狗猫数据集的两阶段分类实验python编程
目录
- 数据集准备
- 安装库
- 狗猫数据集的两阶段分类实验
- 创建三个子集的新数据集
- 构建小型卷积网络
- 数据预处理
- 训练
- 图像数据生成器增强数据
- 构建卷积网络
- 构建VGG16网络
- 将猫狗数据集传递给神经网络
- 参数调优
数据集准备
安装库
狗猫数据集的两阶段分类实验
创建三个子集的新数据集
import keras
import os, shutil
# The path to the directory where the original
# dataset was uncompressed
original_dataset_dir = 'D:\\train\\train'
# The directory where we will
# store our smaller dataset
base_dir = 'D:\\train1'
os.mkdir(base_dir)
# Directories for our training,
# validation and test splits
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'train')
os.mkdir(train_dir)
validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'validation')
os.mkdir(validation_dir)
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'test')
os.mkdir(test_dir)
# Directory with our training cat pictures
train_cats_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'cats')
os.mkdir(train_cats_dir)
# Directory with our training dog pictures
train_dogs_dir = os.path.join(train_dir, 'dogs')
os.mkdir(train_dogs_dir)
# Directory with our validation cat pictures
validation_cats_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, 'cats')
os.mkdir(validation_cats_dir)
# Directory with our validation dog pictures
validation_dogs_dir = os.path.join(validation_dir, 'dogs')
os.mkdir(validation_dogs_dir)
# Directory with our validation cat pictures
test_cats_dir = os.path.join(test_dir, 'cats')
os.mkdir(test_cats_dir)
# Directory with our validation dog pictures
test_dogs_dir = os.path.join(test_dir, 'dogs')
os.mkdir(test_dogs_dir)
# Copy first 1000 cat images to train_cats_dir
fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(train_cats_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# Copy next 500 cat images to validation_cats_dir
fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000, 1500)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(validation_cats_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# Copy next 500 cat images to test_cats_dir
fnames = ['cat.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1500, 2000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(test_cats_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# Copy first 1000 dog images to train_dogs_dir
fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(train_dogs_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# Copy next 500 dog images to validation_dogs_dir
fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1000, 1500)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(validation_dogs_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
# Copy next 500 dog images to test_dogs_dir
fnames = ['dog.{}.jpg'.format(i) for i in range(1500, 2000)]
for fname in fnames:
src = os.path.join(original_dataset_dir, fname)
dst = os.path.join(test_dogs_dir, fname)
shutil.copyfile(src, dst)
打印新数据集的尺寸
print('total training cat images:', len(os.listdir(train_cats_dir)))
print('total training dog images:', len(os.listdir(train_dogs_dir)))
print('total validation cat images:', len(os.listdir(validation_cats_dir)))
print('total validation dog images:', len(os.listdir(validation_dogs_dir)))
print('total test cat images:', len(os.listdir(test_cats_dir)))
print('total test dog images:', len(os.listdir(test_dogs_dir)))
构建小型卷积网络
from keras import layers
from keras import models
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu',
input_shape=(150, 150, 3)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
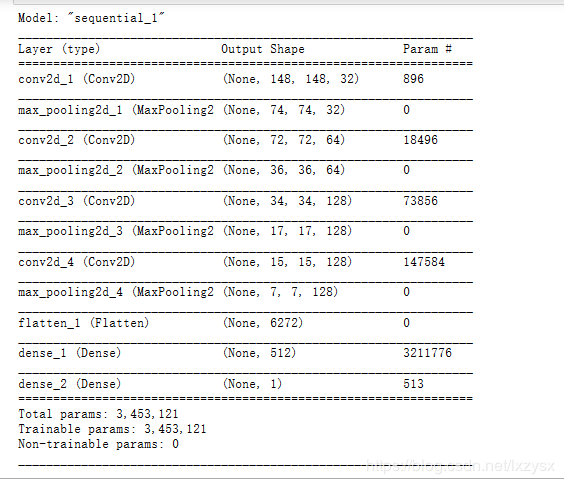
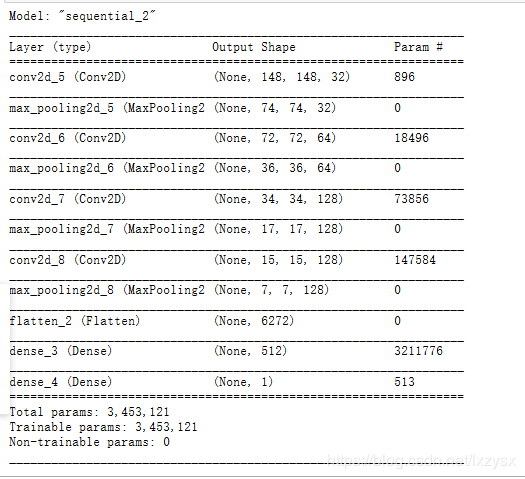
了解征图的尺寸是如何随着每一层变化的
model.summary()
数据预处理
from keras import optimizers
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4),
metrics=['acc'])
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
# All images will be rescaled by 1./255
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
# This is the target directory
train_dir,
# All images will be resized to 150x150
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=20,
# Since we use binary_crossentropy loss, we need binary labels
class_mode='binary')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=20,
class_mode='binary')
for data_batch, labels_batch in train_generator:
print('data batch shape:', data_batch.shape)
print('labels batch shape:', labels_batch.shape)
break
训练
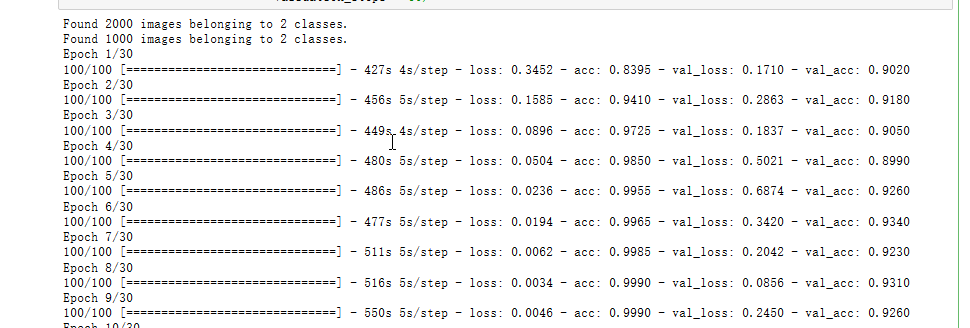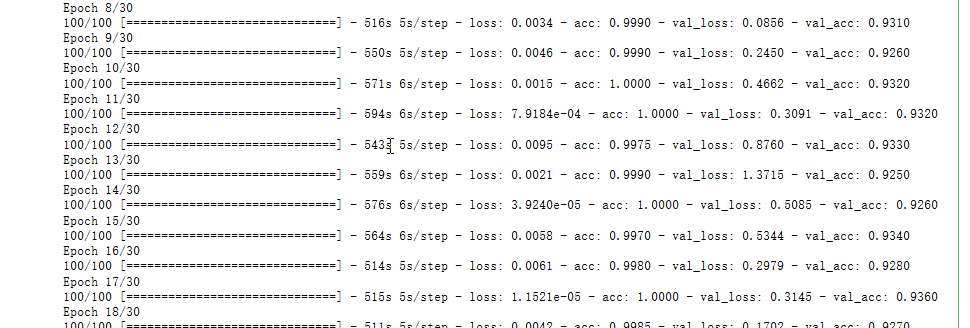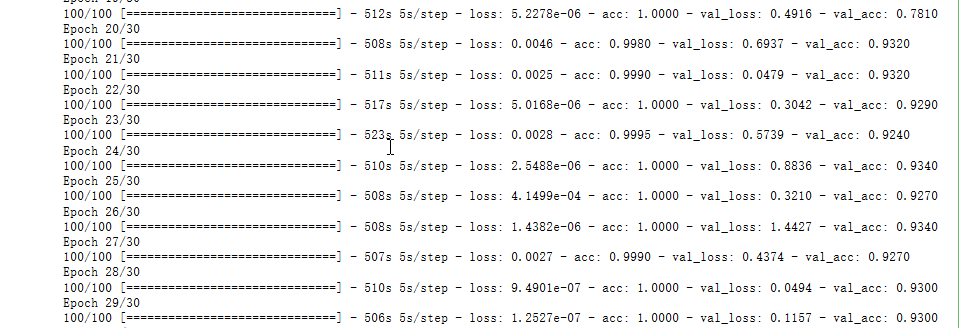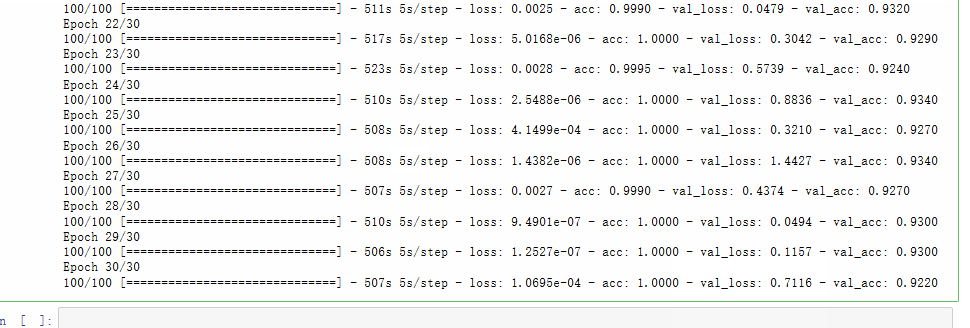
history = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=100,
epochs=30,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=50)
model.save('cats_and_dogs_small_1.h5')
在训练和验证数据上绘制模型的损失和准确性
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(acc))
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
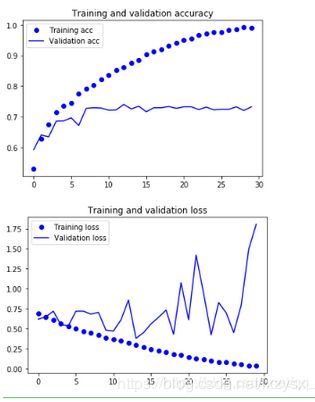
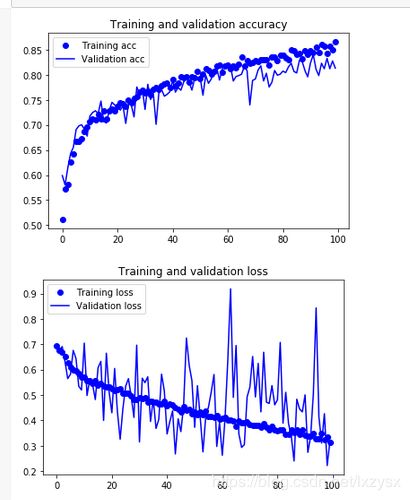
这些图具有过拟合的特点。我们的训练精度随着时间线性增长,直到接近100%,而我们的验证精度停留在70-72%。我们的验证损失在5个epoch后达到最小,然后停止,而训练损失继续线性下降,直到接近0。
因为我们只有相对较少的训练样本(2000),过度拟合将是我们首要关心的问题。你已经知道了一些技术,可以帮助减轻过度拟合,如dropout和重量衰减(L2正则化)。现在我们将介绍一种新的方法,专门针对计算机视觉,在深度学习模型处理图像时几乎普遍使用:数据增强。
图像数据生成器增强数据
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,
fill_mode='nearest')
查看增强后的图像
# This is module with image preprocessing utilities
from keras.preprocessing import image
fnames = [os.path.join(train_cats_dir, fname) for fname in os.listdir(train_cats_dir)]
# We pick one image to "augment"
img_path = fnames[3]
# Read the image and resize it
img = image.load_img(img_path, target_size=(150, 150))
# Convert it to a Numpy array with shape (150, 150, 3)
x = image.img_to_array(img)
# Reshape it to (1, 150, 150, 3)
x = x.reshape((1,) + x.shape)
# The .flow() command below generates batches of randomly transformed images.
# It will loop indefinitely, so we need to `break` the loop at some point!
i = 0
for batch in datagen.flow(x, batch_size=1):
plt.figure(i)
imgplot = plt.imshow(image.array_to_img(batch[0]))
i += 1
if i % 4 == 0:
break
plt.show()
如果我们使用这种数据增加配置训练一个新的网络,我们的网络将永远不会看到两次相同的输入。然而,它看到的输入仍然是高度相关的,因为它们来自少量的原始图像——我们不能产生新的信息,我们只能混合现有的信息。因此,这可能还不足以完全消除过度拟合。
3)、为了进一步对抗过拟合,我们还将在我们的模型中增加一个Dropout层,就在密集连接分类器之前:
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3, 3), activation='relu',
input_shape=(150, 150, 3)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3, 3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2, 2)))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4),
metrics=['acc'])
用数据增强和退出来训练我们的网络
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale=1./255,
rotation_range=40,
width_shift_range=0.2,
height_shift_range=0.2,
shear_range=0.2,
zoom_range=0.2,
horizontal_flip=True,)
