丝绸之路(Silk Road)1
丝绸之路(Silk Road)1
参考资料
http://zh.unesco.org/silkroad/
http://zh.unesco.org/silkroad/network-silk-road-cities-map-app/zh
丝绸之路是什么?
这条东西通路,将中原、西域与阿拉伯、波斯湾紧密联系在一起。
丝绸之路(德语:die Seidenstrasse),简称为丝路,最早来自德国地理学家费迪南·冯·李希霍芬 (Ferdinand von Richthofen)1877年出版的《中国——我的旅行成果》(China, Ergebnisse eigener Reisen)。
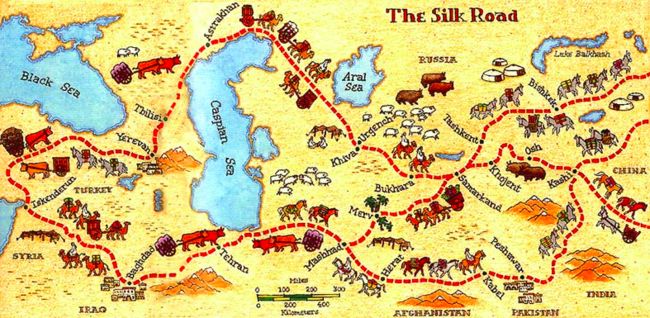
丝绸之路通常是指欧亚北部的商路,与南方的茶马古道形成对比,西汉时张骞和东汉时班超出使西域开辟的以长安(今西安)、洛阳为起点,经甘肃、新疆,到中亚、西亚,并联结地中海各国的陆上通道。这条道路也被称为“陆路丝绸之路”,以区别日后另外两条冠以“丝绸之路”名称的交通路线。因为由这条路西运的货物中以丝绸制品的影响最大,故得此名。其基本走向定于两汉时期。
广义的丝绸之路指从上古开始陆续形成的,遍及欧亚大陆甚至包括北非和东非在内的长途商业贸易和文化交流线路的总称。除上述路线之外,还包括约前5世纪形成的草原丝绸之路,中古初年形成,在宋代发挥巨大作用的海路丝绸之路和与西北丝绸之路同时出现,在宋初取代西北丝绸之路成为路上交流通道的南方丝绸之路。
虽然丝绸之路是沿线各国共同促进经贸发展的产物,但很多人认为,中国的张骞两次出使西域,开辟了中外交流的新纪元。从此,这条路线就成为了“国道”,各国使者、商人沿着张骞开通的道路,进行贸易。这条东西通路,将中原、西域与阿拉伯、波斯湾紧密联系在一起。经过几个世纪的不断努力,丝绸之路向西伸展到了地中海。广义上丝路的东段已经到达了韩国、日本,西段至法国、荷兰。通过海路还可达意大利、埃及,成为亚洲和欧洲、非洲各国经济文化交流的友谊之路。
丝绸之路是历史上横贯欧亚大陆的贸易交通线,在历史上促进了欧亚非各国和中国的友好往来。
远古时期,在尼罗河流域、两河流域、印度河流域和黄河流域之北的草原上,有着一线由许多不连贯的小规模贸易路线大体衔接而成的草原之路。这一点已经被沿路诸多的考古发现所证实。这条路就是最早的丝绸之路的雏形。
早期的丝绸之路上并不是以丝绸为主要交易物资,在公元前15世纪左右,中国商人就已经出入塔克拉玛干沙漠边缘,购买产自现新疆地区的和田玉石,同时出售海贝等沿海特产,同中亚地区进行小规模贸易往来。而良种马及其他适合长距离运输的动物也开始不断被人们所使用,令大规模的贸易文化交流成为可能。比如阿拉伯半岛的经常使用,耐渴、耐旱、耐饿的单峰骆驼,在公元前11世纪便用于商旅运输。而分散在亚欧大陆的雅利安人和斯基泰人据传在公元前31世纪左右即开始饲养马。双峰骆驼则在不久后也被运用在商贸旅行中。另外,欧亚大陆腹地是广阔的草原和肥沃的土地,对于游牧民族和商队运输的牲畜而言可以随时随地安定下来,就近补给水、食物和燃料。这样一支商队、旅行队或军队可以在沿线各强国没有注意到他们的存在或激发敌意的情况下,进行长期,持久而路途遥远的旅行。
1、月氏:(yuèzhī或ròuzhī)为公元前3世纪至公元1世纪一个民族名称。早期以游牧为生,住在今中国的甘肃一带,并经常与匈奴发生冲突,到后来被匈奴攻击,一分为二:西迁至伊犁的,被称为大月氏;居留于中国甘肃及青海的祁连山西北麓一带的,被称为小月氏。这时,月支开始发展,慢慢具有国家的雏型。由于大月氏位处于丝绸之路,控制着东西贸易,使它慢慢变得强大。《后汉书•西羌传》记载:月氏“被服饮食言语略与羌同”,说明月氏的语言很可能属于汉藏语系。
2、祆(xiān)教:即琐罗亚斯德教是流行于古代波斯(今伊朗)及中亚等地的宗教,中国史称祆教、火祆教、拜火教。相传为公元前六世纪琐罗亚斯德创。波斯萨珊王朝奉为国教。其教创善、恶二元论,以火为善神的代表。南北朝时传入中国后又称“火祆教”或“祆教”。唐代曾一度于长安建祠盛行,并立官专管。 武宗反佛后渐废不传。琐罗亚斯德教是基督教诞生之前中东和西亚最有影响的宗教,古代波斯帝国的国教,曾被伊斯兰教徒贬称为“拜火教”。琐罗亚斯德教的教义一般认为是神学上的一神论和哲学上的二元论。琐罗亚斯德教的经典主要是《阿维斯塔》,意为知识、谕令、或经典,通称《波斯古经》。
关于丝绸之路
简介
人类历史在不断迁徙中发展,随之产生的是频繁的商品交换,以及技能和思想的交流。这样的通信与贸易之路在欧亚大陆上纵横交错,在历史上逐渐形成了我们今天所称的丝绸之路。丝绸之路覆盖着路上和海上交通,来自各个地域的人们在此沿线进行着丝绸与其他商品的交易。海上丝路将东方与西方以航线连接起来,是广义上的丝绸之路的重要组成部分。海上之路曾经是贸易香料的主要渠道,后来被人们以香料之路而知晓。
然而这个庞大的网络承载的不只是商品的交易。频繁的活动和人口的混合引起了知识、思想、文化和信仰的交流,给亚欧人的历史和文化带来了深远的影响。在沿线城市上这样的思想文化交流不断发展,逐渐形成了多个教育与文化中心,吸引着行客们踏上这条商路。自然科学、艺术、文学以及手工艺和技术在这里被分享与传播。随之,语言、宗教和文化也在各自发展中互相产生了影响。
实际上“丝绸之路”只是现代的一种叫法。在其悠长的历史中,这条古老的道路并没有一个确切的名字。十九世纪中期,德国地理学家,费迪南·冯·李希霍芬,把这个商道命名为Die Seidenstrasse (丝绸之路),神秘且令人浮想联翩。
丝绸的制作与贸易
丝绸是将蚕茧中提取的蛋白纤维编织而制成的纺织品。丝绸制作技艺来源于古代中国,公元前约两千七百年。作为价值极高的手工制品,丝绸被中国朝廷保留为御用服饰、家纺、横幅以及其他外交赠品。湖北省发现的公元前三到四世纪的古墓里出土了一批精美的绸缎,包括锦缎,纱和绢绣,以最古老的完整的丝制服饰。
