NDK的OpenGLes2.0 官方例子解析
提要
NDK自带了一个OpenGLes的例子,下面就一起来学习一下。
环境:Ubuntu14.04 NDK r10 ADT13.02 Android Native Development Tools 8.12
注:在ubuntu的adt需要手动安装Android Native Development Tools才能很好的支持NDK。
如果你对Java调用C/C++的代码还不了解,可以参考:JNI原理及实现 利用JNI进行对象操作
如果你对NDK还不了解,可以参考:Android的NDK开发(1)-不一样的HelloWorld
如果你对NDK下的OpenGL es 编程不了解,可以参考:Android的NDK开发(2)-基于NDK的OpenGL开发
加载项目
File -> Import -> Existing Android Code Into Workspace
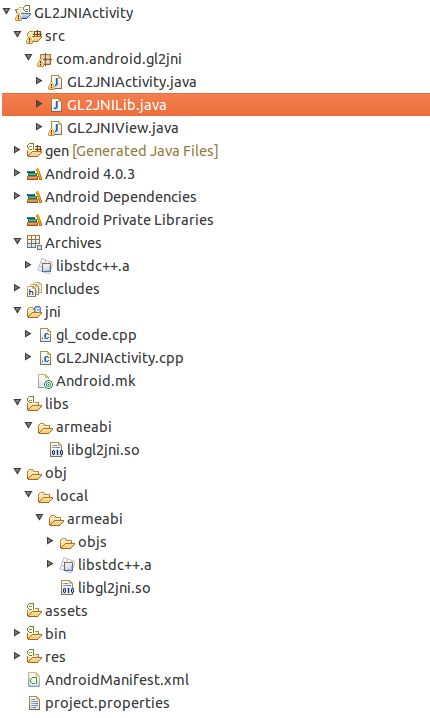
定位到ndk的目录,samples -> hello-gl2,加载就可以了。加载好之后目录的结构是像这样的:
Java的代码主要aom.android.gl2jni目录下面,C++的代码主要就在jni目录,obj目录是ndk编译产生的一些文件,libs下面是ndk交叉编译出的各个版本cpu所使用的库版本。
运行结果非常简单,中间一个三角形,背景从白到黑不断变换。
代码分析
首先来看下java的代码
GL2JNILib.java
public class GL2JNILib {
static {
System.loadLibrary("gl2jni");
}
/**
* @param width the current view width
* @param height the current view height
*/
public static native void init(int width, int height);
public static native void step();
}
这个类作为Java和C++的桥,用System.loadLibrary()方法来加载C++的库,接着声明一些C++实现好的一些静态公有方法。算是一种小小的封装吧。
GL2JNIView.java
class GL2JNIView extends GLSurfaceView {
private static String TAG = "GL2JNIView";
private static final boolean DEBUG = false;
public GL2JNIView(Context context) {
super(context);
init(false, 0, 0);
}
public GL2JNIView(Context context, boolean translucent, int depth, int stencil) {
super(context);
init(translucent, depth, stencil);
}
private void init(boolean translucent, int depth, int stencil) {
/* By default, GLSurfaceView() creates a RGB_565 opaque surface.
* If we want a translucent one, we should change the surface's
* format here, using PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT for GL Surfaces
* is interpreted as any 32-bit surface with alpha by SurfaceFlinger.
*/
if (translucent) {
this.getHolder().setFormat(PixelFormat.TRANSLUCENT);
}
/* Setup the context factory for 2.0 rendering.
* See ContextFactory class definition below
*/
setEGLContextFactory(new ContextFactory());
/* We need to choose an EGLConfig that matches the format of
* our surface exactly. This is going to be done in our
* custom config chooser. See ConfigChooser class definition
* below.
*/
setEGLConfigChooser( translucent ?
new ConfigChooser(8, 8, 8, 8, depth, stencil) :
new ConfigChooser(5, 6, 5, 0, depth, stencil) );
/* Set the renderer responsible for frame rendering */
setRenderer(new Renderer());
}
private static class ContextFactory implements GLSurfaceView.EGLContextFactory {
private static int EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION = 0x3098;
public EGLContext createContext(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLConfig eglConfig) {
Log.w(TAG, "creating OpenGL ES 2.0 context");
checkEglError("Before eglCreateContext", egl);
int[] attrib_list = {EGL_CONTEXT_CLIENT_VERSION, 2, EGL10.EGL_NONE };
EGLContext context = egl.eglCreateContext(display, eglConfig, EGL10.EGL_NO_CONTEXT, attrib_list);
checkEglError("After eglCreateContext", egl);
return context;
}
public void destroyContext(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display, EGLContext context) {
egl.eglDestroyContext(display, context);
}
}
private static void checkEglError(String prompt, EGL10 egl) {
int error;
while ((error = egl.eglGetError()) != EGL10.EGL_SUCCESS) {
Log.e(TAG, String.format("%s: EGL error: 0x%x", prompt, error));
}
}
private static class ConfigChooser implements GLSurfaceView.EGLConfigChooser {
public ConfigChooser(int r, int g, int b, int a, int depth, int stencil) {
mRedSize = r;
mGreenSize = g;
mBlueSize = b;
mAlphaSize = a;
mDepthSize = depth;
mStencilSize = stencil;
}
/* This EGL config specification is used to specify 2.0 rendering.
* We use a minimum size of 4 bits for red/green/blue, but will
* perform actual matching in chooseConfig() below.
*/
private static int EGL_OPENGL_ES2_BIT = 4;
private static int[] s_configAttribs2 =
{
EGL10.EGL_RED_SIZE, 4,
EGL10.EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 4,
EGL10.EGL_BLUE_SIZE, 4,
EGL10.EGL_RENDERABLE_TYPE, EGL_OPENGL_ES2_BIT,
EGL10.EGL_NONE
};
public EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display) {
/* Get the number of minimally matching EGL configurations
*/
int[] num_config = new int[1];
egl.eglChooseConfig(display, s_configAttribs2, null, 0, num_config);
int numConfigs = num_config[0];
if (numConfigs <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No configs match configSpec");
}
/* Allocate then read the array of minimally matching EGL configs
*/
EGLConfig[] configs = new EGLConfig[numConfigs];
egl.eglChooseConfig(display, s_configAttribs2, configs, numConfigs, num_config);
if (DEBUG) {
printConfigs(egl, display, configs);
}
/* Now return the "best" one
*/
return chooseConfig(egl, display, configs);
}
public EGLConfig chooseConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display,
EGLConfig[] configs) {
for(EGLConfig config : configs) {
int d = findConfigAttrib(egl, display, config,
EGL10.EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, 0);
int s = findConfigAttrib(egl, display, config,
EGL10.EGL_STENCIL_SIZE, 0);
// We need at least mDepthSize and mStencilSize bits
if (d < mDepthSize || s < mStencilSize)
continue;
// We want an *exact* match for red/green/blue/alpha
int r = findConfigAttrib(egl, display, config,
EGL10.EGL_RED_SIZE, 0);
int g = findConfigAttrib(egl, display, config,
EGL10.EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 0);
int b = findConfigAttrib(egl, display, config,
EGL10.EGL_BLUE_SIZE, 0);
int a = findConfigAttrib(egl, display, config,
EGL10.EGL_ALPHA_SIZE, 0);
if (r == mRedSize && g == mGreenSize && b == mBlueSize && a == mAlphaSize)
return config;
}
return null;
}
private int findConfigAttrib(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display,
