leetcode 1-100 medium难度题目汇总
写在前面
近半个月的整理, 终于完成了前一百题的easy和medium题目的分析 ? 秋招已经开始了, 祝自己好运 ? 以后有空逐渐把hard补上 ?
文章目录
- 2. Add Two Numbers (Medium)
- 3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters (Medium)
- 5. Longest Palindromic Substring (Medium)
- 6. ZigZag Conversion (Medium)
- 8. String to Integer (atoi) (Medium)
- 11. Container With Most Water (Medium)
- 12. Integer to Roman (Medium)
- 15. 3Sum (Medium) **
- 16. 3Sum Closest (Medium)
- 17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number (Medium)
- 18. 4Sum (Medium)
- 19. Remove Nth Node From End of List (Medium)
- 22. Generate Parentheses (Medium)
- 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs (Medium)
- 29. Divide Two Integers (Medium) X
- 31. Next Permutation (Medium)
- 33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array (Medium)
- 81. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II (Medium)
- 34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array (Medium)
- 36. Valid Sudoku (Medium)
- 39. Combination Sum (Medium)
- 40. Combination Sum II (Medium)
- 42. Trapping Rain Water (Hard)
- 43. Multiply Strings (Medium)
- 46. Permutations (Medium)
- 47. Permutations II (Medium)
- 48. Rotate Image (Medium)
- 49. Group Anagrams (Medium)
- 54. Spiral Matrix (Medium)
- 59. Spiral Matrix II (Medium)
- 55. Jump Game (Medium)
- 56. Merge Intervals (Medium)
- 60. Permutation Sequence (Medium)
- 61. Rotate List (Medium)
- 62. Unique Paths (Medium)
- 63. Unique Paths II (Medium)
- 64. Minimum Path Sum (Medium)
- 71. Simplify Path (Medium)
- 73. Set Matrix Zeroes (Medium)
- 74. Search a 2D Matrix (Medium)
- 77. Combinations (Medium)
- 78. Subsets (Medium)
- 90. Subsets II (Medium)
- 79. Word Search (Medium)
- 80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II (Medium)
- 82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II (Medium)
- 86. Partition List (Medium)
- 89. Gray Code (Medium)
- 91. Decode Ways (Medium) **
- 92. Reverse Linked List II (Medium)
- 93. Restore IP Addresses (Medium)
- 94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Medium)
- 96. Unique Binary Search Trees (Medium)
- 95. Unique Binary Search Trees II (Medium)
- 98. Validate Binary Search Tree (Medium)
2. Add Two Numbers (Medium)
题目描述
给两个链表, 做加法
Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
解题思路
"""
类似于合并两个链表
1. 依顺序把l2的元素加到l1中
2. 当一个链表已经加完, 接下来做的就是把进位和剩下的链表加和
3. 当两个链表长度相等, 要判断最后一个节点值是否大于10, 可能产生进位值
4. 当遍历完所有节点后, 如果仍有进位值, 则加入一个新节点
"""
class Solution:
def addTwoNumbers(self, l1: ListNode, l2: ListNode) -> ListNode:
head = l1
carry = 0
while l1 or l2:
if l1 and l2:
s = l1.val + l2.val + carry
l1.val = s%10
carry = s//10
last = l1 # 如果l1为空, 把最后一个node指l2
l1 = l1.next
l2 = l2.next
elif l1: # l1比l2长
s = l1.val + carry # 补全进位
l1.val = s%10
carry = s//10
if carry == 0: # 如果不再有进位, 提前终止加和.
break
last = l1
l1 = l1.next
elif l2: # l1比l2短
last.next = l2
s = l2.val + carry
l2.val = s%10
carry = s//10
if carry == 0:
break
last = l2
l2 = l2.next
if last.val >= 10:
last.val = last.val % 10
carry = 1
if carry: #如果carry有值需要加入一个新节点.
last.next = ListNode(1)
return head
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/
题目描述
给一个字符串, 返回最长的没有重复元素的子串.
Input: "abcabcbb"
Output: 3
Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3.
解题思路
"""
设置一个滑动窗口.
每次右边界滑动一个位置, check左边界是否会重复, 如果重复了, 左边界向右滑动, 直到左边界的字符不等于右边界位置上的字符未知.
每次移动结束后, check当前窗口长度.
"""
class Solution:
def lengthOfLongestSubstring(self, s: str) -> int:
if s == '':
return 0
start = end = result = 0
while end < len(s):
if s[end] not in s[start:end]:
end += 1
result = max(result, end-start)
else:
start = start + s[start:end].find(s[end]) + 1 #return the index of s[end] in s[start:end]
end += 1
return result
5. Longest Palindromic Substring (Medium)
题目描述
给一个字符串, 找到最长的回文子字符串.
Input: "babad"
Output: "bab"
Note: "aba" is also a valid answer.
解题思路
"""
遍历所有节点.
1. 从当前节点, 向两边遍历, 直到元素不相等为止. 得到一个回文字符串.
2. check当前回文字符串
注意原字符串的奇偶长度
"""
class Solution:
def longestPalindrome(self, s: str) -> str:
Max = 0
longest = ''
for i in range(len(s)):
#odd case, like'aba'
subStr = self.helper(s, i, i)
if len(subStr) >= Max:
Max = len(subStr)
longest = subStr
#even case, like'abba'
subStr = self.helper(s, i, i+1)
if len(subStr) >= Max:
Max = len(subStr)
longest = subStr
return longest
def helper(self, s, start, end):
subStr = ''
while start >= 0 and end <len(s) and s[start] == s[end]:
subStr = s[start:end+1]
start -= 1
end += 1
return subStr
6. ZigZag Conversion (Medium)
题目描述
字符串 “PAYPALISHIRING"以Z形走法书写, 逐行输出结果为"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR”
P A H N
A P L S I I G
Y I R
设计转换函数.
解题思路
# 倒着的Z字拼接在一起,先找组成Z字的规律
'''
(* *) 虽然是z型看起来复杂,其实简单,走势符合直下斜上的顺序
* * * 创建五个存储空间来保存每次走过的字母即可。
* * *
* * *
* *
'''
class Solution:
def convert(self, s: str, numRows: int) -> str:
# 特殊情况,字符只够摆第一竖列
if numRows == 1 or numRows >= len(s):
return s
L = [''] * numRows
index = 0
# step往下走,当step=-1即回头,往上走
for x in s:
L[index] += x
if index == 0: step = 1
if index == numRows - 1: step = -1
index += step
return ''.join(L)
8. String to Integer (atoi) (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi/
题目描述
解题思路
class Solution:
def myAtoi(self, s: str) -> int:
if s == '':
return 0
# 将字符串去掉空格保存在列表中,只要研究列表第一个元素即可
s2 = s.strip().split(' ')[0]
# 仍然需要判断一次,不然报错
if s2 == '':
return 0
flag = 1
num = {'1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','0'}
#保存符号
if s2[0] == '-':
flag = -1
s2 = s2[1:]
elif s2[0] == '+':
s2 = s2[1:]
# 临界判断, 太重要了!单独一个字符'+'或'-'
if s2 == '':
return 0
# 首字符是字母返回0
if s2[0] not in num:
return 0
# 后面如果跟字母要想办法去掉
for i in s2:
if i not in num:
index = s2.index(i)
s2 = s2[:index]
break
s2 = flag * int(s2)
if s2 > 2**31 - 1:
return 2**31 - 1
elif s2 < -(2**31):
return -(2**31)
return s2
11. Container With Most Water (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/container-with-most-water/
题目描述
给一个数组, 每个数字代表隔板长度, 确定能容纳水的最大体积.