丝绸的生产过程被严格保密了约三千年。当时朝廷对个人向外国人泄露丝绸生产过程的处罚是死刑。中国在制丝业上的垄断并没有使其消费市场局限于中国。一方面,丝绸作为外交贡品流入他国。另一方面,丝绸贸易也一直非常频繁:开始仅是向邻国销售,而后推广到更远的国家。到汉朝(公元前206年到公元220年)时,丝绸已成为了中国的主要出口产品。近年来埃及、北蒙古等地都出土了中国在汉时期的纺织品。
公元前一世纪,丝绸传入罗马帝国。丝绸被视为颇具异国风情的奢侈品而变得极为流行,甚至使得罗马帝国颁发诏令以控制其价格。丝绸的流行一直被延续到中世纪。当时丝绸既是皇室使用的典型面料,也是财政的重要来源。拜占庭对于丝绸制作的严格法令规定也体现了丝绸的特殊地位。此外,拜占庭教堂对于丝制服饰与室内装饰需求也非常大。因此,丝绸成为了欧洲至远东的商路发展的早期动力之一。
关于制丝技术的知识在当时是非常宝贵的。尽管中国朝廷竭力保密制作方法,这个秘密还是在中国外传播开来。在公元前6世纪,此项技术首先流传到了印度和日本,接着传播到波斯王国,最后到西方。在公元6世纪,历史学家普罗科匹厄斯描述道:大约在同一时期 [公元前550年],印度的一些僧侣来到了罗马帝国。他们说服了查士丁尼大帝罗马不应该再从波斯购买丝绸,并达成了他们从中国带回来的养蚕缫丝的技术传授给罗马的协定,以便罗马今后拒绝从其敌国波斯或者其他任何国家购买丝绸。这些僧侣们说先前他们在一个印度人经常到访的地区,Serinda,完全掌握了制作丝绸的艺术。此外,僧侣们对不断追问试探他们的皇帝说,蚕是丝绸的制作者,大自然在驱使他们不断制作丝绸。虽说不能直接将火蚕运输过来,但是蚕的养殖却很容易。一批蚕卵可以孵化出无数只幼虫,而人们只需在孵化后用粪便盖住幼虫作为保暖,直至它们成长为成虫。僧侣们分享了这些信息之后,他们与皇帝达成了约定并回到了印度。当他们将蚕卵带回拜占庭,教其上述养殖方法,将蚕卵孵化成幼虫,以桑叶来饲养。罗马帝国的制丝艺术之路就此开始。
丝绸之外:丝绸之路商品的多样性
虽然丝绸贸易是中亚商道的最早的催化剂之一,这仅仅是东、西方之间贸易的广泛商品中的一类。其他商品包括丝绸之外的纺织品、调味品、粮食、蔬菜和水果、动物皮草、工具、木工、五金、宗教物品、艺术品、宝石等等。
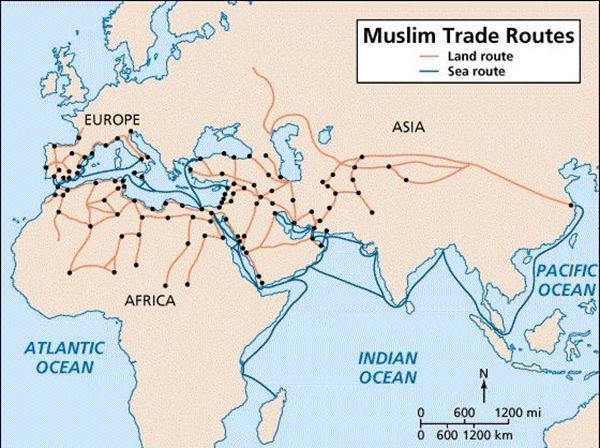
在中世纪,丝绸之路开始流行,人们的往来越来越多,直至19世纪,人们还在使用这条商道。这不仅证明丝绸之路的重要性,还说明其弹性和适应性能够满足不断发展变化的社会需求。这些商道也并没有沿着任何特定道路 — 商人们往往自由选择通往东欧、中东、中亚地区和远东多个地区的不同交通路线。除陆路之外,商人们还可以选择从中国和东南亚,经由印度洋到非洲、印度和近东的海上丝绸之路。
纵观历史,根据时间的推移和地缘政治环境的变化,丝绸之路也一直发展。例如,罗马帝国的商人们为了避开经过罗马之敌区帕提亚领土,选择了向北出发,经过高加索地区,途经里海的路线。相似地,中世纪早期,频繁的商业往来发生在横跨中亚的河道运输网上。与此同时,这条河道中的水位时而上升时而下降,有时干涸,这条贸易之路也相应的转移。
海上贸易是当时另一个极其重要的世界贸易网络。其最有名的用途是香料运输,来自印尼摩鹿加群岛(以香料岛之名而闻名)的肉桂、胡椒、姜、丁香和豆蔻供给全球市场。故海上丝绸之路又被称为‘香料之路’。商人经由丝绸之路,交易纺织品、木制品、宝石、金属制品、香料、木材和藏红花。丝绸之路超过十五万公里,从日本西海岸,经过中国海岸线、东南亚和印度一直到中东和地中海。海上丝绸之路连接了阿拉伯半岛,美索不达米亚和印度河流域的,其历史可以追溯到几千年前。在中世纪初,来自阿拉伯半岛的船员们开拓并了跨越阿拉伯海直到印度洋的新航线,海上丝绸之路网络也因此扩张。实际上,早在八世纪,阿拉伯与中国之间的海上贸易交通已初步建立。
航海术、天文学和造船术的发展实现了长途的海上旅行。位于海上丝绸之路沿岸的城市因港口而壮大起来,如桑给巴尔,亚历山大,马斯喀特,和果阿。这些城市经常有来来往往的商人和水手以及大规模的集市,也是商品、思想、语言和信仰的交换的中心,因而成为了财富的集聚地。15世纪晚期,葡萄牙探险家达伽马,在好望角周围航行,这是欧洲船员初次参与东南亚海上贸易。到了16、17 世纪,丝绸之路和它的利润丰厚的贸易成为了葡萄牙、荷兰和英国之间激烈竞争的焦点。这些殖民国家给他们占领的海上之路沿岸港口带来了财富和保障。他们有效治理了海上贸易通道,授权当地权力机构对于需求极大的进口商品的垄断进行管制,并针对商船征收了巨额的税款。
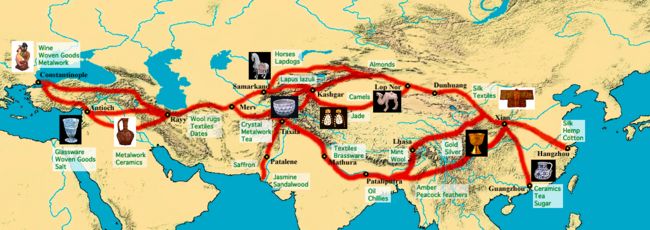
上方地图显示了各种不同的陆上与海上商道。来自世界各地的商人靠着这个交通网络运输交易着种类丰富的商品。商人的驼队通常选择在一些路段停留。他们或稍作歇息、补充用品,或留下扎营做买卖。这样的停留点遍布整个丝绸之路,沿线城市和港口因而欣欣向荣。
丝绸之路既活跃又有渗透性。商人们与当地人做买卖,将外来商品卖给当地人的同时也购买并带走各地的土产品。丝绸之路不仅丰富了商人的物质财富与商品的多样性,还促进了在丝绸之路上沿线的文化、语言、思想的交流。
交流与对话
也许在所有的丝绸之路的角色中,最有历史意义的即其对不同地区的人们互相交流往来的促进作用。在实践层面上,商人们若要成功地进行谈判就必须学习他们所经国家的语言和风俗习惯。因此文化交流是物质交换的一个重要因素。此外,许多行客为了体验沿线城市的知识和文化交流而踏上了这条冒险之路。
横跨丝绸之路的沿线区域分享了科学、艺术、文学以及手工艺和技术的知识。同时,语言、宗教和文化也在各自的发展中相互影响。通过丝绸之路在世界范围内得到传播的最闻名的技术包括造纸术以及印刷术。类似地,由于得到了行客的学习和传播,整个中亚地区的灌溉系统普遍具有相似特征。这些行客不仅携带和传播自己的知识,同时也吸收了不同社会的当地文化技术。
