springboot-包扫描源码分析
SpringApplication类提供了一种方便的方法来引导从main()方法启动的Spring应用程序
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springbootv2Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建ApplicationContext并启动
new SpringApplication(Springbootv2Application.class).run(args);
}
}下面我们来看下spring boot是怎么来实现我们的包扫描的 我们从run方法开始进入:
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
//记录应用启动时间
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
//启动SpringApplicationRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
//打印banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建applicationContext 我们这次的重点在这里面
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
} 我们来看下spring boot里面是怎么创建applicationContext的:
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
//主要是根据webApplicationType这个属性
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
//如果是SERVLET创建"org.springframework.boot.
//web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext"
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
//如果是REACTIVE创建"org.springframework.
//boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext"
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
//默认是创建org.springframework.context.
//annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, "
+ "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}我们来看下webApplicationType这个属性是怎么取值的:
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
/**
** 如果程序中有org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler这个类且没有
** org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet和
** org.glassfish.jersey.servlet.ServletContainer 这两类那么就是REACTIVE
**/
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
//SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
// "org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" }
// 如果程序中这两个类有一个不存在就是NONE
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
//如果上面都不是那就是SERVLET
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}根据上面的代码我们可以看出如果我们不引入reactive和web的依赖那么我们的程序默认就是使用的NONE,对应的
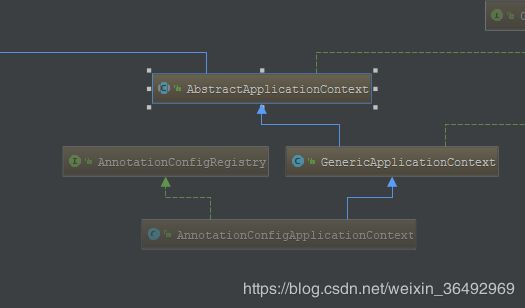
ApplicationContext就是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext这个类,接下来我们再看下这个类的构造方法:
public AnnotationConfigApplicationContext() {
//创建一个AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}public AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Environment environment) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
Assert.notNull(environment, "Environment must not be null");
this.registry = registry;
this.conditionEvaluator = new ConditionEvaluator(registry, environment, null);
//注册AnnotationConfigProcessors 重点看这里
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}public static Set registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
// 如果registry不包含ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个类信息时注册到registry
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
//注册AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
//是否需要支持jpa 是的话注册对应的bean
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
} 看到这里我们先记着我们注册了ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 和AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这两个类,我们继续往下看,我们现在来看refreshContext(context)的流程我们根据代码可以看到
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
//刷新applicationContext
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}上面代码调用到ApplicationContext的refresh 因为我们程序根据依赖推导出我们的ApplicationContext是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext这个类,所以我们来看下AnnotationConfigApplicationContext的refresh方法:
因为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext是继承于AbstractApplicationContext这个类的,所以我们的refresh就是AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法:
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
//调用程序里的BeanFactoryPostProcessors
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
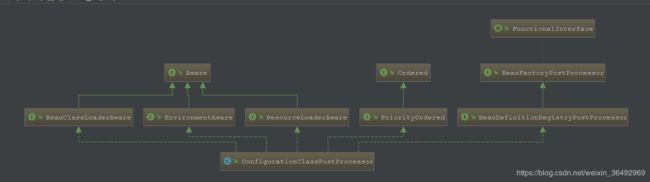
}因为我们这次主要是要看spring boot是怎么扫描包的 所以我们重点看invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors这个方法,在这之前我们先记住ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的类图:
因为方法太长所以我去掉了一些不是这次重点的代码:
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
...
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//记得我们之前注册的ConfigurationClassPostProcessor吗,因为他是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的,所以这里会被取到
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 类同时也实现了PriorityOrdered接口
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//创建ConfigurationClassPostProcessor对象并把它加到list中
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//调用方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
继续跟踪代码的话会调用到ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的processConfigBeanDefinitions方法
public void processConfigBeanDefinitions(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
List configCandidates = new ArrayList<>();
String[] candidateNames = registry.getBeanDefinitionNames();
...
// Parse each @Configuration class
ConfigurationClassParser parser = new ConfigurationClassParser(
this.metadataReaderFactory, this.problemReporter, this.environment,
this.resourceLoader, this.componentScanBeanNameGenerator, registry);
Set candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>(configCandidates);
Set alreadyParsed = new HashSet<>(configCandidates.size());
do {
//这里我们只有我们的启动类Springbootv2Application 这个parser是ConfigurationClassParser所以我们进入它的parse方法
parser.parse(candidates);
parser.validate();
...
} 最后会进入下面这方法
protected void processConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) throws IOException {
...
// Recursively process the configuration class and its superclass hierarchy.
