bindService源码分析
bindService
AIDL中使用了
bindService(intent, mServiceConnection, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE)进行服务绑定,这里对这个方法进行源码分析。
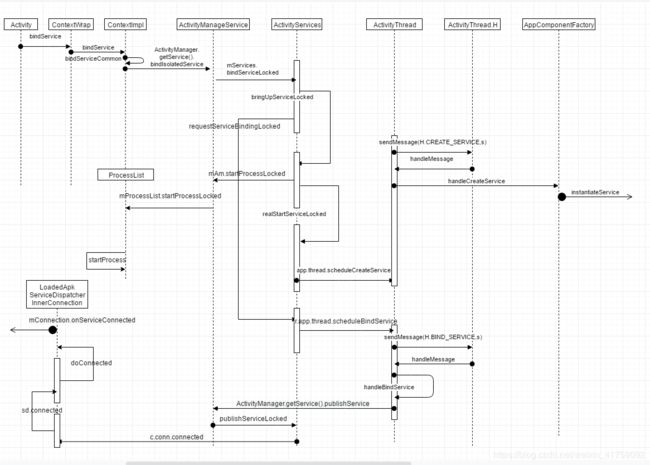
调用了ContextWrapper中的
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn,
int flags) {
return mBase.bindService(service, conn, flags);
}
基本类是Context
public abstract boolean bindService(@RequiresPermission Intent service,
@NonNull ServiceConnection conn, @BindServiceFlags int flags);
具体实现类是ContextImpl
@Override
public boolean bindService(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return bindServiceCommon(service, conn, flags, null, mMainThread.getHandler(), null,
getUser());
}
都是调用下面的方法
private boolean bindServiceCommon(Intent service, ServiceConnection conn, int flags,
String instanceName, Handler handler, Executor executor, UserHandle user) {
// Keep this in sync with DevicePolicyManager.bindDeviceAdminServiceAsUser.
IServiceConnection sd;
if (conn == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("connection is null");
}
if (handler != null && executor != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Handler and Executor both supplied");
}
if (mPackageInfo != null) {
if (executor != null) {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), executor, flags);
} else {
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), handler, flags);
}
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Not supported in system context");
}
validateServiceIntent(service);
try {
IBinder token = getActivityToken();
if (token == null && (flags&BIND_AUTO_CREATE) == 0 && mPackageInfo != null
&& mPackageInfo.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion
< android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.ICE_CREAM_SANDWICH) {
flags |= BIND_WAIVE_PRIORITY;
}
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
int res = ActivityManager.getService().bindIsolatedService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), getActivityToken(), service,
service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(getContentResolver()),
sd, flags, instanceName, getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());
if (res < 0) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Not allowed to bind to service " + service);
}
return res != 0;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
主要看一下这个地方ActivityManager.getService().bindIsolatedService
class ActivityManager
@UnsupportedAppUsage
public static IActivityManager getService() {
return IActivityManagerSingleton.get();
}
class ActivityManager
@UnsupportedAppUsage
private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> IActivityManagerSingleton =
new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
@Override
protected IActivityManager create() {
final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
final IActivityManager am = IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);
return am;
}
};
public class ActivityManagerService extends IActivityManager.Stub
这里返回的是一个IActivityManager
IActivityManager 相当于 aidl接口
ActivityManagerService 相当与Stub和Proxy
IActivityManager.Stub 就相当于服务端,IActivityManager.Stub.asInterface就相当于服务端的代理或者就是自己本身。
bindIsolatedService方法,实现了绑定服务,个人感觉有点想dark中的Isolate
class ActivityManagerService
public int bindIsolatedService(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, IServiceConnection connection, int flags, String instanceName,
String callingPackage, int userId) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("bindService");
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (service != null && service.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
if (callingPackage == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("callingPackage cannot be null");
}
// Ensure that instanceName, which is caller provided, does not contain
// unusual characters.
if (instanceName != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < instanceName.length(); ++i) {
char c = instanceName.charAt(i);
if (!((c >= 'a' && c <= 'z') || (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z')
|| (c >= '0' && c <= '9') || c == '_' || c == '.')) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal instanceName");
}
}
}
synchronized(this) {
return mServices.bindServiceLocked(caller, token, service,
resolvedType, connection, flags, instanceName, callingPackage, userId);
}
}
调用了ActiveServices中的bindServiceLocked
class ActiveServices
int bindServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, IBinder token, Intent service,
String resolvedType, final IServiceConnection connection, int flags,
String instanceName, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException
在ActiveServices类中的bindServiceLocked方法,调用了bringUpServiceLocked
class ActiveServices
int bindServiceLocked
if ((flags&Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE) != 0) {
s.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
if (bringUpServiceLocked(s, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false,
permissionsReviewRequired) != null) {
return 0;
}
}
在ActiveServices类中的bringUpServiceLocked方法,再调用了bringUpServiceLocked
class ActiveServices
int bringUpServiceLocked
//应用启动了,APP已经创建了
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.longVersionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
bringUpServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortInstanceName, e);
}
// If a dead object exception was thrown -- fall through to
// restart the application.
}
public final class ActiveServices
int bringUpServiceLocked
// Not running -- get it started, and enqueue this service record
// to be executed when the app comes up.
////APP没有创建
if (app == null && !permissionsReviewRequired) {
if ((app=mAm.startProcessLocked(procName, r.appInfo, true, intentFlags,
hostingRecord, false, isolated, false)) == null) {
String msg = "Unable to launch app "
+ r.appInfo.packageName + "/"
+ r.appInfo.uid + " for service "
+ r.intent.getIntent() + ": process is bad";
Slog.w(TAG, msg);
bringDownServiceLocked(r);
return msg;
}
if (isolated) {
r.isolatedProc = app;
}
}
//调用一系列方法进行创建
class ActivityManagerService
final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked()
mProcessList.startProcessLocked()
//一直到下面得方法,创建进程
Process.start
bringUpServiceLocked的方法
class ActiveServices
/**
* Note the name of this method should not be confused with the started services concept.