在公元前2世纪,将军张骞开辟了第一个从中国至西方的丝绸之路。说起这位英雄,比起贸易开拓者,他更是一位外交官。汉武帝在公元前139年,联盟外国,以抗击中国的世袭敌人—匈奴。张骞被派往西部时,被匈奴抓获并被监禁起来。十三年后,他越狱并逃回了中国,给汉武帝讲述了丰富的经历及细节并做了一些详细的报告。在公元前119年,汉武帝又派张骞拜访邻国,建立一个早期从中国到中亚的路线。
宗教和求知成为了人们沿线的旅行的动机。到印度取经后将圣文带回中国的僧侣们在途中书写的旅行日记,如今是关于丝绸之路的重要考据。玄奘在629至公元到654年的25年期间写下的日记不仅具有巨大的历史价值,同时也启发了16世纪神魔小说的诞生。“西游记”,即这样一部中国古代的经典之作。在中世纪,欧洲的僧侣胜任外交和宗教使团,访问东部。Giovanni da Pian del Carpini在1245年至1247年由教皇Innocent 四世派出访问蒙古;随后,佛兰德方济各会修士William of Rubruc在1253年至1255年由法国国王路易九世派出,再次访问蒙古汗国。其中最著名的应属威尼斯探险家马可·波罗。他的游历约于1271和1292之间,长达20多年。他逝世后其书写的游记在欧洲变得极受欢迎。
横跨整个欧亚大陆的路线是宗教的传播基础。佛教是丝绸之路沿途上宗教传播一个例子。在阿富汗巴米扬、在中国五台山以及在印度尼西亚婆罗浮屠都留有佛教艺术圣地和寺庙基督教,伊斯兰教,印度教,琐罗亚斯德教和一神教以相似的方式传播。行客们吸收他们所接受到的文化,并将这些不同的文化分享给自己的同胞。如此,印度教和伊斯兰教被商人们通过海上丝绸之路从印度和阿拉伯引入到印尼和马来西亚。
行走在丝绸之路上
丝绸之路本身的发展基于人们在其区域的交通往来。在中世纪,马或骆驼是商队在陆路物流上的典型方式。丝绸之路上的客栈是专门为了大型长途旅行商队所设计的。这些客栈对于这条路线上人和货物的交通发挥了至关重要的作用。通过对土耳其到中国这一段丝绸之路的观察可得,这些客栈不仅为旅客提供了可口的饭菜和安全的歇息地以为未来的行程做准备,同时也提供了与当地市场交换货物、贸易和购买当地产品并与其他商人们交流的平台,促进商人们互相交流文化、语言和思想。
随着丝绸之路发展壮大,沿线的生意机会越来越多。商旅客栈日渐其需,从10世纪开始,商旅客栈的建立遍布了整个中亚地区,一直延续至19世纪。这个商旅客栈网,从中国延伸至印度大陆、伊朗、高加索、土耳其、北非、俄罗斯和东欧国家。其中部分商旅客栈至今尚存。商旅客栈的位置是依据丝绸之路上每一天的行程来分布的。这样商人和其他行客能够避免数天数夜停留在危机重重的丝绸之路上,并保护珍贵货物的安全。平均每30至40公里就会有一些商旅客栈,周边环境维护较好。
历史上商人在漫长的海上贸易旅程中面临着不同的挑战。至中世纪以来,航海术,尤其是造船术的发展,提高了海上旅行的安全。在中世纪,对船员们最大的威胁之一就是缺乏饮用水。海上沿线丝绸之路港口的发展,不仅为商人贸易提供做买卖的机会,而且保证了淡水供应。商船所面临的另一种风险是海盗。船上利润丰厚的货物往往成为海盗的目标。
丝绸之路遗产
在19世纪,考古学家、地理学家以及一些热情的探险者踏上了丝绸的探险之路。来自法国、英国、德国、俄罗斯和日本,这些研究者穿越中国西部,今位于新疆的塔克拉玛干沙漠,沿着丝路追寻古迹。因他们的贡献,如今有许多考古学上的发现和大量的学术研究。这些发现使得丝路之历史又重新引起了世界的关注。
如今,许多历史建筑和纪念碑、标志着丝路通道的商旅客栈、港口和城市尚存。不同但相互关联的文化、语言、习俗和宗教在丝路上发展了上千年,恰是历史悠久的丝绸之路的映射。商人们及许多不同国籍的旅行者的往来不仅在商业交流上,而且在文化融合的过程中,带来了持续并广泛的影响。从早期的探索阶段开始,丝绸之路逐渐成为横跨欧亚大陆上,促进社会的形成的推动力。
相关链接:
UNESCO Integral Study of the Silk Roads, Roads of Dialogue
Recommendations for transnational heritage corridors of Silk Roads site nomination
Caravanserais
History of civilizations of Central Asia
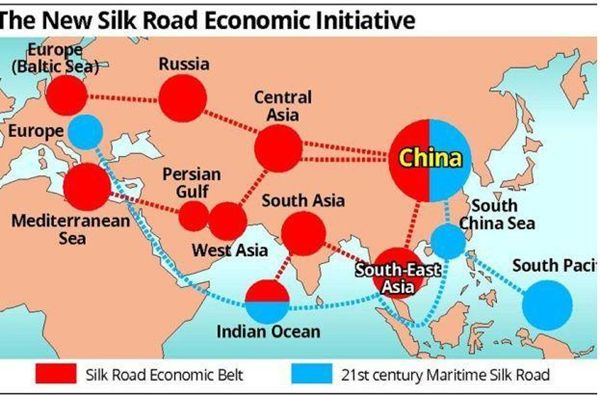
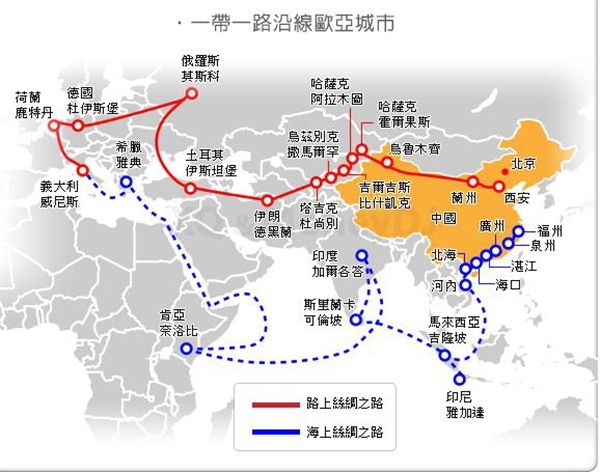
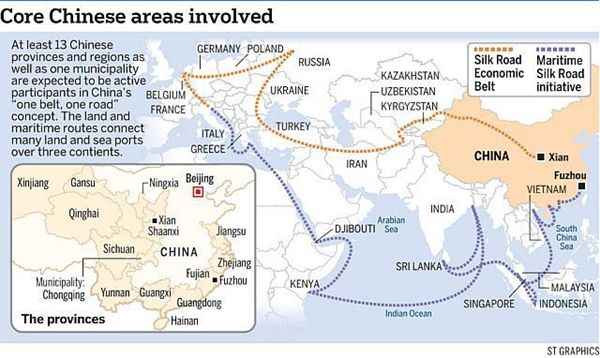
21 世纪 新丝绸之路
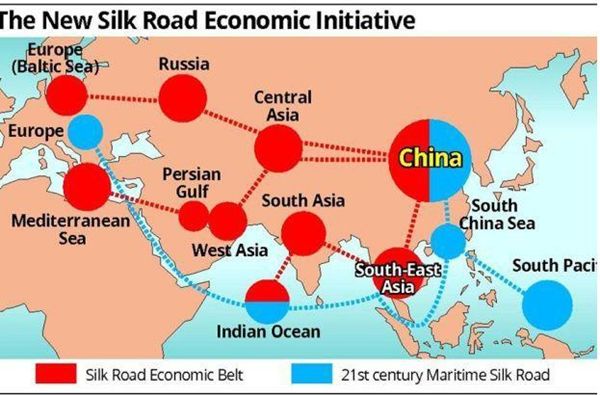
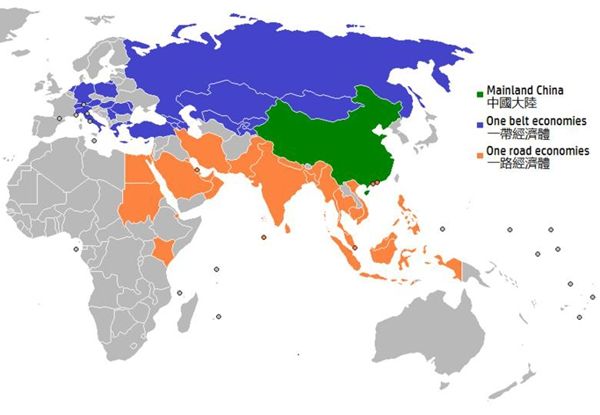
丝绸之路经济带和21世纪的海上丝绸之路 (Belt & Road, B&R) 是一项发展战略和框架, 重点是国家间的连通性和合作, 主要是中国之间还有欧亚大陆的其他地方它由两个主要组成部分, 陆上 "丝绸之路经济带" (SREB) 和远洋 "海上丝绸之路" (MSR) 与战略计划发布于2015年。 自那时以来, 已在这一倡议中开发了许多经济带和道路中心、研究所、出版物、网站和政府分支机构。中国希望建立一个新的经济区, 从中国, 包括所有的国家在亚欧大陆组成的东盟成员国, 印度的亚欧国家, 上海合作组织的成员国,中东北非国家, 西亚国家, 欧洲和东非的一部分。 它包括几乎所有主要的全球经济实体 (除去美洲, 澳大利亚和新西兰, 西非, 韩国和日本等与美国关系密切的经济体)。
