Spring Boot的底层原理
一,Spring Boot简介
1.什么是Spring Boot
Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。
该框架使用了特定的方式(继承starter,约定优先于配置)来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。通过这种方式,Boot致力于在蓬勃发展的快速应用开发领域(rapid application development)成为领导者。
Spring Boot并不是一个框架,从根本上将,它就是一些库的集合,maven或者gradle项目导入相应依赖即可使用Spring Boot,而且无需自行管理这些库的版本。。
2.为什么要使用Spring Boot;
Spring Boot是为简化Spring项目配置而生,使用它使得jar依赖管理以及应用编译和部署更为简单。Spring Boot提供自动化配置,使用Spring Boot,你只需编写必要的代码和配置必须的属性。
使用Spring Boot,只需20行左右的代码即可生成一个基本的Spring Web应用,并且内置了tomcat,构建的fat Jar包通过Java -jar就可以直接运行。
如下特性使得Spring Boot非常契合微服务的概念,可以结合Spring Boot与Spring Cloud和Docker技术来构建微服务并部署到云端:
一个可执行jar即为一个独立服务很容易加载到容器,每个服务可以在自己的容器(例如docker)中运行
通过一个脚本就可以实现配置与部署,很适合云端部署,并且自动扩展也更容易
简单而言,即Spring Boot使编码更简单,使配置更简单,使部署更简单,使监控更简单。!
3 Spring Boot提供哪些功能
(1)无需手动管理依赖jar包的版本
Spring boot通过spring boot starter项目管理其提供的所有依赖的版本,当升级spring boot时,这些依赖的版本也会随之升级。个人无需指定版本号。
但是也可以自定义版本号覆盖springboot的默认值。每个版本的boot都有对应的base spring version,不建议明确地指定spring版本。
例如,使用maven时,只需简单的在pom中包含spring-boot-starter-web即引入了Spring MVC和Tomcat的依赖。
下面是Spring Boot在 org.springframework.boot 组下提供的一些Starters:
二,Spring boot入门
1.环境要求
开发环境JDK 1.8
项目管理工具( Maven )
开发工具(Eclipse)
2.入门
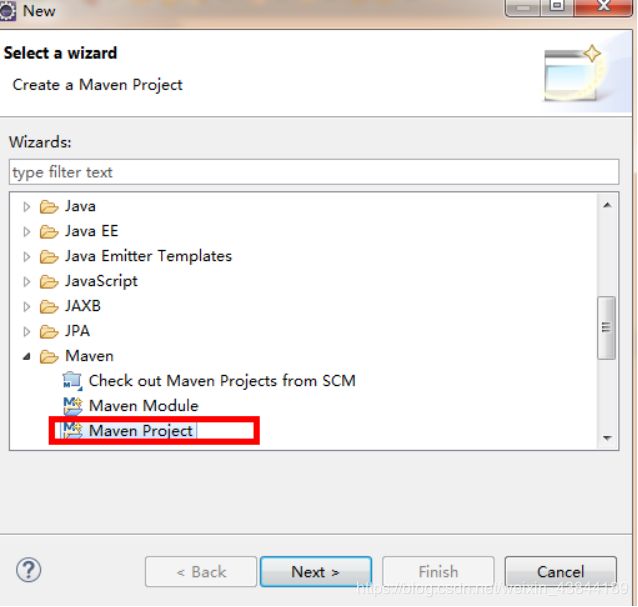
(1)创建Maven项目
2.导入Spring Boot依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.5.10.RELEASE
java.version 指定jdk版本号:
1.8
添加spring-boot-starter-web依赖
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
3.编码测试
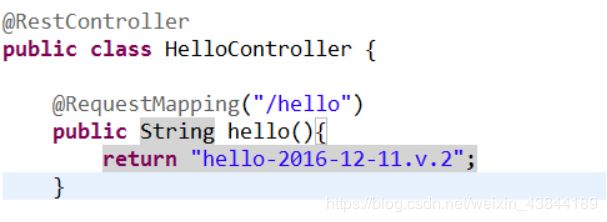
新建一个Controller类
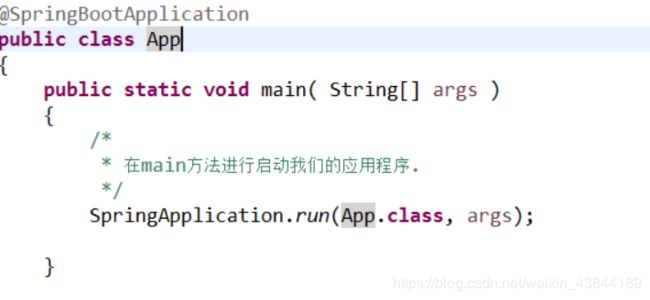
新建启动类(App – Main方法)
测试代码
运行:App
浏览器:http://localhost:8080/hello
4.热部署
即使修改了输出内容也要重启APP,非常麻烦!可以使用spring-boot-devtools来实现!
