以太坊虚拟机原理及源代码深入挖掘
-
一. 概述
EVM为以太坊虚拟机,以太坊底层通过EVM支持智能合约的执行和调用。调用智能合约时根据合约的地址获取合约代码,生成具体的执行环境,然后将代码载入到EVM虚拟机中运行。通常目前开发智能合约的高级语言为Solidity,在利用solidity实现智能合约逻辑后,通过编译器编译成元数据(字节码)最后发布到以太坊上。
-
二. 架构设计
-
1. 位宽设计
EVM机器位宽为256位,即32个字节,256位机器位宽不同于经常见到主流的32/6位机器字宽,这就标明EVM设计上将考虑一套自己的关于操作,数据,逻辑控制的指令编码。目前主流的处理器原生的支持的计算数据类型有:8bits整数,16bits整数,32bits整数,64bits整数。一般情况下宽字节的计算将更加的快一些,因为它可能包含更多的指令被一次性加载到pc寄存器中,同时伴有内存访问次数的减少。从两个整形数相加来对比具体的操作时间消耗。
1. 32bits相加的X86的汇编代码
-
mov eax, dword [9876ABCD] //将地址9876ABCD中的32位数据放入eax数据寄存器
-
add eax, dword [1234DCBA] //将1234DCBA地址指向32位数和eax相加,结果保存在eax中
2. 64bits相加的X86汇编代码
-
mov rax, qword [123456789ABCDEF1] //将地址指向的64位数据放入64位寄存器
-
add rax, qword [1020304050607080] //计算相加的结果并将结果放入到64位寄存器中
3. 64bits机器上完成256bits的加法汇编代码
-
mov rax, qword [9876ABCD]
-
add qword [1234DCBA], rax
-
mov rax, qword [9876ABCD+8]
-
adc qword [1234DCBA+8], rax//这里应用adc带进位的加法指令,影响进位标记CF
-
mov rax, qword [9876ABCD+16]
-
adc qword [1234DCBA+16], rax
-
mov rax, qword [9876ABCD+24]
-
adc qword [1234DCBA+24], rax
从以上汇编指令可以看出256位操作要比系统原生支持的要复杂的多,从时间上考虑采用256位这样的字节宽度,实际的收益并不大。空间上,由上面的汇编操作可以看出,如果直接对地址进行操作似乎是一种快速的方式,并减少了操作数,进而操作码也有所减少,相应的智能合约的字节流大小就会小很多,gas花费也会有所下降。但是从另外一个层面来讲,支持宽字节的数据类型势必会造成在处理低字节宽度的数据时候带来存储上的浪费。从时间和空间角度来看,仅支持256字节宽度的选择有利有弊,EVM之所以设计为256位位宽可能是因为一下几方面的原因:
-
256位的宽度方便进行密码学方面的计算(sha256)
-
仅支持256位的比要支持其他类型的操作要少,单一,实现简单可控
-
和gas的计算相关,仅支持一种,方便计算,同时也考虑到了安全问题
-
2. 结构体模型
3. 代码结构
代码结构
.
├── analysis.go //跳转目标判定
├── common.go
├── contract.go //合约数据结构
├── contracts.go //预编译好的合约
├── errors.go
├── evm.go //执行器 对外提供一些外部接口
├── gas.go //call gas花费计算 一级指令耗费gas级别
├── gas_table.go //指令耗费计算函数表
├── gen_structlog.go
├── instructions.go //指令操作
├── interface.go
├── interpreter.go //解释器 调用核心
├── intpool.go //int值池
├── int_pool_verifier_empty.go
├── int_pool_verifier.go
├── jump_table.go //指令和指令操作(操作,花费,验证)对应表
├── logger.go //状态日志
├── memory.go //EVM 内存
├── memory_table.go //EVM 内存操作表 主要衡量操作所需内存大小
├── noop.go
├── opcodes.go //Op指令 以及一些对应关系
├── runtime
│ ├── env.go //执行环境
│ ├── fuzz.go
│ └── runtime.go //运行接口 测试使用
├── stack.go //栈
└── stack_table.go //栈验证
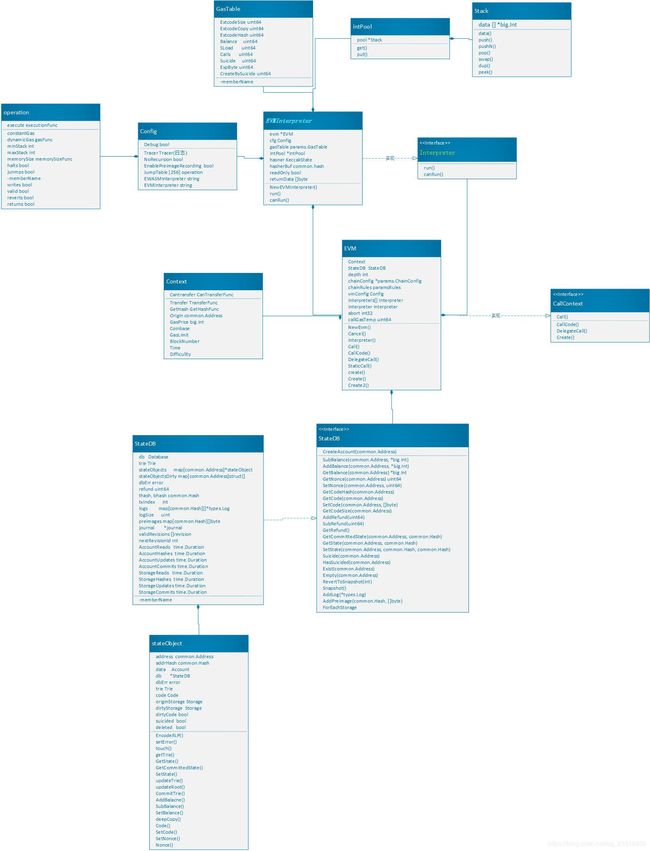
三.EVM设计
1.解释器
1.1 解释器结构体图
解释器是以太坊的虚拟机的核心,主要用来执行智能合约。从上面的UML图可以清楚的看出,以太坊智能合约解释器主要由一个接口,一个实现类和一个配置类和其他两个组件组成。以下主要介绍接口和实现类:
- Interpreter 接口
- EVMInterpreter 接口的实现
1.2 Interpreter接口
Interpreter接口中主要包括两个函数:
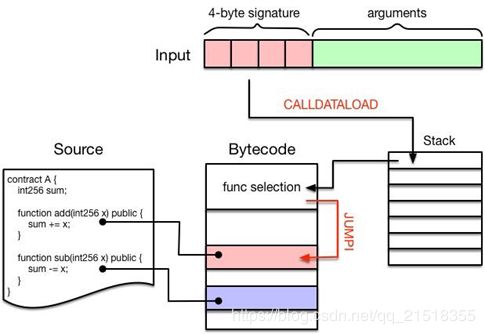
1. Run(contract *Contract, input []byte, static bool) 执行智能合约代码,参数为:智能合约对象、输入的参数,调用方式。其中智能合约调用参数(input)通常分两部分构成:
-
前面4个字节被称为“4-byte signature”,是某个函数签名的Keccak哈希值的前4个字节,作为该函数的唯一标识。
-
为调用该函数提供的参数,长度不定。
