axios在Vue项目中进行全局配置,拦截器封装
为什么要全局配置?
- 全局配置在每一次发起请求时都可以单独配置,但如果是一些所有请求都必要添加的配置项时,就可以进行全局配置,会节省很多代码,并且更加优雅
- 是不是全局配置后,组件里每次使用axios发起请求,就不用引入了?答案是:是的
axiox安装
如果你使用的是 npm
$ npm install axios -S
cnpm 同样
$ cnpm install axios -S
如果你使用 yarn
$ yarn add axios -S
标题目录
- 文件目录
- 全局配置
- 添加配置项
- 引入配置
- 在组件中使用
- 拦截器封装
- 拦截器工作流程
- 请求和响应封装
- 带有全局配置的拦截器封装
- 引入拦截器
- axios所有配置项
文件目录
axios的全局配置和拦截器封装,你可以创建一个js文件来管理,可以放在任何你想放的位置
但是,最后一定要在main.js项目入口文件中引入,并且与Vue实例进行关联。
当然你也可以直接写在main.js中,但可能会显得入口文件的代码过于臃肿。
我选择在src目录下创建一个axios文件夹,然后在里面创建一个index.js文件,用来管理axios的全局配置和拦截器封装
路径: ./src/axios/index.js
全局配置
步骤:
- 添加配置项
- 引入配置实例
- 在组件中使用
添加配置项
在axios/index.js文件中按照以下步骤,进行全局配置:
- 引入axios
- 创建一个axios实例
- 对该实例的传递一个对象,该对象就是全局配置信息
- 将该实例导出
axios/index.js
// 1. 引入
import axios from "axios";
// 2. 创建实例
const instance = axios.create(config)
// 3. 配置信息
let config = {
// 每次请求的协议、IP地址。 设置该配置后,每次请求路径都可以使用相对路径,例如"/admin/login"
baseURL: "http://localhost",
// 请求超时时间
timeout: 10000,
// 每次请求携带cookie
withCredentials: true
}
// 4. 导出
export default instance
如果你想进行更多的全局配置,可在文章末尾查看:axios所有请求配置项
引入配置
既然要实现整个项目全局的操作,那么就要在入口文件main.js里面下文章
-
在main.js中引入刚才进行配置的axios实例
-
把该实例设置为Vue原型中的一个方法
main.js
import ...
// 1. 引入实例
import axios from './axios'
// 因为我在 axios 文件夹下只创建了一个 index.js 文件,那么 webpack 会默认把该文件打包,所以这里的路径可以不用加上 '/index.js'
// 如果你创建的文件名不是 index,那么一定要加上文件名
// 如果你的 axios 配置文件跟我创建的路径不一样,那么按照你的路径引入就可以了
// 2. 与Vue实例关联
Vue.prototype.$axios = axios
new Vue({
...
})
在组件中使用
因为我们把 axios 封装成 Vue原型中的一个方法,那么我们在组件中就不用再引入 axios
并且我们进行了全局配置,再在组件中单独引入axios ,引入的是一个新的实例,而不是包含全局配置项的实例
test.vue
<template>
<div>
<button @click="handleClick">button>
div>
template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
handleClick(){
// 就像使用 $store、$route 一样
this.$axios.post("/getList", {pid: 157})
.then(res => console.log(res))
.catch(err => console.log(err))
}
}
}
script>
拦截器封装
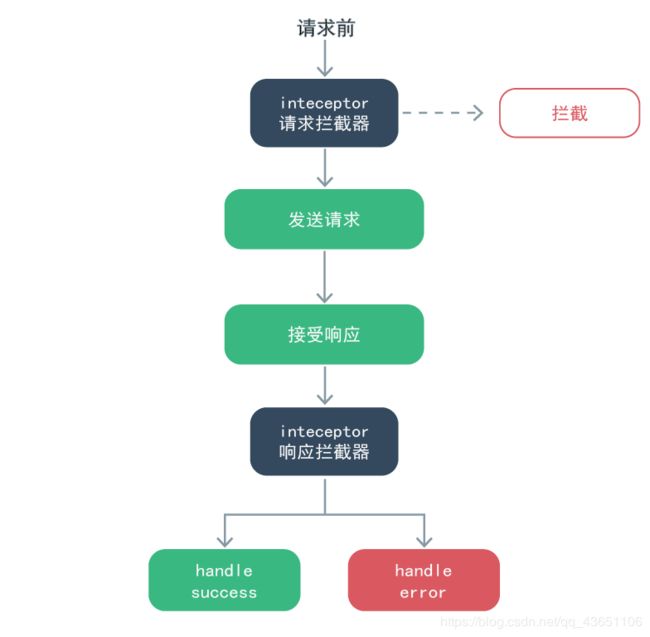
拦截器工作流程
抛出问题:拦截器是拦截什么的?在哪拦截?什么时候拦截?