The Silk Road Economic Belt and the 21st-century Maritime Silk Road, also known as The Belt and Road (B&R) is a development strategy and framework, proposed in 2013 by Xi Jinping that focuses on connectivity and cooperation among countries primarily between the China and the rest of Eurasia. It composes of two main components, the land-based "Silk Road Economic Belt" (SREB) and oceangoing "Maritime Silk Road" (MSR) with a strategic plan issued in 2015. Since then, numerous Belt and Road centres, institutes, publications, web sites and Government branches have been developed on this initiative. In a nut shell, China wants to create a new economic zone that spans from China to include all the countries on the Eurasian continents comprising of ASEAN member nations, Indian Sub continent countries, SCO (Shanghai Cooperation Organization) member nations, countries of MENA (Middle East North Africa), West Asian countries, Europe and part of East Africa. It includes almost ALL of the major global economic entities minus Americas, Australia and New Zealand, West Africa, Korea and Japan --political economic powers that traditionally closely linked with USA .
从地缘政治的角度来看, 中国对欧亚大陆的影响, 一直是自美国撤出阿富汗/伊拉克和苏联解体以来的一个权力真空, 以抵消美国在亚太地区 re-asserting 的影响。特别是自从奥巴马政府。 此外, 中国利用经济而非军事或文化力量作为万有引力的中心, 因为贸易--而非战争--历来是亚洲主要的区域间纽带。此外, 中国目前在包括钢铁、水泥、技能劳动力等的基础设施领域的巨大产能过剩, 需要找到出路, 利用其他地方的经济可持续的基本结构在中国正达到饱和点投资具有合理的经济回报。此外, 中国自身在经济成就上的成功--即经济发展而不损害其政治意识形态和结构--可能是许多国家的政治领导人的一个欢迎模式。
From a geopolitical perspective, China pivots its influence on Eurasian Continent, hitherto a power vacuum since US withdrawal from Afghanistan/Iraq and the collapse of USSR, to counter balance US influence which is re-asserting in the Asia Pacific region especially since the Obama Administration. Furthermore, China utilizes economic rather than military or cultural power to service as the centre of gravitation as trade--rather than war--has historically been the major inter-regional bonds in Asia. Also China's current huge overcapacity in infra-structure sector, including steel, cement, skill labour and expertises, needs to find means to utilize elsewhere economic sustainable infrastructures in China are reaching a saturation point as further investment with have few justifiable economic returns. Furthermore, China’s own success in economic achievement--economic development without compromise its political ideology and structure--may be an welcoming model for political leaders in many B&R countries.