例如:部署一个智能合约A,调用A中的add(1)方法,对应的input参数为:0x87db03b700000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000000012. CanRun(code []byte) 判断当前合约代码是否能执行,暂时没有实现真正的逻辑
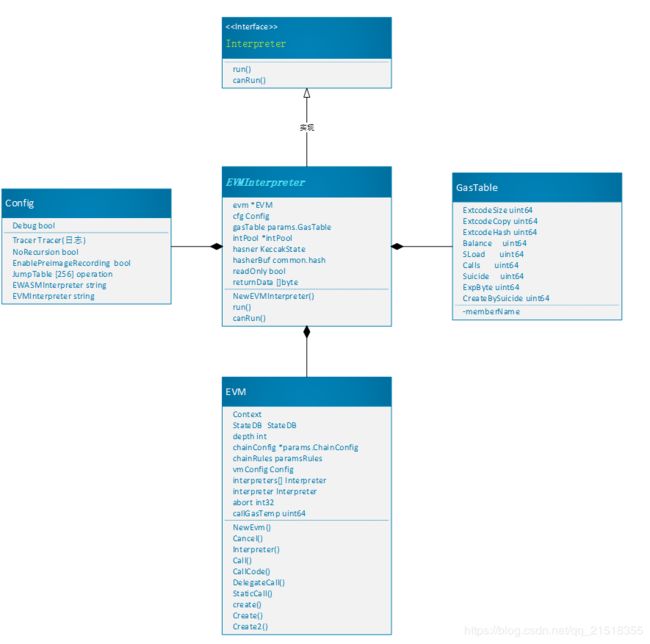
1.3 EVMInterpreter 接口的实现类
Interpreter 接口最终由EVMInterpreter结构体实现
EVMInterpreter 主要包含了四种对象,分别是: intPool、GasTable、Config、EVM:
- intPool : 主要用于回收对象(大整数),这是一个高效的优化。里面存放的是栈里的数据。
- GasTable : 记录了不同时期的需要消耗的gas值 。
- Config : 包含了 EVMInterpreter 用到的配置选项。包含日志配置及操作码的表(不同的 bytecode 对应的不同的 opcode 码)。
- EVM虚拟机 : 一个基于对象并且可以运行智能合约的必要的工具。包含了 EVM虚拟机 的上下文、创建合约及四种部署合约的方式、把数据保存到状态库的内容。
- EVMInterpreter结构体:
实现类结构体:
type EVMInterpreter struct {
evm *EVM //EVM虚拟机对象
cfg Config //当前解释器的配置文件
gasTable params.GasTable //代码执行的gas消耗
intPool *intPool//数据回收对象
hasher keccakState // 签名算法接口
hasherBuf common.Hash // 签名后的数值
readOnly bool // 合约调用方式
returnData []byte // 合约调用后的返回值
}
配置文件结构体:
type Config struct {
Debug bool //是否允许Debug 调用
Tracer Tracer // 操作码日志
NoRecursion bool // Disables call, callcode, delegate call and create
EnablePreimageRecording bool // Enables recording of SHA3/keccak preimages
JumpTable [256]operation // 当前阶段的操作码列表(Frontier,Homestead,Byzantium,Constantinople)
EWASMInterpreter string // WASM虚拟机选项
EVMInterpreter string // EVM虚拟机选项
}
EVMInterpreter Run方法:
EVM主要执行流程如下:
首先PC会从合约代码中读取一个OpCode,然后从一个JumpTable中检索出对应的operation,也就是与其相关联的函数集合。接下来会计算该操作需要消耗的油费,如果油费耗光则执行失败,返回ErrOutOfGas错误。如果油费充足,则调用execute()执行该指令,根据指令类型的不同,会分别对Stack、Memory或者StateDB进行读写操作。
调用合约函数执行流程如下:
首先通过CALLDATALOAD指令将input字段中的前“4-byte signature”压入堆栈中,然后依次跟该合约中包含的函数进行比对,如果匹配则调用JUMPI指令跳入该段代码继续执行。最后根据执行过程中的指令不同,分别对Stack、Memory或者StateDB进行读写操作。
Run方法主要部分源码解析:
func (in *EVMInterpreter) Run(contract *Contract, input []byte, readOnly bool) (ret []byte, err error) {
in.returnData = nil //返回值
var (
op OpCode // 当前操作码
mem = NewMemory() // 内存
stack = newstack() // 栈
pc = uint64(0) // 指令位置
cost uint64 //gas花费
pcCopy uint64 // debug使用
gasCopy uint64 // debug使用
logged bool // debug使用
res []byte //当前操作码执行函数的返回值
)
contract.Input = input //函数入参
for atomic.LoadInt32(&in.evm.abort) == 0 {
//获取一条指令及指令对应的操作
op = contract.GetOp(pc)
operation := in.cfg.JumpTable[op]
//valid校验
if !operation.valid {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid opcode 0x%x", int(op))
}
// 栈校验
if sLen := stack.len(); sLen < operation.minStack {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("stack underflow (%d <=> %d)", sLen, operation.minStack)
} else if sLen > operation.maxStack {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("stack limit reached %d (%d)", sLen, operation.maxStack)
}
// 扣除固定静态操作gas值
if !contract.UseGas(operation.constantGas) {