EGLConfig config, int attribute, int defaultValue) {
if (egl.eglGetConfigAttrib(display, config, attribute, mValue)) {
return mValue[0];
}
return defaultValue;
}
private void printConfigs(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display,
EGLConfig[] configs) {
int numConfigs = configs.length;
Log.w(TAG, String.format("%d configurations", numConfigs));
for (int i = 0; i < numConfigs; i++) {
Log.w(TAG, String.format("Configuration %d:\n", i));
printConfig(egl, display, configs[i]);
}
}
private void printConfig(EGL10 egl, EGLDisplay display,
EGLConfig config) {
int[] attributes = {
EGL10.EGL_BUFFER_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_ALPHA_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_BLUE_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_GREEN_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_RED_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_DEPTH_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_STENCIL_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_CONFIG_CAVEAT,
EGL10.EGL_CONFIG_ID,
EGL10.EGL_LEVEL,
EGL10.EGL_MAX_PBUFFER_HEIGHT,
EGL10.EGL_MAX_PBUFFER_PIXELS,
EGL10.EGL_MAX_PBUFFER_WIDTH,
EGL10.EGL_NATIVE_RENDERABLE,
EGL10.EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_ID,
EGL10.EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_TYPE,
0x3030, // EGL10.EGL_PRESERVED_RESOURCES,
EGL10.EGL_SAMPLES,
EGL10.EGL_SAMPLE_BUFFERS,
EGL10.EGL_SURFACE_TYPE,
EGL10.EGL_TRANSPARENT_TYPE,
EGL10.EGL_TRANSPARENT_RED_VALUE,
EGL10.EGL_TRANSPARENT_GREEN_VALUE,
EGL10.EGL_TRANSPARENT_BLUE_VALUE,
0x3039, // EGL10.EGL_BIND_TO_TEXTURE_RGB,
0x303A, // EGL10.EGL_BIND_TO_TEXTURE_RGBA,
0x303B, // EGL10.EGL_MIN_SWAP_INTERVAL,
0x303C, // EGL10.EGL_MAX_SWAP_INTERVAL,
EGL10.EGL_LUMINANCE_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_ALPHA_MASK_SIZE,
EGL10.EGL_COLOR_BUFFER_TYPE,
EGL10.EGL_RENDERABLE_TYPE,
0x3042 // EGL10.EGL_CONFORMANT
};
String[] names = {
"EGL_BUFFER_SIZE",
"EGL_ALPHA_SIZE",
"EGL_BLUE_SIZE",
"EGL_GREEN_SIZE",
"EGL_RED_SIZE",
"EGL_DEPTH_SIZE",
"EGL_STENCIL_SIZE",
"EGL_CONFIG_CAVEAT",
"EGL_CONFIG_ID",
"EGL_LEVEL",
"EGL_MAX_PBUFFER_HEIGHT",
"EGL_MAX_PBUFFER_PIXELS",
"EGL_MAX_PBUFFER_WIDTH",
"EGL_NATIVE_RENDERABLE",
"EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_ID",
"EGL_NATIVE_VISUAL_TYPE",
"EGL_PRESERVED_RESOURCES",
"EGL_SAMPLES",
"EGL_SAMPLE_BUFFERS",
"EGL_SURFACE_TYPE",
"EGL_TRANSPARENT_TYPE",
"EGL_TRANSPARENT_RED_VALUE",
"EGL_TRANSPARENT_GREEN_VALUE",
"EGL_TRANSPARENT_BLUE_VALUE",
"EGL_BIND_TO_TEXTURE_RGB",
"EGL_BIND_TO_TEXTURE_RGBA",
"EGL_MIN_SWAP_INTERVAL",
"EGL_MAX_SWAP_INTERVAL",
"EGL_LUMINANCE_SIZE",
"EGL_ALPHA_MASK_SIZE",
"EGL_COLOR_BUFFER_TYPE",
"EGL_RENDERABLE_TYPE",
"EGL_CONFORMANT"
};
int[] value = new int[1];
for (int i = 0; i < attributes.length; i++) {
int attribute = attributes[i];
String name = names[i];
if ( egl.eglGetConfigAttrib(display, config, attribute, value)) {
Log.w(TAG, String.format(" %s: %d\n", name, value[0]));
} else {
// Log.w(TAG, String.format(" %s: failed\n", name));
while (egl.eglGetError() != EGL10.EGL_SUCCESS);
}
}
}
// Subclasses can adjust these values:
protected int mRedSize;
protected int mGreenSize;
protected int mBlueSize;
protected int mAlphaSize;
protected int mDepthSize;
protected int mStencilSize;
private int[] mValue = new int[1];
}
private static class Renderer implements GLSurfaceView.Renderer {
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 gl) {
GL2JNILib.step();
}
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
GL2JNILib.init(width, height);
}
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 gl, EGLConfig config) {
// Do nothing.
}
}
}这个类自定义了一个SurfaceView,作为Activity的content,定义了一个Renderer用于渲染内容,分别实现了Render的onDrawFrame和onSurfaceChanged方法,这里就直接调用GL2JNILib的静态共有方法了。
还定义了两个类,一个ContextFactory,用与生成OpenGL的Context。
一个ConfigChooser,用于选定支持es 2.0 的EGLConfig。
感觉这几个类分开写一下会更清晰一些。
GL2JNIActivity.java
public class GL2JNIActivity extends Activity {
GL2JNIView mView;
@Override protected void onCreate(Bundle icicle) {
super.onCreate(icicle);
mView = new GL2JNIView(getApplication());
setContentView(mView);
}
@Override protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
mView.onPause();
}
@Override protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mView.onResume();
}
}
JNI方面,主要看gl_code.cpp就好了。
// OpenGL ES 2.0 code
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define LOG_TAG "libgl2jni"
#define LOGI(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,LOG_TAG,__VA_ARGS__)
#define LOGE(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,LOG_TAG,__VA_ARGS__)
static void printGLString(const char *name, GLenum s) {
const char *v = (const char *) glGetString(s);
LOGI("GL %s = %s\n", name, v);
}
static void checkGlError(const char* op) {
for (GLint error = glGetError(); error; error
= glGetError()) {
LOGI("after %s() glError (0x%x)\n", op, error);
}
}
static const char gVertexShader[] =
"attribute vec4 vPosition;\n"
"void main() {\n"
" gl_Position = vPosition;\n"
"}\n";
static const char gFragmentShader[] =
"precision mediump float;\n"
"void main() {\n"
" gl_FragColor = vec4(0.0, 1.0, 0.0, 1.0);\n"
"}\n";
GLuint loadShader(GLenum shaderType, const char* pSource) {
GLuint shader = glCreateShader(shaderType);
if (shader) {
glShaderSource(shader, 1, &pSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(shader);
GLint compiled = 0;
glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &compiled);
if (!compiled) {
GLint infoLen = 0;
glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &infoLen);
if (infoLen) {
char* buf = (char*) malloc(infoLen);
if (buf) {
glGetShaderInfoLog(shader, infoLen, NULL, buf);
LOGE("Could not compile shader %d:\n%s\n",
shaderType, buf);
free(buf);
}
glDeleteShader(shader);
shader = 0;
}
}
}
return shader;
}
GLuint createProgram(const char* pVertexSource, const char* pFragmentSource) {
GLuint vertexShader = loadShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER, pVertexSource);
if (!vertexShader) {
return 0;
}
GLuint pixelShader = loadShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER, pFragmentSource);
if (!pixelShader) {
return 0;
}
GLuint program = glCreateProgram();
if (program) {
glAttachShader(program, vertexShader);
checkGlError("glAttachShader");
glAttachShader(program, pixelShader);
checkGlError("glAttachShader");
glLinkProgram(program);
GLint linkStatus = GL_FALSE;
glGetProgramiv(program, GL_LINK_STATUS, &linkStatus);
if (linkStatus != GL_TRUE) {
GLint bufLength = 0;
glGetProgramiv(program, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, &bufLength);
if (bufLength) {
char* buf = (char*) malloc(bufLength);
if (buf) {
glGetProgramInfoLog(program, bufLength, NULL, buf);
LOGE("Could not link program:\n%s\n", buf);
free(buf);
}
}
glDeleteProgram(program);
program = 0;
}
}
return program;
}
GLuint gProgram;
GLuint gvPositionHandle;
bool setupGraphics(int w, int h) {
printGLString("Version", GL_VERSION);