这一繁荣的经济圈包含了一些 mindstaggering 的数据: 它包括60多个国家, 63% 的全球人口 (44亿), 24% 全球经济, 和30% 的全球 GDP。 中国设想, 将成为人类历史上最大的贸易直通方式, 是人类文明中最大的交通系统和贸易相关项目, 也是跨越最广范围的最大的一体化经济网络。不同的社会-种族和政治实体。由于大部分的国家仍处于发展阶段, 仍有足够的空间释放他们的经济潜力;如果是这样的话, 它很可能是本世纪最重要的经济发展计划, 因为中国在过去30年的经济奇迹。即使是由于种族、宗教和历史原因, 包括了许多敌对群体--印度(佛教、穆斯林,孔雀王朝)和巴基斯坦、犹太人(基督教)和阿拉伯人、伊朗(波斯王朝)和阿拉伯世界(伊斯兰)等, 而且往往是区域冲突的闪点, 就像目前的叙利亚和 ISIS 的情况一样, 中国似乎孵化的成功的 B&R 倡议的假设双赢的商业利益通过贸易可以克服甚至超越的差异, 导致一个由许多不同的国家和团体通常由商业和贸易联系组成和谐和繁荣的 B&R 区。中国将不得不投入大量的资本投资, 面临高风险, 因为在SREB/MSR 的道路上,有许多易受伤害的地方和瓶颈点, 并期望有可能出现低甚至负的投资回报, 因为许多 B & R 国家是高度 challenged 地方为社会经济发展。中国对经济实力超越文化历史差异的设想的乐观态度的基础, 似乎是基于中国自身在社会主义背景下发生的经济成功的经验, 这是缺乏宗教作为社会政治因素.这项中国成功的项目, 在那些宗教是主要的, 如果不是主宰社会因素的地区, 还有待检验。
This B&R co-prosperity economic circle contains some mindstaggering data: it includes 60+ nations, 63 % of global population (44 Billion), 24% Global economy, and 30% of global GDP. China envisions that B&R will become the largest trade thru-way in human history, the largest infra-structure in transport system and trade related projects in human civilization, and the biggest integrative economic network that span through the widest spectrum of diverse socio-ethnic and political entities. Since most of the nations in B&R are still in developing stage, there are still plenty of rooms to unleash their economic potentials; should that be the case, it may well be the most significant economic development plan in this Century, after China's economic miracles during the past three decades. Even though B&R regions includes many rival groups due to ethnic, religious and historical reasons--India and Pakistan, Jews and Arabs, Iran and the Arab world...etc., and are often flash points of regional conflicts, as in the current case of Syria and ISIS, China seems to hatch the success of the B&R initiative on the assumption the win-win commercial interests through trades can overcome and even transcend differences between rival regional fractions leading to a harmonious and prosper B&R region composed of many different nations and groups commonly bonded by commercial and trade ties. China will have to put in large amount of capital investment, to face high risk as there many vulnerable spots and bottle necks points along the SREB/MSR paths, and to expect the possible of low and even negative investment returns as many of the B&R countries are highly challenged places for socio-economic developments. China's basis on an assumed optimism of B&R initiative on economic power to override cultural-historical difference seemed to be based on China's own experience in economic success happening within a socialist context which lacks religion as a socio-political factor. Such project of China's success onto B&R region where religions are an major, if not dominating social factor, is yet to be tested.
由于 B 和 R 贸易节点正在建立并通过贸易媒介、高速列车、机场、现代港口和电信系统进行连接, 将有许多现有的城镇升级为主要的国际贸易中心;这些中心将通过贸易和服务, 将数十或几十个连接起来, 作为经济基础结构来塑造这个 B 和 R 球体。这些新的城市将有以下功能: 提供设施, 以加强国际贸易, 如运输, 物流, 金融, 数据, 银行, 会计, 翻译, 法律服务等, 并在同一时间成为区域中心发展辐射影响在周围的区域。 这些城市将不可避免地吸引来自 B 和 R 社区及其他地区的专业专业人员提供各种服务。此外, 这些城市的外籍人士也将逐步建立起来, 例如, 中国自35年前开始对外开放以来, 在上海和广州逐渐建立了国际侨民。除了这些外籍人士社区之外, 还需要为他们及其家属提供日常服务, 如学校、商店、娱乐场所、餐馆、诊所和宗教场所, 以满足他们的具体需要, 以便有一个稳定的外籍社区支持越来越多的区域间贸易服务。
As the B&R trading nodes are building up and are connecting by trade vectors, high speed trains, airports, modern harbours and telecommunication systems, there will be the upgrading of many existing towns or cities into major international trading hubs; these hubs will number several tens or dozens interconnected through trades and services as the economic infrastructure to shape this B&R sphere. These new cities will have the following functions: provide facilities to enhance international trading such as transport, logistics, finance, data, banking, accounting, translation, legal services ...etc. and at the same time become the centre of regional development radiating influence in surrounding areas. These cities will inevitable draw specialized professionals from B&R communities and beyond to provide various services. Also there will be a gradual build up of these B&R expats in these cities such as the gradual building up of international expats in Shanghai and Guangzhou when China began to open up since 35 years ago. Along with these expat communities, there are need to provide daily services to them as well as their dependents, such as school, shop, recreation, restaurants, clinic and religious venues catering to their specific needs in order to have a stable expat community to support the increasing volumes of inter-regional trade services.
由于跨区域移徙, B 和 R 侨民社区预计将增加, 这些外籍社区和东道社会之间的动态互动将产生深刻的文化-宗教影响。本文将对这种情况进行推测, 并推测一些可能的结果。本文所用的基本假设有三种: 一是经济推动和拉动理论认为, 人类的迁徙模式主要是由经济力量塑造的--经济条件较差的地区会促使人们离开富裕地区如果有更多的机会获得更好的收入, 富裕地区将吸引人们来获得更好的经济机会和服务。 其次: 人是宗教影响和传播的主要活动主体, 几乎所有的宗教传教活动。宗教内容需要通过信徒的化身来表达, 以一种真实的方式来传达宗教的信息, 以吸引新的信徒, 因为宗教不仅仅是一套哲学思想, 而是一种生活方式, 需要在生命形式。第三: 由于传教士可能会挑战当地的宗教信仰体系, 像传教士工作这样的蓄意传教活动可能会加剧社会文化紧张。 无意的传教, 如外国侨民社区的存在等宗教信仰的被动证人, 只要这一群体不打乱东道社会目前的社会宗教动态, 就可以促进社会容忍和多样性。 基于这些假设, 本文建议, "B 和 R" 倡议将迎来一个更具宗教多样性的环境, 增加宗教间的紧张关系, 并挑战中国对商业利益的假定, 这将取代了区域间的历史、文化和宗教差异, 经济纽带可以克服社会-宗教紧张关系, 这是中国决策者所持有的传统观念。然而, 最初的研究已经强烈地表明, 穆斯林极端主义者是由意识形态造成的, 而不是经济上的--贫穷--原因。 中国对繁荣和谐的经济开发区的愿景, 可能会因特定语境下宗教动态的复杂性而产生一般的混合和对立的后果。随着全球政治秩序的不断波动, b 和 r 倡议可能需要经常进行重大调整中国境内的相关移民
With the projected increase of B&R expat communities due to inter-regional migration, there will be profound cultural-religious implications between the dynamic interactions of these expat communities and hosting societies. This paper will speculate on such scenario and conjecture on some of the possible outcomes. There are three basic presuppositions used in this paper: Firstly the economic push and pull theory which suggests that that human migration patterns are largely shaped by economic forces--areas with poor economic conditions will push people to leave for rich areas where there are more opportunities for better incomes, and rich areas will attract people to come for better economic opportunities and services. Secondly: human being is the main active agent for religious influences and transmission in almost all religious proselytising activities. Religious content needs to be expressed through the embodiment of the believers to convey the religious message in an authentic way to attract new followers as religion is more than a set of philosophical ideas but rather a way of live that needs to be demonstrated in a life form. Thirdly: Intentional proselytising activities such as missionary work may contribute to the escalation of socio-cultural tensions as missionaries may challenge the local religious believe system. Unintentional proselytising such as passive witness of religious faith like the presence of an expat community may promote social tolerance and diversities so long as this group does not upset the current socio-religious dynamics of the hosting society. Based on this these presuppositions, this paper suggests that the B&R initiative will usher in a more religious diversity environment, increase inter and intra religious tensions, and challenge the China's assumptions on commercial interests that would supersede inter-regional historical, cultural and religious differences, and that economic ties can overcome social-religious tensions, a conventional belief held by Chinese policy makers. However, initial researches have already strongly suggested that Muslim extreme fundamentalists are caused more by ideological than by economic--poverty--reasons. China's vision of a prosper and harmonious B&R economic zone may general mix and perhaps opposing consequences depending on the complexity of the religious dynamics of a particular context. With the increase fluctuating of global political order, B&R initiative may need constant major readjustment B&R related Migrants within China