# Note that the validation data should not be augmented!
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
# This is the target directory
train_dir,
# All images will be resized to 150x150
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32,
# Since we use binary_crossentropy loss, we need binary labels
class_mode='binary')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size=(150, 150),
batch_size=32,
class_mode='binary')
history = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=100,
epochs=100,
validation_data=validation_generator,
validation_steps=50)
保存模型
model.save('cats_and_dogs_small_2.h5')
结果:
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(len(acc))
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label='Training acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label='Validation acc')
plt.title('Training and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label='Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
构建卷积网络
from keras import layers
from keras import models
from keras import optimizers
import keras
model = models.Sequential()
#输入图片大小是150*150 3表示图片像素用(R,G,B)表示
model.add(layers.Conv2D(32, (3,3), activation='relu', input_shape=(150 , 150, 3)))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(64, (3,3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2)))
model.add(layers.Conv2D(128, (3,3), activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.MaxPooling2D((2,2)))
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(512, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-4),
metrics=['acc'])
model.summary()
构建VGG16网络
from keras.applications import VGG16
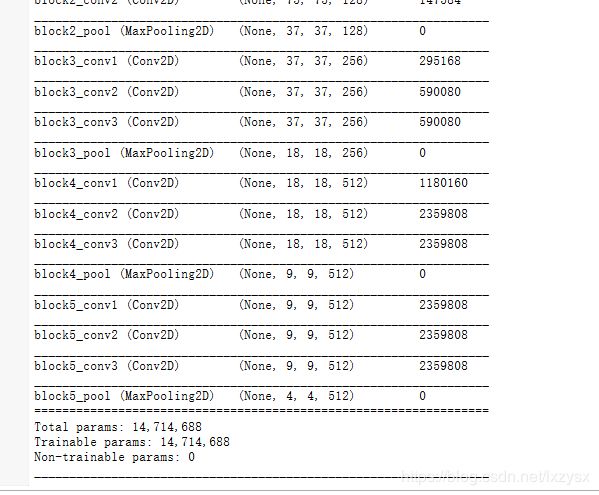
conv_base = VGG16(weights = 'imagenet', include_top = False, input_shape=(150, 150, 3))
conv_base.summary()
将猫狗数据集传递给神经网络
import os
import numpy as np
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
base_dir = 'D:\\train1'
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'train')
validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'validation')
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir, 'test')
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1. / 255)
batch_size = 20
def extract_features(directory, sample_count):
features = np.zeros(shape = (sample_count, 4, 4, 512))
labels = np.zeros(shape = (sample_count))
generator = datagen.flow_from_directory(directory, target_size = (150, 150),
batch_size = batch_size,
class_mode = 'binary')
i = 0
for inputs_batch, labels_batch in generator:
#把图片输入VGG16卷积层,让它把图片信息抽取出来
features_batch = conv_base.predict(inputs_batch)
#feature_batch 是 4*4*512结构
features[i * batch_size : (i + 1)*batch_size] = features_batch
labels[i * batch_size : (i+1)*batch_size] = labels_batch
i += 1
if i * batch_size >= sample_count :
#for in 在generator上的循环是无止境的,因此我们必须主动break掉
break
return features , labels
#extract_features 返回数据格式为(samples, 4, 4, 512)
train_features, train_labels = extract_features(train_dir, 2000)
validation_features, validation_labels = extract_features(validation_dir, 1000)
test_features, test_labels = extract_features(test_dir, 1000)
train_features = np.reshape(train_features, (2000, 4 * 4 * 512))
validation_features = np.reshape(validation_features, (1000, 4 * 4 * 512))
test_features = np.reshape(test_features, (1000, 4 * 4* 512))
from keras import models
from keras import layers
from keras import optimizers
#构造我们自己的网络层对输出数据进行分类
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(256, activation='relu', input_dim = 4 * 4 * 512))
model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid'))
model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr = 2e-5), loss = 'binary_crossentropy', metrics = ['acc'])
history = model.fit(train_features, train_labels, epochs = 30, batch_size = 20,
validation_data = (validation_features, validation_labels))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1, len(acc) + 1)
plt.plot(epochs, acc, 'bo', label = 'Train_acc')
plt.plot(epochs, val_acc, 'b', label = 'Validation acc')
plt.title('Trainning and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs, loss, 'bo', label = 'Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs, val_loss, 'b', label = 'Validation loss')
plt.title('Training and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
参数调优
参数调优的步骤:
将我们自己的网络层添加到VGG16的卷积层之上。
固定VGG16的卷积层保持不变。
用数据训练我们自己添加的网络层
将VGG16的卷积层最高两层放开
用数据同时训练放开的那两层卷积层和我们自己添加的网络层
model = models.Sequential()
#将VGG16的卷积层直接添加到我们的网络
model.add(conv_base)
#添加我们自己的网络层
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(256, activation = 'relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation = 'sigmoid'))
model.summary()

把它最高三层与我们自己的网络层结合在一起训练,同时冻结最低四层
conv_base.trainable = True
set_trainable = False
#一旦读取到'block5_conv1'时,意味着来到卷积网络的最高三层
#可以使用conv_base.summary()来查看卷积层的信息
for layer in conv_base.layers:
if layer.name == 'block5_conv1':
set_trainable = True
if set_trainable:
#当trainable == True 意味着该网络层可以更改,要不然该网络层会被冻结,不能修改
layer.trainable = True
else:
layer.trainable = False
数据传入网络
#把图片数据读取进来
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1. / 255)
train_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(train_dir, target_size = (150, 150), batch_size = 20,
class_mode = 'binary')
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(validation_dir, target_size = (150,150),
batch_size = 20,
class_mode = 'binary')
model.compile(loss = 'binary_crossentropy', optimizer = optimizers.RMSprop(2e-5),
metrics = ['acc'])
history = model.fit_generator(train_generator, steps_per_epoch = 100, epochs = 30,
validation_data = validation_generator,
validation_steps = 50)