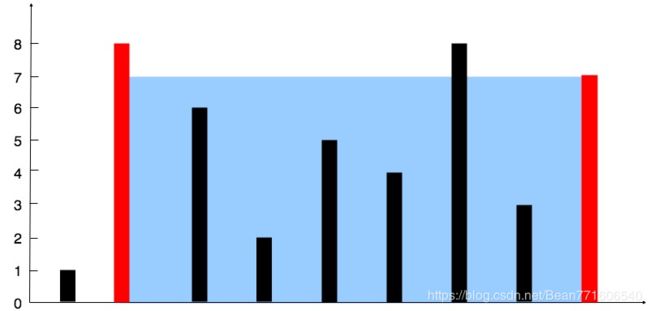
Input: [1,8,6,2,5,4,8,3,7]
Output: 49
解题思路
"""
短的隔板决定容器的高度.
设置两个指针, 分别从头尾向中间移动.
1.如果头指针大于尾指针, 则尾指针向头部移动.
2.如果头指针小于尾指针, 则头指针向尾部移动.
3.每次移动完, check当前容积.
"""
class Solution:
def maxArea(self, height: List[int]) -> int:
result = 0
start = 0
end = len(height)-1
while start < end:
result = max(result, min(height[start], height[end]) * (end - start))
#将两条线往对方方向走。
if height[start] < height[end]:
start += 1
else:
end -= 1
return result
12. Integer to Roman (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/integer-to-roman/
题目描述
把罗马数字转换成十进制数字.
解题思路
class Solution:
def intToRoman(self, num: int) -> str:
value_roman = {1000:"M", 900:"CM", 500:"D", 400:"CD",
100:"C", 90:"XC", 50:"L", 40:"XL",
10:"X", 9:"IX", 5:"V", 4:"IV", 1:"I"}
roman = ""
for v in [1000,900,500,400,100,90,50,40,10,9,5,4,1]:
roman += value_roman[v] * (num//v)
num %= v
return roman
15. 3Sum (Medium) **
https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum/
题目描述
给定一个数组, 找到有所能使得和为0的组合. 组合不能重复.
Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
A solution set is:
[ [-1, 0, 1], [-1, -1, 2] ]
解题思路
"""
动态规划
先将数组排序.
从头开始逐个元素遍历, 位置为i, 左指针指向i+1, 右指针指向tail.
当 左指针 < 右指针 时:
1. 加和三个指针指向的值.
2. 和大于0, 说明和需要减小, 右指针左移一个位置(因为数组有序, 右边数大于左边)
3. 和小于0, 说明和需要增大. 左指针右移一个位置
4. 当和等于0时, 继续移动左右指针去掉与当前值相同的元素
"""
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
if len(nums) <3: # deal with special input
return []
elif len(nums) == 3:
if sum(nums) == 0:
return [sorted(nums)]
res = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
if i > 0 and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
l, r = i+1, len(nums)-1
while l < r:
s = nums[i] + nums[l] + nums[r]
if s < 0:
l +=1
elif s > 0:
r -= 1
else:
res.append((nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]))
while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]:
l += 1
while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]:
r -= 1
l += 1; r -= 1
return res
16. 3Sum Closest (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum-closest/
题目描述
同上一题, 只是给定一个target, 找出同target最接近的值.
解题思路
"""
同上一题, 三个指针.
"""
class Solution:
def threeSumClosest(self, nums, target):
nums.sort()
res = sum(nums[:3])
for i in range(len(nums)):
l, r = i+1, len(nums)-1
while l < r:
s = sum((nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]))
if abs(s-target) < abs(res-target):
res = s
if s < target:
l += 1
elif s > target:
r -= 1
else: # break early
return res
return res
17. Letter Combinations of a Phone Number (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/
题目描述

输入数字字符串, 输出可能的字母组合. (九宫格按键)
Input: "23"
Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
解题思路
递归
"""
"""
class Solution:
def letterCombinations(self, digits: str) -> List[str]:
if digits == "":
return []
mapp = {'2': 'abc',
'3': 'def',
'4': 'ghi',
'5': 'jkl',
'6': 'mno',
'7': 'pqrs',
'8': 'tuv',
'9': 'wxyz'}
res = []
self.combinate(digits, mapp, 0, len(digits), '', res)
return res
def combinate(self, s, mapp, n, m, path, res):
if n == m:
res.append(path)
return
for i in mapp[s[n]]:
self.combinate(s, mapp, n+1, m, path+i, res)
非递归做法
class Solution:
def letterCombinations(self, digits: str) -> List[str]:
pad = {
'2': 'abc',
'3': 'def',
'4': 'ghi',
'5': 'jkl',
'6': 'mno',
'7': 'pqrs',
'8': 'tuv',
'9': 'wxyz'
}
if not digits:
return []
output = ['']
for digit in digits:
temp = output
output = []
for s in temp:
output.extend([s + pad[digit][0], s + pad[digit][1], s+ pad[digit][2]])
if digit == '7' or digit == '9':
output.append(s + pad[digit][3])
return output
18. 4Sum (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/4sum/
题目描述
同3Sum, 只是改为四个数和为0.
解题思路
"""
3Sum的拓展
在4Sum中将0-当前数作为target传入3Sum函数
"""
class Solution:
def fourSum(self, nums, target):
results = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)-3):
if i == 0 or nums[i] != nums[i-1]:
threeResult = self.threeSum(nums[i+1:], target-nums[i])
for item in threeResult:
results.append([nums[i]] + item)
return results
def threeSum(self, nums, target):
results = []
nums.sort()
for i in range(len(nums)-2):
l = i + 1; r = len(nums) - 1
t = target - nums[i]
if i == 0 or nums[i] != nums[i-1]:
while l < r:
s = nums[l] + nums[r]
if s == t:
results.append([nums[i], nums[l], nums[r]])
while l < r and nums[l] == nums[l+1]: l += 1
while l < r and nums[r] == nums[r-1]: r -= 1
l += 1; r -=1
elif s < t:
l += 1
else:
r -= 1
return results
==
19. Remove Nth Node From End of List (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/
题目描述
Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
解题思路
"""
创建一前一后两个指针, 可以解决需要求倒数的节点.
"""
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: ListNode, n: int) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
fast, slow = dummy, dummy
for i in range(n+1):
fast = fast.next
while fast:
fast, slow = fast.next, slow.next
slow.next = slow.next.next
return dummy.next
22. Generate Parentheses (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/generate-parentheses/
题目描述
给定n对括号, 输出所有可能的合法的组合.