The economic push and pull factors in human migration has well been documented in China as more than 150 million China's internal migrants are moving form mostly impoverished homeland to prosper regions, from rural areas to urban cities, and from regional cities to metropolitans, to seek better economic opportunities. Similar patterns are also observed in Eurasia as migrant workers such as Filipinos in Gulf States, Indonesians in Hong Kong, Turkish in Germany, or Vietnamese in Taiwan. Almost all of these migrants are induced by higher incomes in hosting nations than in their home countries. The flows are often dynamic responding to economic changes. For example, as China's rural areas are improving in economic opportunities since about five years ago, there has been a decrease in flow of rural population into the Pearl Delta areas for factory works, and increase flow of population to the second tier cities as economic tempo is picking up in those cities while the major urban canters are slowing down the developmental pace. With the B&R initiatives, one may expect those cities and regions in China directly benefitted by B&R will attract domestic skilled labours and professionals from all over China building up B&R related projects. Those cities will mostly be the Southern coastal provinces and South-western boarding provinces for the Maritime Belt and the North-western Provinces for the Silk Road as illustrated shown by the following picture
http://www.postwesternworld.com/2015/03/10/chinas-pivot-eurasia/
As for domestic migrants, they will mostly be specialized professionals engaging in trade, commerce, logistic, telecommunication, finance and transports, as most of these B&R gateway cities, such as those on Maritime harbour port cities and bordering region cities, will serve as commercial and transport hub from the China side for OBOR. There may perhaps be many construction works for building of infrastructures such as railway and ports, but these construction workers will leave once the constructions are completed and not leaving any long-term socio-religious impacts. However the commercial related domestic professionals drawn from all over the nation, along with their dependants, will probably stay on to keep these commercial hubs in function. These internal migrant professionals will most likely be drawn from major international commercial centres in China such as Shanghai, Shenzhen and Beijing, where a vast pool of skilled professionals are readily available.
The second major pool of migrants will be those expats related with B&R countries. One may expected to see increasing expat populations from ASEAN countries aggregated in Yunnan, Central and West Asians in Xinjiang, Central Europeans in Xian, and many others such as Russians, Iranians, Thais, Indians, Turks, Hungarians..etc. in cities where trade opportunities are available. Just as one had seen the gradual building up of Japanese, American and European expat communities in Shanghai and Beijing when China began the trading with the West since 25 years ago, and the increase of Korean expat in Northeast China as China-Korean trade increases. This group of B&R will significantly increase the international dimension as well as representation of the current expats in China who are predominantly represented by Westerners (American, European, Australians) Japanese and Korean.The third group of new migrants may perhaps be the professionals drawn from overseas Chinese population as many of them speak Chinese and come from the Chinese Diaspora communities; and perhaps most may be drawn from the vast pool of Mainland students who had studies and worked in overseas with international trading experience and are now seeking opportunities back in China. They may have a variety of residency or citizenship along with different relational contacts in China. They are neither entirely foreigners nor local Chinese and often form their own overseas returnee communities in China. May have Chinese nationals as spouses and often may not be part of the expat community of their citizenship.
B&R migrants in China: religious dynamics and interactions
All three groups will have their different cultural-religious values and interact with local society in various ways. For the first group of migrants from major commercial Chinese cities, they carry new ideas and secular values to these mostly second tier cities which are more traditional and conservative in social values. For example, a Shanghai accountant will carry with him or her not only the international auditing standard, but also the social cultural that favours international commercial activities such as meritocracy than despotism, gender equality or liberal gender relations. Strain in cultural difference will be an growing edge for those hosting cities to strive for development. The potential religious tension would mostly likely be in Muslim dominated areas of the North Western regions where Islamic influence are strong to perhaps oppose non Islamic social values such as the more casual gender relations popular in coastal regions of China where Western cultural influence are strongest. Should that be the case, these Muslim dominated areas in North-western part of China would have to embrace a more diverse society including the acceptances of the more liberal social values which may contradict the traditional Islamic social values in order to sustain the B&R operation on China side. Or some of the Muslims will find these new domestic migrants as a threat challenging their traditional religious values, and may find various means to oppose such new incursion of social values leading to social unrest.
As for the second group, regardless of where they come from, they will usually bring along with them their own religious culture into the new hosting Chinese cities which are officially secular or non-religious, as B&R region contains the majority of the worlds' Muslim, Buddhist , Hinduism, Jainism, Sikhism, Zoroastrian as well as the Orthodox Christian populations. It is also a place where most of the world's relgions are originated. Just as the Muslim traders since the 8th Centuries built up the Muslim community in Asia for generations, these new B&R expat communities will stay in those gateway Chinese cities for prolong period of time necessity for trade . They will bring with them their dependents, their religious practice and their life styles. A recent example will be the large expat Muslim communities in Yiwu along with their own schools, shops, mosques and Arabic speaking community. These Chinese B&R related cities will have to learn to make provisions for these new communities along with their perhaps exotic religious practices. It will be an eye opener for many local Chinese who has little exposure to world religions and some Chinese may even be drawn as devotees of these religions, just like many in US and Europe are drawn into Hari Krishna or the Unification Church (the Moonies) in the 1960s and 1970s.
There is also a high possibility that the new B&R expat groups in China may also escalate the already strained inter-ethnic relations, such as the Turkish merchants in Uyghur dominated Xinjiang may promote the pan-Turkic sentiment which will indirectly lend support to the East Turkistan Independent Movement challenging the sovereign claim of China over Xinjiang. Similarly the Jingpo or Dai expat from Myanmar in Yunnan may bring along with them their own ethnic-political complications from the tension between Shan or Kachin Autonomous States with the Myanmar authorities into China which may further destabilizing the already fragile China border regions with Myanmar and Laos. After all, the Jingpo ethnic minorities in Yunnan often identify themselves with their ethnic Jingpo (Kachin) across the border sharing common language, tradition and religions for centuries; many Jingpo people in China also serves in the Kachin Independent Army in Myanmar. One can find many of such examples as many of China's ethnic minorities have strong ties with their ethnic counterparts across the China border with increasing autonomous or ethno-nationalistic sentiments often enhanced by religion.
