操作系统原理
参考博客:https://riboseyim.github.io/2017/05/29/Linux-Works/
操作系统原理:How Linux Works(Initial)
分享
- DevOps
- Linux
- SRE
- 架构师
摘要
- 一、How the Linux Kernel Boots
- 二、How User Space Starts
- 三、The Initial RAM filesystem
史蒂夫·乔布斯(Steve Jobs):“假设你可以缩短10秒钟的开机时间,把这个乘上500万,那就是每天5000万秒了。一年下来大概是好几十辈子的时间。想想看,如果你可以让开机速度快10秒钟的话,就拯救了数十条生命。这很值得啊,你不觉得吗?” 《硅谷革命:成就苹果公司的疯狂往事》
一、How the Linux Kernel Boots
- The machine’s BIOS or boot firmware loads and runs a boot loader.(Boot Loader 是在操作系统内核运行之前运行的一段小程序,它严重地依赖于硬件而实现)
- The boot loader finds the kernel image on disk, loads it into memory, and starts it. (选择内核镜像,加载到内存空间,为最终调用操作系统内核准备好正确的环境。)
- The kernel initializes the devices and its drivers.(初始化硬件设备及其驱动程序)
- The kernel mounts the root filesystem.(挂载根目录。根目录指文件系统的最上一级目录,它是相对子目录来说的;它如同一棵大树的“根”一般,所有的树杈以它为起点)
- The kernel starts a program called init with a process ID of 1. This point is the user space start.(内核启动一个初始化程序,从这里开始虚拟内存开始划分出使用者空间,与内核空间(Kernel space)对应)
- init sets the rest of the system processes in motion
- At some point, init starts a process allowing you to log in, usually at the end or near the end of the boot.
Startup Messages
有两种方式可以查看内核引导和运行诊断信息:
- 查看内核系统日志文件。文件路径: /var/log/kern.log
- 执行dmesg命令
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
[root@li1437-101 ~]# dmesg
[ 0.000000] Linux version 4.9.7-x86_64-linode80 (maker@build) (gcc version 4.7.2 (Debian 4.7.2-5) ) #2 SMP Thu Feb 2 15:43:55 EST 2017
[ 0.000000] Command line: root=/dev/sda console=tty1 console=ttyS0 ro devtmpfs.mount=1
[ 0.000000] x86/fpu: Supporting XSAVE feature 0x001: 'x87 floating point registers'
[ 0.000000] x86/fpu: Supporting XSAVE feature 0x002: 'SSE registers'
[ 0.000000] x86/fpu: Supporting XSAVE feature 0x004: 'AVX registers'
[ 0.000000] x86/fpu: xstate_offset[2]: 576, xstate_sizes[2]: 256
[ 0.000000] x86/fpu: Enabled xstate features 0x7, context size is 832 bytes, using 'standard' format.
[ 0.000000] x86/fpu: Using 'eager' FPU context switches.
[ 0.000000] e820: BIOS-provided physical RAM map:
…….
[ 0.000000] NX (Execute Disable) protection: active
[ 0.000000] SMBIOS 2.8 present.
[ 0.000000] DMI: QEMU Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996), BIOS rel-1.9.1-0-gb3ef39f-prebuilt.qemu-project.org 04/01/2014
[ 0.000000] Hypervisor detected: KVM
……
[ 0.371925] raid6: sse2x1 gen() 7490 MB/s
[ 0.428689] raid6: sse2x1 xor() 5953 MB/s
[ 0.485463] raid6: sse2x2 gen() 9289 MB/s
[ 0.542230] raid6: sse2x2 xor() 6754 MB/s
[ 0.599013] raid6: sse2x4 gen() 10954 MB/s
[ 0.656189] raid6: sse2x4 xor() 5522 MB/s
[ 0.656943] raid6: using algorithm sse2x4 gen() 10954 MB/s
[ 0.657588] raid6: .... xor() 5522 MB/s, rmw enabled
……
[ 1.053697] Netfilter messages via NETLINK v0.30.
[ 1.054471] nfnl_acct: registering with nfnetlink.
[ 1.055332] nf_conntrack version 0.5.0 (8192 buckets, 32768 max)
[ 1.056324] ctnetlink v0.93: registering with nfnetlink.
[ 1.057335] nf_tables: (c) 2007-2009 Patrick McHardy
[ 1.058393] nf_tables_compat: (c) 2012 Pablo Neira Ayuso
[ 1.059599] xt_time: kernel timezone is -0000
[ 1.060296] ip_set: protocol 6
[ 1.060791] IPVS: Registered protocols (TCP, UDP, SCTP, AH, ESP)
[ 1.061940] IPVS: Connection hash table configured (size=4096, memory=64Kbytes)
[ 1.063162] IPVS: Creating netns size=2104 id=0
[ 1.064139] IPVS: ipvs loaded.
