OpenTSDB写数据的三种方法之Java API详解
OpenTSDB写数据的三种方法之Java API详解
1.Telnet Style API
见我博客:openTSDB详解之Telnet Style API
2.HTTP API
见我博客【待完善】
3.Java API
3.1 简介
接下来我主要分析一下使用Java API将数据写入到openTSDB中。因为openTSDB官方并没有提供Java API,所以这个API需要使用我们自己开发。但是整个开源世界何其广阔,在你需要使用java往openTSDB写入数据时,早就有前辈遇到这个问题。所以我就从网上下载了一个包,然后继续倒腾。接下来我就针对这个包的代码进行写入数据过程的分析。
3.2 源码分析
public class OpentsdbClientTest {
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(OpentsdbClientTest.class);
static OpentsdbClient client = new OpentsdbClient("http://192.168.211.4:4399");
public static void testPutData() {
try {
Map tagMap = new HashMap();
tagMap.put("aaa", "bbb");
client.putData("metric-t", DateTimeUtil.parse("20180902 23:10", "yyyyMMdd HH:mm"), 330l, tagMap);
client.putData("metric-t", DateTimeUtil.parse("20180902 23:06", "yyyyMMdd HH:mm"), 440l, tagMap);
client.putData("metric-t", DateTimeUtil.parse("20180902 22:50", "yyyyMMdd HH:mm"), 460l, tagMap);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
OpentsdbClientTest是一个测试类,用于测试将数据写入到openTSDB中。
- 使用sl4j的日志对象,记录OpentClientTest这个类。
- 同时OpentsdbClient对象访问的url是"http://192.168.211.4:4399"【笔者注:这个是笔者的局部网址,外界是不能ping通的】
- 使用
testPutData()方法进行数据的写入测试。
testPutData()方法中有一个Map对象tagMap。这个是用于记录tag对。这里我随便使用了一组tag。接着在client端使用putData(…)方法。其中putData(…)方法如下:
/**
* 写入数据 *
* @param metric 指标
* @param timestamp 时间戳
* @param value type is long
* @param tagMap
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public boolean putData(String metric, Date timestamp, long value, Map tagMap) throws Exception {
/*
1.Returns the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT represented by this Date object.
2.but why did timestamp divide 1000?[译者注:这个地方我不大理解!!!]
*/
long timsSecs = timestamp.getTime() / 1000;
//call the simple function putData(...), but the parameter is Long instead of Date.
return this.putData(metric, timsSecs, value, tagMap);
}
这个putData(…)方法将Date 型的timestamp转型成long型。并再次调用下面的putData(…)方法:
/**
* 写入数据
* @param metric 指标
* @param timestamp 转化为秒的时间点
* @param value
* @param tagMap
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public boolean putData(String metric, long timestamp, long value, Map tagMap) throws Exception {
/* 1.Builder used to create the JSON to push metrics to openTSDB.
*/
MetricBuilder builder = MetricBuilder.getInstance();
//addMetric(metric) return on Metric's instance
//设置metric的数据值、标签
builder.addMetric(metric).setDataPoint(timestamp, value).addTags(tagMap);
try {
log.debug("write quest:{}", builder.build());
/*1.first,putMetrics()
*/
Response response = httpClient.pushMetrics(builder, ExpectResponse.SUMMARY);
//sometimes : 22:00:48.898 [main] DEBUG enn.cn.dataimport.OpentsdbClient - response.statusCode: 200
log.debug("response.statusCode: {}", response.getStatusCode());
return response.isSuccess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("put data to opentsdb error: ", e);
throw e;
}
}
这里有两个主要的方法调用:
- 使用
MetricBuilder构建一个builder实例,这个builder用于构建一个metric。使用addmetric()方法,将传入到方法中的metric添加到其中,然后使用setDataPoint()设置这个metric的数据点,最后为这个数据点添加一个tag 对。 - 最后使用httpClient对象将这个builder对象发送出去。具体的发送方法是putMetrics()。方法如下:
public Response pushMetrics(MetricBuilder builder,
ExpectResponse expectResponse) throws IOException {
//checkNotNull(): Ensures that an object reference passed as a parameter to the calling method is not null.
//see above: import static com.google.common.base.Preconditions.checkNotNull;
checkNotNull(builder);
/*1.TODO 错误处理,比如IOException或者failed>0,写到队列或者文件后续重试。*/
SimpleHttpResponse response = httpClient
.doPost(buildUrl(serviceUrl, PUT_POST_API, expectResponse),
builder.build());
return getResponse(response);
}
因为导入了checkNotNull()所在的方法包,所以可以直接使用checkNotNull(builder)方法。那这里的httpClient又是个什么呢?看下面的这个定义:
private PoolingHttpClient httpClient = new PoolingHttpClient();as the name,PoolingHttpClient is a http client pool。需要记住这个httpClient是一个连接到远端服务器[在本文里,就是192.168.211.4:4399这个服务器的端口]的client端即可。
然后使用doPost方法将整个builder发送出去。如下介绍两个地方:
doPost()方法
相信熟悉网络编程的人对这个都很熟悉,我对其稍作简介,这个doPost方法是最后一击——我们已经准备好了metric,tag pair,data等,但是还没有发送出去,这个doPost方法就是作为一个发送功能。
首先:这个doPost方法是对象httpClient所拥有的,而这个httpClient就是我们上述的PoolingHttpClient的一个实例。下面这张图是对PoolingHttpClient这个类的UML图:

该类有一个CloseableHttpClient实例对象httpClient,其定义方式如下:
private CloseableHttpClient httpClient = null;
然后将这个对象在构造函数中实例化:
public PoolingHttpClient() {
···
httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setKeepAliveStrategy(keepAliveStrategy)
.setConnectionManager(connManager)
.setDefaultRequestConfig(config).build();
···
}
再往下探索,发现这个HttpClients类是一个工厂方法,在其类的API介绍中,有这么一句话:Factory methods for CloseableHttpClient instances。好了,关于httpClient就介绍到这里。这个httpClient就是实现http协议的一个客户端【这么理解就大致ok】。接着看doPost方法,如下:
public SimpleHttpResponse doPost(String url, String data)
throws IOException {
/*
1.StringEntity: A self contained, repeatable entity that obtains its content from a String.