* The "start" here means bring up the instance in the client, and this method is called
* from bindService() as well.
*/
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
//创建服务
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackage(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.getReportedProcState());
}
thread 是 IApplicationThread thread;
//是ActivityThread的内部类
private class ApplicationThread extends IApplicationThread.Stub
class ApplicationThread
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
class ActivityThread
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final ApplicationThread mAppThread = new ApplicationThread();
class ActivityThread
class H extends Handler
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, ("serviceCreate: " + String.valueOf(msg.obj)));
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
}
handleCreateService就是创建服务的方法。
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = packageInfo.getAppFactory()
.instantiateService(cl, data.info.name, data.intent);
通过类加载器创建服务。真正的服务创建出来。
mServices.put(data.token, service);
这里把服务放到ArrayMap
回到之前的方法总
public final class ActiveServices
int bindServiceLocked()
if (s.app != null && b.intent.received) {
// Service is already running, so we can immediately
// publish the connection.
try {
c.conn.connected(s.name, b.intent.binder, false);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failure sending service " + s.shortInstanceName
+ " to connection " + c.conn.asBinder()
+ " (in " + c.binding.client.processName + ")", e);
}
// If this is the first app connected back to this binding,
// and the service had previously asked to be told when
// rebound, then do so.
if (b.intent.apps.size() == 1 && b.intent.doRebind) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, true);
}
} else if (!b.intent.requested) {
requestServiceBindingLocked(s, b.intent, callerFg, false);
}
public final class ActiveServices
private final boolean requestServiceBindingLocked()
r.app.thread.scheduleBindService(r, i.intent.getIntent(), rebind,
r.app.getReportedProcState());
同样跑到
class ActivityThread
private class ApplicationThread extends IApplicationThread.Stub
public final void scheduleBindService(IBinder token, Intent intent,
boolean rebind, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
BindServiceData s = new BindServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.intent = intent;
s.rebind = rebind;
if (DEBUG_SERVICE)
Slog.v(TAG, "scheduleBindService token=" + token + " intent=" + intent + " uid="
+ Binder.getCallingUid() + " pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid());
sendMessage(H.BIND_SERVICE, s);
}
class ActivityThread
class H extends Handler
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
case BIND_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "serviceBind");
handleBindService((BindServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
}
private void handleBindService(BindServiceData data) {
IBinder binder = s.onBind(data.intent);
ActivityManager.getService().publishService(
data.token, data.intent, binder);
}
又跑到ActivityManagerService
class ActivityManagerService
public void publishService(IBinder token, Intent intent, IBinder service) {
// Refuse possible leaked file descriptors
if (intent != null && intent.hasFileDescriptors() == true) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("File descriptors passed in Intent");
}
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.publishServiceLocked((ServiceRecord)token, intent, service);
}
}
跳转到
class ActiveServices
void publishServiceLocked()
c.conn.connected(r.name, service, false);
相当与
override fun onServiceConnected(name: ComponentName?, service: IBinder?) {
mAidl = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service)
}
可以反推出
class ContextImpl
private boolean bindServiceCommon(
IServiceConnection sd;
sd = mPackageInfo.getServiceDispatcher(conn, getOuterContext(), executor, flags);
调用的是下面方法
class LoadedApk
public final IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcher(ServiceConnection c,
Context context, Executor executor, int flags) {
return getServiceDispatcherCommon(c, context, null, executor, flags);
}
private IServiceConnection getServiceDispatcherCommon(){
return sd.getIServiceConnection();
}
也就是返回了一个 private final ServiceDispatcher.InnerConnection mIServiceConnection;
class LoadedApk
private static class InnerConnection extends IServiceConnection.Stub {
@UnsupportedAppUsage
final WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher> mDispatcher;
InnerConnection(LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd) {
mDispatcher = new WeakReference<LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher>(sd);
}
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead)
throws RemoteException {
LoadedApk.ServiceDispatcher sd = mDispatcher.get();
if (sd != null) {
sd.connected(name, service, dead);
}
}
}
就相当于调用了InnerConnection的connected方法
class LoadedApk
public void connected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
if (mActivityExecutor != null) {
mActivityExecutor.execute(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else if (mActivityThread != null) {
mActivityThread.post(new RunConnection(name, service, 0, dead));
} else {
doConnected(name, service, dead);
}
}
public void doConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service, boolean dead) {
// If there was an old service, it is now disconnected.
if (old != null) {
mConnection.onServiceDisconnected(name);
}
if (dead) {
mConnection.onBindingDied(name);
}
// If there is a new viable service, it is now connected.
if (service != null) {
mConnection.onServiceConnected(name, service);
} else {
// The binding machinery worked, but the remote returned null from onBind().
mConnection.onNullBinding(name);
}
}
正好返回。
private val mServiceConnection = object : ServiceConnection {
override fun onServiceConnected(name: ComponentName?, service: IBinder?) {
mAidl = IMyAidlInterface.Stub.asInterface(service)
}
override fun onServiceDisconnected(name: ComponentName?) {
mAidl = null
}
}
总结
-
进程,整个进程都没有启动
-
进程启动了,但是里面的Service没创建出来
-
进程启动了,里面的Service也创建了,但是Service没有被绑定过,回调onBind()
-
进程启动了,里面的Service也创建了,但是Service已经被绑定过,回调onRebind()