vuex中几个核心概念: state, getters, mutations, actions, module
getters
可以认为是store的计算属性;与计算属性一样,getter的返回值会根据它的依赖缓存起来,且只有当它的依赖值发生变化才会被重新计算
mapGetters
辅助函数仅仅是将 store 中的 getter 映射到局部计算属性:
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
computed: {
// 使用对象展开运算符将 getter 混入 computed 对象中
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
mutations 只能是同步操作
更改vuex的store中的状态的唯一方法就是提交 mutations
在 mutation 中混合异步调用会导致你的程序很难调试。例如,当你能调用了两个包含异步回调的 mutation 来改变状态,你怎么知道什么时候回调和哪个先回调呢?
mutation必须是同步函数
mutations: {
someMutation (state) {
api.callAsyncMethod(() => {
state.count++
})
}
}
现在想象,我们正在 debug 一个 app 并且观察 devtool 中的 mutation 日志。每一条 mutation 被记录,devtools 都需要捕捉到前一状态和后一状态的快照。然而,在上面的例子中 mutation 中的异步函数中的回调让这不可能完成:因为当 mutation 触发的时候,回调函数还没有被调用,devtools 不知道什么时候回调函数实际上被调用——实质上任何在回调函数中进行的状态的改变都是不可追踪的。
在组件中提交mutations
你可以在组件中使用 this.$store.commit('xxx') 提交 mutation,或者使用 mapMutations 辅助函数将组件中的 methods 映射为 store.commit 调用(需要在根节点注入 store)。
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
}
actions 可以是异步操作
- action提交的是mutation,而不是直接更改状态
- action 可以包含任何异步操作
分发 action
在组件中分发Action
你在组件中使用 this.$store.dispatch('xxx') 分发 action,或者使用 mapActions 辅助函数将组件的 methods 映射为 store.dispatch 调用(需要先在根节点注入 store):
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
// ...
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
组合 Action
Action 通常是异步的,那么如何知道 action 什么时候结束呢?更重要的是,我们如何才能组合多个 action,以处理更加复杂的异步流程?
首先,你需要明白 store.dispatch 可以处理被触发的 action 的处理函数返回的 Promise,并且 store.dispatch 仍旧返回 Promise:
// 假设 getData() 和 getOtherData() 返回的是 Promise
actions: {
async actionA ({ commit }) {
commit('gotData', await getData())
},
async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) {
await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成
commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData())
}
}
module
由于使用单一状态树,应用的所有状态会集中到一个比较大的对象;当应用变得非常复杂时,store 对象就有可能变得相当臃肿。
为了解决以上问题,Vuex 允许我们将 store 分割成模块(module)。每个模块拥有自己的 state、mutation、action、getter、甚至是嵌套子模块——从上至下进行同样方式的分割:
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
如果你希望使用全局 state 和 getter,rootState 和 rootGetter 会作为第三和第四参数传入 getter,也会通过 context 对象的属性传入 action。
命名空间
默认情况下,模块内部的 action、mutation 和 getter 是注册在全局命名空间的——这样使得多个模块能够对同一 mutation 或 action 作出响应。
如果希望你的模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,你可以通过添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为命名空间模块。当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名。例如:
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
account: {
namespaced: true,
// 模块内容(module assets)
state: { ... }, // 模块内的状态已经是嵌套的了,使用 `namespaced` 属性不会对其产生影响
getters: {
isAdmin () { ... } // -> getters['account/isAdmin']
},
actions: {
login () { ... } // -> dispatch('account/login')
},
mutations: {
login () { ... } // -> commit('account/login')
},
// 嵌套模块
modules: {
// 继承父模块的命名空间
myPage: {
state: { ... },
getters: {
profile () { ... } // -> getters['account/profile']
}
},
// 进一步嵌套命名空间
posts: {
namespaced: true,
state: { ... },
getters: {
popular () { ... } // -> getters['account/posts/popular']
}
}
}
}
}
})
如果你希望使用全局 state 和 getter,rootState 和 rootGetter 会作为第三和第四参数传入 getter,也会通过 context 对象的属性传入 action。
若需要在全局命名空间内分发 action 或提交 mutation,将 { root: true } 作为第三参数传给 dispatch 或 commit 即可。
需要注意的点
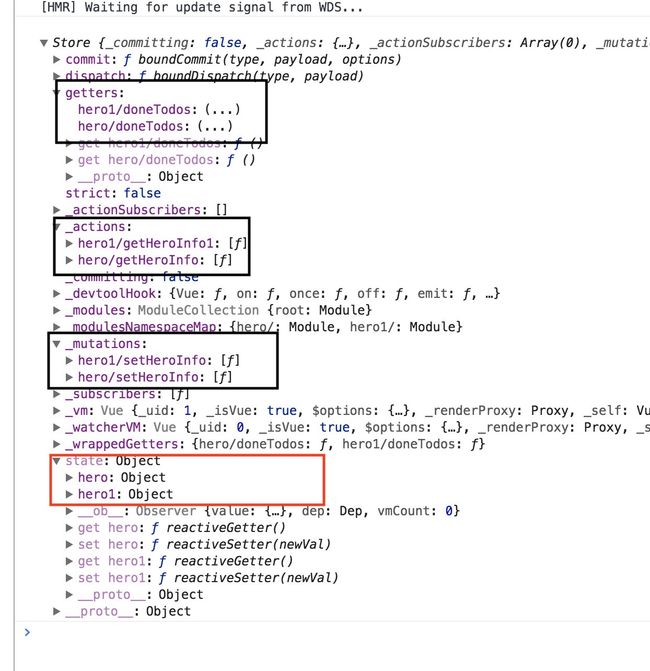
1.默认情况下,模块内的getter, mutation,action是注册在全局空间的,state只注册在局部命名空间的;
要想使模块内的getter, mutation,action注册在模块命名空间,必须在模块内加上 namespaced: true
使用命名空间在调用action时必须使用
this.$store.dispatch('hero1/getHeroInfo');
computed: {
doneTodosCount () {
return this.$store.getters['hero1/doneTodos'][0].item;
}
},
参考链接
2.页面刷新时,store中的数据会清空
解决方案
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/43027499/vuex-state-on-page-refresh
3.双向绑定(v-model)和 vuex 是否冲突
test.js
import Vue from 'vue';
const test = {
state: {
obj: {}
},
mutations: {
updateMessage(state, message) {
state.obj = { message };
}
},
}
export default test;
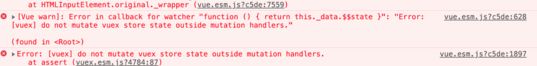
以上代码在严格模式下会报错
vuex开启严格模式, 仅需要在创建store的时候传入 strict: true
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
strict: true
})
在严格模式下, 无论何时发生了状态变更且且不是由mutation函数引起的, 经会抛出错误, 这能保证所有的状态变更都能被调试工具跟踪到;
那我们应该怎么处理呢, vuex的官方文档中给给了解决方法: 表单处理
- 给 中绑定 value,然后侦听 input 或者 change 事件,在事件回调中调用 action:
- 双向绑定的计算属性: v-model + 使用带有 setter 的双向绑定计算属性