ES maping 学习笔记
一Filed type(字段类型)
1. 核心数据类型:
String datatype
string
Numeric datatypes
long, integer, short, byte, double, float
Date datatype
date
默认format:"strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis"是或的关系
strict_date_optional_time 参考:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-date-format.html#strict-date-time
epoch_millis:milliseconds-since-the-epoch 如:"2015-01-01T12:10:30Z" 还可以是yyyy-MM-dd,yyyy-MM-dd mm:ss等等格式
例子:
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}}
Boolean datatype
boolean
接受json 值true或是false
false值:false,“false”,”off”,”no”,”0”,””,0,0.0
true值:除了false值以外的值 如1,true.......
Binary datatype
binary
只是一个Base64编码的字符串 this field is not stored by default,and not searchable
2.复杂数据类型
Array datatype
数组不需要是一个专门的类型
Arry 可以为空值null_value或者是直接跳过,
Object datatype
为单一json对象
Nested datatype
nested 为json对象数组
3.Geo 数据类型:
Geo-point datatype
geo_point for lat/lon points 接受经纬度对(latitude-longitude pairs)
在一个边界框内,离具体点的具体距离,多边形内,找geo_point
根据文档里中心节点的物理位置或是距离,聚集(aggregation)文档
根据距离对文档(document)排序
将距离整合为关联性得分(relevance score)
Geo-Shape datatype
geo_shape for complex shapes like polygons
4. 特殊数据类型
IPv4 datatype
ip for IPv4 addresses
Completion datatype
completion to provide auto-complete suggestions
Token count datatype
token_count to count the number of tokens in a string
mapper-murmur3
murmur3 to compute hashes of values at index-time and store them in the index
Attachment datatype
See the mapper-attachments plugin which supports indexing attachments like Microsoft Office formats, Open Document formats, ePub, HTML, etc. into an attachment datatype.
二 Meta-fields
1、_all:主要指的是All Field字段,我们可以将一个或都多个包含进不,在进行检索时无需指定字段的情况下检索多个字段。前提是你得开启All Field字段
"_all" : {"enabled" : true}
2、_source:
主要指的是Source Field字段Source可以理解为Es除了将数据保存在索引文件中,另外还有一分源数据。_source字段我在们进行检索时相当重要,如果在{"enabled" : false}情况下默认检索只会返回ID,你需通过Fields字段去倒索索引中去取数据,当然效率不是很高。如果觉得enabale:true时,索引的膨涨率比较大的情况下可以通过下面一些辅助设置进行优化:
不被indexed,该字段不能被search,被stored
Compress:是否进行压缩,建议一般情况下将其设为true
"includes" : ["author", "name"],
"excludes" : ["sex"]
上面的includes和 excludes主要是针对默认情况下面_source一般是保存全部Bulk过去的数据,我们可以通过include,excludes在字段级别上做出一些限索。
3._index
4._type
5._id
_id值可用于query(),但是不能用于aggregation,script,或是sorting,这些情况应该用_uid代替
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"text": "Document with ID 1"}
PUT my_index/my_type/2{
"text": "Document with ID 2"}
GET my_index/_search{
"query": {
"terms": {
"_id": [ "1", "2" ]
}
}}
6._uid 由_type和_id两个域的值构成,用#分隔
7._all
ElasticSearch默认为每个被索引的文档都定义了一个特殊的域 - '_all',它自动包含被索引文档中一个或者多个域中的内容,在进行搜索时,如果不指明要搜索的文档的域,ElasticSearch则会去搜索_all域。_all带来搜索方便,其代价是增加了系统在索引阶段对CPU和存储空间资源的开销。
默认情况,ElasticSarch自动使用_all所有的文档的域都会被加到_all中进行索引。可以使用"_all" : {"enabled":false} 开关禁用它。如果某个域不希望被加到_all中,可以使用"include_in_all":false
例如:
1.{
2. "person": {
3. "_all": { "enabled": true }
