C语言实现简单功能的命令行解析器(simple shell)
用C语言实现简单的命令行解析器,支持用户输入命令行并运行在其他的进程中。该命令行解析器可以运行在任何Linux或Mac系统。
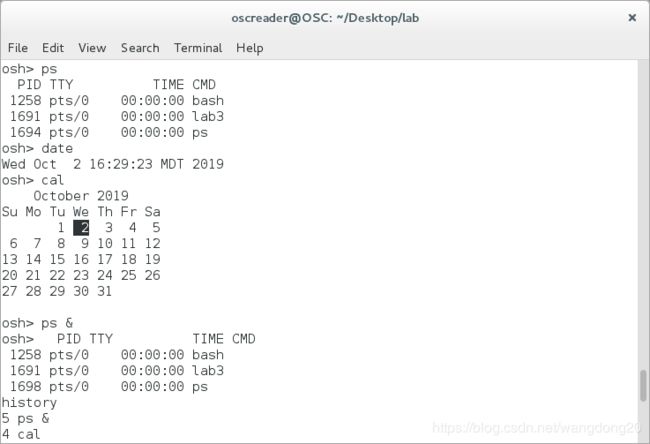
每行命令有osh> 开始,然后由用户输入命令行,例如cat prog.c,该命令将prog.c文件展示于终端上。
osh> cat prog.c
同时也支持&修饰命令行,使命令进入后台运行。本质上就是使命令行在子进程运行于后台,或者子进程和父进程同时运行。
这个project主要分成两部分,一部分是解析用户命令并使其在子进程运行,另一部分是支持我们自己命令行终端特有的history功能。即:当用户输入history命令,系统将展示最近使用的10条命令。
例如:当前history里面存储了6条输入过的命令(从最近使用的到最远使用的顺序排列)
ps -l, ls -l, top, date, cal, whoami
当输入history命令后,系统将会输出
6 ps -l
5 ls -l
4 top
3 date
2 cal
1 whoami
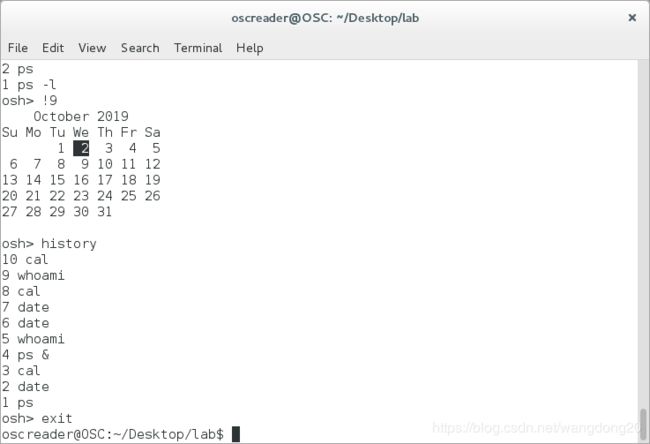
当用户输入!!命令,就运行最近运行的命令,在当前环境下也就是ps -l,
当用户输入!N命令,N代表数字,就运行第N个命令在history中,!2就运行cal.
如果输入!!命令时没有命令在history中,就输出No command in history.
如股票输入!N命令没有对应第N个命令在history中,就输出No such command in history.
用户输入exit将退出当前命令行解析器。
实现
我在实现这个命令行解析器,基本上分为两部分,一部分是解析用户输入的命令,然后在子进程中调用
execvp(char* command, char* params[]).
例如:当用户输入ps -ael命令,系统将会把命令解析到args[]字符串数组中,args[] = {"ps", "-ael", NULL}
运行时就调用execvp(args[0], args); 另外要注意解析命令里是否有&在最后,如果有&在命令最后,那么父进程就要wait子进程exit。
代码如下:
//
// main.c
// Comp322 lab3
//
// Created by 王栋 on 2019/9/26.
// Copyright © 2019 CSUN. All rights reserved.