return nil, ErrOutOfGas
}
var memorySize uint64
//计算内存 按操作所需要的操作数来算
if operation.memorySize != nil {
memSize, overflow := operation.memorySize(stack)
if overflow {
return nil, errGasUintOverflow
}
if memorySize, overflow = math.SafeMul(toWordSize(memSize), 32); overflow {
return nil, errGasUintOverflow
}
}
if operation.dynamicGas != nil {
// 校验cost 调用前面提到的costfunc 计算本次操作动态cost消耗
cost, err = operation.dynamicGas(in.gasTable, in.evm, contract, stack, mem, memorySize)
if err != nil || !contract.UseGas(cost) {
return nil, ErrOutOfGas
}
}
if memorySize > 0 {
//如果本次操作需要消耗memory ,扩展memory
mem.Resize(memorySize)
}
// 执行操作
res, err = operation.execute(&pc, in, contract, mem, stack)
if verifyPool {
verifyIntegerPool(in.intPool)
}
// 如果遇到return 设置返回值
if operation.returns {
in.returnData = res
}
switch {
case err != nil:
return nil, err //报错
case operation.reverts: //出错回滚
return res, errExecutionReverted
case operation.halts:
return res, nil //停止
case !operation.jumps: //跳转
pc++
}
}
return nil, nil
}执行流程:
1. 从合约中取得第pc个指令,放⼊入当前opcode(op)中(下面简称op)
2. 从JumpTable查到op对应的操作operation
3. 验证operation的有效性
4. 验证栈空间是否足够
5. readOnly一直给它传的值是false
6. 支付gas
7. 计算多少内存可以适应operation
8. 支付动态分配内存需要gas
9. 分配内存
10. 执行operation
11. 返回结果放入返回数据的变量中
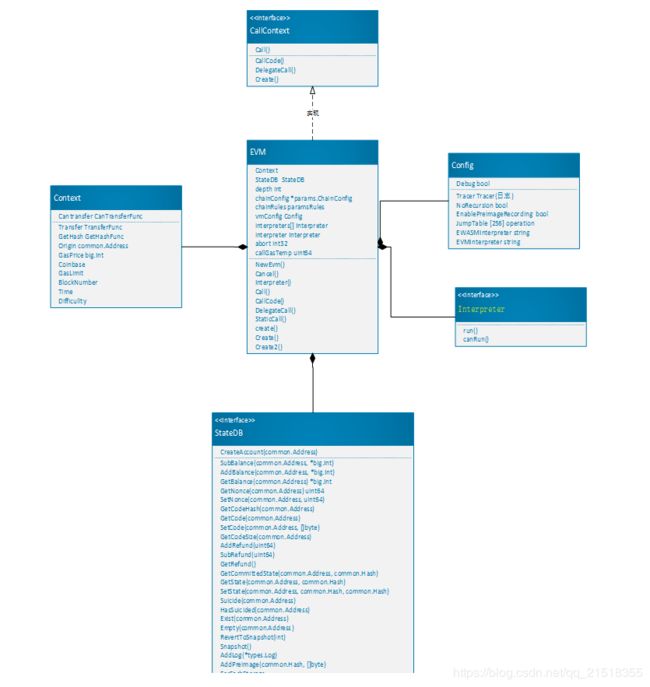
2. EVM对象
2.1 解释器结构体图
以太坊的虚拟机主要有四部分组成:
- 实现了CallContext接口,该接口内定义了创建、调用合约的四种方法(Call,CallCode,DelegateCall,Create)
- Context 合约执行的上下文
- 集成解释器接口类,调运解释器执行智能合约
- 集成StateDB接口类,操作StateDB
下面主要对虚拟机比较核心的代码进行分析:
2.2. 核心机构体
1. 虚拟机结构体
type EVM struct {
Context //上下文环境
StateDB StateDB //stateDB 函数接口
depth int //当前调用的深度
chainConfig *params.ChainConfig //当前链配置
chainRules params.Rules // 当前区块链所使用的版本
vmConfig Config //虚拟机配置
interpreters []Interpreter //解释器数组
interpreter Interpreter//当前使用的解释器
abort int32 //用于中止EVM调用操作
callGasTemp uint64 //保存当前可用的gas
}
2. Context结构体
type Context struct {
// CanTransfer returns whether the account contains
// sufficient ether to transfer the value
CanTransfer CanTransferFunc //返回账户是否有足够的ether用来转账
// Transfer transfers ether from one account to the other
Transfer TransferFunc //用来从一个账户给另一个账户转账
// GetHash returns the hash corresponding to n
GetHash GetHashFunc //用来返回入参n的对应的hash
// Message information
Origin common.Address // 用来提供Origin的信息 sender的地址
GasPrice *big.Int // 用来提供GasPrice信息
// Block information
Coinbase common.Address // Provides information for COINBASE
GasLimit uint64 // Provides information for GASLIMIT
BlockNumber *big.Int // Provides information for NUMBER
Time *big.Int // Provides information for TIME
Difficulty *big.Int // Provides information for DIFFICULTY