4. "properties": {
5. "name": {
6. "type": "object",
7. "dynamic": false,
8. "properties": {
9. "first": {
10. "type": "string",
11. "store": true,
12. "include_in_all": false
13. },
14. "last": {
15. "type": "string",
16. "index": "not_analyzed"
17. }
18. }
19. },
20. "address": {
21. "type": "object",
22. "include_in_all": false,
23. "properties": {
24. "first": {
25. "properties": {
26. "location": {
27. "type": "string",
28. "store": true,
29. "index_name": "firstLocation"
30. }
31. }
32. },
33. "last": {
34. "properties": {
35. "location": {
36. "type": "string"
37. }
38. }
39. }
40. }
41. },
42. "simple1": {
43. "type": "long",
44. "include_in_all": true
45. },
46. "simple2": {
47. "type": "long",
48. "include_in_all": false #---simple2 字段不包含在_all
49. }
50. }
51. }
52.} 查询时,_all和其它域一样使用:
1. GET /profiles/_search
2. {
3. "query": {
4. "match": {
5. "_all": "food"
6. }
7. }
8. }
或者在不提供搜索域的情况下,默认会搜索_all,例如:
1. GET /profiles/_search
2. {
3. "query": {
4. "query_string": {
5. "query": "food"
6. }
7. }
8. } 在head插件的混合查询中 选GET会查询所有document信息,query不起作用,用query要选POST
8._field_names
用来索引document中包含除了null以外其他任何值的字段名字
这个字段可用到exists和missing query中,用以查找document中含有或是不含non-null值得特殊字段
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"title": "This is a document"}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"title": "This is another document",
"body": "This document has a body"}
GET my_index/_search{
"query": {
"terms": {
"_field_names": [ "title" ]
}},
"aggs": {
"Field names": {
"terms": {
"field": "_field_names",
"size": 10
} }
},
"script_fields": {
"Field names": {
"script": "doc['_field_names']"
}
}}
VIEW IN SENSE
| Querying on the _field_names field (also see the exists and missing queries) |
| Aggregating on the _field_names field |
| Accessing the _field_names field in scripts (inline scripts must be enabled for this example to work) |
9._meta
10._parent
11._routing
12._timestamp
13._ttl
Document生存时间 ,超过就会自动删除document
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"_ttl": {
"enabled": true,
"default": "5m"
}
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1?ttl=10m {#--document 将在被索引后的十分钟后期满
"text": "Will expire in 10 minutes"}
PUT my_index/my_type/2 {#--没有ttl设定,应用默认的索引后5分钟期满
"text": "Will expire in 5 minutes"}
三. Mapping parameters
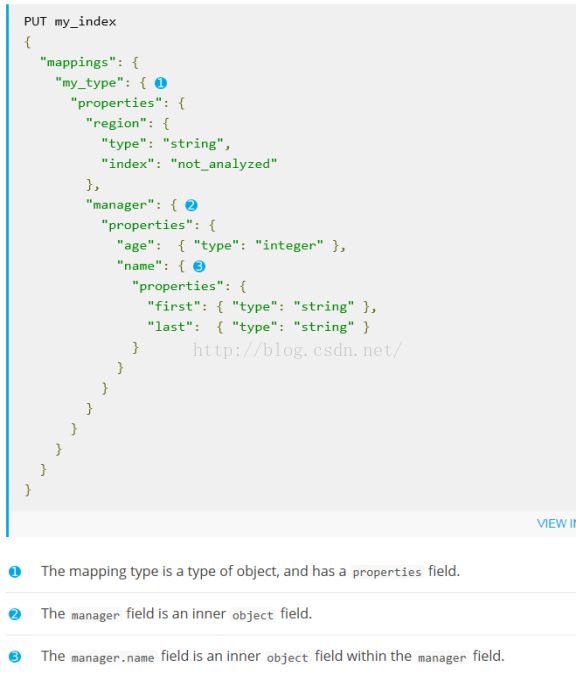
1.Properites
部分是最重要的部分主要是针对索引结构和字段级别上面的一些设置
"NAME": { //字段项名称对应lucene里面FiledName
"type": "string",//type为字段项类型
"analyzer": "keyword"//字段项分词的设置对应Lucene里面的Analyzer
},
2.Index
Index选项控制字段如何被索引和可被搜素,有三个值选项
· 如果是no,则无法通过检索查询到该字段(不被索引,不可查询);
· 如果设置为not_analyzed则会将整个字段存储为关键词,常用于汉字短语、邮箱等复杂的字符串;
除了string类型,是其他所有类型字段默认选项
· 如果设置为analyzed则将会通过默认的standard分析器进行分析,字符串首先转换为项,然后索引。在查询的时候,query会通过同样的analyzer转换成项格式进行匹配查询。
是string类型字段默认选项