For example, given n = 3, a solution set is:
[
"((()))",
"(()())",
"(())()",
"()(())",
"()()()"
]
解题思路
递归
class Solution:
def generateParenthesis(self, n: int) -> List[str]:
combos = []
left = n
right = n
path = ''
self.formParen(left,right,path,combos)
return combos
def formParen(self,left,right,path,combos):
# 左右括号同时用完, 将当前生成的path加入combos.
if left == 0 and right == 0:
combos.append(path)
# 当左括号用完, 补齐所有右括号.
elif left == 0:
combos.append(path+')'*right)
# 前面的左右括号成对, 只能使用左括号.
elif right == left:
self.formParen(left-1,right,path+'(',combos)
#
else:
self.formParen(left-1,right,path+'(',combos)
self.formParen(left,right-1,path+')',combos)
24. Swap Nodes in Pairs (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs/
题目描述
Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
解题思路
"""
需要熟悉指针指向什么.
last p1 p2
移动前: dummy -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> None
last p1 p2
移动后: dummy(last) -> 2(p2) -> 1(p1) -> 3 -> 4 -> None
(括号里表示指针上一次的位置)
每次操作需要移动三个指针, temp是原先p2指向内容, p2指向p1, p1指向temp, last指向p2
每次移动完节点, 需要更新p1, p2, last
"""
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
if head == None:
return
if head.next == None:
return head
cur1, cur2 = head, head.next
dummy = ListNode(0)
last = dummy
last.next = cur1
while cur1:
temp = cur2.next
cur2.next = cur1
cur1.next = temp
last.next = cur2
last = cur1
cur1 = cur1.next
if not cur1 or not cur1.next:
break
else:
cur2 = cur1.next
return dummy.next
29. Divide Two Integers (Medium) X
https://leetcode.com/problems/divide-two-integers/
题目描述
两数相除, 不能使用乘法, 除法, 取模.
解题思路
31. Next Permutation (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/next-permutation/
题目描述

下一个排列, 就是介于当前数和下一个数之间不能有其他介于两者之间的数.
解题思路
"""
原排列: 7 8 6 9 8 7 2
下一个: 7 8 7 2 6 8 9
两种排列间找不到介于两数的排列.
假设数组大小为 n
1.从后往前, 找到第一个A[i-1] < A[i]的. 也就是第一个排列中的6那个位置,可以看到A[i]到A[tail]这些都是单调递减序列.
2.在A[i:tail]中找到比A[i-1]大的值中最小的一个. 比如[9 8 7 2]中的7.
3.交换这两个值, 并且把A[i:tail]排序, 从小到大.
"""
class Solution:
def nextPermutation(self, nums: List[int]) -> None:
for i in range(len(nums)-1, 0, -1):
if nums[i] > nums[i-1]:
nums[i:] = sorted(nums[i:])
for j in range(i, len(nums)):
if nums[j] > nums[i-1]:
temp = nums[j]
nums[j] = nums[i-1]
nums[i-1] = temp
return
nums.sort()
33. Search in Rotated Sorted Array (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/
题目描述
一个不重复的递增数组在某个位置旋转, 给定一个数, 返回它的索引值.
要求时间复杂度O(logn).
Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
Output: 4
解题思路
"""
二分查找找到最小值. 最小值处就是旋转点. 得到一个偏移值offset.
重新使用二分查找. 每次mid需要加上offset矫正得到realMid, 将它与target比较.
"""
class Solution:
def search(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> int:
left, right = 0, len(nums)-1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right)//2
if nums[mid] > nums[right]: left = mid + 1
else: right = mid
# when finish the while, we get left == right
offset = left
left, right = 0, len(nums)-1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right)//2
realMid = (mid + offset)%len(nums)
if nums[realMid] == target:
return realMid
if nums[realMid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid - 1
return -1
81. Search in Rotated Sorted Array II (Medium)
https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array-ii/
题目描述
30题的拓展, 数组可能存在重复数字.
解题思路
思路转自: 详细思路及与Search in Rotated Sorted Array I 的区别(python code)
这道题与“搜索旋转排序数组 I”比,不同之处在于判断中间位置mid时需作预处理:
while low < high and nums[low] == nums[high]:
low += 1
这也导致算法的最坏时间复杂度变为O(n)。整体还是基于二分查找
同时,我在I的基础优化了分类的方式:首先判断mid位置(属于高区还是低区)、进一步判断target位置是否在一个特定范围(所谓特定范围是指类似于正常排序的可二分查找的范围)直接分成四类。
python知识点: 2 代码: https://leetcode.com/problems/find-first-and-last-position-of-element-in-sorted-array/ 给定一个递增序列, 找到给定target的起始和终止位置(target重复且连续).不存在返回[-1, -1]. 要求时间复杂度O(logN) 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-sudoku/ 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum/ 给一个集合, 找出所有和为target的组合. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/combination-sum-ii/ 给一个数组, 找出所有和为target的组合. 解题思路 利用栈来实现,每次比较current bar与栈顶的bar的大小,如果小于栈顶,则新bar入栈,否则计算current bar与栈顶bar的储水量,然后栈顶出栈,重复比较的操作直到current bar小于栈顶或者栈空,此时current bar入栈。当没有新的current bar的时候结束。 https://leetcode.com/problems/multiply-strings/ 两个字符串相乘, 结果也输出字符串 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations/ 给定一个数组, 输出所有可能的排列. 数组中不存在重复字符. 解题思路 非递归 https://leetcode.com/problems/permutations-ii/ 非递归 https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-image/ 给一个n*n矩阵, 输出顺时针旋转90度后的矩阵. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/group-anagrams/ 给一个包含字符串的数组, group所有含有相同字母的字符串. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix/ 给一个mxn数组, 螺旋输出. 解题思路 注意点: https://leetcode.com/problems/spiral-matrix-ii/ 输入n, 输出对应的 N*N 螺旋数组. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/jump-game/ https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-intervals/ 类似题目 https://blog.csdn.net/bigtree_3721/article/details/89911532 题目描述 给一个包含区间的collection, 合并所有重复的区间. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/permutation-sequence/ 解题思路 From 21/6 = 3…3, we know that the 21th element is the 3rd element in the (3+1)th group. In this group, we can divide it into 3 sub-groups again: “41xx”, “42xx” and “43xx”, and each group has 2!=2 members. Then, we calculate 3/2 and get 1…1, so it’s the 1st element of (1+1)nd sub-group - “421x”, and now it reach the base case with only one possibility - “4213”. Anyone pass the problem with different ideas? https://leetcode.com/problems/rotate-list/ Given a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places, where k is non-negative. Example 1: 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-paths/ 给定一个 m*n 的棋盘, 机器人只允许走右和下, 请问到终点有几种方法 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-paths-ii/ 给定一个 m*n 的棋盘, 其中某个位置有一个障碍物, 机器人只允许走右和下, 请问到终点有几种方法. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/ 有点类似机器人走棋盘, 给定一个 m*n 的棋盘, 从左上走到右下, 求出总和最小的路径. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/simplify-path/ 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/set-matrix-zeroes/ 给一个 m*n 矩阵, 如果它某个位置是0, 则把其所在行和列全部置位0. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/ 在一个有序二维数组里寻找target. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/combinations/ 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets/ 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/subsets-ii/ 同上一题, 只是给的数组中可能存在重复元素. 解题思路 方法二: 用DFS来做. https://leetcode.com/problems/word-search/ https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array-ii/ 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/ 删除一个有序链表中所有重复的节点. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/partition-list/ https://leetcode.com/problems/gray-code/ 给定n, 从0000开始, 只有某个位置变化得到新的二进制数. 求所有能得到的二进制数. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/decode-ways/ 类似问题 62. Unique Paths 可以放在一起练习一下. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/ 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/restore-ip-addresses/ 输入一个数字字符串, 输出所有可能的有效IP. 解题思路 首先来看下 有效的ip定义是什么: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/ 用迭代的方式中序遍历数组. 左 -> 中 -> 右 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees/ 输入n, 输出由n个数构成的所有可能构成的二叉查找树的个数 解题思路 拿输入4的情况来解释, 当我们取根节点为1时, 右边可放三个数, 又由当输入为3时, 我们知道有5种排列情况, 因此得到当根节点取1, 有5中排列. 当取根节点为2时, 左边能放1个数, 有一种排列, 右边放2个数, 有两种排列. 结果是 1 x 2 = 2, 因此当根节点取2时, 有两种排列. 因此得到状态转移方程是: https://leetcode.com/problems/unique-binary-search-trees-ii/ 输入n, 输出由n个数构成的所有可能构成的二叉查找树的集合. 解题思路 https://leetcode.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/ 判断一个树是否是二叉搜索树. 解题思路 1.递归方法: 2.迭代方法:class Solution:
def search(self, nums, target):
if not nums:
return False
low = 0
high = len(nums) - 1
while low <= high:
while low < high and nums[low] == nums[high]:#这样的目的是为了能准确判断mid位置,所以算法的最坏时间复杂度为O(n)
low += 1
mid = (low+high)//2
if target == nums[mid]:
return True
elif nums[mid] >= nums[low]: #高区
if nums[low] <= target < nums[mid]:
high = mid - 1
else:
low = mid + 1
elif nums[mid] <= nums[high]: #低区
if nums[mid] < target <= nums[high]:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return False
34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array (Medium)
题目描述Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8
Output: [3,4]
"""
开始位和终止位都使用二分查找. 这里注意mid = right, 当nums[mid] = nums[right]时候, 最后输出位置就是right, right保持不变.
