有文件描述符就绪的情况下,将一直阻塞(I/O多路服用中提过:select是一个阻塞函数)。如果有一个或者多个描述符就绪,那么select将就绪的文件描述符置位,然后select返回。返回后,由程序遍历查看哪个请求有数据。
Select的缺陷
-
每次调用select,都需要把fd集合从用户态拷贝到内核态,fd越多开销则越大;
-
每次调用select都需要在内核遍历传递进来的所有fd,这个开销在fd很多时也很大
-
select支持的文件描述符数量有限,默认是1024。参见
/usr/include/linux/posix_types.h中的定义:#define __FD_SETSIZE 1024
二、Poll机制
API简介
linux系统中/usr/include/sys/poll.h文件中对poll方法的定义如下:
/* Data structure describing a polling request. */
struct pollfd
{
int fd; /* File descriptor to poll. */
short int events; /* Types of events poller cares about. */
short int revents; /* Types of events that actually occurred. */
};
/* Poll the file descriptors described by the NFDS structures starting at
FDS. If TIMEOUT is nonzero and not -1, allow TIMEOUT milliseconds for
an event to occur; if TIMEOUT is -1, block until an event occurs.
Returns the number of file descriptors with events, zero if timed out,
or -1 for errors.
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int poll (struct pollfd *__fds, nfds_t __nfds, int __timeout);
__fds参数时Poll机制中定义的结构体pollfd,用来指定一个需要监听的描述符。结构体中fd为需要监听的文件描述符,events为需要监听的事件类型,而revents为经过poll调用之后返回的事件类型,在调用poll的时候,一般会传入一个pollfd的结构体数组,数组的元素个数表示监控的描述符个数。
__nfds和**__timeout**参数都和Select机制中的同名参数含义类似
运行机制
poll的实现和select非常相似,只是描述fd集合的方式不同,poll使用pollfd结构代替select的fd_set(网上讲:类似于位图)结构,其他的本质上都差不多。所以Poll机制突破了Select机制中的文件描述符数量最大为1024的限制。
Poll的缺陷
Poll机制相较于Select机制中,解决的文件描述符数量为1024的缺陷。但另外两点缺陷依然存在:
- 每次调用select,都需要把fd集合从用户态拷贝到内核态,fd越多开销则越大;
- 每次调用select都需要在内核遍历传递进来的所有fd,这个开销在fd很多时也很大
三、Epoll机制
Epoll在Linux2.6内核正式提出,是基于事件驱动的I/O方式,相对于select来说,epoll没有描述符个数限制,使用一个文件描述符管理多个描述符,将用户关心的文件描述符的事件存放到内核的一个事件表中,这样在用户空间和内核空间的copy只需一次。
API简介
linux系统中/usr/include/sys/epoll.h文件中有如下方法:
/* Creates an epoll instance. Returns an fd for the new instance.
The "size" parameter is a hint specifying the number of file
descriptors to be associated with the new instance. The fd
returned by epoll_create() should be closed with close(). */
extern int epoll_create (int __size) __THROW;
/* Manipulate an epoll instance "epfd". Returns 0 in case of success,
-1 in case of error ( the "errno" variable will contain the
specific error code ) The "op" parameter is one of the EPOLL_CTL_*
constants defined above. The "fd" parameter is the target of the
operation. The "event" parameter describes which events the caller
is interested in and any associated user data. */
extern int epoll_ctl (int __epfd, int __op, int __fd,
struct epoll_event *__event) __THROW;
/* Wait for events on an epoll instance "epfd". Returns the number of
triggered events returned in "events" buffer. Or -1 in case of
error with the "errno" variable set to the specific error code. The
"events" parameter is a buffer that will contain triggered
events. The "maxevents" is the maximum number of events to be
returned ( usually size of "events" ). The "timeout" parameter
specifies the maximum wait time in milliseconds (-1 == infinite).