【一个自包含的、可重复的实体,这个实体包涵可以从字符串中得到的内容。【译者注:比如下面的这个构造函数就是使用String 对象作为参数传递进去构造出
一个StringEntity】】
2.HttpPost: HTTP POST method.
*/
StringEntity requestEntity = new StringEntity(data);
HttpPost postMethod = new HttpPost(url);
postMethod.setEntity(requestEntity);
//这里没有写httpClient.execute(),就说明执行这个方法的对象就是当前这个类的对象[PoolingHttpClient]
HttpResponse response = execute(postMethod);
int statusCode = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();//查看返回值
/**
* 1.SimpleHttpResponse is a custom class.
*/
SimpleHttpResponse simpleResponse = new SimpleHttpResponse();
simpleResponse.setStatusCode(statusCode);//set statusCode
/*1.HttpEntity: An entity that can be sent or received with an HTTP message. */
HttpEntity entity = response.getEntity();
if (entity != null) {
// should return: application/json; charset=UTF-8
String ctype = entity.getContentType().getValue();
String charset = getResponseCharset(ctype);
//EntityUtils:Static helpers for dealing with HttpEntitys.
String content = EntityUtils.toString(entity, charset);
simpleResponse.setContent(content);
}
return simpleResponse;
}
该方法有两个参数:分别是url和data,均为String类型。
首先,将需要post的data封装到一个StringEntity中,得到一个叫做requestEntity的对象,接着声明一个HttpPost的对象,注入参数中url。然后将刚才的那个requestEntity放到postMethod这个对象里。最后执行execute()方法,其中的参数是postMethod。
但是发出了一个Http Post之后,总会有响应的吧,那该怎么接收这个响应呢?定义了一个HttpResponse对象response,该对象指向返回实例。
这里自定义了一个SimpleHttpResponse类,为的是只取响应的返回码和返回内容。最后返回这个simpleResponse对象。
SimpleHttpResponse response = httpClient.doPost(
buildUrl(serviceUrl,
PUT_POST_API,
expectResponse),
builder.build());
接着看buildUrl(serviceUrl,PUT_POST_API,expectResponse)语句。查看buildUrl方法:
private String buildUrl(String serviceUrl, String postApiEndPoint,
ExpectResponse expectResponse) {
//what is postApiEndPoint?
String url = serviceUrl + postApiEndPoint;
switch (expectResponse) {
case SUMMARY:
url += "?summary";
break;
case DETAIL:
url += "?details";
break;
default:
break;
}
return url;
}
这里使用serviceUrl和postApiEndPoint构造一个实际的url,并且根据expectResponse去判断是否需要何种url,然后拼接成一个真正的url【笔者注:这里的SUMMARY/DETAIL是什么意思?=> 我猜测应该是Opentsdb通过http获取数据的一种方式】
builder.build()方法
/**
* Returns the JSON string built by the builder. This is the JSON that can
* be used by the client add metrics.
*
* @return JSON
* @throws IOException
* if metrics cannot be converted to JSON
*/
public String build() throws IOException {
// verify that there is at least one tag for each metric
for (Metric metric : metrics) {
checkState(metric.getTags().size() > 0, metric.getName()
+ " must contain at least one tag.");
}
/*
1.toJson(): This method serializes the specified object into its equivalent Json representation.
*/
return mapper.toJson(metrics);
}
3.3 执行结果
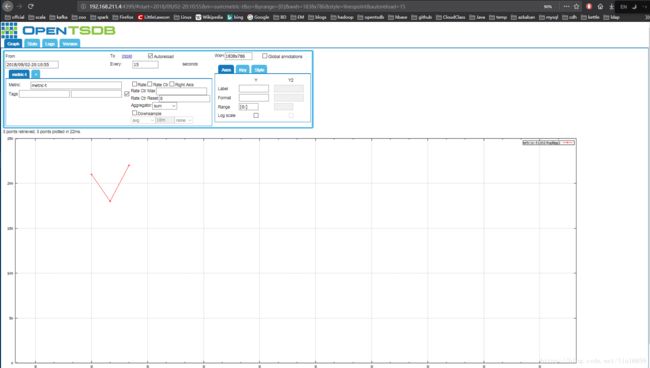
写入到openTSDB之后,可以打开浏览器查看写入效果,如下:
4.注
有需要jar包的可留言告知博主。