//获得我们的启动类全名 xxx.xxx.Springbootv2Application
SourceClass sourceClass = asSourceClass(configClass);
do {
//spring 的命名规则就是do开头的就是真正干活的地方
sourceClass = doProcessConfigurationClass(configClass, sourceClass);
}
while (sourceClass != null);
this.configurationClasses.put(configClass, configClass);
}protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass)
throws IOException {
...
// Process any @ComponentScan annotations
//获取启动类的componentScans属性
Set componentScans = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), ComponentScans.class, ComponentScan.class);
if (!componentScans.isEmpty() &&
!this.conditionEvaluator.shouldSkip(sourceClass.getMetadata(), ConfigurationPhase.REGISTER_BEAN)) {
for (AnnotationAttributes componentScan : componentScans) {
// The config class is annotated with @ComponentScan -> perform the scan immediately
//扫描beanDefinition
Set scannedBeanDefinitions =
this.componentScanParser.parse(componentScan, sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName());
// Check the set of scanned definitions for any further config classes and parse recursively if needed
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : scannedBeanDefinitions) {
BeanDefinition bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition().getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
if (bdCand == null) {
bdCand = holder.getBeanDefinition();
}
if (ConfigurationClassUtils.checkConfigurationClassCandidate(bdCand, this.metadataReaderFactory)) {
parse(bdCand.getBeanClassName(), holder.getBeanName());
}
}
}
}
...
return null;
} 下面就是重点了:
public Set parse(AnnotationAttributes componentScan, final String declaringClass) {
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this.registry,
componentScan.getBoolean("useDefaultFilters"), this.environment, this.resourceLoader);
Class generatorClass = componentScan.getClass("nameGenerator");
boolean useInheritedGenerator = (BeanNameGenerator.class == generatorClass);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(useInheritedGenerator ? this.beanNameGenerator :
BeanUtils.instantiateClass(generatorClass));
//配置scanner的属性
ScopedProxyMode scopedProxyMode = componentScan.getEnum("scopedProxy");
if (scopedProxyMode != ScopedProxyMode.DEFAULT) {
scanner.setScopedProxyMode(scopedProxyMode);
}
else {
Class resolverClass = componentScan.getClass("scopeResolver");
scanner.setScopeMetadataResolver(BeanUtils.instantiateClass(resolverClass));
}
scanner.setResourcePattern(componentScan.getString("resourcePattern"));
for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("includeFilters")) {
for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) {
scanner.addIncludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
for (AnnotationAttributes filter : componentScan.getAnnotationArray("excludeFilters")) {
for (TypeFilter typeFilter : typeFiltersFor(filter)) {
scanner.addExcludeFilter(typeFilter);
}
}
boolean lazyInit = componentScan.getBoolean("lazyInit");
if (lazyInit) {
scanner.getBeanDefinitionDefaults().setLazyInit(true);
}
Set basePackages = new LinkedHashSet<>();
String[] basePackagesArray = componentScan.getStringArray("basePackages");
for (String pkg : basePackagesArray) {
String[] tokenized = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.environment.resolvePlaceholders(pkg),
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS);
Collections.addAll(basePackages, tokenized);
}
for (Class clazz : componentScan.getClassArray("basePackageClasses")) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(clazz));
}
//重点就是这里,如果我们没有配置basePackages的话那么这里就取启动类的包名
if (basePackages.isEmpty()) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(declaringClass));
}
scanner.addExcludeFilter(new AbstractTypeHierarchyTraversingFilter(false, false) {
@Override
protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
return declaringClass.equals(className);
}
});
//这里就是扫描包下的类,这里是数组如果我们有配置的话就是我们配置的包,没有的话就是启动类的包名
return scanner.doScan(StringUtils.toStringArray(basePackages));
}
private Set scanCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
try {
//扫描包下的所有**/*.class
String packageSearchPath = ResourcePatternResolver.CLASSPATH_ALL_URL_PREFIX +
resolveBasePackage(basePackage) + '/' + this.resourcePattern;
Resource[] resources = getResourcePatternResolver().getResources(packageSearchPath);
boolean traceEnabled = logger.isTraceEnabled();
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Scanning " + resource);
}
if (resource.isReadable()) {
try {
MetadataReader metadataReader = getMetadataReaderFactory().getMetadataReader(resource);
//这里会排除掉不需要注册的bean
if (isCandidateComponent(metadataReader)) {
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
if (isCandidateComponent(sbd)) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Identified candidate component class: " + resource);
}
candidates.add(sbd);
}
else {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug("Ignored because not a concrete top-level class: " + resource);
}
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not matching any filter: " + resource);
}
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Failed to read candidate component class: " + resource, ex);
}
}
else {
if (traceEnabled) {
logger.trace("Ignored because not readable: " + resource);
}
}
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException("I/O failure during classpath scanning", ex);
}
return candidates;
} 源码太多,我这里去掉一些这次不是重点关注的代码,有兴趣的可以自己去看下