}
2.3. 核心函数设计
2.3.1 合约创建函数create
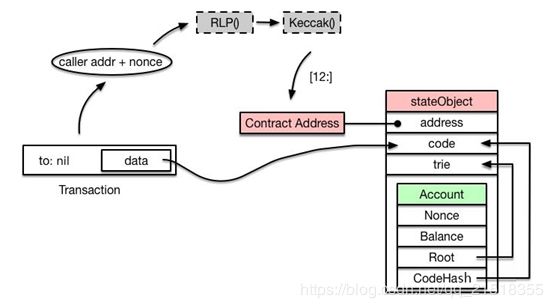
如果某一笔交易的to地址为nil,则表明该交易是用于创建智能合约的。首先需要创建合约地址,采用下面的计算公式:Keccak(RLP(call_addr, nonce))[12:]。也就是说,对交易发起人的地址和nonce进行RLP编码,再算出Keccak哈希值,取后20个字节作为该合约的地址。其次根据合约地址创建对应的stateObject,然后存储交易中包含的合约代码。该合约的所有状态变化会存储在一个storage trie中,最终以Key-Value的形式存储到StateDB中。代码一经存储则无法改变,而storage trie中的内容则是可以通过调用合约进行修改的,比如通过SSTORE指令。
源码分析:
func (evm *EVM) create(caller ContractRef, codeAndHash *codeAndHash, gas uint64, value *big.Int, address common.Address) ([]byte, common.Address, uint64, error) {
//合约调用深度检查
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, common.Address{}, gas, ErrDepth
}
//balance检查
if !evm.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, common.Address{}, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
//确保特定的地址没有合约存在
nonce := evm.StateDB.GetNonce(caller.Address())
evm.StateDB.SetNonce(caller.Address(), nonce+1)
contractHash := evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(address)
if evm.StateDB.GetNonce(address) != 0 || (contractHash != (common.Hash{}) && contractHash != emptyCodeHash) {
return nil, common.Address{}, 0, ErrContractAddressCollision
}
//创建一个StateDB的快照,以便回滚
snapshot := evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(address)//创建合约账号
if evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) {
evm.StateDB.SetNonce(address, 1)
}
//转账
evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), address, value)
//创建一个新的合约
contract := NewContract(caller, AccountRef(address), value, gas)
contract.SetCodeOptionalHash(&address, codeAndHash)
//如果是委托合约
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, address, gas, nil
}
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), address, true, codeAndHash.code, gas, value)
}
start := time.Now()
ret, err := run(evm, contract, nil, false)//执行合约
// 检查初始化生成的代码的长度不超过限制
maxCodeSizeExceeded := evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) && len(ret) > params.MaxCodeSize
//如果合同创建成功并且没有错误返回,则计算存储代码所需的GAS。
// 如果由于没有足够的GAS而导致代码不能被存储设置错误,并通过下面的错误检查条件来处理。
if err == nil && !maxCodeSizeExceeded {
createDataGas := uint64(len(ret)) * params.CreateDataGas
if contract.UseGas(createDataGas) {
evm.StateDB.SetCode(address, ret)
} else {
err = ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas
}
}
//当发生错误是回滚,但是gas不退回
if maxCodeSizeExceeded || (err != nil && (evm.ChainConfig().IsHomestead(evm.BlockNumber) || err != ErrCodeStoreOutOfGas)) {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
// Assign err if contract code size exceeds the max while the err is still empty.
if maxCodeSizeExceeded && err == nil {
err = errMaxCodeSizeExceeded
}
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, gas-contract.Gas, time.Since(start), err)
}
return ret, address, contract.Gas, err
}
执行流程:
1. 判断虚拟机EVM的调用深度,不能超过限定值,默认是1024
2. 根据 value 判断合约发布者是否有足额的以太币
3. 合约部署者caller的 nonce 加1
4. 根据 address 确保上面创建的合约地址没有被使用
5. 创建当前状态的快照,用于后结出错的回滚
6. 创建新的帐户 nonce设置为1
7. 给该合约转帐,转帐值为 value
8. 使用 caller address value gas 创建合约对象
9. 把代码和哈希值 codeAndHash 放进去
10. 运行虚拟机EVM,传⼊入参数有:evm contract input(nil)
readOnly(false)
11. 检查合约允许的最大字节码,即代码是否溢出
12. 花费gas并保存合约代码
13. 如果执行失败,回滚到快照的状态
2.3.2 合约调用函数
在以太坊合约调用一共有四种方法,分别为:
- Call
- CallCode
- StaticCall
- DelegateCall
上面四种合约调用方法中,StaticCall实际没有被调用,所以在此处不再说它,下面主要说明另外三种方法的异同之处。
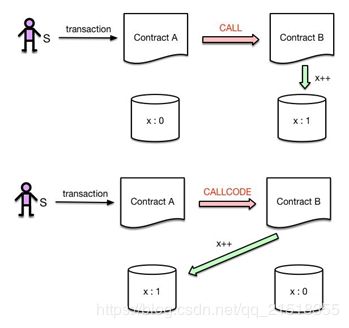
1. Call和CallCode
Call和CallCode的区别在于:代码执行的上下文环境不同。具体来说,Call修改的是被调用者的storage,而CallCode修改的是调用者的storage。
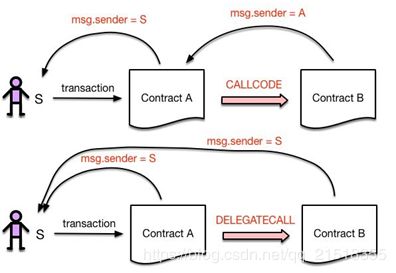
2. CallCode 和DelegateCall
CallCode和DelegateCall的区别在于:msg.sender不同。具体来说,DelegateCall会一直使用原始调用者的地址,而CallCode不会。
3. Call函数分析
Call 执行与给定的input作为参数与addr相关联的合约。处理所需的任何必要的转账操作,采取必要的步骤来创建帐户,在任意错误的情况下回滚所做的操作。
源码分析:
func (evm *EVM) Call(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
// 调用深度最多1024
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
//查看账户是否有足够钱
if !evm.Context.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
var (
to = AccountRef(addr)
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
)
if !evm.StateDB.Exist(addr) { // 查看指定地址是否存在
precompiles := PrecompiledContractsHomestead
if evm.ChainConfig().IsByzantium(evm.BlockNumber) {
precompiles = PrecompiledContractsByzantium
}
if precompiles[addr] == nil && evm.ChainConfig().IsEIP158(evm.BlockNumber) && value.Sign() == 0 {
// Calling a non existing account, don't do anything, but ping the tracer
if evm.vmConfig.Debug && evm.depth == 0 {
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureStart(caller.Address(), addr, false, input, gas, value)
evm.vmConfig.Tracer.CaptureEnd(ret, 0, 0, nil)
}
return nil, gas, nil
}
// 负责在本地状态创建addr
evm.StateDB.CreateAccount(addr)
}
//执行转账
evm.Transfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), to.Address(), value)
//创建一个新的合约对象
contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
start := time.Now()
//执行合约
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, false)
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}参数分析:
-
caller ContractRef 合约部署者
-
addr common.Address 合约的地址
-
input []byte 合约的输⼊入,或者说传入的参数
-
gas uint64支付的gas
-
value *big.Int支付的以太币
代码执行流程:
1. 判断虚拟机EVM的调用深度,不能超过限定值,默认是1024
2. 根据 value 判断合约发布者是否有⾜足额的以太币
3. 根据 addr 设置合约地址
4. 创建当前状态的快照,用于后结出错的回滚
5. 根据 addr 判断该地址是否在状态库中已存在,如果不存在,则创建该帐户
6. 给该合约地址转帐,转帐值为 value
7. 使⽤用 caller to value gas 创建合约对象
8. 根据 addr 把库中查到的合约的地下、代码和哈希值放进去
9. 运行虚拟机EVM,传入参数有:evm contract input
readOndy(false)
10. 如果执行失败,回滚到快照的状态
4. CallCode(已被代替掉)函数分析
//CallCode与Call不同的地方在于它使用caller的context来执行给定地址的代码。
func (evm *EVM) CallCode(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64, value *big.Int) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
// Fail if we're trying to transfer more than the available balance
if !evm.CanTransfer(evm.StateDB, caller.Address(), value) {
return nil, gas, ErrInsufficientBalance
}
var (
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
//这里是不同的地方 to的地址被修改为caller的地址了 而且没有转账的行为
to = AccountRef(caller.Address())
)
// Initialise a new contract and set the code that is to be used by the EVM.
