刚接触编程的同学可以看看的几个编程练习(python实现)(六)
本大白最近带一只小白入手编程,想法是在练习中学习,所以弄了几个题目。其中不少是经典的练习题,在很多编程入门书籍中都有出现;有的题涉及到一点数据结构的理念。在这里分享出来,刚接触编程的同学可以和我们一起做一做(无论学的是哪种语言都可以看一看,思路是通用的。这里我们学的是python),也欢迎大家指正。
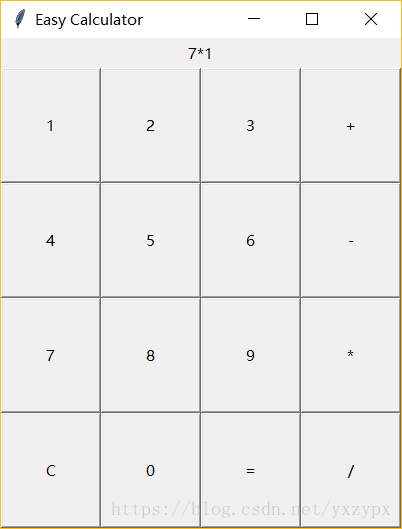
25. 计算器
这里我用tkinter工具,编写一个图形界面的计算器。
这里编写的计算器比较简单,只能进行一次计算,不能进行复合运算、带括号的运算等。如果想拓展到这些功能,可以使用“中缀表达式”及堆栈结构实现,大家可以查阅相关资料。
from tkinter import *
class Calculator():
def __init__(self, master):
self.string = StringVar()
self.stack = []
self.first_num = 0
self.second_num = 0
self.method = ''
self.frame = Frame(master)
self.frame.pack()
self.message = Message(self.frame, textvariable=self.string,
width=500, justify="right").grid(
row=0, column=0, columnspan=4)
self.button_1 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text="1",
command=self.push_1).grid(row = 1, column = 0)
self.utton_2 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "2",
command=self.push_2).grid(row = 1, column = 1)
self.button_3 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "3",
command=self.push_3).grid(row = 1, column = 2)
self.button_4 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "4",
command=self.push_4).grid(row = 2, column = 0)
self.button_5 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "5",
command=self.push_5).grid(row = 2, column = 1)
self.button_6 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "6",
command=self.push_6).grid(row = 2, column = 2)
self.button_7 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "7",
command=self.push_7).grid(row = 3, column = 0)
self.button_8 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "8",
command=self.push_8).grid(row = 3, column = 1)
self.button_9 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "9",
command=self.push_9).grid(row = 3, column = 2)
self.button_0 = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "0",
command=self.push_0).grid(row = 4, column = 1)
self.button_add = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "+",
command=self.prepare_add).grid(row = 1, column = 3)
self.button_minus = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "-",
command=self.prepare_minus).grid(row = 2, column = 3)
self.button_multiply = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5,
text = "*", command=self.prepare_multiply).grid(row = 3,
column = 3)
self.button_divide = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "/",
command=self.prepare_divide).grid(row = 4, column = 3)
self.button_equal = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "=",
command=self.equal).grid(row = 4, column = 2)
self.button_clear = Button(self.frame, width=10, height=5, text = "C",
command=self.clear).grid(row = 4, column = 0)
def push_1(self):
self.stack.append(1)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(1))
def push_2(self):
self.stack.append(2)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(2))
def push_3(self):
self.stack.append(3)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(3))
def push_4(self):
self.stack.append(4)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(4))
def push_5(self):
self.stack.append(5)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(5))
def push_6(self):
self.stack.append(6)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(6))
def push_7(self):
self.stack.append(7)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(7))
def push_8(self):
self.stack.append(8)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(8))
def push_9(self):
self.stack.append(9)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(9))
def push_0(self):
self.stack.append(0)
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + str(0))
def prepare_add(self):
self.get_number()
if self.method == "":
self.method = '+'
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + '+')
else:
self.string.set("only once calcuation allowed")
def prepare_minus(self):
self.get_number()
if self.method == "":
self.method = '-'
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + '-')
else:
self.string.set("only once calcuation allowed")
def prepare_multiply(self):
self.get_number()
if self.method == "":
self.method = '*'
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + '*')
else:
self.string.set("only once calcuation allowed")
def prepare_divide(self):
self.get_number()
if self.method == "":
self.method = '/'
string = self.string.get()
self.string.set(string + '/')
else:
self.string.set("only once calcuation allowed")
def clear(self):
self.string.set("")
self.stack.clear()
self.first_num = 0
self.second_num = 0
self.method = ''
def equal(self):
self.get_number()
if self.method == '+':
self.string.set(str(self.first_num + self.second_num))
elif self.method == '-':
self.string.set(str(self.first_num - self.second_num))
elif self.method == '*':
self.string.set(str(self.first_num * self.second_num))
elif self.method == '/':
try:
temp = self.first_num / self.second_num
except ZeroDivisionError:
self.string.set("Can not divided by 0")
else:
self.string.set(str(temp))
def get_number(self):
digit = 1
number = 0
while len(self.stack) > 0:
number += digit * self.stack.pop()
digit *= 10
if self.method == '':
self.first_num = number
else:
self.second_num = number
##########
root = Tk()
root.title("Easy Calculator")
Calculator(root)
root.mainloop() 26. 生产者与消费者
一个容量固定的商品池,许多生产者,许多消费者。当某个生产者来到时,如果商品池有空位,他就放入一个商品;当某个消费者来到时,如果商品池有商品,他就取走一个商品。
我们可以定义一个类来表示商品池。
这里我通过产生随机数来决定是生产者来到还是消费者来到。
class Pool():
def __init__(self):
self.pool = []
self.goods = 0
def put_in(self, i):
if self.goods < 2:
self.pool.append(i)
print("Producer put in " + str(i))
self.goods += 1
return True
else:
print("Producer fail")
return False
def get_out(self):
if self.goods > 0:
print("Consumer get out good " + str(self.pool.pop(0)))
self.goods -= 1
else:
print("Consumer fail")
count = 1
market = Pool()
for i in range(10):
r = random.uniform(0, 1)
if r > 0.3:
if market.put_in(count):
count += 1
else:
market.get_out()
(这是操作系统中的一个经典问题,涉及到多线程概念,生产者与消费者的独立操作可能会产生错误的影响,需要对商品池“上锁”来避免。 不过我们这里进行了简化,不涉及这种影响)
27. 面向对象的简单例子——车
我们在随机游走、计算器、生产者与消费者中用到了类,这里再看一个关于类的例子。
我们定义一个“车”的类,车有速度和里程两个变量,通过获取速度、获取里程的方法获取车的当前速度和里程,通过加速、减速、运行、停止方法模拟车的功能。
class Car():
def __init__(self, speed=0, mileage=0):
self.speed = speed
self.mileage = mileage
def get_speed(self):
return self.speed
def get_mileage(self):
return self.mileage
def accelerate(self):
if self.speed <= 90:
self.speed += 10
else:
self.speed = 100
def decelerate(self):
if self.speed >= 20:
self.speed -= 20
else:
self.speed = 0
def run(self, time):
self.mileage += self.speed * time
def stop(self):
self.speed = 0
car = Car()
car.get_speed()
car.get_mileage()
for i in range(9):
car.accelerate()
car.run(1)
for i in range(4):
car.decelerate()
car.run(1)
print(car.get_speed())
print(car.get_mileage())