- 介绍
spring-boot-devtools 是一个为开发者服务的一个模块,其中最重要的功能就是自动应用代码更改到最新的App上面去。原理是在发现代码有更改之后,重新启动应用,但是速度比手动停止后再启动还要更快,更快指的不是节省出来的手工操作的时间。
其深层原理是使用了两个ClassLoader,一个Classloader加载那些不会改变的类(第三方Jar包),另一个ClassLoader加载会更改的类,称为 restart ClassLoader
,这样在有代码更改的时候,原来的restart ClassLoader 被丢弃,重新创建一个restart ClassLoader,由于需要加载的类相比较少,所以实现了较快的重启时间(5秒以内)
2)使用
添加依赖包:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
三,Spring boot web
1.跳转Jsp
步骤:
创建Maven web project
引入依赖
配置application.properties对jsp支持
编写测试Controller
编写JSP
编写启动App
(1)创建Maven Web Project
使用Eclipse新建一个Maven Web Project ,项目取名为:spring-boot-jsp
(2)导入Maven依赖
1.8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-parent
1.5.10.RELEASE
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-devtools
true
org.apache.tomcat.embed
tomcat-embed-jasper
provided
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-maven-plugin
(3)配置application.properties对jsp支持
添加src/main/resources/application.properties:
#tomcat server port
server.port=80
# 页面默认前缀目录
spring.mvc.view.prefix=/WEB-INF/jsp/
# 响应页面默认后缀
spring.mvc.view.suffix=.jsp
# 自定义属性,可以在Controller中读取
application.hello=Hello Angel From application
Yaml 方式
server:
port: 8080
name: kd
spring:
mvc:
view:
prefix: /WEB-INF/jsp/
suffix: .jsp
(3)编写测试Controller
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String helloJsp(Model model){
System.out.println("HelloController.helloJsp().hello=hello");
model.addAttribute("hello", "你好");
return "hello";
}
}(5)编写JSP
在 src/main 下面创建 webapp/WEB-INF/jsp 目录用来存放我们的jsp页面:helloJsp.jsp:
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8"
pageEncoding="UTF-8"%>
Insert title here
helloJsp
${hello}
(6)编写启动App
2.获取Json数据
要把Java对象转换为Json框架,使用的是JackSon,maven依赖的jar也有
@RequestMapping("/json")
@ResponseBody
public Person json(){
return new Person(1L,"kd");
}
四,Spring boot 持久化
1.Spring boot JdbcTemplate
引入spring-boot-starter-jdbc
那么只需要在需要使用的类中加入:
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
(1)引入Maven依赖-mysql,jdbc
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-jdbc
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
(2)数据库信息配置
在application.properties文件中配置mysql连接配置文件
########################################################
###datasource
########################################################
spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
