gradle启动流程
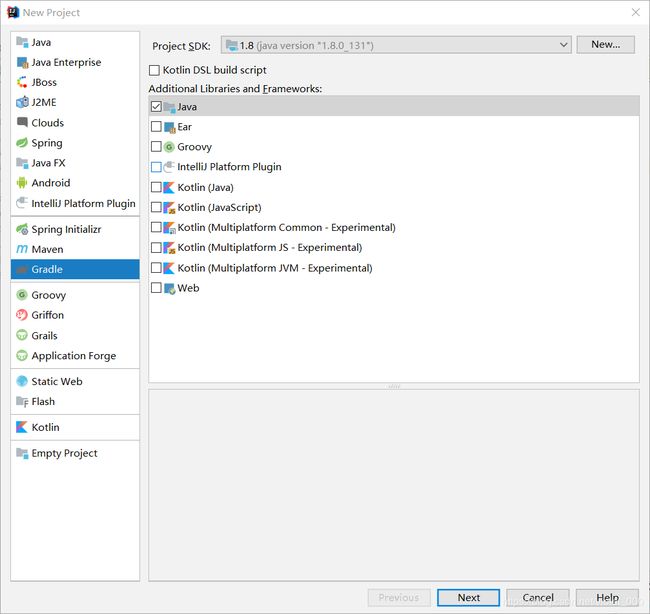
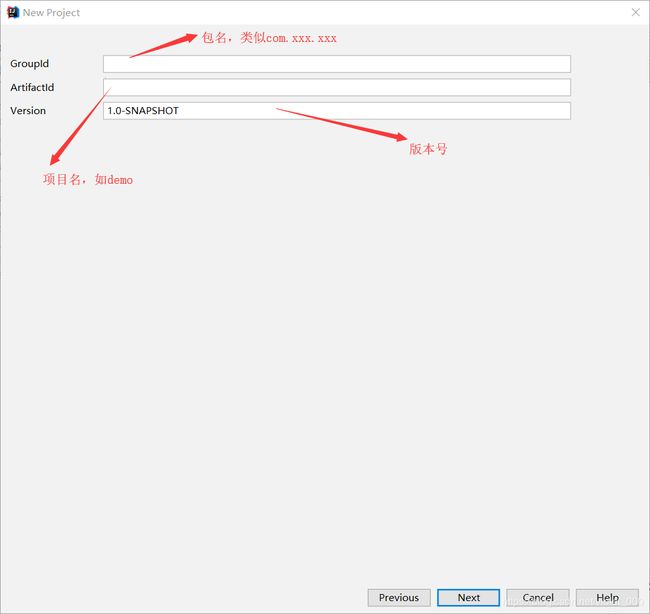
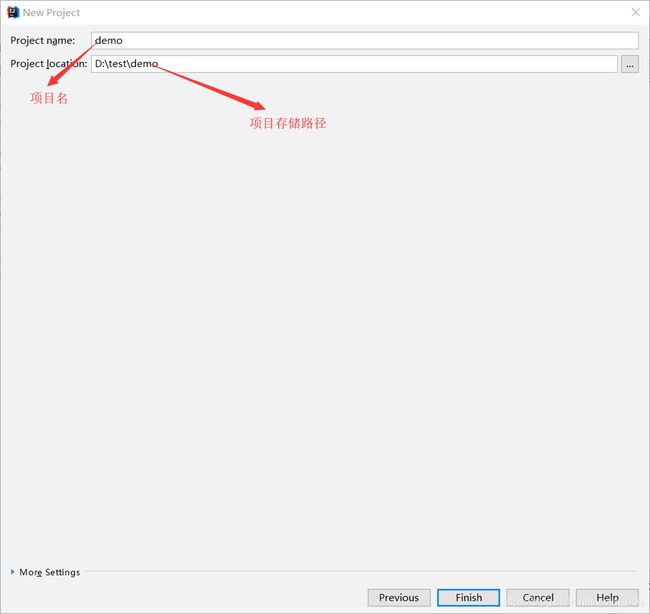
1、创建gradle项目
2、项目中使用的注解
1、@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
@SpringBootApplication是@Configuration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan 注解合起来的功能相同
1、@Configuration
@Configuration一般与@Bean一起使用,主要是用于提供类似于XML文件中实体类对象的管理,具体使用方法如下:
比如XML中有这样一段
如果不想在XML文件中配置的话,可以直接使用如下方式实现
@Configuration
public class Config {
@Bean
public UserDAO getUserDAO(){
return new UserDAO();
}
}
2、@EnableAutoConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解的类会基于你的 classpath 和已经定义的 beans 对象进行应用。
3、@ComponentScan
@ComponentScan如果指定的包没有被定义,则将从声明该注解的类所在的包进行扫描。
2、@Target
@Target返回的是一个数组,这个数组可以表明该注解可以使用的范围。
3、启动gradle
启动gradle是从main方法中启动,main方法是一个项目的起始方法
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
main中执行的是一个run()方法,这个方法点进去如下,此方法执行成功,会将程序暂停,等待人为的对该项目行为,并根据这个行为进行下一步操作(我自己感觉,这个东西很像是scanner方法,都是暂停,然后等待一个行为,根据行为去判定下一步的操作)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList();
this.configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = this.getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
Collection exceptionReporters;
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = this.prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
this.configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = this.printBanner(environment);
context = this.createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = this.getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class, new Class[]{ConfigurableApplicationContext.class}, context);
this.prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
this.refreshContext(context);
this.afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
(new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)).logStarted(this.getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
this.callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable var10) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var10, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(var10);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
return context;
} catch (Throwable var9) {
this.handleRunFailure(context, var9, exceptionReporters, (SpringApplicationRunListeners)null);
throw new IllegalStateException(var9);
}
具体暂停等待操作的方法如下,
public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
Iterator var2 = this.listeners.iterator();
while(var2.hasNext()) {
SpringApplicationRunListener listener = (SpringApplicationRunListener)var2.next();
listener.running(context);
}
}