参考:Android开发艺术探索一书
MeasureSpec##
MeasureSpec 由view自身的layoutparams(xml 中指定) 和 父容器的约束(父容器大小)来 共同生成;
MeasureSpec 与测量相关的类,是一个32位的int值,其中高2位表示SpecMode,低30位表示SpecSize;
SpecMode 是测量模式,SpecSize指在某种测量模式下的大小;
SpecMode有3种:
- UNSPECIFIED:未指定状态;
- EXACTLY:表示精确大小,LayoutParams中的 match_parent 与具体数值就是这个;
- AL_MOST: 至多,父容器指定了一个可用大小的SpecSize,view 的大小不能大于这个 SpecSize,
LayoutParams 中wrap_content与之对应;
LayoutParams##
给View设置LayoutParams,view的LayoutParams会在父容器的约束下,转换成对应的MeasureSpec,然后再跟进此MeasureSpec来确定View的宽高;
注意: MeasureSpec不是唯一由LayoutParams决定的,View 的 LayoutParams与其父容器一起决定出来View的MeasureSpec;
DecorView:
DecorView是顶层父容器,她的MeasureSpec创建时根据屏幕大小来的;
规则:
- 当View采用固定宽、高时,不管父容器的 MeasureSpec 是什么,View的MeasureSpec都是精确模式(EXACTLY),并且其大小遵循 LayoutParams 设置的大小;
- 当View的宽高为match_parent时,如果父容器是精准模式,则View也是精准模式,并且大小是父容器的剩余空间(父容器可能有 margin),如果父容器是最大模式,则View也是最大模式,大小不超过父容器的剩余空间;
- 当View的宽高wrap_content,不管父容器的模式是啥,View的模式总是最大化并且大小不超过父(这里指的是自定义view,继承view,没有重写onMeasure方法的情况;TextView 等系统控件有具体的onMeasure实现);
View measure的过程##
先从 ViewGroup类中的measureChildWithMargins方法入手:
protected void measureChildWithMargins(View child,
int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int widthUsed,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec, int heightUsed) {
final MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin
+ widthUsed, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin
+ heightUsed, lp.height);
// 测量子元素
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
从上面的代码可以看到 测量 子 view 的时候,会先调用 getChildMeasureSpec方法来获得子view的MeasureSpec;子View的MeasureSpec明显与父容器有关;
getChildMeasureSpec方法代码如下:
/**
* @param spec: 父容器的 MeasureSpec
* @param padding:父容器已占用的空间大小,意思是子view布局大小时,需要减去这部分空间
@param childDimension: 子View的LayoutParams 设置的大小
***/
public static int getChildMeasureSpec(int spec, int padding, int childDimension) {
// 父布局模式
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(spec);
// 父布局大小
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(spec);
// 父布局剩余大小,即子元素可用的空间大小
int size = Math.max(0, specSize - padding);
int resultSize = 0;
int resultMode = 0;
switch (specMode) {
// Parent has imposed an exact size on us
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size. So be it.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent has imposed a maximum size on us
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... so be it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size, but our size is not fixed.
// Constrain child to not be bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size. It can't be
// bigger than us.
resultSize = size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.AT_MOST;
}
break;
// Parent asked to see how big we want to be
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
if (childDimension >= 0) {
// Child wants a specific size... let him have it
resultSize = childDimension;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.EXACTLY;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT) {
// Child wants to be our size... find out how big it should
// be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
} else if (childDimension == LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT) {
// Child wants to determine its own size.... find out how
// big it should be
resultSize = View.sUseZeroUnspecifiedMeasureSpec ? 0 : size;
resultMode = MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED;
}
break;
}
//noinspection ResourceType
return MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(resultSize, resultMode);
}
如果原始View是一个view,通过measure方法就完成了其测量过程,如果是ViewGroup,除了完成自己的测量过程,还要负责调用所有子元素的measure方法,子元素在递归执行;
View的measure过程来measure方法来完成,measure方法会调用View的onMeasure方法:
/**
* @param widthMeasureSpec 父容器宽 MeasureSpec
**/
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
// 设置测量后的宽高 setMeasureDimension()
setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec),
getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec));
}
// 返回 MeasureSpec的 specSize, UNSPECIFIED 模式时,大小为 getSuggestedMinimumWidth()
public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) {
int result = size;
int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec);
int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec);
switch (specMode) {
case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED:
result = size;
break;
case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST:
case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY:
result = specSize;
break;
}
return result;
}
// 获取最小宽度,最小宽度 为 minWidth属性 对应 android:minWidth,或者 background 背景的宽
protected int getSuggestedMinimumWidth() {
return (mBackground == null) ? mMinWidth : max(mMinWidth, mBackground.getMinimumWidth());
}
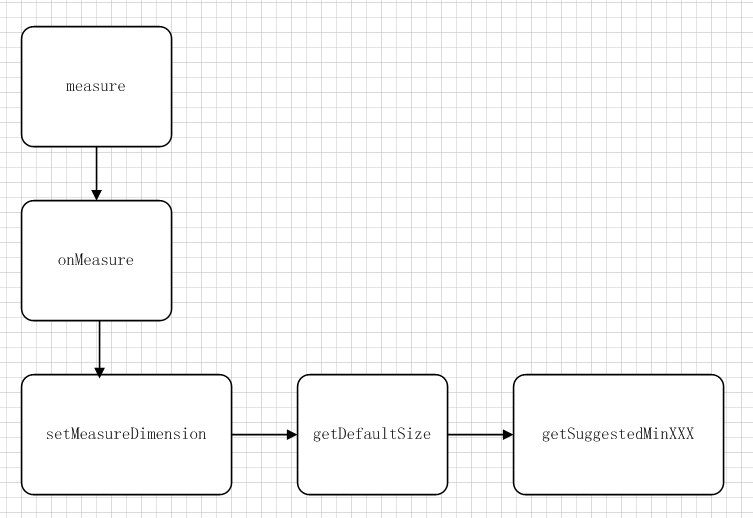
View measure 调用嵌套图,最先执行 getSuggestedMinXXX,逐步往上走
ViewGroup measure 过程
Viewgroup 没有重写 View 的 onMeasure方法,但提供了 measureChildren 方法,
如果 孩子 不是 GONE,则分别用 measureChild来测量孩子;
protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int size = mChildrenCount;
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
final View child = children[i];
if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) {
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
}
protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec,
int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams();
// 获取子View的 MeasureSpec
final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec,
mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width);
final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec,
mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height);
// 调用view的measure方法来测量,这里,就会走 上面的 view 的 measure了
child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
因为ViewGroup是抽象类,其测量过程由子类实现,如:LinearLayout
View的measure过程是比较复杂的,通过 measure后,就可以通过getMeasureHeight() getMeasureWidth 获取测量后的高宽了;但最终的宽高是在 onLayout方法中取获取,因为系统 可能多次调用 measure过程;