Dom4j工具--XML的DOM解析(上)--读操作
前言:
什么是DOM解析
DOM解析原理:xml解析器一次性把整个xml文档加载进内存,然后在内存中构建一颗Document的对象树,通过Document对象,得到树上的节点对象,通过节点对象访问(操作)到xml文档的内容。
可以看一下图片了解一下:(图片来自于黑马)
![]()
个人理解的单个DOM图:
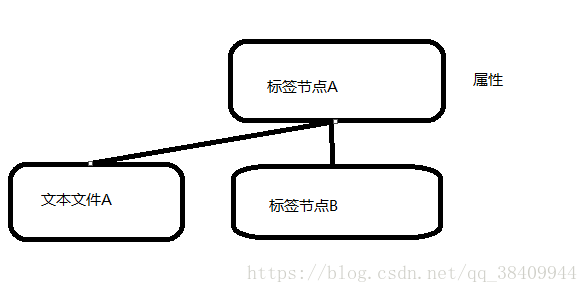
标签节点和文本内容是同一层级别的,而属性节点不是。
XML解析工具
DOM解析原理:
1)JAXP (oracle-Sun公司官方)
2)JDOM工具(非官方)
3)Dom4J工具(非官方)
三大框架(默认读取xml的工具就是Dom4j)
.......
SAX解析原理:
1)Sax解析工具(oracle-sun公司官方)这里只介绍Dom4j工具
Dom4j工具(原理:DOM解析,非官方,不在JDK需要导包)
现在最好用解析器
所以 我也学的是这一个
下载:先去官网下载核心jar包:dom4j-2.1.0.jar
dom4j
导包操作:
1. 右击项目new–>Folder 创建一个lib文件夹(其实什么名字无所谓啦,不过lib是库文件夹 这样起名字比较好理解)

2. 然后将 dom4j-2.1.0.jar拖入创建的lib文件夹中
3. 右击dom4j核心包 右击–>Build Path–>Add to Build path 将添加进来的核心包导入到项目中 项目中显示如下内容即可。
![]()
获取document对象:
为什么要获取document对象呢,因为我们是通过这个对象来获取 ,修改 xml文件中的元素
第一个Dom4j读取xml文档的例子:
也许有人对 . 这个符号不是很理解,意思就是当前文件的目录 ,具体可以参考这篇中间提到的部分
IO流学习笔记–操作文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
//1.创建一个xml解析器对象
SAXReader saxReader=new SAXReader();
//2.读取xml文档,返回Document对象
Document document=(Document) saxReader.read(new File(".\\src\\day13\\contains.xml"));
} catch (DocumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
//包装成RuntimeException类型错误抛出
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}注意:头文件是这几个 尤其是dom4j下面的包 别导错了 不然报错
import java.io.File;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentException;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;题外话:
如果你想try一整块 代码 ,有快速try的 就是选中你要的代码块 右击 Surround With –>Try catch 即可
Domj4读取xml文件:
读取xml文件的操作 我没与放在main函数里 而是通过单元测试来操作的。
具体的想了解测试单元的 可以看单元测试–JUnit4了解一下(eclipse环境)
设置xml文件内容:src包下
<constrant id="12">
sdf
<const id="11">
我是const1
<name>
我是name1
name>
const>
<const>
我是const2
<name>
我是name2
name>
const>
constrant>测试用例:
Element.nodeIterator(); //获取当前标签节点下的所有子节点
@Test
public void xx() throws DocumentException {
SAXReader saxReader=new SAXReader();
Document document=saxReader.read(
new File(".\\src\\day33\\ss.xml"));
//得到当前节点下的所有子节点对象(不包含孙以下的节点)
//就是指直接子节点
Iterator iterator=document.nodeIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Node node=iterator.next();
System.out.println(node.getName());
System.out.println(node.getClass());
}
} 输出:
constrant
class org.dom4j.tree.DefaultElement注意:没有输出constrant的id和sdf 说明了nodeIterator()得到的只是当前标签节点下的所有子节点 而xml的第一个字节点就是根节点 就一个
遍历xml文档的所有标签节点:
Document.getRootElement(); //获取xml文档的根标签