请求和响应封装
如果你进行了全局配置,那么封装拦截器的方法不太一样,axios基于全局配置的拦截器封装
同样在 ./src/axios/index.js 文件中,对拦截器进行封装
-
是对引入的 axios 实例进行封装,所以最后要把引入的 axios 实例导出去
-
请求拦截器参数:
...request.use( (config) => {}, (err) => {} ),其中 config 为请求配置项 -
响应拦截器参数:
...response.use( (res) => {}, (err) => {} ) -
如果你取消请求,那么在请求拦截器的第一个匿名函数参数中
return Promise.reject("cancel request")
axios/index.js
import axios from "axios";
// 1. 请求拦截
axios.interceptors.request.use(
// 请求之前做些什么
config => {
if(...){
// 符合判断条件,做出响应处理,例如携带token
config.headers["Authorization"] = localStorage.getItem("token")
// 最后返回 config 代表继续发送请求
return config
} else {
// 如果想取消请求
return Promise.reject()
}
},
// 处理错误
err => Promise.reject()
);
// 2. 响应拦截
instance.interceptors.response.use(
// 对于成功响应的处理
res => {
return res;
},
// 处理错误响应
err => Promise.reject()
);
// 3. 导出实例
export default axios
带有全局配置的拦截器封装
如果你进行了全局配置,那么对于封装拦截器的方法与上面的有些不一样
不同之处:对你使用 axios.create() 创建的带有全局配置项的实例进行封装
axios/index.js
import axios from "axios"
// 全局配置
const instance = axios.create({
...
})
// 请求拦截
instance.interceptors.request.use(
config => {...},
err => Promise.reject()
)
// 响应拦截
instance.interceptors.response.use(
res => {...},
err => Promise.reject()
)
// 导出也要导正确
export default instance
引入拦截器
同样在入口文件 main.js 中引入
main.js
import ...
import axios from "./axios"
// 设置为全局方法
Vue.prototype.$axios = axios
new Vue({
...
})
axios所有请求配置项
可转到官网:axios中文网–请求配置项
{
// `url` 是用于请求的服务器 URL
url: '/user',
// `method` 是创建请求时使用的方法
method: 'get', // default
// `baseURL` 将自动加在 `url` 前面,除非 `url` 是一个绝对 URL。
// 它可以通过设置一个 `baseURL` 便于为 axios 实例的方法传递相对 URL
baseURL: 'https://some-domain.com/api/',
// `transformRequest` 允许在向服务器发送前,修改请求数据
// 只能用在 'PUT', 'POST' 和 'PATCH' 这几个请求方法
// 后面数组中的函数必须返回一个字符串,或 ArrayBuffer,或 Stream
transformRequest: [function (data, headers) {
// 对 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `transformResponse` 在传递给 then/catch 前,允许修改响应数据
transformResponse: [function (data) {
// 对 data 进行任意转换处理
return data;
}],
// `headers` 是即将被发送的自定义请求头
headers: {'X-Requested-With': 'XMLHttpRequest'},
// `params` 是即将与请求一起发送的 URL 参数
// 必须是一个无格式对象(plain object)或 URLSearchParams 对象
params: {
ID: 12345
},
// `paramsSerializer` 是一个负责 `params` 序列化的函数
// (e.g. https://www.npmjs.com/package/qs, http://api.jquery.com/jquery.param/)
paramsSerializer: function(params) {
return Qs.stringify(params, {arrayFormat: 'brackets'})
},
// `data` 是作为请求主体被发送的数据
// 只适用于这些请求方法 'PUT', 'POST', 和 'PATCH'
// 在没有设置 `transformRequest` 时,必须是以下类型之一:
// - string, plain object, ArrayBuffer, ArrayBufferView, URLSearchParams
// - 浏览器专属:FormData, File, Blob
// - Node 专属: Stream
data: {
firstName: 'Fred'
},
// `timeout` 指定请求超时的毫秒数(0 表示无超时时间)
// 如果请求话费了超过 `timeout` 的时间,请求将被中断
timeout: 1000,
// `withCredentials` 表示跨域请求时是否需要使用凭证
withCredentials: false, // default
// `adapter` 允许自定义处理请求,以使测试更轻松
// 返回一个 promise 并应用一个有效的响应 (查阅 [response docs](#response-api)).