UT /my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"status_code": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed" #--整个字段存储为关键词,不进行分词
}
}
}
}}
3.Store
定义了字段是否存储
在ES中原始的文本会存储在_source里面(除非你关闭了它)。默认情况下其他提取出来的字段都不是独立存储的,是从_source里面提取出来的。当然你也可以独立的存储某个字段,只要设置store:true即可。
独立存储某个字段,在频繁使用某个特殊字段时很常用。而且获取独立存储的字段要比从_source中解析快得多,而且额外你还需要从_source中解析出来这个字段,尤其是_source特别大的时候。
不过需要注意的是,独立存储的字段越多,那么索引就越大;索引越大,索引和检索的过程就会越慢....
在各种类型字段中store和index参数的使用
字符串类型,es中最常用的类型,官方文档
比较重要的参数:
index分析
· analyzed(默认)
· not_analyzed
· no
store存储
· true 独立存储
· false(默认)不存储,从_source中解析
numeric
数值类型,注意numeric并不是一个类型,它包括多种类型,比如:long,integer,short,byte,double,float,每种的存储空间都是不一样的,一般默认推荐integer和float。官方文档参考
重要的参数:
index分析
· not_analyzed(默认) ,设置为该值可以保证该字段能通过检索查询到
· no
store存储
· true 独立存储
· false(默认)不存储,从_source中解析
Date
日期类型,该类型可以接受一些常见的日期表达方式,官方文档参考。
重要的参数:
index分析
· not_analyzed(默认) ,设置为该值可以保证该字段能通过检索查询到
· no
store存储
· true 独立存储
· false(默认)不存储,从_source中解析
format格式化
· strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis(默认)
·
你也可以自定义格式化内容,比如
·
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format":"yyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss||yyyy-MM-dd||epoch_millis"
}
·
·
更多的时间表达式可以参考这里
IP
这个类型可以用来标识IPV4的地址,参考官方文档
常用参数:
index分析
· not_analyzed(默认) ,设置为该值可以保证该字段能通过检索查询到
· no
store存储
· true 独立存储
· false(默认)不存储,从_source中解析
Boolean
布尔类型,所有的类型都可以标识布尔类型,参考官方文档
· False: 表示该值的有:false, "false", "off", "no", "0", "" (empty string), 0, 0.0
· True: 所有非False的都是true
重要的参数:
index分析
· not_analyzed(默认) ,设置为该值可以保证该字段能通过检索查询到
· no
store存储
· true 独立存储
· false(默认)不存储,从_source中解析
4.analyzer
默认的全局analyzer, 默认的analyzer是标准analyzer,这个标准analyzer有三个filter:token filter, lowercase filter和stop token filter
默认字段都是被分析的,字母全转换为小写,忽略单个字母,按单词分词
5.copy_to
6.dynamic
是否可以动态添加新字段,有三个取值
true 新检测到的字段被添加到mapping(默认)自动添加到document或是object中
False 新检测到的字段被忽略,要么明确的加入
strict 检测到新字段就抛出异常,document被注入
可在mapping type层设置,或是内部object设置,内部object继承他们的父object或是mapping type设置,如下
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic": false, #--mapping type不自动添加新字段
"properties": {
"user": { #user继承mapping type dynamic:false
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "string"
},
"social_networks": { #social_networks覆盖mapping type,设 dynamic:true
"dynamic": true,
"properties": {}
}
}
}
}
}
}}
7.Ignore_above
字符串长度大于ignore_above设置的字段将不执行analyzer也不被index的。
主要用于not_analyzied的字符串字段,,通常用作filtering,aggregation ,sorting
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"message": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed",
"ignore_above": 20 #--1
}
}
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1 { #---2
"message": "Syntax error"}
PUT my_index/my_type/2 { #---3
"message": "Syntax error with some long stacktrace"
}
GET _search { #---4
"aggs": {
"messages": {
"terms": {
"field": "message"
}
}
}}
(1) 这个字段忽略所有长度超过 20 的字符串
(2) 这个文档会被成功索引