For the last major group--Chinese overseas returnees, contemporary research by Yang Fenggang suggested that a high percentage, as much as 30%, of them seemed to embrace Christian faith while they were living aboard. Such high percentage of Protestant converts among the returnees are also cause the increasing number of non-registered urban churches established in major Chinese cities patron by these Chinese returnees. Many hold foreign citizenship or residency and technically not Chinese citizens and are in rather grey areas in terms of religious administration by the Chinese authorities as they may have spouse who are not foreign passport holders yet they may worship together in a technically religious venue for foreigners, and often not formally registered. Contrary to many of the local non-registered groups by national are often harassed by local authorities, these new urban based non-registered Christian groups are supported by rich and powerful patrons who are well connected not only with senior authorities but also international religious and commercial networks who serves as a political umbrella to protest these groups from harassments by local authorities. Their presence may easily cause socio-religious tension as their religious gatherings may draw many Chinese, often colleagues or business partners of these religious returnees, to join Christianity, and some local Christians may be drawn to these powerful elite communities for protection from harassment by the authority. If that will be the case, there will be some forms of Foreign Concession zone in China’s religion landscape, envy by national Christian groups and resented by local authorities--a situation that the authority may need to address in future.
Intra B&R migrations: religious dynamics and interactions
As mentioned earlier in this paper, B&R region contains the largest population of many important world and ethnic religions. Although China may be the least religious nation, almost all other B&R nations are very religious with some even embrace religious values as their national policies, such as the case of Indonesia and Iran. Also there is a growing tend to have increasing religious influences to foster national or ethnic identity especially towards the more conservative branches on national governance and identity, such as in the case of Turkey of escalating Turkic identity, India of increasing Hinduism as national identity, Orthodox belief as the de facto Russian national identity, to name a few. There are also the emergence of extreme religious groups imposing religious rules political governance, such as the Taliban movement and the ISIS. Therefore, with the increasing intra B&R migrant populations, one would expect the new socio-religious challenges from B&R expats to various hosting B&R nations. These challenges may range from merely amusement of observing exotic religious practices by the locals in a tolerance society, to offensive behaviours in the eyes of the locals, such polytheistic images and worships in a puritanical religious society such as Hinduism practice in Saudi Arabia, to escalation of inter-regional rivals, such as Iranian Shiite in predominate Sunni's in UAE.
Also some of the interregional tensions, especially those involved with already tensed ethnic and religious revival between countries such as Iran and Saudi Arabia, or Pakistan and India, may also be escalated through the presence of rival expat communities, as these countries are competing for regional influence in political, religious and in ethnic dominancy. Social tension may also increase as the presence of some expat communities could empower, even unintentionally, local minority groups to challenge the ruling regime, such as Iranian merchants may encourage the Shiite in Yemen Shiites to oppose the Sunni ruling tribes, the Kurds in Turkey, the Tamils in Sir Lanka...etc. There are also the rise religious identity overshadowing national boundaries such as the co-ordinated demonstrates of Muslims in India, Bangladesh, Malaysia and Thailand on 25th November, 2016 to support their co-religious Rohingya in Myanmar.
Currently there are already countless religious-ethnics flash points in Eurasian Continent, with many dated back for centuries, which are currently accentuated by the rise of religious fundamentalism mixed with emergence of nationalism or ethno-centrism. The basic tenet of B&R co-prosperity sphere is based on the assumption that trade and commercial interests will override and even overcome the traditional religious-ethnic tension among rival groups or rival nations. However often one observe just the opposite in B&R regional rivals is taken place, such as Israel and the surrounding Arab nations, or India-Pakistan in Kashmir, that these intensive conflicts are contrary to any sound economic reasoning. It seems that this China led B&R initiative could bring socio-political harmony to this ancient Eurasian land through trade and economic development, or may usher in an new era of conflict intensification by inter-mixing rival groups is yet to be seen.
China-B&R religious dynamics interactions.
The increase of Chinese expat merchant or commercial related communities in B&R nations will also bring new socio-religious dynamics into these nations. Although China is an non-religious nation, or having the largest agnostic population in the world, and one can interprets that there is no religious connotation as Chinese interact with nationals from B&R region who are predominately religious. However, nationals of B&R nations with strong religious sentiments may regards Chinese merchants who are mostly secularists with secular values who will be crash with local religious social values. It has been well documented that some Chinese operate restaurants in Afghanistan are doubled as brothels and served alcohols to local Muslim youth which infuriated local Muslim communities. Similarly Chinese run bars and brothels in Peshawar, Pakistan, for international communities yet were patron by local Muslim youth which had already caused protests from local Mullahs leading to the riots and casualties at the Red Mosque in 2007. Also the perhaps hundreds of Chinese prostitutes in Dubai are currently tolerated by local authorities so long as the customers are non Dubai national; but there will come to a point of non-toleration if Dubai nations are involved. It seems many countries were once welcomed Chinese merchants, especially since the 1990s till the turn of the Century, are gradually become ambivalence and even hostile toward Chinese merchants for their generally profit oriented commercialism in lieu of religious sensitivity to local culture and values. The prolong lack of religious knowledge and contact among Chinese population becomes a liability when these secular Chinese merchants with little religious understanding or sensitivity encounter with people in societies where religion is an essential part of the cultural milieu.
Furthermore, the aggressiveness of the Chinese merchants, along with their usually short business cycles especially the small entrepreneurs, are drawing increasing negative reception from many B&R countries, from resentment towards the natural resource exploitation in Myanmar, to disrespect local religious value (mostly Muslim dominated areas), to insensitive to local customs such as in Thailand towards Buddhist customs, and to cause the collapse of local industries such as plastic manufactures in Morocco, are factors that contribute towards the international resentments against Chinese presences leading to many incidents of attacks and expulsion of Chinese expat merchants in recent years from Kyrgyzstan to Vietnam—both are B&R nations. The State Owned Enterprises Projects in B&R regions, usually conducting large scale infrastructure project, are often operated in a hermitic compound with virtually no social interaction with local communities and Chinese managers and worker are rather naivety towards local religious customs. Unless Chinese merchants will have a higher sensitivity on religious cultural of B&R in general, one may expect that the will be an increase of negative sentiments towards Chinese merchants in B&R region as religious values seems to be valued over economic benefits observed from populations in most of the B&Rs nations--a fact that had not been appreciated by Chinese who are mostly non- religious and secular in social values.
Intentional proselytising may escalate inter-religious tensions
Traditional many religions in Asia spreads first through merchants and then missionaries through trade routes as in the case of Islam’s spreading to Asia.