……
[ 1.744221] systemd[1]: Detected virtualization kvm.
[ 1.745058] systemd[1]: Detected architecture x86-64.
[ 1.747402] systemd[1]: Set hostname to
. [ 1.834328] tsc: Refined TSC clocksource calibration: 2800.119 MHz
[ 1.835512] clocksource: tsc: mask: 0xffffffffffffffff max_cycles: 0x285cb16f950, max_idle_ns: 440795333193 ns
[ 1.843476] systemd[1]: Created slice Root Slice.
[ 1.844251] systemd[1]: Starting Root Slice.
[ 1.845835] systemd[1]: Created slice System Slice.
[ 1.846631] systemd[1]: Starting System Slice.
[ 1.848257] systemd[1]: Listening on udev Kernel Socket.
[ 1.849119] systemd[1]: Starting udev Kernel Socket.
[ 2.014715] EXT4-fs (sda): re-mounted. Opts: (null)
[ 2.038202] systemd-journald[2010]: Received request to flush runtime journal from PID 1
[ 2.241341] audit: type=1305 audit(1488188850.897:2): audit_pid=2215 old=0 auid=4294967295 ses=4294967295 res=1
[ 2.287758] Adding 262140k swap on /dev/sdb. Priority:-1 extents:1 across:262140k FS
[ 2.905177] IPVS: Creating netns size=2104 id=1
[ 2.954613] IPv6: ADDRCONF(NETDEV_UP): eth0: link is not ready
[ 2.955987] 8021q: adding VLAN 0 to HW filter on device eth0
[ 8.009765] random: crng init done
在故障排查中,dmesg信息需要首先查看,例如输出最近10条系统信息,
可以查看到引起性能问题的错误。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 |
$ dmesg | tail [1880957.563150] perl invoked oom-killer: gfp_mask=0x280da, order=0, oom_score_adj=0 [...] [1880957.563400] Out of memory: Kill process 18694 (perl) score 246 or sacrifice child [1880957.563408] Killed process 18694 (perl) total-vm:1972392kB, anon-rss:1953348kB, file-r ss:0kB [2320864.954447] TCP: Possible SYN flooding on port 7001. Dropping request. Check SNMP cou nters. |
Kernel initialization and Boot Options
在启动时,Linux内核初始化的顺序如下:
- CPU inspection (检查CPU)
- Memory inspection (检查内存)
- Device bus discovery (发现设备总线)
- Device discovery (发现设备)
- Auxiliary kernel subsystem setup(networking, and so on) (辅助内核子系统启动,例如网络等)
- Root filesystem mount (挂载根目录)
- User space start (用户空间启动)
Kernel Parameters
文件/proc/cmdline记录了系统内核启动参数:
1 2 |
[root@li1437-101 ~]# cat /proc/cmdline root=/dev/sda console=tty1 console=ttyS0 ro devtmpfs.mount=1 |
查看运行级别:
1 2 3 |
[root@li1437-101 ~]# who -r run-level 3 2017-02-27 09:47 [root@li1437-101 ~]# |
二、How User Space Starts
用户空间启动顺序:
- init
- 必要的低层服务例如:udevd 和 syslog
- 网络配置
- 中高层服务例如 :cron , printing
- 登录提示、图形界面及其它高层次应用
天字第一号进程
init(initialization的简写)是 Unix 和 类Unix 系统中用来产生其它所有进程的程序。它以守护进程的方式存在,其进程号为1。Linux系统在开机时加载Linux内核后,便由Linux内核加载init程序,由init程序完成余下的开机过程,比如加载运行级别,加载服务,引导Shell/图形化界面等等。
1 2 3 |
[root@li1437-101 ~]# ps -ef | grep init root 1 0 0 Feb27 ? 00:03:05 /sbin/init root 28683 28663 0 02:44 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto init |
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 |
