springboot进阶-blog-day01
1. 新建项目
idea - new project - Spring Initializr - 选择插件:sprint web、Thymeleaf、sprint boot devTools、Lombok、Spring Data JPA、MySQL Driver;
next
等pom文件加载完毕。
ok
2.配置application文件
springboot支持两种配置文件application的格式,这里用的是yml格式;可以分为开发的生产两种环境:dev为开发环境;pro为生产环境。可以在application.yml中指定使用哪个文件
spring:
profiles:
active:dev
在application文件中的配置为全局配置(不需要再在dev或者pro文件中再次配置)
spring:
#注册数据库
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/blogs?useUnicode=true&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf-8
username: root
password: root
# 设置sql语句
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: update
show-sql: true
# 设置日志所在目录以及日志名称和日志的写入的等级
logging:
level:
root: info
com.my.blog: debug
file: log/blog-dev.log
3.异常处理
springboot可以自定义异常返回的界面
在资源类下的templates中新建error包来存放异常处理的界面
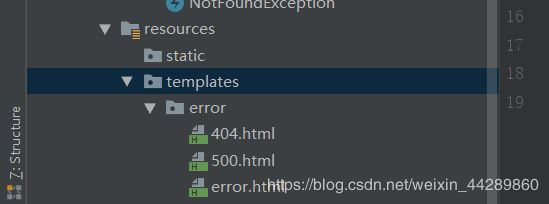
注意文件名称,发生错误是会根据错误类型去找界面。
新建一个controller
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/{id}/{name}")
public String index(@PathVariable Integer id ,@PathVariable String name){
// String blog = null;
// if (blog == null){
// throw new NotFoundException("博客不存在");
// }
System.out.println("-------------------index");
return "index";
}
}
自定义异常处理:
//404错误处理
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public class NotFoundException extends RuntimeException {
public NotFoundException() {
}
public NotFoundException(String message) {
super(message);
}
public NotFoundException(String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
}
}
4.日志处理
编写一个aspect类,使用了AOP面向切面编程。
@Aspect
@Component
public class LogAspect {
private final org.slf4j.Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
// 设置拦路径 本路径为web下的所有控制器中的所有方法(不限参数)
@Pointcut("execution(* com.my.blog.web.*.*(..))")
public void log(){}
@Before("log()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint){
// 拿到HttpServletRequest对象
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 拿到所需值
String url = request.getRequestURL().toString();
String ip = request.getRemoteAddr();
String classMethod = joinPoint.getSignature().getDeclaringTypeName()+"."+joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
Object args[] = joinPoint.getArgs();
RequestLog requestLog = new RequestLog(url,ip,classMethod,args);
logger.info("Request: {}",requestLog);
}
@After("log()")
public void doAfter(){
logger.info("after-----------------");
}
@AfterReturning(returning = "result",pointcut = "log()")
public void doAfterReturn(Object result){
logger.info("afterReturn-----------------Result: {}",result);
}
private class RequestLog{
private String url;
private String ip;
private String ClassMethod;
private Object[] args;
public RequestLog(String url, String ip, String classMethod, Object[] args) {
this.url = url;
this.ip = ip;
ClassMethod = classMethod;
this.args = args;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "RequestLog{" +
"url='" + url + '\'' +
", ip='" + ip + '\'' +
", ClassMethod='" + ClassMethod + '\'' +
", args=" + Arrays.toString(args) +
'}';
}
}
}
本文是在B站看视频所总结,如有错误感谢指正。