第一次查找找到target第一次出现的位置.
第二次查找, 查找target+1, 得到的end有两种情况
target = 1
1. [0,1,1] target+1位置不存在, 得到的是最后一个位置2
2. [0,1,1,3] target+1位置不存在, 但是最后1下一位存在且大于1, 此时会返回位置2
3. [0,1,1,2] target+1位置存在, 返回3
"""
class Solution:
def searchRange(self, nums: List[int], target: int) -> List[int]:
start = self.binarySearch(nums, target)
if start == len(nums) or nums[start] != target:
return [-1,-1]
end = self.binarySearch(nums,target+1)
if nums[end] > nums[start]:
end -= 1
return [start, end]
def binarySearch(self, nums, target):
left, right = 0, len(nums)-1
while left < right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
if nums[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
else:
right = mid
return left
36. Valid Sudoku (Medium)
题目描述

Input:
[
["5","3",".",".","7",".",".",".","."],
["6",".",".","1","9","5",".",".","."],
[".","9","8",".",".",".",".","6","."],
["8",".",".",".","6",".",".",".","3"],
["4",".",".","8",".","3",".",".","1"],
["7",".",".",".","2",".",".",".","6"],
[".","6",".",".",".",".","2","8","."],
[".",".",".","4","1","9",".",".","5"],
[".",".",".",".","8",".",".","7","9"]
]
Output: true
"""
有效的数独要求有三点:
1. 每行包含1-9且不重复: row = set()
2. 每列包含1-9且不重复: col = set()
3. 每个3*3 cube 包含1-9且不重复 cube = set()
每次遇到数字, 把(cur, i)存进row, (j, cur)存进col, (i//3, j//3, cur)存进cube
一个3*3九宫格每小格的location//3得到的值都是一样的, 因此可以借此得到"九宫格坐标", 在该坐标内不能存在重复的数.
"""
class Solution:
def isValidSudoku(self, board: List[List[str]]) -> bool:
row = set()
col = set()
cube = set()
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
if board[i][j] != '.':
cur = board[i][j]
if (i, cur) in row or (cur, j) in col or (i//3, j//3, cur) in cube: #i//3,j//3这样所有3X3方块都能有独自的坐标。remember!
return False
row.add((i, cur))
col.add((cur, j))
cube.add((i//3, j//3, cur))
return True
39. Combination Sum (Medium)
题目描述
ps.所有数都是正数且不重复Input: candidates = [2,3,6,7], target = 7,
A solution set is:
[
[7],
[2,2,3]
]
递归"""
递归思想
每次传入helper的tar值都在减少,当为0的时候,把一路过来的path放入res
"""
class Solution:
def combinationSum(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
self.helper(candidates, target, [], res)
return res
def helper(self, candi, tar, path, res):
if tar == 0:
# 防止重复
if sorted(path) not in res:
res.append(sorted(path))
return
# 加和结果小于0, path无效
if tar < 0:
return
for i in candi:
self.helper(candi, tar-i, path+[i], res)
40. Combination Sum II (Medium)
题目描述
ps.所有数都是正数且不重复Input: candidates = [10,1,2,7,6,1,5], target = 8,
A solution set is:
[
[1, 7],
[1, 2, 5],
[2, 6],
[1, 1, 6]
]
class Solution:
def combinationSum2(self, candidates: List[int], target: int) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
self.helper(candidates, target, [], res)
return res
def helper(self, candi, tar, path, res):
if tar == 0:
# 防止重复
if sorted(path) not in res:
res.append(sorted(path))
return
# 加和结果小于0, path无效
if tar < 0:
return
for i in range(len(candi)):
# 节约运行时间, 如果candidate中的元素大于当前剩的target, 则直接不考虑
if candi[i] > tar:
continue
self.helper(candi[:i]+candi[i+1:], tar-candi[i], path+[candi[i]], res)
42. Trapping Rain Water (Hard)
算法如下:
https://leetcode.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/class Solution:
def trap(self, height) -> int:
ans = 0
cur = 0
stack = [] #(1)
while cur < len(height): #(2)
while stack and height[cur] > height[stack[-1]]:#(2.1)
top = stack.pop() #(2.1.1)
if(not stack):
break
distance = cur - stack[-1] - 1 #(2.1.2)
high = min(height[cur], height[stack[-1]])-height[top] #(2.1.3)
ans += (distance * high) #(2.1.4)
stack.append(cur) #(2.2)
cur += 1 #(2.3)
return ans
43. Multiply Strings (Medium)
题目描述Input: num1 = "2", num2 = "3"
Output: "6"
""
使用内置函数很快但是面试不建议.
使用最基本的竖式乘法计算.
""
class Solution {
public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
int len1 = num1.length(), len2 = num2.length();
int carry = 0;
int[] pos = new int[len1 + len2];
// num1在下, num2在上
for(int i=len1-1; i >= 0; i--){
for(int j=len2-1; j>=0; j--){
int mul = (num1.charAt(i) - '0') * (num2.charAt(j) - '0');
int p1 = i + j, p2 = i + j + 1;
int sum = mul + pos[p2];
pos[p2] = sum % 10; // 个位数位置
pos[p1] += sum / 10;
}
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for(int p : pos)
if(!(sb.length() == 0 && p == 0))
sb.append(p);
return sb.length() == 0 ? "0" : sb.toString();
}
}
46. Permutations (Medium)
题目描述Input: [1,1,2]
Output:
[
[1,1,2],
[1,2,1],
[2,1,1]
]
方法一: 递归class Solution:
def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
self.merge(nums, [], res)
return res
def merge(self, nums, path, res):
if nums == []:
if path not in res:
res.append(path)
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
# 去掉位置i的数, 添加进path
self.merge(nums[:i]+nums[i+1:], path+[nums[i]], res)
class Solution:
def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = [[]]
#
for n in nums:
new_ans = []
# 取出ans中每个list, 在每个list的所有可插入位置插入n
for arr in ans:
# 对于ans中每个arr, 都有len(arr)+1个位置可以填入n
# 当len(arr)==0时, 只有一个位置. 即得到[n].
for i in range(len(arr)+1):
new_ans.append(arr[:i]+[n]+arr[i:])
ans = new_ans
return ans
47. Permutations II (Medium)
方法一: 递归class Solution:
def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
res = []
self.merge(nums, [], res)
return res
def merge(self, nums, path, res):
if nums == []:
if path not in res:
res.append(path)
return
for i in range(len(nums)):
# 去掉位置i的数, 添加进path
self.merge(nums[:i]+nums[i+1:], path+[nums[i]], res)
与上一题仅仅加了一条if i"""
这里需要注意, 处理排列中存在重复元素, 造成得到重复排列的问题.
