作者:黄湘龙
研究HTTPS的双向认证实现与原理,踩了不少坑,终于整个流程都跑通了,现在总结出一篇文档来,把一些心得,特别是容易踩坑的地方记录下来。
1.原理
双向认证,顾名思义,客户端和服务器端都需要验证对方的身份,在建立Https连接的过程中,握手的流程比单向认证多了几步。单向认证的过程,客户端从服务器端下载服务器端公钥证书进行验证,然后建立安全通信通道。双向通信流程,客户端除了需要从服务器端下载服务器的公钥证书进行验证外,还需要把客户端的公钥证书上传到服务器端给服务器端进行验证,等双方都认证通过了,才开始建立安全通信通道进行数据传输。
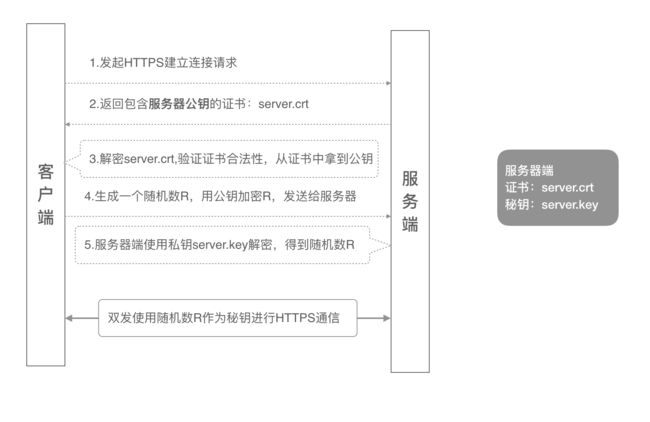
1.1 单向认证流程
单向认证流程中,服务器端保存着公钥证书和私钥两个文件,整个握手过程如下:
- 客户端发起建立HTTPS连接请求,将SSL协议版本的信息发送给服务器端;
- 服务器端将本机的公钥证书(server.crt)发送给客户端;
- 客户端读取公钥证书(server.crt),取出了服务端公钥;
- 客户端生成一个随机数(密钥R),用刚才得到的服务器公钥去加密这个随机数形成密文,发送给服务端;
- 服务端用自己的私钥(server.key)去解密这个密文,得到了密钥R
- 服务端和客户端在后续通讯过程中就使用这个密钥R进行通信了。
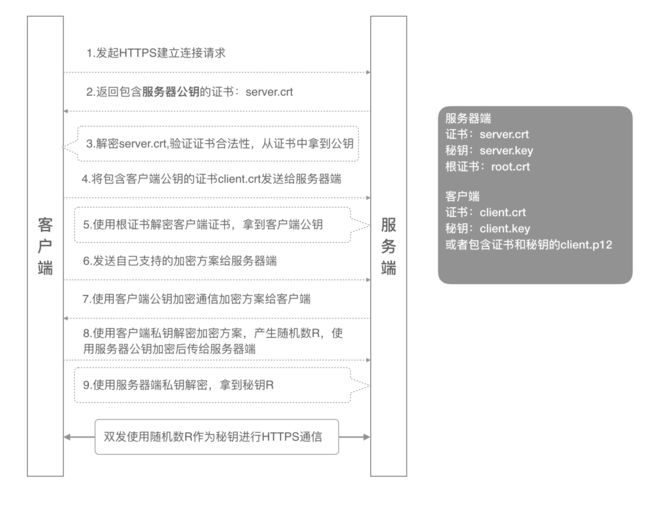
1.2 双向认证流程
- 客户端发起建立HTTPS连接请求,将SSL协议版本的信息发送给服务端;
- 服务器端将本机的公钥证书(server.crt)发送给客户端;
- 客户端读取公钥证书(server.crt),取出了服务端公钥;
- 客户端将客户端公钥证书(client.crt)发送给服务器端;
- 服务器端使用根证书(root.crt)解密客户端公钥证书,拿到客户端公钥;
- 客户端发送自己支持的加密方案给服务器端;
- 服务器端根据自己和客户端的能力,选择一个双方都能接受的加密方案,使用客户端的公钥加密8. 后发送给客户端;
- 客户端使用自己的私钥解密加密方案,生成一个随机数R,使用服务器公钥加密后传给服务器端;
- 服务端用自己的私钥去解密这个密文,得到了密钥R
- 服务端和客户端在后续通讯过程中就使用这个密钥R进行通信了。
2. 证书生成
从上一章内容中,我们可以总结出来,如果要把整个双向认证的流程跑通,最终需要六个证书文件:
- 服务器端公钥证书:server.crt
- 服务器端私钥文件:server.key
- 根证书:root.crt
- 客户端公钥证书:client.crt
- 客户端私钥文件:client.key
- 客户端集成证书(包括公钥和私钥,用于浏览器访问场景):client.p12
生成这一些列证书之前,我们需要先生成一个CA根证书,然后由这个CA根证书颁发服务器公钥证书和客户端公钥证书。为了验证根证书颁发与验证客户端证书这个逻辑,我们使用根证书办法两套不同的客户端证书,然后同时用两个客户端证书来发送请求,看服务器端是否都能识别。下面是证书生成的内在逻辑示意图:
我们可以全程使用openssl来生成一些列的自签名证书,自签名证书没有听过证书机构的认证,很多浏览器会认为不安全,但我们用来实验是足够的。需要在本机安装了openssl后才能继续本章的实验。
2.1生成自签名根证书
(1)创建根证书私钥:
openssl genrsa -out root.key 1024
(2)创建根证书请求文件:
openssl req -new -out root.csr -key root.key
后续参数请自行填写,下面是一个例子:
Country Name (2 letter code) [XX]:cn
State or Province Name (full name) []:bj
Locality Name (eg, city) [Default City]:bj
Organization Name (eg, company) [Default Company Ltd]:alibaba
Organizational Unit Name (eg, section) []:test
Common Name (eg, your name or your servers hostname) []:root
Email Address []:a.alibaba.com
A challenge password []:
An optional company name []:
(3)创建根证书:
openssl x509 -req -in root.csr -out root.crt -signkey root.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
在创建证书请求文件的时候需要注意三点,下面生成服务器请求文件和客户端请求文件均要注意这三点:
根证书的Common Name填写root就可以,所有客户端和服务器端的证书这个字段需要填写域名,一定要注意的是,根证书的这个字段和客户端证书、服务器端证书不能一样;
其他所有字段的填写,根证书、服务器端证书、客户端证书需保持一致
最后的密码可以直接回车跳过。
经过上面三个命令行,我们最终可以得到一个签名有效期为10年的根证书root.crt,后面我们可以用这个根证书去颁发服务器证书和客户端证书。
2.2 生成自签名服务器端证书
(1)生成服务器端证书私钥:
openssl genrsa -out server.key 1024
(2) 生成服务器证书请求文件,过程和注意事项参考根证书,本节不详述:
openssl req -new -out server.csr -key server.key
(3) 生成服务器端公钥证书
openssl x509 -req -in server.csr -out server.crt -signkey server.key -CA root.crt -CAkey root.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
经过上面的三个命令,我们得到:
- server.key:服务器端的秘钥文件
- server.crt:有效期十年的服务器端公钥证书,使用根证书和服务器端私钥文件一起生成
2.3 生成自签名客户端证书
(1)生成客户端证书秘钥:
openssl genrsa -out client.key 1024
openssl genrsa -out client2.key 1024
(2) 生成客户端证书请求文件,过程和注意事项参考根证书,本节不详述:
openssl req -new -out client.csr -key client.key
openssl req -new -out client2.csr -key client2.key
(3) 生客户端证书
openssl x509 -req -in client.csr -out client.crt -signkey client.key -CA root.crt -CAkey root.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
openssl x509 -req -in client2.csr -out client2.crt -signkey client2.key -CA root.crt -CAkey root.key -CAcreateserial -days 3650
(4) 生客户端p12格式证书,需要输入一个密码,选一个好记的,比如123456
openssl pkcs12 -export -clcerts -in client.crt -inkey client.key -out client.p12
openssl pkcs12 -export -clcerts -in client2.crt -inkey client2.key -out client2.p12
重复使用上面的三个命令,我们得到两套客户端证书:
client.key/client2.key:客户端的私钥文件
client.crt/client2.key:有效期十年的客户端证书,使用根证书和客户端私钥一起生成
client.p12/client2.p12:客户端p12格式,这个证书文件包含客户端的公钥和私钥,主要用来给浏览器访问使用
3.Nginx配置
有了上面的一些列证书,我们可以在Nginx服务器上配置双向认证的HTTPS服务了,具体配置方式如下:
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name www.yourdomain.com;
ssl on;
ssl_certificate /data/sslKey/server.crt; #server公钥证书
ssl_certificate_key /data/sslKey/server.key; #server私钥
ssl_client_certificate /data/sslKey/root.crt; #根证书,可以验证所有它颁发的客户端证书
ssl_verify_client on; #开启客户端证书验证
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
具体就是将服务器端的两个证书文件(server.crt/server.key)和根证书文件(root.crt)的路径配置到nginx的server节点配置中,并且把ssl_verify_client这个参数设置为on。
有一点需要注意的就是,如果客户端证书不是由根证书直接颁发的,配置中还需要加一个配置:ssl_verify_depth 1;
配置完成后,执行nginx -s reload重新加载下就生效了。
4.使用curl作为客户端调用验证
使用curl加上证书路径,可以直接测试Nginx的HTTPS双向认证是否配置成功。下面我们测试三个用例:
- 使用client.crt/client.key这一套客户端证书来调用服务器端
- 使用client.crt2/client2.key这一套客户端证书来调用服务器端
- 不使用证书来调用服务器端
下面是三个用例的测试结果:
- 带证书的成功调用:
#--cert指定客户端公钥证书的路径
#--key指定客户端私钥文件的路径
#-k不校验证书的合法性,因为我们用的是自签名证书,所以需要加这个参数
#可以使用-v来观察具体的SSL握手过程
curl --cert ./client.crt --key ./client.key https://integration-fred2.fredhuang.com -k -v
* Rebuilt URL to: https://47.93.245.203/