Yaml 方式
spring:
datasource:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url : jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring-boot-demo?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
username : root
password : root
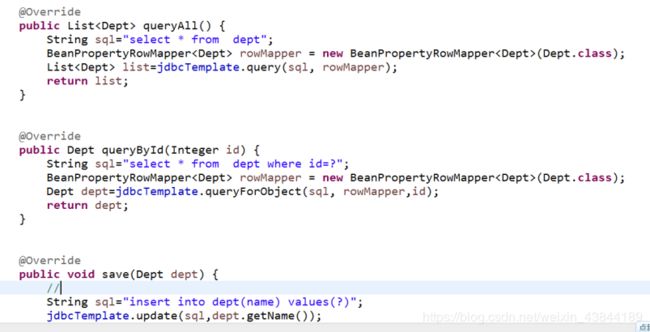
(3)代码示例
1) Dao
声明为:@Repository,引入JdbcTemplate
public Demo getById(long id){
String sql = "select *from Demo where id=?";
RowMapper rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper(Demo.class);
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper,id);
}
2)Service
声明为:@Service 引入dao
@Resource
private DemoDao demoDao;
public void getById(Long id){
demoDao.getById(id);
}
3)Controller
@Resource
private DemoService demoService;
@RequestMapping("/getById")
public Demo getById(long id){
return demoService.getById(id);
} Springboot 测试
2.Spring boot-spring data Jpa
(1)Spring data jpa简介
- Spring data
Spring Data是一个用于简化数据库访问,并支持云服务的开源框架。其主要目标是使得数据库的访问变得方便快捷,并支持map-reduce框架和云计算数据服务。此外,它还支持基于关系型数据库的数据服务,如Oracle RAC等。对于拥有海量数据的项目,可以用Spring Data来简化项目的开发,就如Spring Framework对JDBC、ORM的支持一样,Spring Data会让数据的访问变得更加方便。
- Jpa
“规范”: 所谓的规范意指明文规定或约定俗成的标准。如:道德规范、技术规范,公司管理规范。那么“持久化规范”就是Sun针对持久化这一层操作指定的规范,如果没有指定JPA规范,那么新起的框架就随意按照自己的标准来了,那我们开发人员就没法把我们的经历全部集中在我们的业务层上,而是在想如何进行兼容,这种情况有点像Android开发,Android本身有官方的SDK,但是由于SDK过于开源了,结果导致很多厂商基于SDK二次开发,但是兼容性就不是很好,最好的例子就是Android的头像上传,就是一件很烦人的事情。好了,JPA就介绍到这里。
- Hibernate
JPA是一种规范,而Hibernate是它的一种实现。除了Hibernate,还有EclipseLink(曾经的 toplink),OpenJPA等可供选择,所以使用Jpa的一个好处是,可以更换实现而不必改动太多代码。
- Spring data Jpa
Spring Data JPA能干什么
可以极大的简化JPA的写法,可以在几乎不用写实现的情况下,实现对数据的访问和操作。除了CRUD外,还包括如分页、排序等一些常用的功能。
首先我们需要清楚的是Spring Data是一个开源框架,在这个框架中Spring Data JPA只是这个框架中的一个模块,所以名称才叫Spring Data JPA。如果单独使用JPA开发,你会发现这个代码量和使用JDBC开发一样有点烦人,所以Spring Data JPA的出现就是为了简化JPA的写法,让你只需要编写一个接口继承一个类就能实现CRUD操作了
5)Spirng data jpa常用接口或类
Spring Data 的一个核心接口为我们提供了常用的接口
Repository 接口是 Spring Data 的一个核心接口,它不提供任何方法,开发者需要在自己定义的接口中声明需要的方法 :
public interface Repository
1. Repository是一个空接口,即是一个标记接口;
2. 若我们定义的接口继承了Repository,则该接口会被IOC容器识别为一个Repository Bean纳入到IOC容器中,进而可以在该接口中定义满足一定规范的方法。
3. 实际上也可以通过@RepositoryDefinition,注解来替代继承Repository接口。
4. 查询方法以find | read | get开头;
5. 涉及查询条件时,条件的属性用条件关键字连接,要注意的是条件属性以首字母大写。
6.使用@Query注解可以自定义JPQL语句实现更灵活的查询。
List
select * from t_user where name=? or age=?