解决方法是, 当第一次遇到重复元素, 把遇到的重复元素排在已有元素前, 然后跳出循环.
防止重复元素又排到已有元素的其他位置. 如[1,1,2,1], 一轮后得到[[1]],
第二轮开始又加入一个1, 这个1放到最前面, 然后就break循环.
之后还可能遇到一个1, 也做同样处理.
初始化ans=[[]]
依次取出nums中的元素n:
依次取出先有ans中的每个list:
在每个list中可插入位置都插入n
如果当前可插入位置元素等于n, break循环, 防止元素重复
把所有得到的排列加入ans
"""
class Solution:
def permuteUnique(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
ans = [[]]
#
for n in nums:
new_ans = []
# 取出ans中每个list, 在每个list的所有可插入位置插入n
for arr in ans:
# 对于ans中每个arr, 都有len(arr)+1个位置可以填入n
# 当len(arr)==0时, 只有一个位置. 即得到[n].
for i in range(len(arr)+1):
new_ans.append(arr[:i]+[n]+arr[i:])
# handles duplication
# 如果这次循环里加的是重复的数, 就放在起始位置, 然后break.
if i<len(arr) and arr[i]==n: break
ans = new_ans
return ans
48. Rotate Image (Medium)
题目描述Given input matrix =
[
[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]],
rotate the input matrix in-place such that it becomes:
[
[7,4,1],
[8,5,2],
[9,6,3]]
"""
clockwise rotate
first reverse up to down, then swap the symmetry
1 2 3 7 8 9 7 4 1
4 5 6 => 4 5 6 => 8 5 2
7 8 9 1 2 3 9 6 3
"""
class Solution:
def rotate(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
matrix.reverse()
for i in range(len(matrix)):
for j in range(i+1, len(matrix[0])):
matrix[i][j], matrix[j][i] = matrix[j][i], matrix[i][j]
49. Group Anagrams (Medium)
题目描述Input: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
Output:
[
["ate","eat","tea"],
["nat","tan"],
["bat"]
]
"""
使用字典提高检索效率.
每个单词按字母排序完得到的string作为key.
"""
class Solution:
def groupAnagrams(self, strs: List[str]) -> List[List[str]]:
dic = {}
for word in strs:
key = ''.join(sorted(word))
if key not in dic:
dic[key] = [word]
else:
dic[key].append(word)
ans = []
for key in dic.keys():
ans.append(dic[key])
return ans
54. Spiral Matrix (Medium)
题目描述Input:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 4, 5, 6 ],
[ 7, 8, 9 ]
]
Output: [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
如果用字符串 ‘right’ 来标记方向 direct 的时候, 要注意字符串和元组一样都是不可改变的对象, 所以不能使用 direct = ‘left’ 来赋值, 要使用 direct = direct.replace(‘right’, ‘right’) 来改变值. 比较麻烦, 所以还是用整型来表示方向."""
程序主要分为三个模块:
1. visit当前点:
如果当前点未探索, 输出到res, 标记该点未已探索.
如果当前点已探索, 转向并将坐标回退到上一点.
2. 转向:
没什么好说的
3. 往前走一格, 遇到边界转向:
根据当前方向改变坐标, 如果遇到边界, 转向并改变坐标
探索结束条件: 当res长度等于matrix里数字个数.
"""
class Solution:
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
# four direction right->down->left-> up -> roop
# 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> roop
if len(matrix) == 0:
return []
if len(matrix) == 1:
return matrix[0]
direct = 0
x, y, lastX, lastY= 0, 0, 0, 0
row, col= len(matrix), len(matrix[0])
res = []
while len(res) < row * col:
# the flag 'x' 表示已经走过.
# 直走.
if matrix[x][y] != 'x':
res.append(matrix[x][y])
matrix[x][y] = 'x'
elif matrix[x][y] == 'x':
# turn the direction
direct = self.turnDirect(direct)
# 当前点已经探索过, 返回上一个点
x, y = lastX, lastY
# 按照方向走一格.
# 如果右走到尽头, y不能+1, 改为向下走, x+1
lastX, lastY = x, y
x, y, direct = self.walk(x, y, row, col, direct)
return res
def turnDirect(self, direct):
if direct == 0: return 1
elif direct == 1: return 2
elif direct == 2: return 3
elif direct == 3: return 0
def walk(self, x, y, row, col, direct):
if direct == 0:
y += 1
if y == n:
y -= 1
direct = 1
x += 1
elif direct == 1:
x += 1
if x == row:
x -= 1
direct = 2
y -= 1
elif direct == 2:
y -= 1
if y < 0:
y += 1
direct = 3
x -= 1
elif direct == 3:
x -= 1
if x < 0:
x += 1
direct = 0
y += 1
return x, y, direct
59. Spiral Matrix II (Medium)
题目描述Input: 3
Output:
[
[ 1, 2, 3 ],
[ 8, 9, 4 ],
[ 7, 6, 5 ]
]
Python的二维数组建议使用列表生成式:matrix = [[0 for i in range(n)] for j in range(n)]."""
和上一题类似.
只不过把输入的二维数组变为全0数组, 遇到0则修改当前值, 遇到非零需要turn direction.
其余没有什么不同.
"""
class Solution:
def generateMatrix(self, n: int) -> List[List[int]]:
if n == 0:
return []
if n == 1:
return [[1]]
matrix = [[0 for i in range(n)] for j in range(n)]
self.spiralOrder(matrix)
return matrix
def spiralOrder(self, matrix):
# four direction right->down->left-> up -> roop
# 0 -> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> roop
direct = 0
x, y, lastX, lastY= 0, 0, 0, 0
n = len(matrix)
res = []
num = 1
while num <= n * n:
# the flag 'x' 表示已经走过.
# 直走.
if matrix[x][y] == 0:
matrix[x][y] = num
num += 1
elif matrix[x][y] != 0:
# turn the direction
direct = self.turnDirect(direct)
# 当前点已经探索过, 返回上一个点
x, y = lastX, lastY
# 按照方向走一格.
# 如果右走到尽头, y不能+1, 改为向下走, x+1
lastX, lastY = x, y
x, y, direct = self.walk(x, y, n, direct)
def turnDirect(self, direct):
if direct == 0: return 1
elif direct == 1: return 2
elif direct == 2: return 3
elif direct == 3: return 0
def walk(self, x, y, n, direct):
if direct == 0:
y += 1
if y == n:
y -= 1
direct = 1
x += 1
elif direct == 1:
x += 1
if x == n:
x -= 1
direct = 2
y -= 1
elif direct == 2:
y -= 1
if y < 0:
y += 1
direct = 3
x -= 1
elif direct == 3:
x -= 1
if x < 0:
x += 1
direct = 0
y += 1
return x, y, direct
55. Jump Game (Medium)
题目描述

解题思路
可以用递归, 解题思路和之前的题目一样. 但是在这里会超时."""