printGLString("Vendor", GL_VENDOR);
printGLString("Renderer", GL_RENDERER);
printGLString("Extensions", GL_EXTENSIONS);
LOGI("setupGraphics(%d, %d)", w, h);
gProgram = createProgram(gVertexShader, gFragmentShader);
if (!gProgram) {
LOGE("Could not create program.");
return false;
}
gvPositionHandle = glGetAttribLocation(gProgram, "vPosition");
checkGlError("glGetAttribLocation");
LOGI("glGetAttribLocation(\"vPosition\") = %d\n",
gvPositionHandle);
glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
checkGlError("glViewport");
return true;
}
const GLfloat gTriangleVertices[] = { 0.0f, 0.5f, -0.5f, -0.5f,
0.5f, -0.5f };
void renderFrame() {
static float grey;
grey += 0.01f;
if (grey > 1.0f) {
grey = 0.0f;
}
glClearColor(grey, grey, grey, 1.0f);
checkGlError("glClearColor");
glClear( GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
checkGlError("glClear");
glUseProgram(gProgram);
checkGlError("glUseProgram");
glVertexAttribPointer(gvPositionHandle, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0, gTriangleVertices);
checkGlError("glVertexAttribPointer");
glEnableVertexAttribArray(gvPositionHandle);
checkGlError("glEnableVertexAttribArray");
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 3);
checkGlError("glDrawArrays");
}
extern "C" {
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_android_gl2jni_GL2JNILib_init(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj, jint width, jint height);
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_android_gl2jni_GL2JNILib_step(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj);
};
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_android_gl2jni_GL2JNILib_init(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj, jint width, jint height)
{
setupGraphics(width, height);
}
JNIEXPORT void JNICALL Java_com_android_gl2jni_GL2JNILib_step(JNIEnv * env, jobject obj)
{
renderFrame();
}
首先说几个C++的几个关键字的用法。
全局static变量与static函数
在全局变量之前加上关键字static,全局变量就被定义成为一个全局静态变量。
1)内存中的位置:静态存储区(静态存储区在整个程序运行期间都存在)
2)初始化:未经初始化的全局静态变量会被程序自动初始化为0(自动对象的值是任意的,除非他被显示初始化)
3)作用域:全局静态变量在声明他的文件之外是不可见的。准确地讲从定义之处开始到文件结尾。
好处:
定义全局静态变量的好处:
1)不会被其他文件所访问,修改
2)其他文件中可以使用相同名字的变量,不会发生冲突。
静态函数
在函数的返回类型前加上关键字static,函数就被定义成为静态函数。
函数的定义和声明默认情况下是extern的,但静态函数只是在声明他的文件当中可见,不能被其他文件所用。
定义静态函数的好处:
<1> 其他文件中可以定义相同名字的函数,不会发生冲突
<2> 静态函数不能被其他文件所用。
extern "C" 的用法
被extern "C"修饰的变量和函数是按照C语言方式编译和连接的;实现C++与C及其它语言的混合编程。
而在C语言的头文件中,对其外部函数只能指定为extern类型,C语言中不支持extern "C"声明,在.c文件中包含了extern "C"时会出现编译语法错误。
如果C++调用一个C语言编写的.DLL时,当包括.DLL的头文件或声明接口函数时,应加extern "C" { }。
在这里用 extern "C"框住两个函数,主要是让Jni来调用它们。
代码分析
首先是在c++代码中打tag的方法。
#include
#define LOG_TAG "libgl2jni"
#define LOGI(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_INFO,LOG_TAG,__VA_ARGS__)
#define LOGE(...) __android_log_print(ANDROID_LOG_ERROR,LOG_TAG,__VA_ARGS__)
static void printGLString(const char *name, GLenum s) {
const char *v = (const char *) glGetString(s);
LOGI("GL %s = %s\n", name, v);
} 首先先是包含头log.h文件,
接下来是将自带的log函数用用预定义的方法简化一下。
printGLString等于是又封装了一层,同时可以打印gl的信息。
checkGlError用于检查OpenGL内部发生的错误,OpenGL在运行过程中所产生的错误都可以用glGetError来获得。
vertext shader和fregment shader的内容还有三角形的顶点位置都用已经在程序中写死。如果想加载外部的shader的话,要么在ndk中实现文件的读写,要么就在用java读取,然后传到C里面来处理。
shader相关的流水线可以参考 - GLSL入门
setupGraphics用于shader的一些初始化,还有context的一些初始化。
renderframe非常简单,就是渲染三角形,改变背景颜色,不断刷新。
打完收工