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
//1.读取xml文档,返回Document对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(new File(".\\src\\day33\\ss.xml"));
//得到根标签
Element rooElem = doc.getRootElement();
getChildNodes(rooElem);
}
private void getChildNodes(Element elem){
System.out.println(elem.getName());
//得到子节点
Iterator it = elem.nodeIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Node node = it.next();
if(node instanceof Text) {
System.out.println("内容:"+node.getText());
}
if(node instanceof Attribute) {
System.out.print("Attribute");
}
//1.判断是否是标签节点
if(node instanceof Element){
Element el = (Element)node;
//递归
getChildNodes(el);
}
};
} 输出:
constrant
内容:
sdf
const
内容:
我是const1
name
内容:
我是name1
内容:
内容:
const
内容:
我是const2
name
内容:
我是name2
内容:
内容:
结论:
nodeIterator()只能得到当前标签下的子节点 (标签节点和自身的文本文字)
如开头总结的:
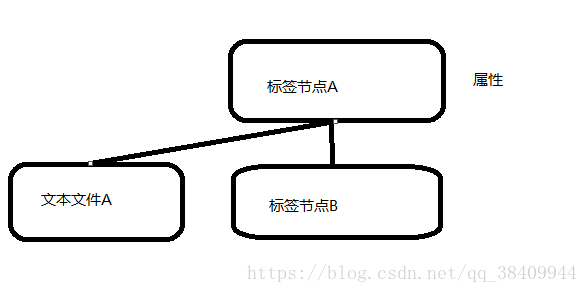
那你们是不是注意到 有些内容是空的 这个又是怎么一回事呢 ?
空格和换行也是xml的内容
所以 标签和标签之间格式如
codingCoge 和
codingCoge
是不一样的
如上文本 因为:
之间是不是换行了 那也是xml内容 所以还是被nodeIterator()读取到了 而且是文本节点即 换行符号
只要改成下述格式就不会有空白内容显示了
获取标签:
//获取xml文档的根标签 返回 Element
1. Document.getRootElement();
//指定名称的第一个子标签 返回 Element
2. ELement.element("标签名")
// 指定名称的所有子标签 返回Iterator<Element>
3. Element.elementIterator("标签名");
//获取所有子标签 返回 List<Element>
4. Element.elements();
@Test
public void test3() throws Exception{
//1.读取xml文档,返回Document对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(new
File(".\\src\\day33\\ss.xml"));
//2.得到根标签
Element rootElem = doc.getRootElement();
//得到标签名称
String name = rootElem.getName();
System.out.println(name);
//3.得到当前标签下指定名称的第一个子标签
Element contactElem = rootElem.element("contact");
System.out.println(contactElem.getName());
//4.得到当前标签下指定名称的所有子标签
Iterator it =
rootElem.elementIterator("contact");
while(it.hasNext()){
Element elem = it.next();
System.out.println(elem.getName());
}
//5.得到当前标签下的的所有子标签
List list = rootElem.elements();
} 当前标签下的的所有子标签 ,遍历List的方法
1)传统for循环:
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++){
Element e = list.get(i);
System.out.println(e.getName());
}2)增强for循环
for(Element e:list){
System.out.println(e.getName());
}3)迭代器
Iterator it = list.iterator(); //ctrl+2 松开 l
while(it.hasNext()){
Element elem = it.next();
System.out.println(elem.getName());
} 获取更深层次的标签(方法只能一层层地获取)
Element nameElem = doc.getRootElement().