时间复杂度O(N), 遍历一遍数组即可. 只要能满足能跳过所有的0即可.
把每格能跳多远看作最大能储备多少energy, 每走一格energy减少1, 在走到终点前如果
energy为0, 表示失败. 这样在走0的时候只会减少能量不会增加, 0的格数如果大于等于
之前储备的能量, 说明一定会耗尽.
"""
class Solution:
def canJump(self, nums):
if len(nums) == 1:
return True
if nums[0] == 0:
return False
energy = nums[0]
for i in range(1,len(nums)):
energy -= 1
if nums[i] != 0 and energy < nums[i]:
energy= nums[i]
if energy == 0 and i != len(nums)-1:
return False
return True
56. Merge Intervals (Medium)
Input: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
# Definition for an interval.
# class Interval:
# def __init__(self, s=0, e=0):
# self.start = s
# self.end = e
# 学会使用lambda,给元素先进行排序
class Solution:
def merge(self, intervals: List[Interval]) -> List[Interval]:
if len(intervals) == 0: return []
# 按照start值进行排序
intervals = sorted(intervals, key = lambda x: x.start)
res = [intervals[0]]
for i in intervals[1:]:
# 如果i的起点小于res[-1]的终点,res[-1]的终点取i终点和自身的最大值
if i.start <= res[-1].end :
res[-1].end = max(res[-1].end, i.end)
else:
res.append(i)
return res
60. Permutation Sequence (Medium)
题目描述

Briefly take (n,k) = (4,21) for example, in the first iteration we divide the solution set into 4 groups: “1xxx”, “2xxx”, “3xxx”, and “4xxx”, while each group has 3! = 6 members.class Solution:
# @return a string
def getPermutation(self, n, k):
ll = [str(i) for i in range(1,n+1)] # build a list of ["1","2",..."n"]
divisor = 1
for i in range(1,n): # calculate 1*2*3*...*(n-1)
divisor *= i
answer = ""
while k>0 and k<=divisor*n: # there are only (divisor*n) solutions in total
group_num = k//divisor
k %= divisor
if k>0: # it's kth element of (group_num+1)th group
choose = ll.pop(group_num)
answer += choose
else: # it's last element of (group_num)th group
choose = ll.pop(group_num-1)
answer += choose
ll.reverse() # reverse the list to get DESC order for the last element
to_add = "".join(ll)
answer += to_add
break
divisor //= len(ll)
return answer
61. Rotate List (Medium)
题目描述Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, k = 2
Output: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
Explanation:
rotate 1 steps to the right: 5->1->2->3->4->NULL
rotate 2 steps to the right: 4->5->1->2->3->NULL
"""
受先前 24. Swap Nodes in Pairs 启发.
low, fast指针, fast提前k个位置, 当fast到末尾时, 停止遍历.
此时[low:fast]就是需要移动的一段链表.
移到链表头即可.
"""
class Solution:
def rotateRight(self, head: ListNode, k: int) -> ListNode:
if head == None:
return None
node = head
lenth = 0
while node:
node = node.next
lenth += 1
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
low, fast = head, head
pre = k % lenth
if pre == 0:
return head
for i in range(pre):
fast = fast.next
while fast.next:
low = low.next
fast = fast.next
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = low.next
fast.next = head
low.next = None
return dummy.next
62. Unique Paths (Medium)
题目描述
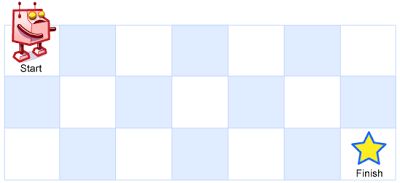
这是一个7x3的棋盘, m=7, n=3Example:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Right
递归暴力求解时间复杂度太高, 无法通过编译. 使用二维数组 lab , 值表示图中到达当前坐标的走法有多少种.
每个格子的走法数等于左边一格和上面一格的走法数加和. 类似青蛙跳."""
"""
class Solution:
def uniquePaths(self, m, n):
if not m or not n: # mxn 矩阵, m是x列号, n是y行号
return 0
# 这里默认第一列, 第一行的方法都是1(只有一种走法).
lab = [[1 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
# 因此遍历下标从1开始, 略过第一行第一列.
for i in range(1, n):
for j in range(1, m):
lab[i][j] = lab[i-1][j] + lab[i][j-1] #到达每一个格子的方法数都是前两个格子的和
return lab[-1][-1]
63. Unique Paths II (Medium)
题目描述

Example:
Input:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
class Solution:
def uniquePathsWithObstacles(self, obstacleGrid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not obstacleGrid:
return 0
n = len(obstacleGrid)
m = len(obstacleGrid[0])
# 所有格子方法数置为1, 不能像上一题默认第一行第一列都是一种走法.
# 因为障碍物可能出现在第一行或第一列. 所有格子置为0.
lab = [[0 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
# 第一格如果不是障碍的话, 置为1
if i == 0 and j == 0 and obstacleGrid[i][j] != 1:
lab[i][j] = 1
continue
# 如果坐标对应图中是障碍物的话, 当前方法数置位0.
if obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1:
lab[i][j] = 0
else:
# 注意边界条件.
if i - 1 < 0: lab[i][j] = lab[i][j-1]
elif j - 1 < 0: lab[i][j] = lab[i-1][j]
else: lab[i][j] = lab[i-1][j] + lab[i][j-1] #到达每一个格子的方法数都是前两个格子的和
return lab[-1][-1]
64. Minimum Path Sum (Medium)
题目描述Input:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.
"""
解题思路一样, 只不过lab保存的不是方法数总和, 而是到达当前点累计的最小和.
lab[i][j] = min(lab[i-1][j], lab[i][j-1])
"""
# 可以不用开辟lab二维数组, 直接在grid处修改.
class Solution:
def minPathSum(self, grid: List[List[int]]) -> int:
if not grid:
return 0
n = len(grid)
m = len(grid[0])
# 二维数组, 保存当前能取到的最小和.
lab = [[0 for i in range(m)] for j in range(n)]
for i in range(n):
for j in range(m):
if i == 0 and j == 0:
lab[i][j] = grid[i][j]
continue
# 注意边界条件.
if i - 1 < 0: lab[i][j] = grid[i][j] + lab[i][j-1]
elif j - 1 < 0: lab[i][j] = grid[i][j] + lab[i-1][j]
else: lab[i][j] = grid[i][j] + min(lab[i-1][j],lab[i][j-1]) #到达每一个格子的方法数都是前两个格子的和
return lab[-1][-1]
71. Simplify Path (Medium)
题目描述

Example 1:
Input: "/home/"
Output: "/home"
Explanation: Note that there is no trailing slash after the last directory name.
Example 2:
Input: "/../"
Output: "/"
Explanation: Going one level up from the root directory is a no-op,
as the root level is the highest level you can go.
Example 3:
Input: "/home//foo/"
Output: "/home/foo"
Explanation: In the canonical path, multiple consecutive slashes are
replaced by a single one.