//
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MAX_LINE 80 /* The maximum length command */
#define MAX_HISTORY 10 /* The maximum number of commands in history */
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
int parseInput(char * command, const char* delim, char* args[]) {
char *s = strdup(command);
char *token;
int n = 0;
for(token = strsep(&s, delim); token != NULL; token = strsep(&s, delim)) {
if(strlen(token) > 0) {
args[n] = (char*) malloc(strlen(token) * sizeof(char));
strcpy(args[n++], token);
}
}
args[n] = NULL;
free(s);
return n;
}
int contain(char * str, int length, char c) {
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if(*(str + i) == c) {
return TRUE;
}
}
return FALSE;
}
void freeMemory(char * args[], int length) {
for(int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if(args[i] != NULL) {
free(args[i]);
args[i] = NULL;
}
}
}
void freeHistory(char * history[], int size) {
for(int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if(history[i] != NULL) {
free(history[i]);
history[i] = NULL;
}
}
}
int insertInHistory(char* history[], int size, char * command) {
if(strcmp(command, "") != 0) {
char * s = strdup(command);
if(size < MAX_HISTORY) {
history[size] = strdup(s);
free(s);
return size + 1;
} else {
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_HISTORY - 1; i++) {
free(history[i]);
history[i] = strdup(history[i + 1]);
}
free(history[MAX_HISTORY - 1]);
history[MAX_HISTORY - 1] = strdup(s);
free(s);
return MAX_HISTORY;
}
}
return size;
}
void printHistoryCommand(char* history[], int size) {
for(int i = size - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
printf("%d %s", i + 1, history[i]);
}
}
void execute(char* args[], int index, char* history[], int size, char* command) {
pid_t pid;
/* fork a child process */
pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) { /* error occurred */
fprintf(stderr, "Fork Failed");
freeMemory(args, index);
freeHistory(history, size);
return;
}
else if (pid == 0) { /* child process */
if (execvp(*args, args) < 0) { /* execute the command */
printf("*** ERROR: exec failed\n");
freeMemory(args, index);
freeHistory(history, size);
exit(1);
}
}
else { /* parent process */
/* parent will wait for the child to complete */
if(contain(command, (int)strlen(command), '&') == FALSE) {
while (wait(NULL) != pid); /* wait for completion */
}
}
}
int main(void) {
char *args[MAX_LINE/2 + 1]; /* command line arguments */
int should_run = 1; /* flag to determine when to exit program */
int index = 0;
int sizeInHistory = 0;
char command[MAX_LINE];
char *commandInHistory[MAX_HISTORY];
while (should_run) {
printf("osh> ");
fflush(stdout);
fgets(command, MAX_LINE, stdin);
index = parseInput(command, " !&\n", args);
if(args[0] != NULL && strcmp(args[0], "exit") == 0) {
should_run = 0;
} else if(args[0] != NULL && strcmp(args[0], "history") == 0){
printHistoryCommand(commandInHistory, sizeInHistory);
} else if(command[0] == '!') {
if(strcmp(command, "!!\n") == 0) {
if(sizeInHistory > 0) {
freeMemory(args, index);
index = parseInput(commandInHistory[sizeInHistory - 1], " !&\n", args);
sizeInHistory = insertInHistory(commandInHistory, sizeInHistory, commandInHistory[sizeInHistory - 1]);
execute(args, index, commandInHistory, sizeInHistory, command);
} else {
printf("No commands in history.\n");
}
} else if(atoi(args[0]) != 0) {
int num = atoi(args[0]);
if(num > 0 && num <= sizeInHistory) {
freeMemory(args, index);
index = parseInput(commandInHistory[num - 1], " !&\n", args);
sizeInHistory = insertInHistory(commandInHistory, sizeInHistory, commandInHistory[num - 1]);
execute(args, index, commandInHistory, sizeInHistory, command);
} else {
printf("No such command in history.\n");
}
} else {
printf("No such command in history.\n");
}
} else {
execute(args, index, commandInHistory, sizeInHistory, command);
sizeInHistory = insertInHistory(commandInHistory, sizeInHistory, command);
}
memset(command, 0, strlen(command) * sizeof(char));
freeMemory(args, index);
}
freeHistory(commandInHistory, sizeInHistory);
return 0;
}
运行效果图: