初识opencl
初识opencl
- 以一个例子开头
以一个例子开头
在自己的笔记本电脑上(win10)安装intel的那个opencl包,安装后,记得将include与lib包拷贝出来,然后在以后的使用中只要链接这个库就ok了。
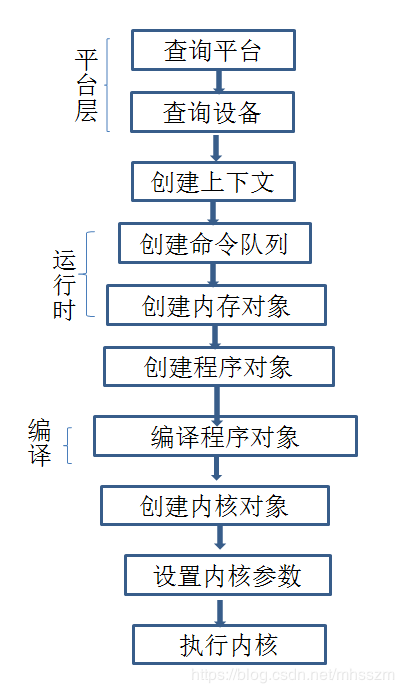
例子代码如下:(出自opencl in action)
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#define PROGRAM_FILE "matvec.cl"
#define KERNEL_FUNC "matvec_mult"
#include
#include
#include
#ifdef MAC
#include
#else
#include
#endif
int test1() {
/* Host/device data structures 主机、设备数据结构体*/
cl_platform_id platform;
cl_device_id device;
cl_context context;
cl_command_queue queue;
cl_int i, err;
/* Program/kernel data structures 程序、内核 数据结构体 */
cl_program program;
FILE *program_handle;
char *program_buffer, *program_log;
size_t program_size, log_size;
cl_kernel kernel;
/* Data and buffers 数据与缓存*/
float mat[16], vec[4], result[4];
float correct[4] = { 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f };
cl_mem mat_buff, vec_buff, res_buff;
size_t work_units_per_kernel;
/* Initialize data to be processed by the kernel 初始化数据 */
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
mat[i] = i * 2.0f;
}
//初始化数据并在cpu上计算结果
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
vec[i] = i * 3.0f;
correct[0] += mat[i] * vec[i];
correct[1] += mat[i + 4] * vec[i];
correct[2] += mat[i + 8] * vec[i];
correct[3] += mat[i + 12] * vec[i];
}
/* Identify a platform 定义平台*/
err = clGetPlatformIDs(1, &platform, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't find any platforms");
exit(1);
}
/* Access a device 获取设备*/
err = clGetDeviceIDs(platform, CL_DEVICE_TYPE_GPU, 1, &device, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't find any devices");
exit(1);
}
/* Create the context 创建上下文*/
context = clCreateContext(NULL, 1, &device, NULL, NULL, &err);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't create a context");
exit(1);
}
/* Read program file and place content into buffer 读取内核程序文件 */
program_handle = fopen(PROGRAM_FILE, "r");
if (program_handle == NULL) {
perror("Couldn't find the program file");
exit(1);
}
fseek(program_handle, 0, SEEK_END);
program_size = ftell(program_handle);
rewind(program_handle);
program_buffer = (char*)malloc(program_size + 1);
program_buffer[program_size] = '\0';
fread(program_buffer, sizeof(char), program_size, program_handle);
fclose(program_handle);
/* Create program from file 从程序文件与上下文得到 program 程序 */
program = clCreateProgramWithSource(context, 1,
(const char**)&program_buffer, &program_size, &err);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't create the program");
exit(1);
}
free(program_buffer);
/* Build program 编译程序 */
err = clBuildProgram(program, 0, NULL, NULL, NULL, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
/* Find size of log and print to std output */
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG,
0, NULL, &log_size);
program_log = (char*)malloc(log_size + 1);
program_log[log_size] = '\0';
clGetProgramBuildInfo(program, device, CL_PROGRAM_BUILD_LOG,
log_size + 1, program_log, NULL);
printf("%s\n", program_log);
free(program_log);
exit(1);
}
/* Create kernel for the mat_vec_mult function 创建内核 */
kernel = clCreateKernel(program, KERNEL_FUNC, &err);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't create the kernel");
exit(1);
}
/* Create CL buffers to hold input and output data 创建cl 内存去保存输入与输出数据 */
mat_buff = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY |
CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(float) * 16, mat, &err);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't create a buffer object");
exit(1);
}
vec_buff = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_READ_ONLY |
CL_MEM_COPY_HOST_PTR, sizeof(float) * 4, vec, NULL);
res_buff = clCreateBuffer(context, CL_MEM_WRITE_ONLY,
sizeof(float) * 4, NULL, NULL);
/* Create kernel arguments from the CL buffers 由Cl内存数据设置内核参数*/
err = clSetKernelArg(kernel, 0, sizeof(cl_mem), &mat_buff);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't set the kernel argument");
exit(1);
}
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 1, sizeof(cl_mem), &vec_buff);
clSetKernelArg(kernel, 2, sizeof(cl_mem), &res_buff);
/* Create a CL command queue for the device 由Device,context创建命令队列 */
//queue = clCreateCommandQueue(context, device, 0, &err);
queue = clCreateCommandQueueWithProperties(context, device, 0, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't create the command queue");
exit(1);
}
/* Enqueue the command queue to the device 执行内核,使用4 work-units per kernel */
work_units_per_kernel = 4; /* 4 work-units per kernel */
err = clEnqueueNDRangeKernel(queue, kernel, 1, NULL, &work_units_per_kernel,
NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't enqueue the kernel execution command");
exit(1);
}
/* Read the result 读结果 */
err = clEnqueueReadBuffer(queue, res_buff, CL_TRUE, 0, sizeof(float) * 4,
result, 0, NULL, NULL);
if (err < 0) {
perror("Couldn't enqueue the read buffer command");
exit(1);
}
/* Test the result 核对结果 */
if ((result[0] == correct[0]) && (result[1] == correct[1])
&& (result[2] == correct[2]) && (result[3] == correct[3])) {
printf("Matrix-vector multiplication successful.\n");
}
else {
printf("Matrix-vector multiplication unsuccessful.\n");
}
/* Deallocate resources */
clReleaseMemObject(mat_buff);
clReleaseMemObject(vec_buff);
clReleaseMemObject(res_buff);
clReleaseKernel(kernel);
clReleaseCommandQueue(queue);
clReleaseProgram(program);
clReleaseContext(context);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Matrix-vector multiplication successful.