Example 4:
Input: "/a/./b/../../c/"
Output: "/c"
Example 5:
Input: "/a/../../b/../c//.//"
Output: "/c"
Example 6:
Input: "/a//b////c/d//././/.."
Output: "/a/b/c"
Note:
有除了数字或者字母外的符号(空格,分号,etc.)都会False
isalnum()必须是数字和字母的混合
isalpha()不区分大小写class Solution:
def simplifyPath(self, path):
# 用栈保存文件目录即可.
stack = []
for token in path.split('/'):
# split分割完数组里会有空字符""出现.
if token in ('', '.'):
pass
elif token == '..':
if stack: stack.pop()
else:
stack.append(token)
return '/' + '/'.join(stack)
73. Set Matrix Zeroes (Medium)
题目描述
Do it in-place.
Note:
in-place算法不依赖额外的资源或者依赖少数的额外资源,仅依靠输出来覆盖输入的一种算法操作"""
类似数岛屿那一题. 遇到0后行列不能马上改为0, 会影响后续判断.
只需要"标记"一下, 在结束第一轮遍历之后, 再遍历一遍数组, 把所有
标记过的数改为0.
"""
class Solution:
def setZeroes(self, matrix: List[List[int]]) -> None:
height = len(matrix)
if(height ==0): return
width = len(matrix[0])
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
if matrix[i][j] == 0:
for tmp in range(height):
if matrix[tmp][j] != 0:
matrix[tmp][j] = None
for tmp in range(width):
if matrix[i][tmp] != 0:
matrix[i][tmp] = None
for i in range(height):
for j in range(width):
if matrix[i][j] == None:
matrix[i][j] = 0
74. Search a 2D Matrix (Medium)
题目描述Input:
matrix = [
[1, 3, 5, 7],
[10, 11, 16, 20],
[23, 30, 34, 50]
]
target = 3
Output: true
"""
查找+有序 首先想到二分法, 时间复杂度低.
多一步转化, 将mid转化成index, 其中m是二维数组一行有多少个数.
midi = mid // m
midj = mid % m
其余没有什么不同.
"""
class Solution:
def searchMatrix(self, matrix: List[List[int]], target: int) -> bool:
n = len(matrix)
if n == 0: return False
m = len(matrix[0])
if m == 0: return False
left, right= 0, m * n - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right)//2
# get the real index of mid in 2D array.
midi = mid // m
midj = mid % m
if matrix[midi][midj] > target:
right = mid - 1
elif matrix[midi][midj] < target:
left = mid + 1
if matrix[midi][midj] == target:
return True
return False
77. Combinations (Medium)
题目描述Given two integers n and k
return all possible combinations of k numbers out of 1 ... n.
Example:
Input: n = 4, k = 2
Output:
[
[2,4],
[3,4],
[2,3],
[1,2],
[1,3],
[1,4],
]
"""
又可以使用万能dfs思路. 但是时间效率太低了.
"""
class Solution:
def combine(self, n, k):
res = []
self.dfs(range(1,n+1), k, 0, [], res)
return res
def dfs(self, nums, k, index, path, res):
#if k < 0: #backtracking
#return
if k == 0:
res.append(path)
return # backtracking
for i in range(index, len(nums)):
self.dfs(nums, k-1, i+1, path+[nums[i]], res)
78. Subsets (Medium)
题目描述

class Solution:
def subsets(self, nums):
nums.sort()
result = [[]]
for num in nums:
result += [i + [num] for i in result]
return result
90. Subsets II (Medium)
题目描述
方法一: 做法同上一题. 每次添加list时候判断是否重复, 时间复杂度较高.class Solution:
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
nums.sort()
result = [[]]
for num in nums:
for j in [i + [num] for i in result]:
if j not in result:
result.append(j)
return result
# DFS
def subsetsWithDup(self, nums):
res = []
nums.sort()
self.dfs(nums, 0, [], res)
return res
def dfs(self, nums, index, path, res):
res.append(path)
for i in range(index, len(nums)):
if i > index and nums[i] == nums[i-1]:
continue
self.dfs(nums, i+1, path+[nums[i]], res)
79. Word Search (Medium)
题目描述

解题思路"""
search grid 类型, dfs探索多个方向, 递归调用, 当触及边界或满足要求当前递归结束.
"""
class Solution:
def exist(self, board, word):
if not board:
return False
for i in range(len(board)):
for j in range(len(board[0])):
if self.dfs(board, i, j, word):
return True
return False
# check whether can find word, start at (i,j) position
def dfs(self, board, i, j, word):
if len(word) == 0: # all the characters are checked
return True
if i<0 or i>=len(board) or j<0 or j>=len(board[0]) or word[0]!=board[i][j]:
return False
tmp = board[i][j] # first character is found, check the remaining part
board[i][j] = "#" # avoid visit agian
# check whether can find "word" along one direction
res = self.dfs(board, i+1, j, word[1:]) or self.dfs(board, i-1, j, word[1:]) \
or self.dfs(board, i, j+1, word[1:]) or self.dfs(board, i, j-1, word[1:])
board[i][j] = tmp
return res
80. Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array II (Medium)
题目描述

class Solution:
def removeDuplicates(self, nums):
if nums==[]:
return 0
i = 0
count = 1
while i < len(nums) - 1:
# 如果计数等于2, 且下一个数仍然重复,则移除下一个数
if count == 2 and nums[i] == nums[i+1]:
nums.pop(i+1)
#i -= 1
# 如果计数等于2, 且下一个数不一样,计数清零。指针下移一位。
elif count == 2 and nums[i] != nums[i+1]:
#nums.pop(i)
i += 1
count = 1
elif count != 2 and nums[i] == nums[i+1]:
if count < 2:
i += 1
count += 1
# 如果计数满2,指针不能再走。
else:
i += 1
# 处理最后一个数。
return len(nums)
82. Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II (Medium)
题目描述"""
当遇到重复节点,用一个指针指向第一个重复节点的父节点,
将其链接到最后一个重复节点的下一个节点
"""
class Solution:
def deleteDuplicates(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
dummy = ListNode(0)
dummy.next = head
# 保存新的节点.
pre = dummy
cur = dummy.next
while cur:
if cur.next and cur.val == cur.next.val:
#遍历到cur.next值不再重复
while cur.next and cur.val == cur.next.val:
cur = cur.next
#将父节点链接到下一个不重复的值处
pre.next = cur.next
#指针移动到next
cur = pre.next
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
return dummy.next
86. Partition List (Medium)
题目描述

解题思路"""
简单. 准备两个指针, 一个保存比3小的, 另一个保存比3大的, 最后链接在一起.
"""
class Solution:
def partition(self, head: ListNode, x: int) -> ListNode:
p1, p2 = ListNode(0), ListNode(0)
head1, head2 = p1, p2
while head:
if head.val < x:
p1.next = head
p1 = p1.next
else:
p2.next = head
p2 = p2.next
head = head.next
p2.next = None
p1.next = head2.next
return head1.next
89. Gray Code (Medium)
题目描述Input: 2
Output: [0,1,3,2]
Explanation:
00 - 0
01 - 1
11 - 3
10 - 2
For a given n, a gray code sequence may not be uniquely defined.
For example, [0,2,3,1] is also a valid gray code sequence.
00 - 0
10 - 2
11 - 3
01 - 1
"""
Not every path leads to the complete combination. eg.