// The contract is a scoped environment for this execution context only.
contract := NewContract(caller, to, value, gas)
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, false)
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
5. DelegateCall函数分析
//DelegateCall 和 CallCode不同的地方在于 caller被设置为 caller的caller
func (evm *EVM) DelegateCall(caller ContractRef, addr common.Address, input []byte, gas uint64) (ret []byte, leftOverGas uint64, err error) {
if evm.vmConfig.NoRecursion && evm.depth > 0 {
return nil, gas, nil
}
// Fail if we're trying to execute above the call depth limit
if evm.depth > int(params.CallCreateDepth) {
return nil, gas, ErrDepth
}
var (
snapshot = evm.StateDB.Snapshot()
to = AccountRef(caller.Address())
)
// Initialise a new contract and make initialise the delegate values
contract := NewContract(caller, to, nil, gas).AsDelegate()
contract.SetCallCode(&addr, evm.StateDB.GetCodeHash(addr), evm.StateDB.GetCode(addr))
ret, err = run(evm, contract, input, false)
if err != nil {
evm.StateDB.RevertToSnapshot(snapshot)
if err != errExecutionReverted {
contract.UseGas(contract.Gas)
}
}
return ret, contract.Gas, err
}
3. 合约对象
在EVM中,执行智能合约代码之前首先会先生成一个合约对象,合约对象里面定义了合约的调用者等属性。
3.1 合约对象结构体:
type Contract struct {
CallerAddress common.Address//是初始化这个合约的人。 如果是delegate,这个值被设置为调用者的调用者
caller ContractRef //是转帐转出方地址(账户)
self ContractRef //转入方地址
jumpdests map[common.Hash]bitvec // Aggregated result of JUMPDEST analysis.
analysis bitvec // Locally cached result of JUMPDEST analysis
Code []byte //合约代码
CodeHash common.Hash //合约代码hash值
CodeAddr *common.Address //合约代码地址
Input []byte//输入参数
Gas uint64 //合约的gas值
value *big.Int //转账值
}
3.2 初始化合约对象
func NewContract(caller ContractRef, object ContractRef, value *big.Int, gas uint64) *Contract {
c := &Contract{CallerAddress: caller.Address(), caller: caller, self: object}
if parent, ok := caller.(*Contract); ok {
// 如果 caller 是一个合约,说明是合约调用了我们。 jumpdests设置为caller的jumpdests
c.jumpdests = parent.jumpdests
} else {
c.jumpdests = make(map[common.Hash]bitvec)
}
// Gas should be a pointer so it can safely be reduced through the run
// This pointer will be off the state transition
c.Gas = gas
// ensures a value is set
c.value = value
return c
}
3.3 设置委托调用
//AsDelegate将合约设置为委托调用并返回当前合同(用于链式调用)
func (c *Contract) AsDelegate() *Contract {
// NOTE: caller must, at all times be a contract. It should never happen
// that caller is something other than a Contract.
parent := c.caller.(*Contract)
c.CallerAddress = parent.CallerAddress
c.value = parent.value
return c
}
四. 存储模型
EVM中数据可以在三个地方进行存储,分别是栈,临时存储,永久存储。由于EVM是基于栈的虚拟机,因此基本上所有的操作都是在栈上进行的,并且EVM中没有寄存器的概念,这样EVM对栈的依赖就更大,虽然这样的设计使实现比较简单且易于理解,但是带来的问题就是需要更多数据的相关操作。在EVM中栈是唯一的免费(几乎是)存放数据的地方。栈自然有深度的限制,目前的限制是1024。因为栈的限制,因此栈上的临时变量的使用会受限制。临时内存存储在每个VM实例中,并在合约执行完后消失永久内存存储在区块链的状态层。
1. 栈存储
EVM中栈用于保存操作数,每个操作数的类型是big.int。执行opcode的时候,从上往下弹出操作数,作为操作的参数。
栈中的主要函数:
1. Data():返回栈中的数据
2. push():把一个元素放入栈中
3. pushN():把多个元素放入栈中
4. pop():取出栈顶元素
5. len():栈的长度
6. swap():第几个元素和栈顶元素交换
7. dup():复制第几个元素到栈顶
8. peek():偷看栈顶元素
9. Back():返回栈中的第几个元素
10. require():确定是否有该元素
11. Print():打印栈中的内容临时存储
2. 临时存储
内存用于一些内存操作(MLOAD,MSTORE,MSTORE8)及合约调用的参数拷贝(CALL,CALLCODE)。内存数据结构,维护了一个byte数组,MLOAD,MSTORE读取存入的时候都要指定位置及长度才能准确的读写。
主要方法:
1. Set():把数据放入内存中
2. Set32():把32字节的数据放入内存中,不足部分用0补齐
3. Resize():扩展内存到指定大小
4. Get():从内存中获取数据,作为一个新的slice返回
5. GetPtr():从内存中获取数据
6. Len():返回内存的长度
7. Data():返回内存中的数据
8. Print():打印内存中的数据
3. 持久存储
合约及其调用类似于数据库的日志,保存了合约定义以及对他的一系列操作,只要将这些操作执行一遍就能获取当前的结果,但是如果每次都要去执行就太慢了,因而这部分数据是会持久化到stateDb里面的。code中定义了两条指令SSTORE SLOAD用于从db中读写合约当前的状态。
五.GAS消耗模型
以太坊中发送交易固定收取21000gas,除此之外gas收取主要分为两种:
-
固定消耗的gas(例如:加减乘除消耗的gas)
-
动态调整的gas(例如:扩展内容的gas大小根据内存大小而定)
1. 固定消耗的gas
const (
GasQuickStep uint64 = 2
GasFastestStep uint64 = 3
GasFastStep uint64 = 5
GasMidStep uint64 = 8
GasSlowStep uint64 = 10
GasExtStep uint64 = 20
)2. 动态调整的gas
const (
ExpByteGas uint64 = 10 // Times ceil(log256(exponent)) for the EXP instruction.