// Mac OS bash-3.2$ ps -ef | grep init 0 243 1 0 15 517 ?? 0:00.74 /System/Library/CoreServices/CrashReporterSupportHelper server-init 0 533 1 0 15 517 ?? 0:02.07 /System/Library/CoreServices/SubmitDiagInfo server-init 501 52150 1 0 日01下午 ?? 0:15.49 /usr/libexec/secinitd 0 69864 1 0 11:35上午 ?? 0:00.20 /usr/libexec/secinitd 0 72830 1 0 1:51下午 ?? 0:00.19 /usr/libexec/secinitd Darwin ACA80166.ipt.aol.com 16.5.0 Darwin Kernel Version 16.5.0: Fri Mar 3 16:52:33 PST 2017; root:xnu-3789.51.2~3/RELEASE_X86_64 x86_64 bash-3.2$ |
在Linux发行版中,init有三种主要的实现形式:
- System V init: 传统的
- systemd: 所有主流Linux发行版中的标准init
- Upstart: Ubuntu
Android 和 BSD (运行存放于’/etc/rc’的初始化 shell 脚本)也有它们自己的init版本,一些发行版也将System V init 修改为类似BSD风格的实现。目前大部分Linux发行版都已采用新的systemd替代System V和Upstart,但systemd向下兼容System V。
System V init: 存在一个启动序列,同一时间只能启动一个任务,这种架构下,很容易解决依赖问题,但是性能方面要受一些影响。
systemd is goal oriented. : 针对System V init的不足,systemd所有的服务都并发启动。systemd时基于目标的,需要定义要实现的目标,以及它的依赖项。systemd 将所有过程都抽象为一个配置单元,即 unit。可以认为一个服务是一个配置单元;一个挂载点是一个配置单元。
Upstart is reactionary.:Upstart是基于事件的,Upstart的事件驱动模型允许它以异步方式对生成的事件作出回应。
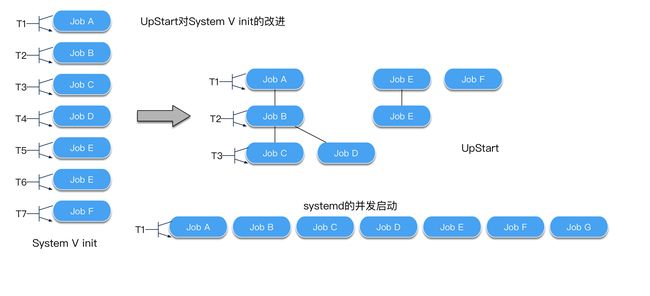 System V init Vs UpStart Vs Systemd
System V init Vs UpStart Vs Systemd
三、The Initial RAM filesystem
Linux内核不能通过访问PC BIOS 或者 EFI接口从磁盘获取数据,所以为了mount它的root filesystem, 对于底层存储需要驱动程序支持。解决方案是在内核运行之前,由boot loader加载驱动模块及工具到内存。在启动时,内核读取相关模块到一个临时的RAM filesystem(initramfs),挂载在/根目录,initramsfs允许内核为真正的root filesystem加载必要的驱动模块。
最后,再挂载真正的root filesystem、启动init。
Linux在很多场景下都需要创建一个基于内存的文件系统,提供一个可以接近零延迟的快速存储区域。目前有两类主要的RAM磁盘可用,她们个有优劣:ramfs和tmpfs。(注意:创建之前可以使用 free 命令查看未使用的RAM)
1 2 3 4 |
# mkdir /mnt/ramdisk # mount -t tmpfs -o size=512m tmpfs /mnt/ramdisk # vi /etc/fstab #tmpfs /mnt/ramdisk tmpfs nodev,nosuid,noexec,nodiratime,size=1024M 0 0 |
源码阅读的一般方法
- 核心子系统(例如进程管理子系统)
- 结构体、数据结构
- 关键程序、加载顺序
- 主题式探索(例如:Linux 支持闰秒吗?)
扩展阅读
电子书《Linux Perf Master》
- https://riboseyim.gitbook.io/perf
- https://www.gitbook.com/book/riboseyim/linux-perf-master/details
How Linux Works
- Linux 性能诊断:负载评估
- Linux 性能诊断:快速检查单
- 操作系统原理 | How Linux Works(一):启动
- 操作系统原理 | How Linux Works(二):空间管理
- 操作系统原理 | How Linux Works(三):内存管理
- 操作系统原理 | How Linux Works(四):网络管理
动态追踪技术
- 动态追踪技术(一):DTrace 导论
- 动态追踪技术(二):strace+gdb 溯源 Nginx 内存溢出异常
- 动态追踪技术(三):Tracing Your Kernel Function!
- 动态追踪技术(四):基于 Linux bcc/BPF 实现 Go 程序动态追踪
- 动态追踪技术(五):Welcome DTrace for Linux
参考文献
- 《Linux 的启动过程》,白崎博生,2004 (暂无中文版)
- 《深入理解 Linux 内核》,Daniel P.Bovert (经典)
- Inside the Linux boot process
- linfo.org:Root Filesystem Definition
- 阮一峰:Systemd 入门教程:命令篇
- 阮一峰:Systemd 入门教程:实战篇
- IBM developerworks:浅析 Linux 初始化 init 系统,第 3 部分: Systemd
- 维基百科:Systemd
- differences between ramfs and tmpfs
- Unix Background (Signal、Messages & Queue) | Simon Hørup Eskildsen
- (推荐) How the Kernel Manages Your Memory | Gustavo Duarte
- (推荐) What Your Computer Does While You Wait | Gustavo Duarte
- (推荐) What Does an Idle CPU Do? | Gustavo Duarte

