netty粘包断包处理
最近在研究netty组件。Netty对nio的封装极大的方便了我们的业务开发,我们不再需要使用jdk提供的繁琐的nio进行编程,并且netty的扩展性强,健壮性强,不仅是对nio的bug的处理,还是对tcp粘包、断包的处理都是非常出色的。
首先,先看看netty的服务端和客户端的demo。
public class HelloServer {
public void run() throws InterruptedException {
// 管理channel连接
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
//p.addLast("framer", new DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder(8192, Delimiters.lineDelimiter()));
p.addLast("decoder", new StringDecoder());
p.addLast("encoder", new StringEncoder());
p.addLast(new EchoServerHandler());
}
});
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(9999).sync();//监听端口
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();//监听端口关闭, 会一直阻塞
}finally{
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
new HelloServer().run();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/*static class EchoServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
try {
String reqMs = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(reqMs);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String res = "高兴";
ByteBuf resBuf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer(res.getBytes());
//ctx.write(resBuf);
ctx.writeAndFlush(resBuf);
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
System.out.println(cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}*/
static class EchoServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler
/* (non-Javadoc)
* @see io.netty.channel.SimpleChannelInboundHandler#channelRead0(io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext, java.lang.Object)
*/
@Override
protected void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, String msg)
throws Exception {
System.out.println(ctx.channel().remoteAddress() + ":" + msg);
//ctx.channel().writeAndFlush("Received your message...");//从尾端开始流动
ctx.writeAndFlush("Received your message...");//从下一个channelHandler开始流动
// simpleChannelInboundHandler不需要手工释放directBuffer
}
}
}
public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
new HelloClient().send();
}
public void send() throws InterruptedException{
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try{
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
p.addLast(new EchoClientHandler());
//p.removeLast();
}
});
ChannelFuture channelFuture = bootstrap.connect("127.0.0.1", 9999).sync();
//channelFuture.addListener(listener)
channelFuture.channel().closeFuture().sync();
}finally{
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
static class EchoClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
@Override
public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.copiedBuffer("hello server".getBytes());
ChannelFuture future = ctx.writeAndFlush(buf);
future.addListener(new ChannelFutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(ChannelFuture f) throws Exception {
if(!f.isSuccess()){
f.cause().printStackTrace();
f.channel().close();
}
}
});
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) {
try{
ByteBuf buf = (ByteBuf) msg;
byte[] req = new byte[buf.readableBytes()];
buf.readBytes(req);
try {
String res = new String(req, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(res);
} catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}finally{
ReferenceCountUtil.release(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
System.out.println(cause.getMessage());
ctx.close();
}
}
}
这是一个简单的demo,但是实际应用中也是和这个demo一样,应用起来是非常简单的。
下面说说tcp断包和粘包。