SloadGas uint64 = 50 // Multiplied by the number of 32-byte words that are copied (round up) for any *COPY operation and added.
CallValueTransferGas uint64 = 9000 // Paid for CALL when the value transfer is non-zero.
CallNewAccountGas uint64 = 25000 // Paid for CALL when the destination address didn't exist prior.
TxGas uint64 = 21000 // Per transaction not creating a contract. NOTE: Not payable on data of calls between transactions.
TxGasContractCreation uint64 = 53000 // Per transaction that creates a contract. NOTE: Not payable on data of calls between transactions.
TxDataZeroGas uint64 = 4 // Per byte of data attached to a transaction that equals zero. NOTE: Not payable on data of calls between transactions.
LogDataGas uint64 = 8 // Per byte in a LOG* operation's data.
Sha3Gas uint64 = 30 // Once per SHA3 operation.
Sha3WordGas uint64 = 6 // Once per word of the SHA3 operation's data.
SstoreSetGas uint64 = 20000 // Once per SLOAD operation.
SstoreResetGas uint64 = 5000 // Once per SSTORE operation if the zeroness changes from zero.
SstoreClearGas uint64 = 5000 // Once per SSTORE operation if the zeroness doesn't change.
SstoreRefundGas uint64 = 15000 // Once per SSTORE operation if the zeroness changes to zero.
NetSstoreNoopGas uint64 = 200 // Once per SSTORE operation if the value doesn't change.
NetSstoreInitGas uint64 = 20000 // Once per SSTORE operation from clean zero.
NetSstoreCleanGas uint64 = 5000 // Once per SSTORE operation from clean non-zero.
NetSstoreDirtyGas uint64 = 200 // Once per SSTORE operation from dirty.
JumpdestGas uint64 = 1 // Once per JUMPDEST operation.
CallGas uint64 = 40 // Once per CALL operation & message call transaction.
CreateDataGas uint64 = 200 //
ExpGas uint64 = 10 // Once per EXP instruction
LogGas uint64 = 375 // Per LOG* operation.
CopyGas uint64 = 3 //
TierStepGas uint64 = 0 // Once per operation, for a selection of them.
LogTopicGas uint64 = 375 // Multiplied by the * of the LOG*, per LOG transaction. e.g. LOG0 incurs 0 * c_txLogTopicGas, LOG4 incurs 4 * c_txLogTopicGas.
CreateGas uint64 = 32000 // Once per CREATE operation & contract-creation transaction.
Create2Gas uint64 = 32000 // Once per CREATE2 operation
SuicideRefundGas uint64 = 24000 // Refunded following a suicide operation.
MemoryGas uint64 = 3 // Times the address of the (highest referenced byte in memory + 1). NOTE: referencing happens on read, write and in instructions such as RETURN and CALL.
TxDataNonZeroGas uint64 = 68 // Per byte of data attached to a transaction that is not equal to zero. NOTE: Not payable on data of calls between transactions.
EcrecoverGas uint64 = 3000 // Elliptic curve sender recovery gas price
Sha256BaseGas uint64 = 60 // Base price for a SHA256 operation
Sha256PerWordGas uint64 = 12 // Per-word price for a SHA256 operation
Ripemd160BaseGas uint64 = 600 // Base price for a RIPEMD160 operation
Ripemd160PerWordGas uint64 = 120 // Per-word price for a RIPEMD160 operation
IdentityBaseGas uint64 = 15 // Base price for a data copy operation
IdentityPerWordGas uint64 = 3 // Per-work price for a data copy operation
Bn256AddGas uint64 = 500 // Gas needed for an elliptic curve addition
Bn256ScalarMulGas uint64 = 40000 // Gas needed for an elliptic curve scalar multiplication
Bn256PairingBaseGas uint64 = 100000 // Base price for an elliptic curve pairing check
Bn256PairingPerPointGas uint64 = 80000 // Per-point price for an elliptic curve pairing check
)六 . 指令集设计
1. 操作码分类
操作码opcodes按功能分为9组(运算相关,块操作,加密相关等)
1.1. 基础计算相关