adapter: function (config) {
/* ... */
},
// `auth` 表示应该使用 HTTP 基础验证,并提供凭据
// 这将设置一个 `Authorization` 头,覆写掉现有的任意使用 `headers` 设置的自定义 `Authorization`头
auth: {
username: 'janedoe',
password: 's00pers3cret'
},
// `responseType` 表示服务器响应的数据类型,可以是 'arraybuffer', 'blob', 'document', 'json', 'text', 'stream'
responseType: 'json', // default
// `responseEncoding` indicates encoding to use for decoding responses
// Note: Ignored for `responseType` of 'stream' or client-side requests
responseEncoding: 'utf8', // default
// `xsrfCookieName` 是用作 xsrf token 的值的cookie的名称
xsrfCookieName: 'XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `xsrfHeaderName` is the name of the http header that carries the xsrf token value
xsrfHeaderName: 'X-XSRF-TOKEN', // default
// `onUploadProgress` 允许为上传处理进度事件
onUploadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// Do whatever you want with the native progress event
},
// `onDownloadProgress` 允许为下载处理进度事件
onDownloadProgress: function (progressEvent) {
// 对原生进度事件的处理
},
// `maxContentLength` 定义允许的响应内容的最大尺寸
maxContentLength: 2000,
// `validateStatus` 定义对于给定的HTTP 响应状态码是 resolve 或 reject promise 。如果 `validateStatus` 返回 `true` (或者设置为 `null` 或 `undefined`),promise 将被 resolve; 否则,promise 将被 rejecte
validateStatus: function (status) {
return status >= 200 && status < 300; // default
},
// `maxRedirects` 定义在 node.js 中 follow 的最大重定向数目
// 如果设置为0,将不会 follow 任何重定向
maxRedirects: 5, // default
// `socketPath` defines a UNIX Socket to be used in node.js.
// e.g. '/var/run/docker.sock' to send requests to the docker daemon.
// Only either `socketPath` or `proxy` can be specified.
// If both are specified, `socketPath` is used.
socketPath: null, // default
// `httpAgent` 和 `httpsAgent` 分别在 node.js 中用于定义在执行 http 和 https 时使用的自定义代理。允许像这样配置选项:
// `keepAlive` 默认没有启用
httpAgent: new http.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
httpsAgent: new https.Agent({ keepAlive: true }),
// 'proxy' 定义代理服务器的主机名称和端口
// `auth` 表示 HTTP 基础验证应当用于连接代理,并提供凭据
// 这将会设置一个 `Proxy-Authorization` 头,覆写掉已有的通过使用 `header` 设置的自定义 `Proxy-Authorization` 头。
proxy: {
host: '127.0.0.1',
port: 9000,
auth: {
username: 'mikeymike',
password: 'rapunz3l'
}
},
// `cancelToken` 指定用于取消请求的 cancel token
// (查看后面的 Cancellation 这节了解更多)
cancelToken: new CancelToken(function (cancel) {
})
}
如果看完这篇文章感觉没有收获的话,希望可以耐心的再看一次,并且希望你可以学会使用axios的全局配置和拦截器。