element("contact").element("name");
System.out.println(nameElem.getName());既然学了获取标签 ,那我们修改一下前面的代码:获取xml里面的所有标签
private void getChildElement(Element elem) {
System.out.println(elem.getName());
List list=elem.elements();
for(Element element:list) {
getChildElement(element);
}
} 获取属性:
@Test
public void test4() throws Exception{
//1.读取xml文档,返回Document对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(new File(".\\src\\day33\\ss.xml"));
//获取属性:(先获的属性所在的标签对象,然后才能获取属性)
//得到标签对象
Element contactElem = doc.getRootElement().element("contact");
// 得到指定名称的属性值
String idValue = contactElem.attributeValue("id");
System.out.println(idValue);
//得到指定属性名称的属性对象
Attribute idAttr = contactElem.attribute("id");
//getName: 属性名称 getValue:属性值
System.out.println(idAttr.getName() +"=" + idAttr.getValue());
//2.3 得到所有属性对象,返回LIst集合
List list = contactElem.attributes();
//遍历属性
for (Attribute attr : list) {
System.out.println(attr.getName()+"="+attr.getValue());
}
//得到所有属性对象,返回迭代器
Iterator it = contactElem.attributeIterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Attribute attr = it.next();
System.out.println(attr.getName()+"="+attr.getValue());
}
} 获取文本:
@Test
public void test5() throws Exception{
//1.读取xml文档,返回Document对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(new File("./src/contact.xml"));
/**
* 注意: 空格和换行也是xml的内容
*/
String content = doc.getRootElement().getText();
System.out.println(content);
//获取文本(先获取标签,再获取标签上的文本)
Element nameELem =
doc.getRootElement().element("contact").element("name");
//1. 得到文本
String text = nameELem.getText();
System.out.println(text);
//2. 得到指定子标签名的文本内容
String text2 =
doc.getRootElement().element("contact").elementText("phone");
System.out.println(text2);
}最后再来一个栗子:
获取当前标签的所有子标签及内容
public class hah {
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception {
// 1.读取xml文档,返回Document对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(new File(".\\src\\day33\\ss.xml"));
// 得到根标签
Element rooElem = doc.getRootElement();
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
getChildElement(rooElem, stringBuffer);
System.out.print(stringBuffer.toString());
}
private void getChildElement(Element elem, StringBuffer stringBuffer) {
stringBuffer.append("<" + elem.getName());
List list = elem.attributes();
for (Attribute attribute : list) {
stringBuffer.append(" " + attribute.getName() + "=\"" + attribute.getValue()+"\"");
}
stringBuffer.append(">");
Iterator iterator=elem.nodeIterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
Node node=iterator.next();
if (node instanceof Text) {
Text text=(Text)node;
stringBuffer.append(text.getText());
} else if (node instanceof Element) {
Element element=(Element)node;
getChildElement(element, stringBuffer);
}
}
stringBuffer.append("+elem.getName()+">");
}
}
输出:
<constrant id="12">
sd f
<const id="11">
我是const1const>
<const id="11">
我是const1const>
constrant>注意: 空格和换行也是xml的内容 也算text文本节点
把xml文档信息封装到对象中
不过 上面的这些操作都是很少用到的 ,因为我们需要的是不是完整得读取XML内容,编程时面向对象得,所以是把读取到的内容存放到项目创建的对象中,然后以对象为单位进行操作:
举一个栗子:
先创建好一个Contact的对象,包涵属性:
id,
name,
age,
phone,
email,
qq,包涵方法:
setId,
setName,
setAge,
setPhone,
setEmail,
setQq,你可以选择一个一个创建方法,也可以使用快捷方法:
菜单栏:Source–>Generate Getters and Setters
就可以根据属性来自动创建Set和Get方法了
源码:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
List list = new ArrayList();
//读取xml,封装对象
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document doc = reader.read(new File("./src/contact.xml"));
//读取contact标签
Iterator it = doc.getRootElement().elementIterator("contact");
while(it.hasNext()){
Element elem = it.next();
//创建Contact
Contact contact = new Contact();
contact.setId(elem.attributeValue("id"));
contact.setName(elem.elementText("name"));
contact.setAge(elem.elementText("age"));
contact.setPhone(elem.elementText("phone"));
contact.setEmail(elem.elementText("email"));
contact.setQq(elem.elementText("qq"));
list.add(contact);
}
for (Contact contact : list) {
System.out.println(contact);
}
}