spring学习(一)属性管理PropertySource类
一、PropertySource:用于存放key-value对象的抽象,子类需要实现getProperty(String name)返回对应的Value方法,其中value可以是任何类型不局限在字符串
注:PropertySource里的属性name和source都是final的。初始化后不能修改
其中named(String name)是用来判断数组里是否包括当前name的方法,spring给的例子如下
@Test
public void testSource() {
List> sources = new ArrayList>();
sources.add(new MapPropertySource("sourceA", new HashMap()));
sources.add(new MapPropertySource("sourceB", new HashMap()));
Assert.assertEquals(true, sources.contains(PropertySource.named("sourceA")));
Assert.assertEquals(true, sources.contains(PropertySource.named("sourceB")));
Assert.assertEquals(false, sources.contains(PropertySource.named("sourceC")));
} PropertySource.named的方法实现
public static PropertySource named(String name) {
return new ComparisonPropertySource(name);
}其中ComparisonPropertySource只对List有用,只继承了getName方法。其中方法都会抛出异常
ComparisonPropertySource instances are for collection comparison use only对应子类
EnumerablePropertySource:增加了一个方法用于返回所有name值getPropertyNames,同时重写的containsProperty方法,通过getPropertyNames返回的key值进行判断,有助于提升性能
MapPropertySource:其中的source是以Map形式存放的
重写了getProperty和getPropertyNames
PropertiesPropertySoruce:同MapPropertySource,只是构造函数的参数不同
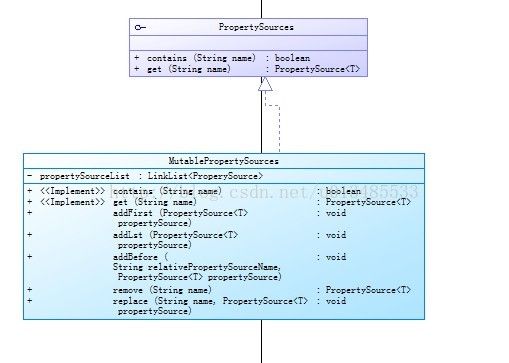
二、PropertySources:用于存放PropertySource的集合
MutablePropertySources:用linkList实现PropertySources,可以方便向List链中首位、末位、中间位置增加或替换或删除一个key-value属性值
每次增加或替换时,都会判断这个PropertySource是否存在,如果存在,先删除。保证整个List中name的唯一
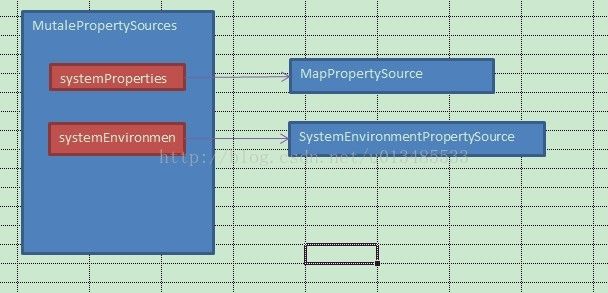
刚开始看源代码,MapPropertySource和MutablePropertySources总是容易弄混。慢慢看了一些应用的源代码。比如spring在预启动时,会加载系统的环境变量。StandardEnvironment代码如下
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(new MapPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}此时的环境变量结构如下图表示,而StandardEnvironment.getProperty(key)是需要遍历MutablePropertySources里面的所有PropertySource,并查看是否有存在的key值
三,PropertySource应用
spring在加载通过xml文件配置的bean文件,可以在文件路径地址中写入一些系统参数信息,比如例子如下(可能配置的没什么意义)
public class TestPropertyEditorRegistrar {
private ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(new String[] { "classpath*:spring/${java.vm.version}/propertyEditor.xml" });
}
}其中的${java.vm.version}会在正式加载之前通过StandardEnvironment替换成相应的变量名称
1)在ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的父类中AbstractRefreshableConfigApplicationContext中的setConfigLocations(String ... locations)有如下方法
protected void setConfigLocations(String[] locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.notNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
} else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
protected String resolvePath(String path) {
//调用PropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders的方法,
//其中getEnvironment得到的对象是StandardEnvironment,而这个方法是由父类AbstractEnvironment中实现
return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);
}2)AbstractEnvironment实现了Envirionment和PropertyResolver接口,但对于PropertyResolver的接口中的方法都是通过PropertySourcesPropertyResolver类实现的,PropertySourcesPropertyResolver这个同PropertyResolver的一个子类
private final MutablePropertySources propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
private final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver = new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(propertySources); @Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
//调用接口PropertyResolver进行具体的解析字串.类PropertySourcesPropertyResolver的对象生成时会传递一个MutablePropertySources对象
//StandardEnvironment的的实现传递了2个PropertySource,(systemEnvironment,systemProperties)
//最终调用的是AbstractPropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}3)AbstractPropertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders的关键实现类是PropertyPlaceholderHelper.replacePlaceholders方法
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String value) {
if (strictHelper == null) {
strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(true);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(value, strictHelper);
}
/**
* 定义一个PropertyPlaceholderHelper,并传参数用于判断是否忽略不能解析的变量
*/
public PropertyPlaceholderHelper createPlaceholderHelper(boolean ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders) {
return new PropertyPlaceholderHelper(placeholderPrefix, placeholderSuffix, valueSeparator, ignoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders);
} private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
//直接调用helper.parseStringValue方法,这个方法也得spring用来解析字符串中所有替换变量实现类,
//这个方法的实现的可以单独说明,主要功能是替换text中的${xxxx}指导xxxx替换成getProperty(placeholderName)取到的变量值
return helper.parseStringValue(text, new PlaceHolderResolver() {
@Override
public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) {
//这个方法是由具体的PropertyResolver的子类实现的
return getProperty(placeholderName);
}
});
}4)PropertyResolver.getProperty(name)的实现,这里是由PropertySourcePropertyResolver类实现,并支持嵌套替换
@Override
public String getProperty(String key) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(format("getProperty(\"%s\")(implicit targetType [String])", key));
}
return getProperty(key, String.class);
}
public T getProperty(String key, Class requiredType) {
boolean debugEnabled = logger.isDebugEnabled();
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace(format("getProperty(\"%s\", %s)", key, requiredType.getSimpleName()));
}
for (PropertySource propertySource : propertySources) {
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug(format("Searching for key '%s' in [%s]", key, propertySource.getName()));
}
Object value;
if ((value = propertySource.getProperty(key)) != null) {
Class valueType = value.getClass();
//如果类型是strng,可以嵌套解析
if (String.class.equals(valueType)) {
value = this.resolveNestedPlaceholders((String)value);
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug(
format("Found key '%s' in [%s] with type [%s] and value '%s'",
key, propertySource.getName(), valueType.getSimpleName(), value));
}
return (T)value;
}
}
if (debugEnabled) {
logger.debug(format("Could not find key '%s' in any property source. Returning [null]", key));
}
return null;
}