spring源码之二:Spring容器启动与单例bean的初始化
在上一篇文章中分析了spring容器的初始化过程,这篇文章分析spring容器的初始化与单例bean的初始化过程
这里说一个IDE看源码的过程,有时候你找不到源码之间的调用关系,在方法上使用快捷键CTRL+G,查找方法被调用的过程
上一篇文章说过spring通过initWebApplicationContext类的initWebApplicationContext()方法初始化web容器,代码如下
/**
* Initialize Spring's web application context for the given servlet context,
* using the application context provided at construction time, or creating a new one
* according to the "{@link #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM contextClass}" and
* "{@link #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM contextConfigLocation}" context-params.
* @param servletContext current servlet context
* @return the new WebApplicationContext
* @see #ContextLoader(WebApplicationContext)
* @see #CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM
* @see #CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM
*/
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " +
"check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!");
}
servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
if (this.context == null) {
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
}
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
// The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as
// setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
// The context instance was injected without an explicit parent ->
// determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext);
cwac.setParent(parent);
}
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext);
}
}
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = this.context;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context);
}
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext initialized in " + elapsedTime + " ms");
}
return this.context;
}
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex) {
logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex);
throw ex;
}
}
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String configLocationParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (configLocationParam != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(configLocationParam);
}
// The wac environment's #initPropertySources will be called in any case when the context
// is refreshed; do it eagerly here to ensure servlet property sources are in place for
// use in any post-processing or initialization that occurs below prior to #refresh
ConfigurableEnvironment env = wac.getEnvironment();
if (env instanceof ConfigurableWebEnvironment) {
((ConfigurableWebEnvironment) env).initPropertySources(sc, null);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
wac.refresh();
}
代码最后一行,容器初始化之后就调用refresh()方法,看名字就知道这个方法就是刷新容器的,具体来看下这个方法的说明
这是类ConfigurableApplicationContext的方法定义,就是启动方法的意思
/**
* Load or refresh the persistent representation of the configuration,
* which might an XML file, properties file, or relational database schema.
* As this is a startup method, it should destroy already created singletons
* if it fails, to avoid dangling resources. In other words, after invocation
* of that method, either all or no singletons at all should be instantiated.
* @throws BeansException if the bean factory could not be initialized
* @throws IllegalStateException if already initialized and multiple refresh
* attempts are not supported
*/
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
接下来看refresh()方法的实现
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
//注册bean processors
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
//注册监听器
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//初始化单例bean
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}看这段代码之前先来介绍两个重要的接口BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor,这两个接口是对spring 容器的扩展点
详情见https://blog.csdn.net/nongfuyumin/article/details/105660371
接下来看finishBeanFactoryInitialization方法
该方法的定义如下
/**
* Ensure that all non-lazy-init singletons are instantiated, also considering
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean FactoryBeans}.
* Typically invoked at the end of factory setup, if desired.
* @throws BeansException if one of the singleton beans could not be created.
* Note: This may have left the factory with some beans already initialized!
* Call {@link #destroySingletons()} for full cleanup in this case.
* @see #destroySingletons()
*/
void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException;实现如下,DefaultListableBeanFactory类为bean factory的默认实现
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
List beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
Object bean = getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
if (bean instanceof FactoryBean) {
final FactoryBean factory = (FactoryBean) bean;
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction)
((SmartFactoryBean) factory)::isEagerInit,
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
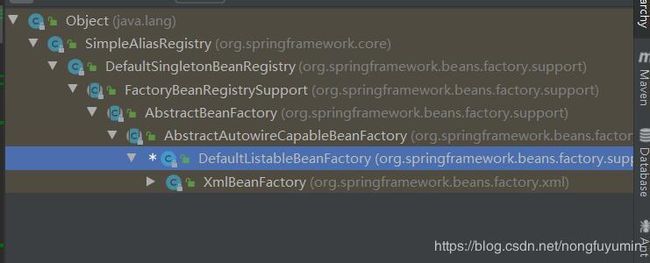
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction 该类的层次结构如下
接着看getBean(beanName);方法,这个方法很熟悉吧,就是获取bean的通用方法,getBean()方法为AbstractBeanFactory的实现
接下来分析AbstractBeanFactory这个类