CrudRepository 接口提供了最基本的对实体类的添删改查操作
--T save(T entity);//保存单个实体
--Iterable
--T findOne(ID id);//根据id查找实体
--boolean exists(ID id);//根据id判断实体是否存在
--Iterable
--long count();//查询实体数量
--void delete(ID id);//根据Id删除实体
--void delete(T entity);//删除一个实体
--void delete(Iterable entities);//删除一个实体的集合
--void deleteAll();//删除所有实体,不用或慎用!
PagingAndSortingRepository接口
该接口提供了分页与排序功能
--Iterable
--Page
JpaRepository:查找所有实体,排序、查找所有实体,执行缓存与数据库同步
JpaSpecificationExecutor:不属于Repository体系,实现一组 JPA Criteria 查询相关的方法,封装 JPA Criteria 查询条件。通常使用匿名内部类的方式来创建该接口的对象。
自定义 Repository:可以自己定义一个MyRepository接口 extends JpaRepository。
(2)引入Maven依赖-mysql,springdatajpa
mysql
mysql-connector-java
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
(3)配置jdbc spring data jpa
在application.properties文件中配置mysql连接配置文件
#tomcat server port
server.port=80
########################################################
###datasource
########################################################
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.max-active=20
spring.datasource.max-idle=8
spring.datasource.min-idle=8
spring.datasource.initial-size=10
########################################################
### Java Persistence Api (可以不设置,用默认的)
########################################################
# Specify the DBMS
spring.jpa.database = MYSQL
# Show or not log for each sql query
spring.jpa.show-sql = true
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
# Naming strategy
#[org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy #org.hibernate.cfg.DefaultNamingStrategy]
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
# stripped before adding them to the entity manager)
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
(4)代码示例
1.创建实体类User。
package cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
import javax.persistence.Column;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.Id;
import javax.persistence.Table;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIgnoreProperties;
@Entity
@Table(name="t_user")
//加上json转换时忽略的属性,否则出错
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value={"hibernateLazyInitializer","handler"})
public class User implements Serializable{
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Column
private String name;
//Getter/setter
}2.创建repository操作持久化接口(继承自JpaRepository)。
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.domain.User;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository{
public User getByName(String name);
} 3.创建service类。
package cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.dao.UserRepository;
import cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.domain.User;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public User get(Long id){
return userRepository.getOne(id);
}
public User getByName(String name){
return userRepository.getByName(name);
}
public User save(User user){
return userRepository.save(user);
}
public User update(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
public void delete(Long id){
userRepository.delete(id);
}
}
4.创建restful controller。
package cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.domain.User;
import cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.service.UserService;
@RestController
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public User get(@PathVariable Long id) {
User user = userService.get(id);
System.out.println("user=" + user);
return user;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/name/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public User get(@PathVariable String name) {
User user = userService.getByName(name);
System.out.println("user=" + user);
return user;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/add", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public User add() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("itsource");
user = userService.save(user);
return user;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/update", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public User update() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(2L);
user.setName("源码时代");
user = userService.update(user);
return user;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user/delete", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String delete() {
userService.delete(2L);
return "success";
}
}5.启动类
package cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}- 测试;
启动项目分别测试对应的Restful接口功能
- 注意事项
JSON转换异常处理:
① 在Domain类中排除注入的特殊属性hibernateLazyInitializer和handler
@Entity
@Table(name="t_user")
//加上json转换时忽略的属性,否则出错
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value={"hibernateLazyInitializer","handler"})
public class User implements Serializable{....}
- 注意事项
JSON转换异常处理:
① 在Domain类中排除注入的特殊属性hibernateLazyInitializer和handler
@Entity
@Table(name="t_user")
//加上json转换时忽略的属性,否则出错
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value={"hibernateLazyInitializer","handler"})
public class User implements Serializable{....}
② 增加Jackson配置类
| package cn.itsource.springboot.datajpa.config; import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper; import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.hibernate4.Hibernate4Module; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.http.converter.HttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter; import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter;