(n = 3) 000 -> 001 -> 011 -> 111 -> 110 -> 100 -> 101 -> X
The goal is to find a path which reaches the level == 2^n
Revert bit one at a time (always from the right most one) and append to the ans list if it is not already.
If the len(ans) == target, stop.
"""
class Solution(object):
def grayCode(self, n):
targetLevel = 2**n
ans = []
self.dfs(n, ans, 0, 1, targetLevel) # Start with number = 0 (000), level = 1
return ans
def dfs(self, n, ans, num, level, targetLevel):
if num in ans:
return
ans.append(num)
if level == targetLevel:
return
for i in range(0, n):
self.dfs(n, ans, num ^ (1 << i), level+1, targetLevel) # num ^ (1 << i): revert a bit at a time
if len(ans) == targetLevel: return # result found. Stop.
91. Decode Ways (Medium) **
题目描述A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
Given a non-empty string containing only digits, determine the total number of ways to decode it.
Example 1:
Input: "12"
Output: 2
Explanation: It could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12).
Example 2:
Input: "226"
Output: 3
Explanation: It could be decoded as "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), or "BBF" (2 2 6).
70. Climbing Stairs
93. Restore IP Addresses (Medium)
509. Fibonacci Number"""
I used a dp array of size n + 1 to save subproblem solutions.
dp[0] means an empty string will have one way to decode,
dp[1] means the way to decode a string of size 1.
I then check one digit and two digit combination and save
the results along the way. In the end, dp[n] will be the end result.
"""
public class Solution {
public int numDecodings(String s) {
if(s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int n = s.length();
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = s.charAt(0) != '0' ? 1 : 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int first = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i-1, i));
int second = Integer.valueOf(s.substring(i-2, i));
if(first >= 1 && first <= 9) {
dp[i] += dp[i-1];
}
if(second >= 10 && second <= 26) {
dp[i] += dp[i-2];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
92. Reverse Linked List II (Medium)
题目描述Reverse a linked list from position m to n. Do it in one-pass.
Note: 1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ length of list.
Example:
Input: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
Output: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
/*
*/
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0); // create a dummy node to mark the head of this list
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy; // make a pointer pre as a marker for the node before reversing
for(int i = 0; i<m-1; i++) pre = pre.next;
ListNode start = pre.next; // a pointer to the beginning of a sub-list that will be reversed
ListNode then = start.next; // a pointer to a node that will be reversed
// 1 - 2 -3 - 4 - 5 ; m=2; n =4 ---> pre = 1, start = 2, then = 3
// dummy-> 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5
for(int i=0; i<n-m; i++)
{
start.next = then.next;
then.next = pre.next;
pre.next = then;
then = start.next;
}
// first reversing : dummy->1 - 3 - 2 - 4 - 5; pre = 1, start = 2, then = 4
// second reversing: dummy->1 - 4 - 3 - 2 - 5; pre = 1, start = 2, then = 5 (finish)
return dummy.next;
}
93. Restore IP Addresses (Medium)
题目描述Example:
Input: "25525511135"
Output: ["255.255.11.135", "255.255.111.35"]
用DFS解题.class Solution:
def restoreIpAddresses(self, s):
res = []
self.dfs(s, 0, "", res)
return res
def dfs(self, s, index, path, res):
if index == 4:
if not s:
res.append(path[:-1])
return # backtracking
for i in xrange(1, 4):
# the digits we choose should no more than the length of s
if i <= len(s):
#choose one digit
if i == 1:
self.dfs(s[i:], index+1, path+s[:i]+".", res)
#choose two digits, the first one should not be "0"
elif i == 2 and s[0] != "0":
self.dfs(s[i:], index+1, path+s[:i]+".", res)
#choose three digits, the first one should not be "0", and should less than 256
elif i == 3 and s[0] != "0" and int(s[:3]) <= 255:
self.dfs(s[i:], index+1, path+s[:i]+".", res)
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal (Medium)
题目描述
因为左边的节点要先输出, 然后才轮到根节点.
"""
用迭代的方式实现中序遍历.
"""
class Solution:
def inorderTraversal(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
stack, ans = [], []
while True:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
if not stack:
return ans
node = stack.pop()
ans.append(node.val)
root = node.right
return ans
96. Unique Binary Search Trees (Medium)
题目描述Input: 3
Output: 5
Explanation:
The above output corresponds to the 5 unique BST's shown below:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
分治解题.
输入
根节点
左节点
右节点
可能的情况数
1
1
0
0
1
总数
1
2
1
0
1
1
-
2
1
0
1
总数
2
3
1
0
2
1 x 2
-
2
1
1
1 x 1
-
3
2
0
2 x 1
总数
2 + 1 + 2 = 5
4
1
0
3
1 x 5
-
2
1
2
1 x 2
-
3
2
1
2 x 1
-
4
3
0
5 x 1
总数
5 + 2 + 2 + 5 = 14
f(1) = 1
f(2) = 2
f(n) = Σ 0 n − 1 \Sigma_0^{n-1} Σ0n−1 f(j) * f(n-1-j)"""
不用递归的写法, 就是使用数组.
每个值表示一个状态. 某个状态的值也是通过前面状态计算出来的.
"""
class Solution:
def numTrees(self, n: int) -> int:
if n == 0 or n == 1: return 1
if n == 2: return 2
num = [1, 1, 2]
for i in range(3, n+1):
s = 0
for j in range(i):
s += num[j]*num[i-1-j]
num.append(s)
return num[-1]
95. Unique Binary Search Trees II (Medium)
题目描述Input: 3
Output:
[
[1,null,3,2],
[3,2,null,1],
[3,1,null,null,2],
[2,1,3],
[1,null,2,null,3]
]
Explanation:
The above output corresponds to the 5 unique BST's shown below:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
class Solution(object):
def generateTrees(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[TreeNode]
"""
if n == 0:
return [[]]
return self.dfs(1, n+1)
def dfs(self, start, end):
if start == end:
return None
result = []
for i in xrange(start, end):
for l in self.dfs(start, i) or [None]:
for r in self.dfs(i+1, end) or [None]:
node = TreeNode(i)
node.left, node.right = l, r
result.append(node)
return result
98. Validate Binary Search Tree (Medium)
题目描述class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if root == None:
return True
tree = []
self.inOrder(root, tree)
if len(tree) == 1:
return True
for i in range(len(tree)-1):
if tree[i] >= tree[i+1]:
return False
return True
def inOrder(self, root, tree):
if root == None:
return
if root.left:
self.inOrder(root.left, tree)
tree.append(root.val)
if root.right:
self.inOrder(root.right, tree)
"""
记录前驱节点prev. 每次visit节点的时候, 记录并把其右节点入栈.
用迭代的方法做, visit节点的顺序都是 左->中->右, 数值大小也是递增, 因此
每次visit的时候, 当前值一定不能<=prev的值.
根节点a在不存在左节点的时候visit, 然后入栈右节点. 此时prev是该根节点a,
右节点同样直到遍历到最左的节点才能visit, 其值要大于prev的值. 如果右节点
不存在, 那出栈的就是a的根节点, 也要大于a的值.
"""
class Solution:
def isValidBST(self, root: TreeNode) -> bool:
if root == None:
return True
stack, ans = [], []
prev = None #
while True:
while root:
stack.append(root)
root = root.left
if not stack:
return ans
node = stack.pop()
###
if prev != None and node.val <= prev.val:
return False
prev = node
###
ans.append(node.val)
root = node.right
return True
