文件处理_月隐学python第21课
目录
⼀、⽂件处理
1 ⽂件读取
2 写⽂件
3 移动⽂件指针
⼆、 os模块
1. os模块
2. os基本⽅法
⼀、⽂件处理
⽂件的处理包括读⽂件和写⽂件,读写⽂件就是请求操作系统打开⼀个⽂件对象,然后,通过操作系统提供的接⼝从这个⽂件对象中读取数据(读⽂件),或者把数据写⼊这个⽂件对象(写⽂件)。
1 ⽂件读取
⽂件读取可分为以下步骤:
- 打开⽂件
- 读取⽂件内容
- 关闭⽂件
打开⽂件要使⽤open内建函数:
open(file [, mode='r', encoding=None, errors=None])
参数说明:
- file:⽂件路径,可以是相对路径和绝对路径
- mode:⽂件打开模式
- encodeing: ⽂件编码⽅式,不⽤于⼆进制⽂件,⼀般是utf-8,gbk
- errors:指定如何处理编码和解码错误 ,适⽤于⽂本⽂件
- 返回值:⼀个可迭代的⽂件对象
注意:⼆进制⽂件⼀般⽤于视频、⾳频、图⽚
读取⽂件常⽤函数: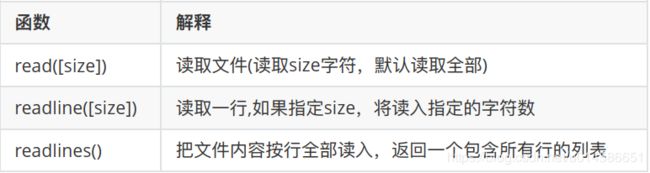
# 打开文件
fp = open('qfile.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
# 读取文件全部内容
# content = fp.read()
# print(content)
#读取指定字符数,包括行尾的换行符\n
# print(fp.read(5))
# 读取一行
# print(fp.readline(6)) #读取指定字符数
# print(fp.readline()) #读取⼀整⾏,直到碰到⼀个\n
# 读取所有行,返回列表
print(fp.readlines())
#关闭文件
fp.close()'''
由于⽂件读写时都有可能产⽣IOError,⼀旦出错,后⾯的f.close()就不会调⽤。
所以,为了保证⽆论是否出错都能正确地关闭⽂件,我们可以使⽤try ...
finally来实现:
'''
try:
fp = open('qfile.txt','r',encoding='utf-8')
print(fp.readlines())
finally:
fp.close()
'''
可以简写为:
with语句会⾃动调⽤close⽅法关闭⽂件
'''
with open('qfile.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as fp:
print(fp.readline())
'''
fread()和freadlines()会⼀次读⼊⽂件全部内容,如果⽂件太⼤,会直接耗尽内存的,
因为⽂件对象可迭代,所以可以⽤for循环遍历⽂件读取
'''
with open('qfile.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as fp:
for line in fp:
print(line.strip()) #注意⽆论是read、 readline、 readlines都会读⼊⾏末的\n,所以需要⼿动剔除\n
# print(line)
2 写⽂件
'''
写文件
'''
path = 'file11.txt'
# 1.打开文件
f = open(path,'w',encoding='utf-8')
'''
2.写⼊内容,将内容写⼊到缓冲区
不会⾃动换⾏,需要换⾏的话,需要在字符串末尾添加换⾏符
'''
f.write('Whatever is worth doing is worth doing well该⾏很骄傲很关键\n')
f.write('Whatever is worth doing is worth doing well该⾏很骄傲很关键\n')
# 3.刷新缓冲区【加速数据的流动,保证缓冲区的流畅】
f.flush()
# 4. 关闭文件 关闭文件也会刷新缓冲区
f.close()
# 简写⽅式:可以不⽤⼿动调⽤close
with open(path,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f1:
f1.write('Whatever is worth doing is worth doing well')
3 移动⽂件指针
⽂件是顺序向后读写的,如果想要移动⽂件指针,可以使⽤seek⽅法:
file_obj.seek(offset,whence=0)
功能:移动⽂件指针
参数: offset 是偏移量,正数表示从⽂件开头向⽂件末尾移动,负数相反。
whence : ⽂件指针的位置,可选参数,值可以是
- SEEK_SET or 0 表示⽂件开头位置,是默认值
- SEEK_CUR or 1 表示当前位置(不能使⽤)
- SEEK_END or 2 ⽂件末尾位置(不能使⽤)
返回值:⽆
#1.txt内容: hello world
with open('file11.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') as fp:
fp.seek(5) #移动到hello后的空格位置
print(fp.read(3)) #wo
fp.seek(0) #移动到开头
print(fp.read(5)) #hello
print(fp.tell()) #tell()显示当前指针位置
⼆、 os模块
1. os模块
需要引⼊os模块
import os

