PAT A1102 Invert a Binary Tree
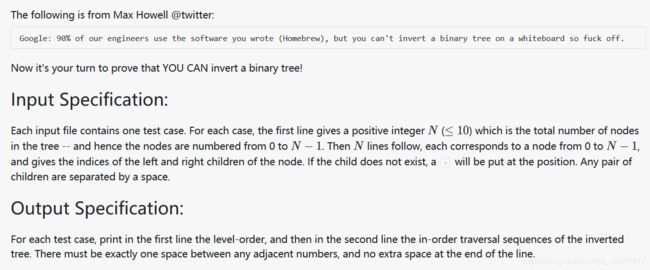
PAT A1102 Invert a Binary Tree
Sample Input:
8
1 -
- -
0 -
2 7
- -
- -
5 -
4 6
Sample Output:
3 7 2 6 4 0 5 1
6 5 7 4 3 2 0 1
| word | meaning |
|---|---|
| Max Howell | 马克斯·豪威尔 |
| indices | (index的复数) |
- 思路 1:使用静态二叉树(含父节点)
- findRoot:从0节点开始,不断向上遍历到父节点为空(f == -1)
- 从root开始,进行逆层序遍历,逆中序遍历(交换遍历左右子树的顺序即可)
- 层序遍历,直接输出每次出队的元素,中序遍历是递归,不好控制输出,故用一个数组存储结果,遍历后再格式化输出
- code 1:
#include - 不需要output控制inOrder的输出:
vector<int> in;
int cnt1 = 0;
void revInOrder(int root){
if(root == -1) return;
if(node[root].rc != -1) revInOrder(node[root].rc);
printf("%d", root);
cnt1++;
if(cnt1 < n) printf(" ");
if(node[root].lc != -1) revInOrder(node[root].lc);
}
-
TIPS: 遍历之前要判断结点是否为空
-
思路 2:
在输入时,就交换左右孩子,然后按正常的层序遍历和中序遍历输出 -
code 2:
#include -
TIPS 2:
"%*c"可以在scanf()中吸收一个字符 -
思路 3:
先用后序遍历交换左右孩子,再层序和中序遍历 -
code 3:
void postOrder(int root){
if(root == -1) return;
if(node[root].lc != -1) postOrder(node[root].lc);
if(node[root].rc != -1) postOrder(node[root].rc);
swap(node[root].lc, node[root].rc);
}
- T2 code:
#include - T3 code: 数组存储二叉树,先逆中序遍历,将中序序列存入一个vector,同时用id控制将节点存入一个数组,在遍历数组即得到逆层序序列
#include