* Trying 47.93.245.203...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to 47.93.245.203 (47.93.245.203) port 443 (#0)
* ALPN, offering h2
* ALPN, offering http/1.1
* Cipher selection: ALL:!EXPORT:!EXPORT40:!EXPORT56:!aNULL:!LOW:!RC4:@STRENGTH
* successfully set certificate verify locations:
* CAfile: /etc/ssl/cert.pem
CApath: none
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server hello (2):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server key exchange (12):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Request CERT (13):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Server finished (14):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Certificate (11):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Client key exchange (16):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, CERT verify (15):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (OUT), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS change cipher, Client hello (1):
* TLSv1.2 (IN), TLS handshake, Finished (20):
* SSL connection using TLSv1.2 / ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
* ALPN, server accepted to use http/1.1
* Server certificate:
* subject: C=CN; ST=BJ; L=BJ; O=Alibaba; OU=Test; CN=integration-fred2.fredhuang.com; [email protected]
* start date: Nov 2 01:01:34 2019 GMT
* expire date: Oct 30 01:01:34 2029 GMT
* issuer: C=CN; ST=BJ; L=BJ; O=Alibaba; OU=Test; CN=root; [email protected]
* SSL certificate verify result: unable to get local issuer certificate (20), continuing anyway.
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> host:integration-fred2.fredhuang.com
> User-Agent: curl/7.54.0
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< Server: nginx/1.17.5
< Date: Sat, 02 Nov 2019 02:39:43 GMT
< Content-Type: text/html
< Content-Length: 612
< Last-Modified: Wed, 30 Oct 2019 11:29:45 GMT
< Connection: keep-alive
< ETag: "5db97429-264"
< Accept-Ranges: bytes
<
Welcome to nginx!
Welcome to nginx!
If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.
For online documentation and support please refer to
nginx.org.
Commercial support is available at
nginx.com.
Thank you for using nginx.
* Connection #0 to host 47.93.245.203 left intact
- 使用client2.crt/client2.key这一套客户端证书来调用服务器端
curl --cert ./client2.crt --key ./client2.key https://integration-fred2.fredhuang.com -k
Welcome to nginx!
