Linux的ubifs文件系统制作
UBIFS是UBI file system的简称,用于裸的flash设备,作为jffs2的后继文件系统之一。UBIFS通过UBI子系统处理与MTD设备之间动作。UBIFS文件系统更适合MLCNAND FLASH。需要注意的是UBIFS并不是为SSD,MMC,SD,Compact Flash等之类的基于flash的存储设备,其是针对于裸flash设备。
1.UBIFS简介
JFFS2和UBIFS最大的不同就是UBIFS将索引存储在flash上,而JFFS2的索引存储在内存中,当文件系统被挂载的时候,内存需要重新建立索引。JFFS2这样就潜在地给自己最大尺寸做了一个限制,因为挂载时间和内存使用情况都随着flash的大小而线性增长,BUIFS就是被设计用来克服这个限制。
不幸的是,将索引存储在flash上是非常复杂的,因为索引本身也需要异地更新。当索引的一部分被异地更新,那么与更新的索引相关的其它部分索引也必须要更新。然后,依次地,相关部分的相关部分也必须被更新。这样看起来好像永无止境地更新下去,一个解决的办法就是使用游离树(wandering tree)。
对于UBIFS,游离树(wandering tree,实际上是一个B+树)只有树上的叶子包含文件信息。他们是文件系统的有效节点。树的内部元素是索引节点(index nodes)并包含子节点的相关信息。也就是说,一个节点记录着它的子节点的位置。所以UBIFS 的游离树可以看成两个部分。顶部分由创建树结构的索引节点组成,底部分由指向实际数据的叶子节点组成。顶部分可以简单地看作索引index。一个文件系统的更新过程由创建一个新的叶子节点和添加该节点到树上(或者代替原来的树中的节点)组成。之后,其父索引节点必须也要被代替,从而父节点的父节点,一直到树的根(root),都必须要被代替。要被代替的索引节点数等于树的高度。这里留下的问题就是怎么知道树的根在哪里。在UBIFS中,根索引节点的位置存储在主节点(master node)里。
2.UBIFS文件系统的制作
ubifs文件系统的制作时在ubuntu上完成,首先需要新建一个 ubi 目录,目录下存放下述所需文件,如下图:
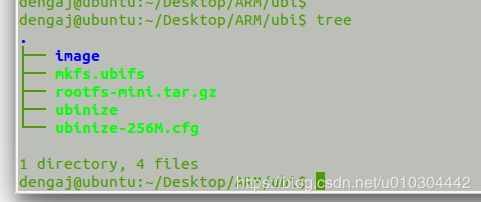
其中image为一个空目录;mkfs.ubifs将某个文件夹制作为UBIFS镜像;ubinize将使用mkfs.ubifs命令制作的UBIFS文件系统镜像转换成可直接在FLASH上烧写的格式;rootfs-mini.tar.gz为标准的root文件;ubinize-256M.cfg为相关参数设置。制作ubi.img的大致过程如下:
1.解压rootfs-mini.tar.gz到当前目录
sudo tar xpf rootfs-mini.tar.gz
2.制作ubifs镜像文件
sudo mkfs.ubifs -F -r ./rootfs-mini -m 2048 -e 126976 -c 18866 ./image/ubifs.img
在image目录下生成一个ubifs.img文件
3.转换ubifs镜像文件为可烧写文件
sudo ubinize -o ./ubi.img -m 2048 -p 128KiB -s 2048 -O 2048 ./ubinize-256M.cfg
在该目录下生成一个ubi.img文件,即为最终可烧写的ubifs镜像文件
3. mkfs.ubifs命令介绍
mkfs.ubifs的用法
Usage: mkfs.ubifs [OPTIONS] target
Make a UBIFS file system image from an existing directory tree
Examples:
Build file system from directory /opt/img, writting the result in the ubifs.img file
mkfs.ubifs -m 512 -e 128KiB -c 100 -r /opt/img ubifs.img
The same, but writting directly to an UBI volume
mkfs.ubifs -r /opt/img /dev/ubi0_0
Creating an empty UBIFS filesystem on an UBI volume
mkfs.ubifs /dev/ubi0_0
Options:
-r, -d, --root=DIR build file system from directory DIR
-m, --min-io-size=SIZE minimum I/O unit size,最小输入输出大小
-e, --leb-size=SIZE logical erase block size逻辑可擦出块大小
-c, --max-leb-cnt=COUNT maximum logical erase block count最大逻辑可擦出块数目
-o, --output=FILE output to FILE输出文件名
-j, --jrn-size=SIZE journal size
-R, --reserved=SIZE how much space should be reserved for the super-user
-x, --compr=TYPE compression type - "lzo", "favor_lzo", "zlib" or
"none" (default: "lzo")
-X, --favor-percent may only be used with favor LZO compression and defines
how many percent better zlib should compress to make
mkfs.ubifs use zlib instead of LZO (default 20%)
-f, --fanout=NUM fanout NUM (default: 8)
-F, --space-fixup file-system free space has to be fixed up on first moun
(requires kernel version 3.0 or greater)
-k, --keyhash=TYPE key hash type - "r5" or "test" (default: "r5")
-p, --orph-lebs=COUNT count of erase blocks for orphans (default: 1)
-D, --devtable=FILE use device table FILE
-U, --squash-uids squash owners making all files owned by root
-l, --log-lebs=COUNT count of erase blocks for the log (used only for debugging)
-v, --verbose verbose operation
-V, --version display version information
-g, --debug=LEVEL display debug information (0 - none, 1 - statistics, 2 - files, 3 - more details)
-h, --help display this help text
4. ubinize命令介绍
Usage: ubinize [-o filename] [-p ] [-m ] [-s ] [-O ] [-e
][-x ] [-Q ] [-v] [-h] [-V] [--output=]
[--peb-size=] [--min-io-size=] [--sub-page-size=]
[--vid-hdr-offset=] [--erase-counter=] [--ubi-ver=]
[--image-seq=] [--verbose] [--help] [--version] ini-file
Example: ubinize -o ubi.img -p 16KiB -m 512 -s 256 cfg.ini - create UBI image
'ubi.img' as described by configuration file 'cfg.ini'
-o, --output= output file name
-p, --peb-size= size of the physical eraseblock of the flash
this UBI image is created for in bytes,
kilobytes (KiB), or megabytes (MiB)
(mandatory parameter)物理可擦出块大小
-m, --min-io-size= minimum input/output unit size of the flash
in bytes
-s, --sub-page-size= minimum input/output unit used for UBI
headers, e.g. sub-page size in case of NAND
flash (equivalent to the minimum input/output
unit size by default)子页大小
-O, --vid-hdr-offset= offset if the VID header from start of the
physical eraseblock (default is the next
minimum I/O unit or sub-page after the EC
header)VID头部偏移量,默认是512
-e, --erase-counter= the erase counter value to put to EC headers (default is 0)
-x, --ubi-ver= UBI version number to put to EC headers (default is 1)
-Q, --image-seq= 32-bit UBI image sequence number to use
(by default a random number is picked)
-v, --verbose be verbose
-h, --help print help message
-V, --version print program version
5. ubinize-256M.cfg配置文件介绍
[ubifs]
mode=ubi
image=./image/ubifs.img //指定根文件系统镜像文件路径
vol_id=0 //指定根文件系统树的卷标为0
vol_size=200MiB //指定该UBI逻辑卷的大小=逻辑擦除块大小*逻辑擦除块个数
vol_type=dynamic
vol_name=rootfs //指定UBI卷的名称
vol_flags=autoresize //UBI Subsystem在系统启动时自动调整逻辑擦除块的个数