java中IO和NIO的区别和适用场景
java.NIO包里包括三个基本的组件
l buffer:因为NIO是基于缓冲的,所以buffer是最底层的必要类,这也是IO和NIO的根本不同,虽然stream等有buffer开头的扩展类,但只是流的包装类,还是从流读到缓冲区,而NIO却是直接读到buffer中进行操作。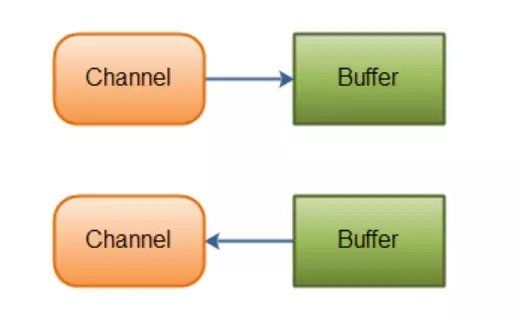
因为读取的都是字节,所以在操作文字时,要用charset类进行编解码操作。
l channel:类似于IO的stream,但是不同的是除了FileChannel,其他的channel都能以非阻塞状态运行。FileChannel执行的是文件的操作,可以直接DMA操作内存而不依赖于CPU。其他比如socketchannel就可以在数据准备好时才进行调用。
l selector:用于分发请求到不同的channel,这样才能确保channel不处于阻塞状态就可以收发消息。
面向流与面向缓冲
Java NIO和IO之间第一个最大的区别是,IO是面向流的,NIO是面向缓冲区的。 Java IO面向流意味着每次从流中读一个或多个字节,直至读取所有字节,它们没有被缓存在任何地方。此外,它不能前后移动流中的数据。如果需要前后移动从流中读取的数据,需要先将它缓存到一个缓冲区。 Java NIO的缓冲导向方法略有不同。数据读取到一个它稍后处理的缓冲区,需要时可在缓冲区中前后移动。这就增加了处理过程中的灵活性。但是,还需要检查是否该缓冲区中包含所有您需要处理的数据。而且,需确保当更多的数据读入缓冲区时,不要覆盖缓冲区里尚未处理的数据。
补充一点:NIO的buffer可以使用直接内存缓冲区,该缓冲区不在JVM中,性能会比JVM的缓冲区略好,不过会增加相应的垃圾回收的负担,因为JVM缓冲区的性能已经足够好,所以除非在对缓冲有特别要求的地方使用直接缓冲区,尽量使用JVM缓冲。
阻塞与非阻塞
Java IO是阻塞式的操作,当一个inputstream或outputstream在进行read()或write()操作时,是一直处于等待状态的,直到有数据读/写入后才进行处理.而NIO是非阻塞式的,当进行读写操作时,只会返回当前已经准备好的数据,没有就返回空,这样当前线程就可以处理其他的事情,提高了资源的使用率.
与传统IO的优势
在老的IO包中,serverSocket和socket都是阻塞式的,因此一旦有大规模的并发行为,而每一个访问都会开启一个新线程。这时会有大规模的线程上下文切换操作(因为都在等待,所以资源全都被已有的线程吃掉了),这时无论是等待的线程还是正在处理的线程,响应率都会下降,并且会影响新的线程。
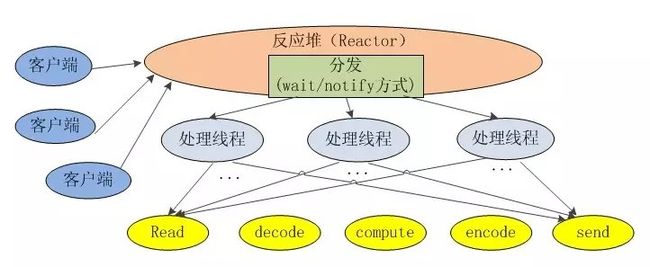
而NIO包中的serverSocket和socket就不是这样,只要注册到一个selector中,当有数据放入通道的时候,selector就会得知哪些channel就绪,这时就可以做响应的处理,这样服务端只有一个线程就可以处理大部分情况(当然有些持续性操作,比如上传下载一个大文件,用NIO的方式不会比IO好)。
通过两个图的比较,可以看出IO是直连的,每个请求都给一条线程来处理,但是NIO却是基于反应堆(selector)来处理,直到读写的数据准备好后,才会通知相应的线程来进行处理。一言以蔽之:“selector不会让channel白占资源,没事的时候给我去睡觉。”
PS:NIO基于字节进行传输,在IO时要注意decode/encode。
这里贴出一个基于Tcp的通信操作,体现出了NIO在处理小字节片的优势,比如用一个服务端程序就可以处理所有的客户端请求:
TCPProtocol接口
/**
* TCPServerSelector与特定协议间通信的接口
*
* @date 2010-2-3
* @time 上午08:42:42
* @version 1.00
*/
publicinterface TCPProtocol{
/**
* 接收一个SocketChannel的处理
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
void handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
/**
* 从一个SocketChannel读取信息的处理
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
void handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
/**
* 向一个SocketChannel写入信息的处理
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
void handleWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException;
}
TCPProtocol实现类
/**
* TCPProtocol的实现类
*
* @date 2010-2-3
* @time 上午08:58:59
* @version 1.00
*/
publicclass TCPProtocolImpl implements TCPProtocol{
privateintbufferSize;
public TCPProtocolImpl(intbufferSize){
this.bufferSize=bufferSize;
}
publicvoid handleAccept(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
SocketChannel clientChannel=((ServerSocketChannel)key.channel()).accept();
clientChannel.configureBlocking(false);
clientChannel.register(key.selector(),SelectionKey.OP_READ,ByteBuffer.allocate(bufferSize));
}
publicvoid handleRead(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// 获得与客户端通信的信道
SocketChannel clientChannel=(SocketChannel)key.channel();
// 得到并清空缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer=(ByteBuffer)key.attachment();
buffer.clear();
// 读取信息获得读取的字节数
longbytesRead=clientChannel.read(buffer);
if(bytesRead==-1){
// 没有读取到内容的情况
clientChannel.close();
}
else{
// 将缓冲区准备为数据传出状态
buffer.flip();
// 将字节转化为为UTF-16的字符串
String receivedString=Charset.forName("UTF-16").newDecoder().decode(buffer).toString();
// 控制台打印出来
System.out.println("接收到来自"+clientChannel.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress()+"的信息:"+receivedString);
// 准备发送的文本
String sendString="你好,客户端. @"+newDate().toString()+",已经收到你的信息"+receivedString;