This function is a cancellation point and therefore not marked with
__THROW. */
extern int epoll_wait (int __epfd, struct epoll_event *__events,
int __maxevents, int __timeout);
epoll_create函数:创建一个epoll实例并返回,该实例可以用于监控__size个文件描述符
epoll_ctl函数:向epoll中注册事件,该函数如果调用成功返回0,否则返回-1。
- __epfd为epoll_create返回的epoll实例
- __op表示要进行的操作
- __fd为要进行监控的文件描述符
- __event要监控的事件
epoll_wait函数:类似与select机制中的select函数、poll机制中的poll函数,等待内核返回监听描述符的事件产生。该函数返回已经就绪的事件的数量,如果为-1表示出错。
- __epfd为epoll_create返回的epoll实例
- __events数组为 epoll_wait要返回的已经产生的事件集合
- __maxevents为希望返回的最大的事件数量(通常为__events的大小)
- __timeout和select、poll机制中的同名参数含义相同
运行机制
epoll操作过程需要上述三个函数,也正是通过三个函数完成Select机制中一个函数完成的事情,解决了Select机制的三大缺陷。epoll的工作机制更为复杂,我们就解释一下,它是如何解决Select机制的三大缺陷的。
- 对于第一个缺点,epoll的解决方案是:它的fd是共享在用户态和内核态之间的,所以可以不必进行从用户态到内核态的一个拷贝,大大节约系统资源。至于如何做到用户态和内核态,大家可以查一下“mmap”,它是一种内存映射的方法。
- 对于第二个缺点,epoll的解决方案不像select或poll一样每次都把当前线程轮流加入fd对应的设备等待队列中,而只在epoll_ctl时把当前线程挂一遍(这一遍必不可少),并为每个fd指定一个回调函数。当设备就绪,唤醒等待队列上的等待者时,就会调用这个回调函数,而这个回调函数会把就绪的fd加入一个就绪链表。那么当我们调用epoll_wait时,epoll_wait只需要检查链表中是否有存在就绪的fd即可,效率非常可观。
- 对于第三个缺点,fd数量的限制,也只有Select存在,Poll和Epoll都不存在。由于Epoll机制中只关心就绪的fd,它相较于Poll需要关心所有fd,在连接较多的场景下,效率更高。在1GB内存的机器上大约是10万左右,一般来说这个数目和系统内存关系很大。
工作模式
相较于Select和Poll,Epoll内部还分为两种工作模式: LT水平触发(level trigger)和ET边缘触发(edge trigger)。
- LT模式: 默认的工作模式,即当epoll_wait检测到某描述符事件就绪并通知应用程序时,应用程序可以不立即处理该事件;事件会被放回到就绪链表中,下次调用epoll_wait时,会再次通知此事件。
- ET模式: 当epoll_wait检测到某描述符事件就绪并通知应用程序时,应用程序必须立即处理该事件。如果不处理,下次调用epoll_wait时,不会再次响应并通知此事件。
由于上述两种工作模式的区别,LT模式同时支持block和no-block socket两种,而ET模式下仅支持no-block socket。即epoll工作在ET模式的时候,必须使用非阻塞套接口,以避免由于一个fd的阻塞I/O操作把多个处理其他文件描述符的任务饿死。ET模式在很大程度上减少了epoll事件被重复触发的次数,因此效率要比LT模式高。
Epoll的优点
- 使用内存映射技术,节省了用户态和内核态间数据拷贝的资源消耗;
- 通过每个fd定义的回调函数来实现的,只有就绪的fd才会执行回调函数。I/O的效率不会随着监视fd的数量的增长而下降;
- 文件描述符数量不再受限;
四、Select、Poll、Epoll机制的对比
下图主流I/O多路复用机制的benchmark:
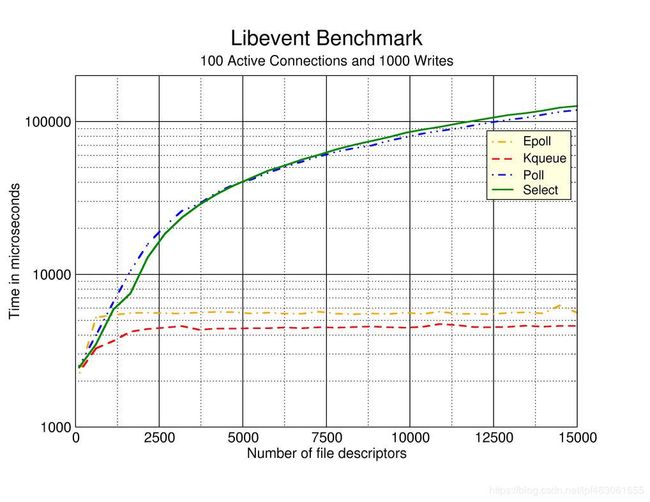 当并发fd较小时,Select、Poll、Epoll的响应效率想差无几,甚至Select和Poll更胜一筹。但是当并发连接(fd)较多时,Epoll的优势便真正展现出来。
当并发fd较小时,Select、Poll、Epoll的响应效率想差无几,甚至Select和Poll更胜一筹。但是当并发连接(fd)较多时,Epoll的优势便真正展现出来。
下面一张表格总结三种模式的区别:
| select | poll | epoll | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 事件集合 | 通过3个参数分别传入感兴趣的可读,可写及异常等事件。 内核通过对这些参数的在线修改来反馈其中的就绪事件 这使得用户每次调用select都要重置这3个参数 |
统一处理所有事件类型,因此只需要一个事件集参数。 用户通过pollfd.events传入感兴趣的事件,内核通过修改pollfd.revents参数反馈其中就绪的事件 |
内核通过一个事件表直接管理用户感兴趣的所有事件。 因此每次调用epoll_wait时,无需反复传入用户感兴趣的事件。epoll_wait系统调用的参数events仅用来反馈就绪的事件 |
| 内核实现和工作效率 | 采用轮询方式检测就绪事件,时间复杂度:O(n) | 采用轮询方式检测就绪事件,时间复杂度:O(n) | 采用回调方式检测就绪事件,时间复杂度:O(1) |
| 最大连接数 | 1024 | 无上限 | 无上限 |
| 工作模式 | LT | LT | LT和ET(高效) |
| fd拷贝 | 每次调用,每次拷贝 | 每次调用,每次拷贝 | 通过mmap的内存映射技术,降低拷贝的资源消耗 |
通过上述的一些总结,希望我们对I/O多路复用的Select、Poll、Epoll机制有一个更深刻的认识。也要明白为什么epoll会成为Linux平台下实现高性能网络服务器的首选I/O多路复用机制。
五、Epoll的使用场景
上面的文章中已经不断介绍了Epoll机制的优势,又提到它是**Linux平台下实现高性能网络服务器的首选I/O复用机制。**实际工作中,我们在哪里会用到它?怎么用呢?
比如下面代码,就是我们使用高性能网络框架Netty实现IM项目中对于netty的bossGroup和workerGroup以及serverChannel的配置
String os = System.getProperty("os.name");
if(os.toLowerCase().startsWith("win") || os.toLowerCase().startsWith("mac")){
// 点开NioEventLoopGroup的源码,对于这个类是这么注释的
// MultithreadEventLoopGroup implementations which is used for NIO Selector based Channel
bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(4);
}else{
// 点开EpollEventLoopGroup的源码,对于这个类是这么注释的
// EventLoopGroup which uses epoll under the covers. Because of this it only works on linux.
bossGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(1);
workerGroup = new EpollEventLoopGroup(4);
}
bootStrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootStrap.group(bossGroup,workerGroup);
if(os.toLowerCase().startsWith("win") || os.toLowerCase().startsWith("mac")) {
// NioServerSocketChannel implementation which uses NIO selector based implementation to accept new connections.
bootStrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
}else{
// ServerSocketChannel implementation that uses linux EPOLL Edge-Triggered Mode for maximal performance.
// 注意看注释中的“linux EPOLL Edge-Triggered Mode”,linux下ET模式的Epoll机制
bootStrap.channel(EpollServerSocketChannel.class);
}
看完这些,我们对Select、Poll、Epoll的了解是不是更多了一点。
如果能帮助到你,点个赞再走呗!