(3) 这个文档会被索引,但是 message 字段却不会被索引
(4) 搜索会返回这两个问答是哪个,但是只有第一个会出现在项的聚合中
8.Fields
Muti_fields通常用作将同一个字段用不同的索引方案,用作不同的目的
如,一个字符串字段可以索引为一个analyzed的字段用做全文搜索,作为一个not_analyzed字段用作聚合和排序
PUT /my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "string",
"fields": {
"raw": { #--1
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
}
}
}}
PUT /my_index/my_type/1{
"city": "New York"}
PUT /my_index/my_type/2{
"city": "York"}
GET /my_index/_search{
"query": {
"match": {
"city": "york" #--2
}
},
"sort": {
"city.raw": "asc" #--3排序
},
"aggs": {
"Cities": {
"terms": {
"field": "city.raw" #--4聚合
}
}
}}
1.city.raw字段是city字段的not_analyzed版本
2.Analyzed 的city字段用做全文搜索
3.4.city.raw字段是city字段可用作聚合和排序
用例二:用两种不同的方法分析同一个字段得到更好的关联性
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"text": { #---1
"type": "string",
"fields": {
"english": { #----2
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}
}
}
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1
{ "text": "quick brown fox" } #----3索引文档fox
PUT my_index/my_type/2
{ "text": "quick brown foxes" } #---4索引文档foxes
GET my_index/_search{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "quick brown foxes",
"fields": [ #--5查询text和text.english字段,结合评分
"text",
"text.english"
],
"type": "most_fields" #--6
}
}}
1.text 字段用标准的analyzed
2.Text.english用的English的analyzer
Text字段包含第一个文档的fox项(term)和第二个文档的foxes项
Text.english字段包含两个文档的fox项,因为英语里fox是foxes的根
More:
在搜索中,使用参数fields允许限制每一个查询命中项(查询结果 hit)返回的列(fields)。这个特性通常被用来优化大批量数据传输,当Elasticsearch查询结果中有大量返回列时,使其只返回相关的列。当然它听起来很简单(实际上它确实很简单),但是它却对性能有极大的影响,查询性能与返回文档的数量和每一个文档大小两个因素成反比。
考虑这样一种情况,当每一个文档的平均大小是20KB,那么每一次查询请求返回10个查询结果则是平均200KB的数据。如果每秒请求100次,那么我们就需要20M的带宽。作一个合理的假设,假如我们如果只返回有用的字段,可以降低文档大小到800字节,那么每一次请求大致就只返回8KB的数据量,每秒请求100次则只需要800KB的带宽。如果想要大规模使用, 那么保证返回结果尽可能小确实是非常重要且非常实用的。
默认情况下,开启的是_source字段,它包含的是解析后的文档内容,并会在每一次查询后返回。当我们并不是需要查找并解析文档所有的内容时,我们通过限制返回的字段(fields)可以节省宝贵的服务器CPU时间和磁盘IO。上面讲到的fields便足以实现这一点。如果我们需要同时返回源文档(document)和一些列(fields),我们可以使用参数_source过滤,后面将会介绍它的用法。
关于fields的另一个特性并不广为人知,它也可以用在查询元字段中(metadata-fields)。这里特指用它查询_ttl字段的值,它可以在毫秒级别返回查询结果,而不是查询原文档需要的时间。这确实是一个非常实用的技巧。
9.Format
在json文档中,日期的格式都是string类型,elasticsearch用一些提前定义好的格式来把这些字符串解析成时间格式类型。
· strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis(默认)
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"date": {
"type": "date",
"format": "yyyy-MM-dd"
}
}
}
}}
Built in format 语法:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/mapping-date-format.html#custom-date-formats
Custom format:
http://www.joda.org/joda-time/apidocs/org/joda/time/format/DateTimeFormat.html
10.doc_value
所有字段默认开启,是存磁盘上存储的数据结构,在document索引时建立。
支持几乎所有的数据类型,numeric, date, Boolean, binary, and geo-point这些字段以及not_analyzed的字符串可以设置Docvalues属性。一般不处理analyze的字符串字段。Docvalues在mapping重的每个字段属性中定义。
如果你确定不需要对一个字段进行排序,聚合,从脚本获取字段值,可以禁用doc value来节省磁盘空间。