const (
STOP OpCode = iota
ADD
MUL
SUB
DIV
SDIV
MOD
SMOD
ADDMOD
MULMOD
EXP
SIGNEXTEND
)
1.2. 比较加密相关
const (
LT OpCode = iota + 0x10
GT
SLT
SGT
EQ
ISZERO
AND
OR
XOR
NOT
BYTE
SHL
SHR
SAR
SHA3 = 0x20
)
1.3 关闭当前状态相关
const (
ADDRESS OpCode = 0x30 + iota
BALANCE
ORIGIN
CALLER
CALLVALUE
CALLDATALOAD
CALLDATASIZE
CALLDATACOPY
CODESIZE
CODECOPY
GASPRICE
EXTCODESIZE
EXTCODECOPY
RETURNDATASIZE
RETURNDATACOPY
EXTCODEHASH
)
1.4. 块操作相关
const (
BLOCKHASH OpCode = 0x40 + iota
COINBASE
TIMESTAMP
NUMBER
DIFFICULTY
GASLIMIT
)1.5. 存储操作相关
const (
POP OpCode = 0x50 + iota
MLOAD
MSTORE
MSTORE8
SLOAD
SSTORE
JUMP
JUMPI
PC
MSIZE
GAS
JUMPDEST
)
1.6. 栈操作相关
const (
PUSH1 OpCode = 0x60 + iota
PUSH2
PUSH3
PUSH4
PUSH5
PUSH6
PUSH7
PUSH8
PUSH9
PUSH10
PUSH11
PUSH12
PUSH13
PUSH14
PUSH15
PUSH16
PUSH17
PUSH18
PUSH19
PUSH20
PUSH21
PUSH22
PUSH23
PUSH24
PUSH25
PUSH26
PUSH27
PUSH28
PUSH29
PUSH30
PUSH31
PUSH32
DUP1
DUP2
DUP3
DUP4
DUP5
DUP6
DUP7
DUP8
DUP9
DUP10
DUP11
DUP12
DUP13
DUP14
DUP15
DUP16
SWAP1
SWAP2
SWAP3
SWAP4
SWAP5
SWAP6
SWAP7
SWAP8
SWAP9
SWAP10
SWAP11
SWAP12
SWAP13
SWAP14
SWAP15
SWAP16
)
1.7. 日志相关
const (
LOG0 OpCode = 0xa0 + iota
LOG1
LOG2
LOG3
LOG4
)
1.8. 执行合约相关
const (
CREATE OpCode = 0xf0 + iota
CALL
CALLCODE
RETURN
DELEGATECALL
CREATE2
STATICCALL = 0xfa
REVERT = 0xfd
SELFDESTRUCT = 0xff
)
1.9. 其他非官方提供的操作
const (
PUSH OpCode = 0xb0 + iota
DUP
SWAP
)
2. 操作指令集
文件jump.table.go定义了四种指令集合,每个集合实质上是个256长度的数组,名字翻译过来是(前沿,家园,拜占庭,君士坦丁堡)估计是对应了EVM的四个发展阶段。指令集向前兼容。
frontierInstructionSet = newFrontierInstructionSet()
homesteadInstructionSet = newHomesteadInstructionSet()
byzantiumInstructionSet = newByzantiumInstructionSet()
constantinopleInstructionSet = newConstantinopleInstructionSet()- FrontierInstructionSet存放的是一堆基础指令。
- HomesteadInstructionSet以上一个指令集为基础,增加了 DELEGATECALL 指令。
- ByzantiumInstructionSet以上一个指令集为基础,增加了 STATICCALL、RETURNDATASIZE、RETURNDATACOPY、REVERT 指令。
- ConstantinopleInstructionSet 以上一个指令集为基础,增加了 SHL、SHR、SAR、EXTCODEHASH、CREATE2 指令。
具体每条指令结构如下:
type operation struct {
execute executionFunc //对应的操作函数
constantGas uint64 // 操作对应的gas消耗
dynamicGas gasFunc //该指令动态调整后的gas值
minStack int //该指令最小需要的栈空间大小
maxStack int //该指令最大需要的栈空间大小
memorySize memorySizeFunc // 操作所需空间
halts bool // 运算中止
jumps bool // 跳转(for)
writes bool //是否写入
valid bool // 操作是否有效
reverts bool // 出错回滚
returns bool // d返回
}3. 指令详解
1. 以 ADD指令为例,该指令是从栈中获取两个元素,然后把相加的结果再放进栈中。
func opAdd(pc *uint64, interpreter *EVMInterpreter, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
x, y := stack.pop(), stack.peek()
math.U256(y.Add(x, y))
interpreter.intPool.put(x)
return nil, nil
}从栈中取出一个元素放进变量 x 中,再查看下一个元素并把值放进变量 y 中,把x和y相加并把结果赋值给 y,最后把 x 缓存起来。
2. 以 MSTORE指令为例,该指令是从栈中获取两个元素,一个标识内存地址,一个表示保存到内存的值。(临时内存)
func opMstore(pc *uint64, interpreter *EVMInterpreter, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
// pop value of the stack
mStart, val := stack.pop(), stack.pop()
memory.Set32(mStart.Uint64(), val)
interpreter.intPool.put(mStart, val)
return nil, nil
}从栈中取第一个元素作为内存地址的偏移量,再取第二个元素作为内存要保存的值,根据这两个值保存到内存中,并且把这两个值缓存起来。
3. 以 SSTORE指令为例,该指令是从栈中获取两个元素,一个标识内存地址,一个表示保存到内存的值。(永久内存)
func opSstore(pc *uint64, interpreter *EVMInterpreter, contract *Contract, memory *Memory, stack *Stack) ([]byte, error) {
loc := common.BigToHash(stack.pop())
val := stack.pop()
interpreter.evm.StateDB.SetState(contract.Address(), loc, common.BigToHash(val))
interpreter.intPool.put(val)
return nil, nil
}永久内存是以 key-value 的形式存储的,key通常是从0开始,并依次增加。上述操作的意思是从栈中取第一个元素,哈希后作为内存的 key,取第二个元素,哈希后作为内存的 value,然后从上下文获取合约的地址,然后保存到永久内存中。最后把从栈中取出的 val 缓存起来。