import java.util.List; /** * 防止在使用jpa/hibernate,如果实体字段上加有FetchType.LAZY,并使用jackson序列化为json串时, * 会遇到SerializationFeature.FAIL_ON_EMPTY_BEANS异常 * @author nixianhua * */ @Configuration public class JacksonConfiguration extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void configureMessageConverters(List converters.add(jacksonMessageConverter()); super.configureMessageConverters(converters); }
private MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter jacksonMessageConverter() { MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter messageConverter = new MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter(); ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper(); mapper.registerModule(new Hibernate4Module()); messageConverter.setObjectMapper(mapper); return messageConverter; } } 4.Spring boot-mybatis
①集成Mybatis
新建一个maven project,取名为:spring-boot-mybatis
(1)基本依赖,jdk版本号; (2)mysql驱动,mybatis依赖包,mysql分页PageHelper: |
(3)创建启动类App.java
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.mapper")
public class App
{
public static void main( String[] args )
{
SpringApplication.run(App.class, args);
}
}
//这里和以往不一样的地方就是MapperScan的注解,这个是会扫描该包下的接口
- 在application.properties添加配置文件;
#tomcat server port
server.port=80
########################################################
###datasource
########################################################
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
spring.datasource.driverClassName = com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.max-active=20
spring.datasource.max-idle=8
spring.datasource.min-idle=8
spring.datasource.initial-size=10
- 编写User测试类;
package cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class User implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2107513802540409419L;
private Long id;
private String name;
getter/setter...
}
- 编写UserMapper;
注解方式 :
| package cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.mapper;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select;
import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain.User; @Mapper public interface UserMapper { @Select("select * from t_user t_user name = #{name}") List
@Select("select * from t_user where id = #{id}") User getById(long id);
@Select("select name from t_user where id = #{id}") String getNameById(long id); } |
XML方式:
| package cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.mapper;
import java.util.List;
import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain.User; public interface UserMapper { List User getById(long id); String getNameById(long id); }
然后在resources下增加mapper.xml文件 /cn/itsource/springboot/mybatis/mapper/UserMapper.xml
xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <mapper namespace="cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper"> <select parameterType="string" resultType="User" id="likeName"> select * from t_user where name like concat('%',#{name},'%') select> <select parameterType="long" resultType="User" id="getById"> select * from t_user where id = #{id} select> <select parameterType="long" resultType="string" id="getNameById"> select name from t_user where id = #{id} select> <insert parameterType="User" id="save" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true"> insert into t_user(name) values(#{name}) insert> mapper>
最后需要在application.properties中增加别名包和mapper xml扫描包的配置 ## Mybatis config mybatis.typeAliasesPackage=cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain mybatis.mapperLocations=classpath:mapper/*.xml
#Yaml 配置
# Mybatis配置 mybatis: typeAliasesPackage: cn.itsource.domain mapperLocations: classpath:cn/itsource/dao/mapper/*.xml
|
- 编写UserService
| package cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.service;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain.User; import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
@Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;
public User get(Long id){ return userMapper.getById(id); } }
|
- 编写UserController;
| package cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.controller;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain.User; import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.service.UserService;
@RestController public class UserController {
@Autowired private UserService userService;
@RequestMapping("/user/{id}") @ResponseBody public User get(@PathVariable Long id) { return userService.get(id); } } |
//运行访问:http://127.0.0.1/user/1 就可以看到返回的数据了
-
-
- 使用PageHelper分页
-
在application.properties中配置分页插件
#pagehelper.
pagehelper.autoDialect=true
pagehelper.closeConn=true
在调用mapper的前面开启分页功能
| package cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.github.pagehelper.PageHelper; import com.github.pagehelper.PageInfo;
import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.domain.User; import cn.itsource.springboot.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper;
@Service public class UserService { @Autowired private UserMapper userMapper;
public User get(Long id){ return userMapper.getById(id); }
public PageInfo PageHelper.startPage(p, 1); List return new PageInfo<>(users); } }
|