buffer=ByteBuffer.wrap(sendString.getBytes("UTF-16"));
clientChannel.write(buffer);
// 设置为下一次读取或是写入做准备
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ | SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}
}
publicvoid handleWrite(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
// do nothing
}
}
服务器
/**
* TCP服务器端
*
* @date 2010-2-3
* @time 上午08:39:48
* @version 1.00
*/
publicclass TCPServer{
// 缓冲区大小
privatestaticfinalintBufferSize=1024;
// 超时时间,单位毫秒
privatestaticfinalintTimeOut=3000;
// 本地监听端口
privatestaticfinalintListenPort=1978;
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throws IOException{
// 创建选择器
Selector selector=Selector.open();
// 打开监听信道
ServerSocketChannel listenerChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 与本地端口绑定
listenerChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(ListenPort));
// 设置为非阻塞模式
listenerChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 将选择器绑定到监听信道,只有非阻塞信道才可以注册选择器.并在注册过程中指出该信道可以进行Accept操作
listenerChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// 创建一个处理协议的实现类,由它来具体操作
TCPProtocol protocol=new TCPProtocolImpl(BufferSize);
// 反复循环,等待IO
while(true){
// 等待某信道就绪(或超时)
if(selector.select(TimeOut)==0){
System.out.print("独自等待.");
continue;
}
// 取得迭代器.selectedKeys()中包含了每个准备好某一I/O操作的信道的SelectionKey
Iterator
while(keyIter.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key=keyIter.next();
try{
if(key.isAcceptable()){
// 有客户端连接请求时
protocol.handleAccept(key);
}
if(key.isReadable()){
// 从客户端读取数据
protocol.handleRead(key);
}
if(key.isValid() &&key.isWritable()){
// 客户端可写时
protocol.handleWrite(key);
}
}
catch(IOException ex){
// 出现IO异常(如客户端断开连接)时移除处理过的键
keyIter.remove();
continue;
}
// 移除处理过的键
keyIter.remove();
}
}
}
}
TCPClient客户端程序
/**
* NIO TCP 客户端
*
* @date 2010-2-3
* @time 下午03:33:26
* @version 1.00
*/
publicclass TCPClient{
// 信道选择器
private Selector selector;
// 与服务器通信的信道
SocketChannel socketChannel;
// 要连接的服务器Ip地址
private String hostIp;
// 要连接的远程服务器在监听的端口
privateinthostListenningPort;
/**
* 构造函数
* @param HostIp
* @param HostListenningPort
* @throws IOException
*/
public TCPClient(String HostIp,intHostListenningPort)throws IOException{
this.hostIp=HostIp;
this.hostListenningPort=HostListenningPort;
initialize();
}
/**
* 初始化
* @throws IOException
*/
privatevoid initialize() throws IOException{
// 打开监听信道并设置为非阻塞模式
socketChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress(hostIp, hostListenningPort));
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// 打开并注册选择器到信道
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
// 启动读取线程
new TCPClientReadThread(selector);
}
/**
* 发送字符串到服务器
* @param message
* @throws IOException
*/
publicvoid sendMsg(String message) throws IOException{
ByteBuffer writeBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap(message.getBytes("UTF-16"));
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
}
publicstaticvoid main(String[] args) throws IOException{
TCPClient client=new TCPClient("127.0.0.1",1978);
String str = "";
for(inti=0; i<1000; i++) {
str+=i+",";
}
client.sendMsg(str);
}
}
客户端接收线程
public TCPClientReadThread(Selector selector){
this.selector=selector;
new Thread(this).start();
}
publicvoid run() {
try {
while (selector.select() > 0) {
// 遍历每个有可用IO操作Channel对应的SelectionKey
for (SelectionKey sk : selector.selectedKeys()) {
// 如果该SelectionKey对应的Channel中有可读的数据
if (sk.isReadable()) {
// 使用NIO读取Channel中的数据
SocketChannel sc = (SocketChannel)sk.channel();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