There is also a similar pattern in the case of Christianity via Silk Route in 7th Century to China, or the Sea Route since the 16th Centuries from Europe to Asia. Also sees the spreading of Manichaeism and Zoroastrianism from East Asian to China via the Silk Route by both merchants and religious personnel. Buddhism spread from India to China, and from China to Korea and Japan, through well established trade routes developed by inter-regional Buddhist traders. The common scenario was that as some expat merchants took resident in hosting society, they brought along with them their religion, be it Christianity or Buddhism. Such religion caught the curiosity and attention of local inhabitants and some may drawn to the new religion. As this new religious community grew in size, with increase in trade hence traders and their dependents, this community would call for some professional clergies back home to provide religious formation and instruction for continuous religious observance. For example, when the Arabic speaking Muslim communities reached a certain size in Indonesia, they invited Imams back home mainly to maintain their religious observance especially to their younger generation than to proselytise others. Eventually, the more zealous members would actively promote their religion to others, and gradually professional religious proselytisers (missionaries) are involved in spreading of this new religion. In the case of Marco Polo, his memories on China aroused interests of Catholic missionaries leading the eventual Catholic mission movement from Europe to Asia. Historical evidence suggest that merchants have been often the and unintentional proselytiser and they served as precursor of missionaries who are intentional proselytisers.
Currently there are already many proselytising activities taken within the B&R regions, from Christians trying to convert believers from other faiths, especially targeting the Muslims as an reaction to the 9/11 aftermath, to the more Fundamentalist Imams to promote the Wahabbi branch of puritanical Islam, to Zen Buddhist monks to spread contemporary Buddhist message targeting intellectuals and business circles, or the Pentecostal pastors to advocate Charismatic movements within Christianity. In fact, almost all religious groups are actively conducting their proselyte activities in both inter-religious circles to win believers to intra religious sphere to promote certain sects or branches within a particular religion. It will be obvious for the intentional proselytisers, regardless of their religious affiliation to utilize whatever means to advance their missionary activities, such as trade vectors like B&R.
B&R will provide a great opportunity to these intentional proselytisers as B&R will established a free-flow inter-connected network in trades, good, services, finances, data and personnel within this huge region. Proselytisers will take advantage of this network of trade route, tagging along with merchants just they had done in the past, to spread their religious messages to whatever places along the B&R trade routes. Therefore B&R will greatly enhance the current intentional proselytising activities, as well as to develop new mission field as B&R will enhance accessibility to regions hitherto not easily reached by outsiders. In fact there has already been mission works from Christian groups, many from non-registered sectors in China, by sending Chinese Christian missionaries to Central and East Asian to convert the Muslim populations, and B&R will surely provide a great opportunity for these mission groups to intensify such movement. From both the historical evident and current religious dynamics, B&R will induce a more intensify level of inter-regional proselyte activities escalating the socio-religious tension of the region and perhaps complicated the already delicate inter-regional political relations.
Conclusion
中国领导的 B 和 R 将迎来一个更连通的欧亚大陆经济领域, 它可能发展成为一个引领全球经济的经济实体, 特别是当世界两大经济体的走强时, 欧盟正受到英美出口的挑战。 随着新的经济机会正在出现, B 和 R 区域贸易的增加也将导致区域内和内部的人口迁移增加。 这些新移民, 特别是来自其他 b 和 r 国民的人, 他们的价值观大多是宗教的, 包括世界上最大的世界宗教的人口, 无论是古代还是当代。 这些新移徙者将无意地将宗教和习俗带入其东道社会, 并将增强社会和宗教的多样性, 并有助于提高当地人口的社会容忍度。 然而, 有意传教的传教士, 传统上遵循商人建立的贸易路线, 或加上区域间的商业活动, 将增加当地的宗教动态。 这些有意的 proselytisers 将招募新的皈依者, 从其他信仰或不同的温和派分支在同一信仰中, 导致更多的社会宗教紧张关系的主办社会, 创造更多的极端或新的宗教团体社区通常对当地社区不满。此外, 中国民众普遍缺乏宗教经验, 因此宗教敏感性, 可能会对阻碍中美关系发展的国家造成负面情绪。因此, B 和 R 倡议将有助于一个更多样化的社会-宗教社会, 这可能会促进更高层次的社会容忍, 从而导致一个更和谐的社会, 或者可能使已经紧张的社会-宗教紧张局势升级, 导致破坏性的社会和区域分裂。至于中国的新经济繁荣的愿景, 以取代目前的社会-宗教历史的支离破碎的和不发达的 b 和 r 地区尚有待检验。
对中国来说, 经济发展是一项高风险、高成本、经济回报不确定的举措。宗教层面将增加这个宏伟项目的风险水平和成本因素。由于美国对中国在太平洋的围堵, 中国的石油供应安全, 巨额外汇储备的积累, 以及基础设施建设的超能力, 中国被迫采取这种定位。然而, 随着中国和全球经济的减速, 美国对中国施压的可能减少, 南海政治紧张缓和, 中东与叙利亚冲突加剧, Britexit 和民族主义欧盟国家的情绪, 可能会有一些较小的成本替代方案, 中国的全球事务进入一个不可预知的时代。也许混沌理论能给我们的水晶球出点光--期待意想不到的事情。
The China-led B&R will usher in a more connected Eurasia economic sphere which may develop into an economic entity leading the global economy especially when the strengthen of world's two largest economies, the EU as it is under challenged by the exit of Britain and USA as the Present-elected Trump cause uncertainties volatilities in Market, are weakening in global economic influence. However the increase inter-B&R region trades will also lead to increase of inter and intra regional human migrations as new economic opportunities are emerging. These new migrants, especially those from other B&R nationals which are mostly religious in values as B&R contains the world's largest populations of most of the world religions, be it ancient or contemporary. These new migrants will unintentionally carry with them religions and practices new to their hosting societies, and will enhance the socio-religious diversities as well as to contribute to the increase of social tolerances of the local population. However the intentional missionaries, traditionally following the trade routes established by merchants, or tagging along with inter-regional commercial activities, will put increase to the local religious dynamics. These intentional proselytisers will recruit new converts be it from other faiths or different moderate branches within the same faith, leading to increase of socio-religious tensions of the hosting society by creating more extreme or new groups of religious communities usually resented by local communities. Furthermore, the general lack of religious experience, hence religious sensitivities, among Chinese population may contribute negative sentiment against China among B&R nations hindering Sino-B&R relations. As a result, B&R initiatives will contribute to a more diverse socio-religious society which may promote a higher level of social tolerance leading to a more harmonious society, or may escalated the already strained social-religious tensions, leading to a destructive social and regional fragmentation. As for China's vision of a new economic prosper B&R region to replace the current socio-religious-historical fragmented and underdeveloped B&R region is yet to be tested.
For China, B&R is an economic development initiative high risk, high cost and with uncertain economic returns. The religious dimension would increase the risk level and cost factors for this grand project. China is forced to take such orientation due to the US containment of China in the Pacific, China's security of oil supply, the accumulating of huge foreign reserves, and the available of over capacity in building of infrastructure. However, with the slowing down of Chinese and global economy, the perhaps decrease of US pressure on China, de-escalation of political tension in South China Sea, the intensification of conflicts in Middle East vis Syria and ISIS, the Britexit and nationalistic sentiments in EU nations, there may be some lesser costing alternatives for China B&R as our Global Affairs enters into an age of unpredictability. Perhaps Chaos Theory can shed some lights to our Crystal Ball--expect the unexpected.