Welcome to nginx!
If you see this page, the nginx web server is successfully installed and
working. Further configuration is required.
For online documentation and support please refer to
nginx.org.
Commercial support is available at
nginx.com.
Thank you for using nginx.
- 不带证书的调用
curl https://integration-fred2.fredhuang.com -k
400 No required SSL certificate was sent
400 Bad Request
No required SSL certificate was sent
nginx/1.17.5
三个用例都符合预期,从第一个测试日志中,我们可以看到,整个通信过程较长,客户端验证服务器端的证书,客户端也将自己的证书上传到服务器端进行验证。使用根证书颁发的两个客户端证书都可以正常发起双向HTTPS认证的调用。没有带客户端证书的调用会被服务器端拒绝服务。
5.使用Java调用
由于使用的是自签名证书,使用ApacheHttpClient去调用的话,需要将服务器证书加入可信任证书库中,才能成功调用,也可以在代码中简单忽略证书。
cd $JAVA_HOME
sudo ./bin/keytool -import -alias ttt -keystore cacerts -file /Users/fred/temp/cert5/server.crt
将服务器端公钥证书设置为可信证书后,使用以下代码可以直接发起带客户端证书的HTTPS请求:
import org.apache.http.HttpEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.conn.ssl.SSLConnectionSocketFactory;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.ssl.SSLContexts;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import javax.net.ssl.SSLContext;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.security.KeyStore;
public class HttpClientWithClientCert {
private final static String PFX_PATH = "/Users/fred/temp/cert5/client.p12"; //客户端证书路径
private final static String PFX_PWD = "123456"; //客户端证书密码
public static String sslRequestGet(String url) throws Exception {
KeyStore keyStore = KeyStore.getInstance("PKCS12");
InputStream instream = new FileInputStream(new File(PFX_PATH));
try {
keyStore.load(instream, PFX_PWD.toCharArray());
} finally {
instream.close();
}
SSLContext sslcontext = SSLContexts.custom().loadKeyMaterial(keyStore, PFX_PWD.toCharArray()).build();
SSLConnectionSocketFactory sslsf = new SSLConnectionSocketFactory(sslcontext
, new String[] { "TLSv1" } // supportedProtocols ,这里可以按需要设置
, null // supportedCipherSuites
, SSLConnectionSocketFactory.getDefaultHostnameVerifier());
CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.custom().setSSLSocketFactory(sslsf).build();
try {
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet(url);
//httpget.addHeader("host", "integration-fred2.fredhuang.com");// 设置一些heander等
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpclient.execute(httpget);
try {
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
String jsonStr = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");//返回结果
EntityUtils.consume(entity);
return jsonStr;
} finally {
response.close();
}
} finally {
httpclient.close();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(System.getProperty("java.home"));
System.out.println(sslRequestGet("https://integration-fred2.fredhuang.com"));
}
}
6. 总结
HTTPS双向认证方式通信在一些安全级别较高的场景非常有用,拥有合法证书的客户端才能正常访问业务。实现这个场景需要以下几步:
- 生成根公钥证书和私钥文件(root.crt/root.key);
- 使用根证书和根证书私钥(root.crt/root.key)配合服务器端私钥颁发服务器端证书(server.crt);
- 使用根证书和根证书私钥(root.crt/root.key)配合客户端私钥颁发客户端证书(server.crt);
- 将根证书(root.crt)、服务器端证书(server.crt)、服务器端秘钥(server.key)配置到Nginx的Server配置中;
- 客户端使用客户端私钥和根证书颁发的客户端证书(client.crt)正常访问业务。
根证书可以任意颁发客户端证书并给业务方使用,为了安全起见,需要注意颁发的证书的有效期。
魔鬼藏在细节,有两个细节再次重点强调下:
- 根证书的Common Name填写root就可以,所有客户端和服务器端的证书这个字段需要填写域名,一定要注意的是,根证书的这个字段和客户端证书、服务器端证书不能一样;
- Nginx的ssl_client_certificate需要配置根证书root.crt,而不是客户端证书;