sc.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
// 将字节转化为为UTF-16的字符串
String receivedString=Charset.forName("UTF-16").newDecoder().decode(buffer).toString();
// 控制台打印出来
System.out.println("接收到来自服务器"+sc.socket().getRemoteSocketAddress()+"的信息:"+receivedString);
// 为下一次读取作准备
sk.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
// 删除正在处理的SelectionKey
selector.selectedKeys().remove(sk);
}
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
ex.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
文件读取的性能
我们已知的文件读写包括三种方式:流读写、channel(缓冲读写)、直接内存缓冲区读写。
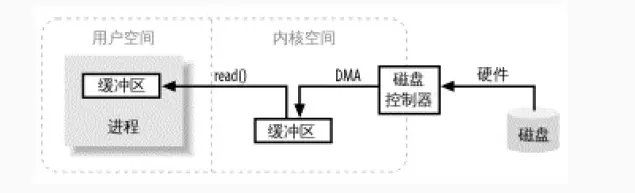
面向流的读写
文件映射的方式
由图可见,文件映射的方式比传统方式不用的是,再也不用磁盘控制器拷贝到内核空间了,只需要根据对物理内存的映射,就能让进程直接操作磁盘了。但是直接内存映射的方式会使用双倍内存,就是说在JVM和物理内存中,他会有两份空间,因此使用的时候可以权衡一下性能。
代码示例:
public class FileCopyTest {
public static void main(String[]args) throws Exception{
StringsourcePath = "F:\\mywork\\javademo\\dir1\\movie.avi";
StringdestPath1 = "F:\\mywork\\javademo\\dir2\\movie1.avi";
StringdestPath2 = "F:\\mywork\\javademo\\dir2\\movie2.avi";
StringdestPath3 = "F:\\mywork\\javademo\\dir2\\movie3.avi";
long t1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
traditionalCopy(sourcePath,destPath1);
long t2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("传统IO方法实现文件拷贝耗时:" + (t2-t1) + "ms");
nioCopy(sourcePath,destPath2);
long t3 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("利用NIO文件通道方法实现文件拷贝耗时:" + (t3-t2) + "ms");
nioCopy2(sourcePath,destPath3);
long t4 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("利用NIO文件内存映射及文件通道实现文件拷贝耗时:" + (t4-t3) + "ms");
}
private static void nioCopy2(StringsourcePath, String destPath) throws Exception {
File source = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()){
dest.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStreamfis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStreamfos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
FileChannelsourceCh = fis.getChannel();
FileChanneldestCh = fos.getChannel();
MappedByteBuffermbb = sourceCh.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, sourceCh.size());
destCh.write(mbb);
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
}
private static void traditionalCopy(StringsourcePath, String destPath) throws Exception{
File source = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()){
dest.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStreamfis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStreamfos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
byte [] buf = newbyte [512];
int len = 0;
while((len =fis.read(buf)) != -1) {
fos.write(buf, 0, len);
}
fis.close();
fos.close();
}
private static void nioCopy(StringsourcePath, String destPath) throws Exception{
File source = new File(sourcePath);
File dest = new File(destPath);
if(!dest.exists()){
dest.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStreamfis = new FileInputStream(source);
FileOutputStreamfos = new FileOutputStream(dest);
FileChannelsourceCh = fis.getChannel();
FileChanneldestCh = fos.getChannel();
destCh.transferFrom(sourceCh, 0, sourceCh.size());
sourceCh.close();
destCh.close();
}
}
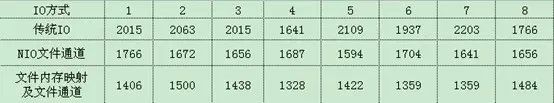
每执行完一次拷贝之后,将F:\mywork\javademo\dir2\目录中的内容删除掉,重复执行8次。观察测试结果如下:时间单位为ms(毫秒)
由上表可知,传统IO方式平均拷贝完成时间约为1968ms,NIO文件通道方式平均拷贝完成时间约为1672ms,文件内存映射及文件通道方式平均拷贝完成时间约为1418ms。
文章参考自:
http://www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1413518521372.html
http://weixiaolu.iteye.com/blog/1479656