假设客户端分别发送了两个数据包D1,D2;因为tcp基于缓冲区发送接收数据,服务器端接收到的数据包可能有以下四种情况:
⑴分两次读取到两个独立的包,D1和D2;
⑵一次读取到D1和D2,称为粘包;
⑶分两次读取,第一次读取到D1的所有数据,D2的部分数据,第二次读取到D2的剩下部分的数据;称为断包;
⑷分两次读取,第一次读取到D1的部分数据,第二次读取到D1剩下部分的数据和D2的所有数据;
对于粘包和断包的情况,有两种解决方案:
⑴包长度固定:每次取固定大小的数据;
⑵设置包长:发送数据包括包长+包体;
⑶设置分隔符;
在tcp的OIO模型中,粘包和断包的情况是非常好处理的,但是在tcp的NIO模型中如果发生断包,其实是会有两个read事件发生的,那么这种情况处理起来就比较麻烦,你得定义一个变量来存储断掉了的数据。但是netty就很好的帮助我们实现了这种机制。
分隔符协议
经常需要处理分隔符协议或创建基于它们的协议,例如SMTP、POP3、IMAP、Telnet等等;Netty附带的handlers可以很容易的提取一些序列分隔:
- DelimiterBasedFrameDecoder,解码器,接收ByteBuf由一个或多个分隔符拆分,如NUL或换行符
LineBasedFrameDecoder,解码器,接收ByteBuf以分割线结束,如"\n"和"\r\n"
长度为基础的协议
一般经常会碰到以长度为基础的协议,对于这种情况Netty有两个不同的解码器可以帮助我们来解码:
- FixedLengthFrameDecoder
- LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder
(摘自Netty in Action中文版)
LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder非常灵活,可以解决我们几乎所有的应用场景。下面看看它的构造函数:
public LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(
ByteOrder byteOrder, int maxFrameLength, int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength,
int lengthAdjustment, int initialBytesToStrip, boolean failFast);
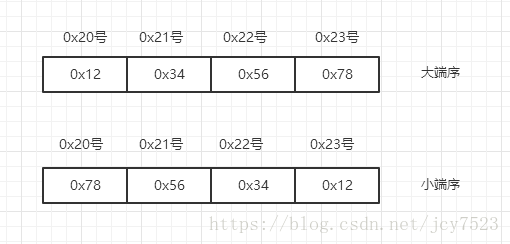
⑴第一个参数byteOrder是网络字节序,可选为大端和小端。大端序:高位字节存放到低位地址;小端序:高位字节存放到高位地址。比如0x20 号开始的地址中保存4字节 int 型数据 0x12345678:
网络传输中,统一为大端字节序。
⑵第二个参数maxFrameLength,表示数据包最大的长度,超过这个长度,会抛出TooLongFrameException。
⑶第三个参数lengthFieldOffset,表示长度字段的偏移量,即从第几个字节开始表示是长度字段。
⑷第四个参数lengthFieldLength,表示长度字段的宽度,即一共几个字节表示是长度字段。
⑸第五个参数lengthAdjustment,表示长度调整量,即lengthAdjustment+length值为实际的长度。
⑹第六个参数initialBytesToStrip,表示包体需要跳过的字节数,比如:00041234,initialBytesToStrip=4,lengthFieldLength=4,lengthFieldOffset=0,那么实际解析后的数据是1234,去掉了包长0004。
⑺第七个参数failFast,true-即不论帧数据有没有读取完,只要数据即将超出最大长度maxFrameLength,就抛出TooLongFrameException,false-即等待帧数据读取完,再抛出异常。
注意:LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder取实际数据包的长度的方法如下:
protected long getUnadjustedFrameLength(ByteBuf buf, int offset, int length, ByteOrder order) {
buf = buf.order(order);
long frameLength;
switch (length) {
case 1:
frameLength = buf.getUnsignedByte(offset);
break;
case 2:
frameLength = buf.getUnsignedShort(offset);
break;
case 3:
frameLength = buf.getUnsignedMedium(offset);
break;
case 4:
frameLength = buf.getUnsignedInt(offset);
break;
case 8:
frameLength = buf.getLong(offset);
break;
default:
throw new DecoderException(
"unsupported lengthFieldLength: " + lengthFieldLength + " (expected: 1, 2, 3, 4, or 8)");
}
return frameLength;
}
在实际场景中,我们可能与默认的取长度方法不同,这种情况我们可以重写此方法,例如,在我的项目中,报文的前四个字节是长度,比如001112345678901,0011代表长度是11,那我的实现类就如下:
public class CommonLengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder extends LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder{
public CommonLengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(int maxFrameLength,
int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength) {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength);
}
public CommonLengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(int maxFrameLength,
int lengthFieldOffset, int lengthFieldLength, int lengthAdjustment,
int initialBytesToStrip, boolean failFast) {
super(maxFrameLength, lengthFieldOffset, lengthFieldLength,
lengthAdjustment, initialBytesToStrip, failFast);
}
protected long getUnadjustedFrameLength(ByteBuf buf, int offset, int length, ByteOrder order) {
buf = buf.order(order);
byte[] lengthByte = new byte[length];
buf.getBytes(offset, lengthByte, 0, length);
long frameLength = Long.valueOf(new String(lengthByte));
return frameLength;
}
}