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"properties": {
"status_code": { #--默认启用 字段存在磁盘上,而非内存中了,减少频繁内存读写(速度稍比内存稍微慢点)
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
},
"session_id": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed",
"doc_values": false #--禁用
}
}
}
}}
11. omit_norms
norms记录了索引中index-time boost信息,但是当你进行搜索时可能会比较耗费内存。omit_norms = true则是忽略掉域加权信息,这样在搜索的时候就不会处理索引时刻的加权信息了
12.Fielddata
当要进行排序,统计,脚本访问时,我们需要不同的数据访问模式,不仅要查询到文档还要能查到字段包含的项,用于analyzed的字段,设置后 排序,聚合(统计)脚本可用
大部分字段可以用到index-time 硬盘存储的doc_values参数实现上述字段接入模式,但analyzed的string字段不支持doc_values。
Analyzed的string字段可使用,fielddata实现,fielddata是第一次查询时产生的数据结构
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/fielddata.html
四.Index template
1._default_
一个默认的mapping,是任何新的mapping type的基本mapping
没有指定type,默认使用_default_ mapping,索引的type name将会是_default_
注:在logstash-out -elasticsearch 中document_type指定索引类型,若不设定值分两种情况
1.event 的type字段有值,则document_type=event type
2.event type没有指定,插件该属性有默认值,log 。
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"_default_": {
"_all": {
"enabled": false #--_default_ type _all禁用
}
},
"user": {}, #-- User type 继承_default_ mapping 设置,_all禁用
"blogpost": {
"_all": {
"enabled": true #--Blogpost type 覆盖_default_ mapping 设置,_all启用
}
}
}}
2. 动态字段匹配
默认情况下,当之前没有见过的字段出现在document时,es会将该字段自动添加到typemapping中,该行为是可以禁止的,在mapping type层或是内部object设dynamic为false。
会使用简单的规则,自动检测字段类型
| JSON datatype |
Elasticsearch datatype |
| null |
不添加字段 |
| True or false |
Boolean field |
| Floating point number 浮点数 |
Double field |
| integer |
Long field |
| object |
Object field |
| array |
取决于数组第一个不为空的值 |
| string |
可以是Date field(通过date detection),doubleor long field(通过了numerical detection),analyzed String |
其他类型需要明确的给出mapp
Date检测
date_detection设为开启(默认)设false,检测成字符串类型
这样string类型的字段将被检测是否匹配dynamic_date_formats指定的date模式,匹配上就添加一个新的date类型字段
dynamic_date_formats 默认值是:参考format参数格式语法
[ "strict_date_optional_time","yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss Z||yyyy/MM/dd Z"]
通常date检测各式:
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic_date_formats": ["MM/dd/yyyy"]
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"create_date": "09/25/2015"}
关闭时间检测:
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"date_detection": false
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1 {
"create": "2015/09/02"}
Create 字段已被添加为string类型
Numeric检测
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"numeric_detection": true
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"my_float": "1.0", #--被添加为double字段
"my_integer": "1" #被添加为long字段
}
3.Dynamic template
动态模板允许你为动态添加的字段定义一个映射,基于以下:
l the datatype detected by Elasticsearch, with match_mapping_type.
l the name of the field, with match and unmatch or match_pattern.
l the full dotted pathto the field, with path_match and path_unmatch.
在字段有确定值的时候回调用mapping配置
动态模板:
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"my_template_name": { # 1.template name随便取得一个名字
... match conditions ... 2.
"mapping": { ... } 3.
}
},
...
]
1. template name 可以是任何字符串值
2. Match条件可以包含: match_mapping_type, match, match_pattern, unmatch, path_match, path_unmatch
3. mapping 是匹配的字段要用到的
match_mapping_type参数
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"integers": {
"match_mapping_type": "long", #datatype检测进行动态匹配
"mapping": {
"type": "integer"
}
}
},
{
"strings": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "string",
"fields": {
"raw": {
"type": "string",
"index": "not_analyzed",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"my_integer": 5,
"my_string": "Some string" }
My_integer字段映射成一个integer
My_String 字段映射成一个 analyzed string,和一个 not_analyzed multi field
Match unmatch用以匹配字段的名字
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"longs_as_strings": { #匹配所有以long_开头的String类型(除了以_text结尾的)字段,并且map成long类型
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"match": "long_*",
"unmatch": "*_text",
"mapping": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
]
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"long_num": "5", #is mapped as a long
"long_text": "foo" #用到default String mapping
}
Match_pattern
用以调整match参数的行为,match可用Java正则表达式作为匹配模式
"match_pattern": "regex",
"match": "^profit_\d+$"
Path_match 和path_unmatch
作用与match和unmatched类似,作用在字段的全点路径,而不仅仅是最终一层的名字
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"full_name": {
"path_match": "name.*", #--匹配字段的顶级名是name的字段
"path_unmatch": "*.middle", #--最终名是middle的字段除外
"mapping": {
"type": "string",
"copy_to": "full_name"
}
}
}
]
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"name": {
"first": "Alice",
"middle": "Mary",
"last": "White"
}}
匹配到name.first,name.last两个字段
{name}和 {dynamic_type}
是占位符,用字段名和动态匹配类型代替mapping
PUT my_index{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"named_analyzers": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",#--匹配为String类型的Json字段
"match": "*", #--匹配任意字段名
"mapping": {
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "{name}" #--annlyzer 为匹配到的字段名
}
}
},
{
"no_doc_values": {
"match_mapping_type":"*", #--按mapping type顺序匹配,行一个匹配字符串类,此处匹配除了String以外的类型的字段
"mapping": {
"type": "{dynamic_type}", #--映射为自动映射到的类型
"doc_values": false }
} }
]
}
}}
PUT my_index/my_type/1{
"english": "Some English text", #--映射为string类型,analyzer:English
"count": 5 #--映射为long(自动映射)类型
}
4.覆盖默认模板
PUT _template/disable_all_field{
"disable_all_field": {
"order": 0, #--1
"template": "*", #--匹配索引名,*也就是所有的索引名都可引用这个mapping
"mappings": {
"_default_": { ##--定义默认type模板
"_all": {
"enabled": false ##--关闭_all
}
}
}
}}
1.order参数功能,默认值为0,就是elasticsearch 在创建一个索引的时候,如果发现这个索引同时匹配上了多个 template ,那么就会先应用 order 数值小的 template 设置,然后再应用一遍 order 数值高的作为覆盖,最终达到一个 merge 的效果。
{
"order": 1,
"template": "logstash-*",
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 10
}
}
覆盖order=0的logstash-*名模板,将setting的分片数改为10